Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Also Check: How Common Is Hepatitis B
Data Analysis And Statistics
All analyses were done using nonparametric statistical software with penalized maximum likelihood to remove first-order bias. A p-value < 0.05 for two-sided tests was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were expressed as means plus/minus standard deviation or mean , categorical variables as numbers . Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for loss of anti-HBs putative associated factors included age, sex, type of rheumatic disease, conventional DMARDs, biologic DMARDs , comorbidity, and baseline anti-HBs titer.
Epidemiology Of Acute And Chronic Hbv In Canada
Acute HBV: Canada is a region of low endemicity however, certain vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected. These include Aboriginal peoples, MSM, street-involved youth, and people who are or have been incarcerated.Endnote 2 Peak incidence is among those aged 3039 years. The most commonly identified risk factors are high-risk sexual activities and injection drug use.
Canada has had universal HBV immunization programs in place since the mid-1990s. All provinces and territories have programs that target children aged 913 years, and some have also implemented a neonatal immunization program.Endnote 3 In addition, some provinces/territories provide coverage for high-risk individuals, but eligibility varies across jurisdictions . Despite the success of these programs, there may be many who remain at risk of acquiring HBV.
Immunization contributes to disease control by interrupting disease transmission and decreasing the pool of susceptible people. It is essential to identify those at risk who would benefit from receiving the HBV vaccine.
There is an urgent need to screen, diagnose, and treat chronic HBV infection so as to reduce associated morbidity and mortality and to prevent further transmission.
You May Like: What Does It Mean To Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not spread through sharing utensils or kissing. It also doesnt spread through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding. Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure and can last for 212 weeks. However, you are still contagious, even
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Infants Schedule
Clinical And Laboratory Assessments
Demographic data, medication history including antiviral agents and comorbidities such as malignancy were assessed based on electronic medical records.
Laboratory tests included assessments of serology associated with HBV infection, liver function, AFP levels, platelet counts, and antibodies against hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus. Serologic markers for HBV including HBsAg, anti-HBs, hepatitis B e antigen , and anti-HBe were assessed by chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassays . The concentration of HBsAg was determined using a previously generated Architect HBsAg calibration curve , and the samples with higher than 250 IU/ml HBsAg levels were diluted to 1:5001:1000. By June 2010, qHBsAg more than 250 were expressed as > 250 IU/ml without presenting an exact value. Thus, we divided subjects into 2 groups as those with qHBsAg> 250 IU/ml and those with qHBsAg250 IU/ml in this study.
Serum HBV DNA levels were measured with Roche COBAS TaqMan quantitative PCR assay, which has a low detection limit of 20 IU/mL. The threshold for anti-HBs positivity was an anti-HBs titer > 10 IU/mL. Blood samples were collected before 10:00 AM after the patients had completed a 12-h overnight fast. All laboratory tests were conducted using standard methods.
Read Also: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Contagious By Touch
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Kinetics And Risk Of De Novo Hepatitis B Infection In Hbsagnegative Patients Undergoing Cytotoxic Chemotherapy
- CheeKin HuiCorrespondenceAddress requests for reprints to: CheeKin Hui, MD, University of Hong Kong, Queen Mary Hospital, Department of Medicine, 102 Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong SAR, China. fax: 2281 84030.Centre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- HaiYing ZhangAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- YuiHung YuengAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- John M. LukAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaDepartment of Surgery, Queen Mary Hospital, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- George K.K. LauAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Background & Aims:Methods:Results:
Abbreviations used in this paper:
Lancet.J Hepatol.
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Does It Spread
Don’t Miss: Immune To Hepatitis B Means
Where Is Your Patient From
This is a figure of a map of the world within Module 1 that is meant to assist clinicians in determining whether a patient is from a country of low , intermediate , or high prevalence of hepatitis B infection. Clinicians are advised that individuals born in regions with intermediate or high endemicity are at particular risk of having chronic hepatitis B infection and that screening populations at high risk of chronic infection is essential to identify anyone who can benefit from monitoring and treatment.
Reproduced with permission from NEJM 359:14 October 2008Endnote 8
Screening populations at high risk of chronic HBV infection is essential to identify anyone who can benefit from monitoring and treatment.
Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Individuals who have received blood component therapies , plasma, or intravenous immunoglobulin infusion) in the previous 3 to 6 months may have false-positive hepatitis B surface antibody results due to passive transfer of anti-HBs present in these products.
