How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Global Efforts To Eliminate Viral Hepatitis
In 2016, WHOs World Health Assembly called for global elimination of viral hepatitis by 2030 and set global targets of achieving 90% reduction in new cases of hepatitis B and hepatitis C, a 65% reduction in deaths from hepatitis B and hepatitis C, and treatment of 80% of people living with these infections . Individual countries are now in different stages of developing their own viral hepatitis elimination plans . At the 2021 WHA, WHO released the Interim Guidance for Country Validation of Viral Hepatitis Eliminationexternal icon providing a global framework for the process and standards for validation of elimination, including absolute impact and programmatic targets .
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 862,000 people were chronically infected with HBV in 2016. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2019, 3,192 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 20,700 acute hepatitis B infections. New HBV infections are likely linked to the ongoing opioid crisis in the United States.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 296 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
You May Like: How To Live With Hepatitis C
Global Immunization Strategic Framework 2021
In 2021, CDC released the Global Immunization Strategic Framework 2021-2030, which provides a roadmap to achieving progress toward a world where everyone is protected from vaccine-preventable diseases , such as hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Three Goals are core immunization program capacities that CDC seeks to strengthen:
-
Prevent VPDs by strengthening immunization services.
-
Detect VPDs by supporting and improving disease surveillance systems.
-
Respond to and prepare for VPD outbreaks.
Two Goals are cross-cutting capacities:
-
Sustain immunization program capacities over time.
-
Innovate to increase immunization program impact through research and evaluation.
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
You May Like: What Is The Best Medicine For Hepatitis C
Hospitalizations Related To Hepatitis B Virus And Hepatitis C Virus Attributable To Immigrants
Approximately 37% of HBV-related hospital events and 9% of those related to HCV occurred among immigrants, who represented 16% of the Canadian population . This resulted in a ratio of 2.3 for HBV-related hospital events and 0.5 for HCV-related hospital events for immigrants. These ratios differed by age group, varying from 1.3 to 4.4 for HBV. In contrast, for HCV, ratios by age group never rose above 1, except for those aged 65 years and older . A sensitivity analysis identified that the ratio for HCV among immigrants aged 65 years and older remained above 1 when the population share for immigrants was increased from 9% Note 35 to 11%.
| Note: HBV = hepatitis B virus.Statistics Canada, 1980 to 2013, Longitudinal Immigration Database and Discharge Abstract Database linked database. |
What Are The Symptoms
- Symptoms can take 2 to 6 months to appear.
- Many people who are infected with hepatitis B have either no symptoms or only mild symptoms.
- Symptoms of acute hepatitis B can include fatigue, loss of appetite, joint pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and dark urine. A small number of people will develop jaundice .
- Some people develop chronic hepatitis B and most remain contagious for the rest of their lives. Chronic infection may lead to cirrhosis and/or liver cancer. Most people with chronic hepatitis B are unaware of their infection.
You May Like: Can Hepatic Steatosis Be Reversed
What Is My Risk
Your risk depends of several factors: destination, length of stay, what you do when you are travelling and whether you have direct contact with blood or other body fluids. In certain destinations, your risk may be higher, as some areas have higher numbers of people with chronic hepatitis B in the general population.
The risk increases with certain activities, such as unprotected sex, sharing needles, tattooing and acupuncture.
Aid and health care workers and anyone who receives medical or dental care with unsterilized or contaminated equipment in a country where hepatitis B occurs are also at greater risk.
Hepatitis B Virus And Hepatitis C Virus Acute Care Hospital Events In Canada: Overall Comparisons
Approximately 166,990 acute care hospital discharges between April 1, 2004, and March 31, 2014, were liver related . Among them, 4,810 were HBV related, and 20,870 were HCV related. After the non-links were removed, 37% of HBV-related hospitalizations and 9% of HCV-related hospitalizations were among immigrants . Although the total number of HCV events was more than four times higher than that for HBV, the numbers of HBV- and HCV-related hospitalizations among immigrants were similar . On average, each immigrant HBV patient was hospitalized 1.5 times over the follow-up period, similar to long-term residents , and this increased with age . For HCV, the corresponding figure was 1.9 times for both immigrants and long-term residents. For both immigrants and long-term residents, HBV and HCV hospitalizations occurred predominantly within the 45 to 64 age group, and admissions occurred more commonly among males . The overall mean length of stay for HBV- and HCV-related hospitalizations was 10 and 11 days, respectively. For HBV, immigrant females stayed longer on average than their male counterparts . For HCV, the mean hospital stays increased with age, especially among long-term residents.
| Note: HCV = hepatitis C virus.Statistics Canada, 1980 to 2013, Longitudinal Immigration Database and Discharge Abstract Database linked database. |
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Worldwide Prevalence Of Hepatitis B Virus And Hepatitis C Virus Among Patients With Cirrhosis At Country Region And Global Levels: A Systematic Review
- Catharina J AlbertsCorrespondenceCorrespondence to: Dr Catharina J Alberts, Early Detection, Prevention and Infections Branch, International Agency for Research on Cancer , 69372 Lyon, France
- Yvan J-F HutinAffiliationsDepartment for Universal Health Coverage/Communicable Diseases, World Health Organization Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean, Cairo, Egypt
Antibodies Which Denote Exposure
Antibody to the hepatitis B core antigen : antibody response is divided into 2 antibody subclasses IgM and IgG:
- anti-HBc IgM subclass indicates acute infection
- anti-HBc IgG subclass occurs during acute, chronic and resolved hepatitis B infection and is indicates exposure to the virus
One antibody test can detect both antibodies, and is reported as total anti-HBc.