Individuals possessing IgM anti-rubella virus may have falsely high results with the VITROS Anti-HBs quantitative test.
Anti-HBs levels from past hepatitis B or hepatitis B virus vaccination may fall below detectable levels over time.
A positive anti-HBs result does not exclude infection by another hepatitis virus.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Reactive
Also Check: How To Check For Hepatitis
Results And Next Steps
The results of a hepatitis B titer panel can help a doctor determine a persons hepatitis B status. The results can be confusing if a person has never been through this type of testing before, but the doctor can explain the findings.
The results for the titer come back as either negative or positive on each subtest of the panel. Positive means that the virus or antibodies showed up on the test, while negative means that they did not.
The following table outlines what positive and negative results mean on different parts of the test and the possible next steps.
The information comes from the Immunization Action Coalition:
| Test |
|---|
Read Also: Is Hepatitis B The Same As Hiv
For Patients With Chronic Hbv
Reducing the risk of liver damage
- Have liver enzymes monitored every 6-12 months.
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol.
- Stop smoking, as it increases the risk of liver cancer.
- You may drink coffee 3 or more cups per day may reduce the risk of liver cancer.Endnote 21
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A if you are not already immune – talk to your HCP or contact your local public health department.
- Stick to your medication schedule and your regular lab testing and follow-up visits.
- Tell your HCP before starting any immunosuppressive therapy.
About medications for patients with cirrhosis
- Avoid aminoglycosides , benzodiazepines, and narcotics including codeine .
- Whenever possible, avoid ASA or NSAIDs. Acetaminophen, oral contraceptive pills, and statins are safe to use.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- If you require surgery, discuss it with your specialist first.
- If you have black stools, call your specialist immediately or go to the ER.
- Tell your HCP about any complementary/alternative therapies or over the counter supplements including herbal remedies that you are taking.
- Follow your HCP’s advice on how frequently you require abdominal ultrasounds.
Living well with HBV
Don’t Miss: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
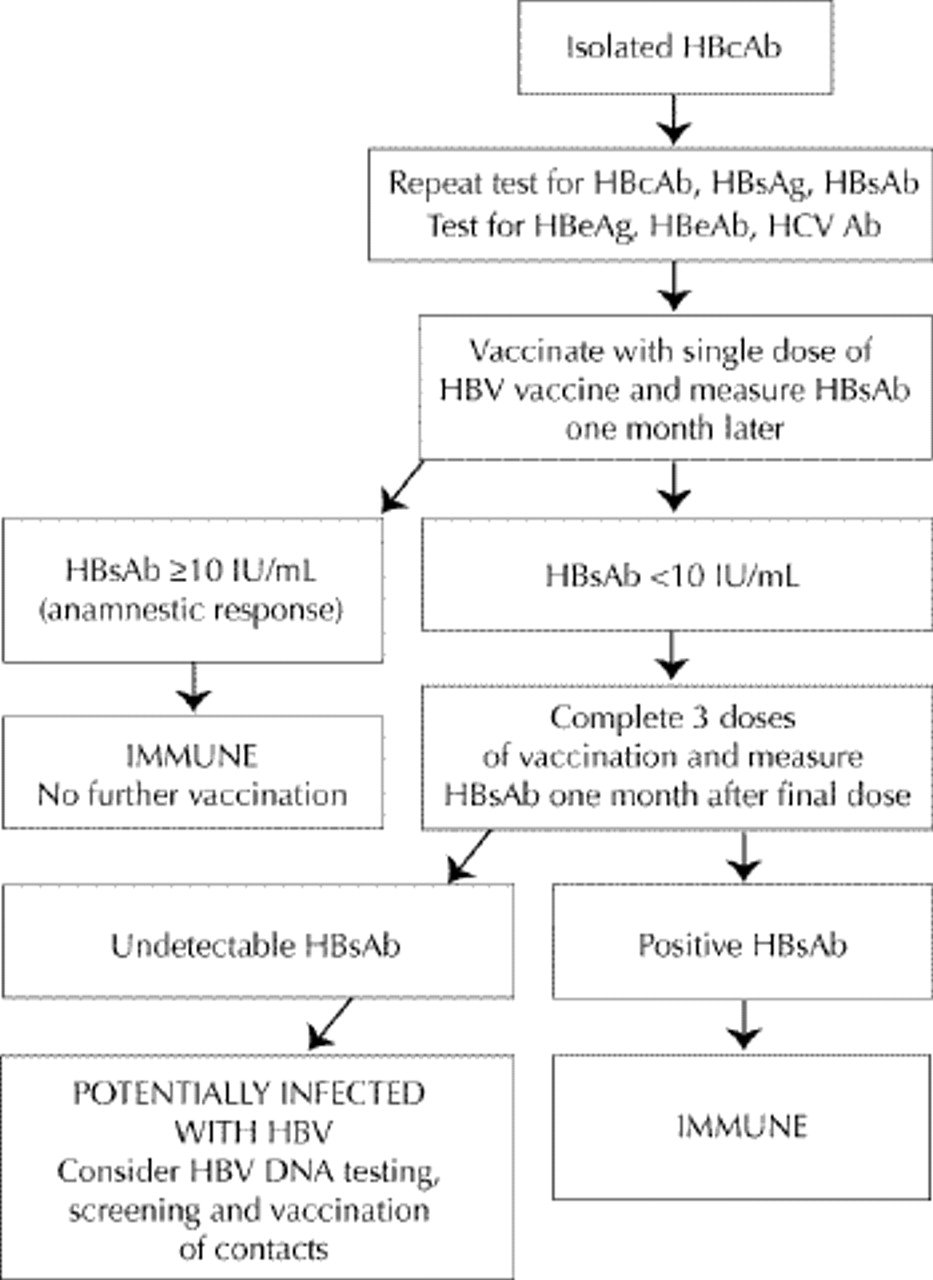
Module 3 Interpretation Of Hbv Diagnostic Test Results
This table describes 6 possible interpretations of diagnostic test results and subsequent recommended actions for clinicians.
In the first scenario of this table, a patient should be considered to be susceptible to hepatitis B when: hepatitis B surface antigen results are negative hepatitis B surface antibody results are negative total hepatitis B core antibody results are negative and the IgM marker of the hepatitis B core antibody is not available/or not done.
It’s noted that approximately 5 percent to 10 percent of people will not respond to vaccine or else do not produce protective levels of antibody post-vaccination .
The recommended action when a patient is considered to be susceptible to hepatitis B is to vaccinate.
In the second scenario of this table, a patient should be considered to be immune to hepatitis B due to vaccination when: hepatitis B surface antigen results are negative hepatitis B surface antibody results are positive total hepatitis B core antibody results are negative and the IgM marker of the hepatitis B core antibody is not available/or not done. Regarding the hepatitis B surface antibody, clinicians are reminded that about 5 percent to 10 percent of people will not respond to the vaccine or else do not produce a protective level of antibody post-vaccination . Note that in immune individuals, levels of hepatitis B surface antibody may decline over time and become undetectable.
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or HBsAg. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or HBcAg, which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Hepatitis B
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Is It Sexually Transmitted
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people who are infected with the hepatitis B virus have mild, flu-like symptoms and some do not become sick at all. Children who are infected are less likely to have an illness or get sick after getting hepatitis B than adults.
In more severe cases, hepatitis B can cause:
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the joints.
- Jaundice .
Normally, these health problems disappear in a few weeks, but even when the person feels much better, they may still be infectious.
Most adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus recover completely and do not become infected again. A few people become very ill in the time just after infection and need to go to hospital some may even die.
High Titers Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk Of Hepatitis B Virus
Sung-Nan Pei, Ming-Chung Wang, Ming-Chung Ma, Ching-Yuan Kuo, Chien-Hung Chen, Po-Nan Wang High Titers of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatitis in Lymphoma Patients Treated with Rituximab-Based Chemotherapy. Blood 2015 126 : 3869. doi:
Also Check: Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantitative
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
Read Also: Hepatitis B Acute Or Chronic
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Don’t Miss: What Are The First Signs Of Hepatitis C
Key Facts And Figures
- HBV is a vaccine-preventable disease that is highly infectious far more so than either HIV or HCV. It is transmitted through perinatal, percutaneous, or sexual exposure to an infected person’s blood / body fluids household contacts are also at risk of infection.
- Acute and chronic HBV infections are frequently asymptomatic or present with nonspecific symptoms about two-thirds of chronically infected people are unaware of their status, and most will only be detected through proactive screening.
- Of those infected as adults, 5% will become chronically infected in contrast, about 90% of infants infected at birth will develop chronic infection.Endnote 1
- Without intervention, 15%40% of chronically infected people will go on to develop cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease, and/or HCC.
HBV is a notifiable disease in all provinces and territories in Canada. As such, it must be reported to the regional/local Medical Officer of Health.