Antibody to the hepatitis B e antigen : antibody is found in individuals who have cleared HBeAg. However, it may fall to undetectable levels over time.
Also Check: Standard Process Canine Hepatic Support
The Prevalence Of Hbsag And Anti
A total of 17 prevalence estimates, six for HBsAg and 11 for anti-HCV, were extracted from the 13 included studies about HIV negative/unknown HIV sero-status MSM. Key study details, including the risk of bias assessment, for all reported estimates among MSM are available in Annex 8 and 9 in the Additional file 1 for this article.
The six HBsAg prevalence estimates covered four countries: one each from Croatia and France and two each from Estonia and the United Kingdom . HBsAg prevalence ranged from 0.0% – 0.1% in Estonia and the UK to 1.4% in France . The prevalence in the UK was derived from STI clinics in Scotland in 20012003 and ranged from 0.0% to 1.0% , with the sample size of the study for the latter estimate considerably larger than the former study . The estimate from France is based on a large , multi-centre, multi venue type study from 2009 .
HBsAg Prevalence among HIV negative/unknown HIV sero-status MSM. Y axis – Country, prevalence estimate and sample size X axis: HBsAg prevalence
Anti-HCV Prevalence among HIV negative/unknown HIV sero-status MSM. Y axis – Country, prevalence estimate and sample size X axis: Anti-HCV prevalence
Current Status Of Prevention And Treatment
Safe and effective vaccines to protect against hepatitis A and hepatitis B are available. The hepatitis A vaccine is used in only a few countries greater use of the vaccine has the potential to control outbreaks. The hepatitis B vaccine is used widely around the world. In 2020, global coverageexternal icon with three doses of hepatitis B vaccine was 83%, and 42% of children received a dose at birth, which is necessary to prevent mother-to-child transmission of this infection. Improving rates of vaccination coverage, especially among infants and children, will reduce HBV infection, which could help reduce rates of liver disease and death.
Even though affordable, safe, and effective treatments can prevent liver disease and liver cancer among people living with hepatitis B and cure those living with hepatitis C, WHO estimated that only 10% of people with hepatitis B and 21% of people with hepatitis C worldwide knew they were infected in 2019. Of these, 22% and 62% had received treatment, respectively. .
You May Like: Hepatitis C And Kidney Failure
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted Through Saliva
How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis B is highly infectious, and is spread from one person to another through exposure to infected blood and body fluids . It can be spread through:
- blood transfusions or organ transplantation in countries where blood or blood products have not been properly screened for hepatitis B and other viruses transmitted through blood
- unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing needles or equipment for injecting drugs
- unsterilized medical/dental equipment and shared/contaminated materials or equipment used for tattooing, body piercing or acupuncture
- sharing toothbrushes or razors
- household contact between family members
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Don’t Miss: Xifaxan Dosage For Hepatic Encephalopathy
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Implementing A Birth Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine In Africa: Findings From Assessments In 5 Countries
Edna Moturi1, Carole Tevi-Benissan1*, José E. Hagan2, Stephanie Shendale3, David Mayenga1, Daniel Murokora1, Minal Patel2, Karen Hennessey3, Richard Mihigo1
1World Health Organization Regional Office for Africa, Brazzaville, Republic of Congo
2Global Immunization Division, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA, USA
3World Health Organization, Expanded Programme on Immunization, Geneva, Switzerland
Abstract
Introduction: Few African countries have introduced a birth dose of hepatitis B vaccine despite a World Health Organization recommendation. HepB-BD given within 24 hours of birth, followed by at least two subsequent doses, is 90% effective in preventing perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus. This article describes findings from assessments conducted to document the knowledge, attitudes, and practices surrounding HepB-BD implementation among healthcare workers in five African countries.
Methods: Between August 2015 and November 2016, a series of knowledge, attitude and practices assessments were conducted in a convenience sample of public and private health facilities in Botswana, the Gambia, Namibia, Nigeria, and São Tomé and Príncipe . Data were collected from immunization and maternity staff through interviewer-administered questionnaires focusing on HepB-BD vaccination knowledge, practices and barriers, including those related to home births. HepB-BD coverage was calculated for each visited facility.
Introduction
Methods
Results
| 9 | 16 |
| Country |
|---|
Recommended Reading: What Is Treatment For Hepatitis B
Cirrhosis And Liver Cancer Cause Most Hepatitis
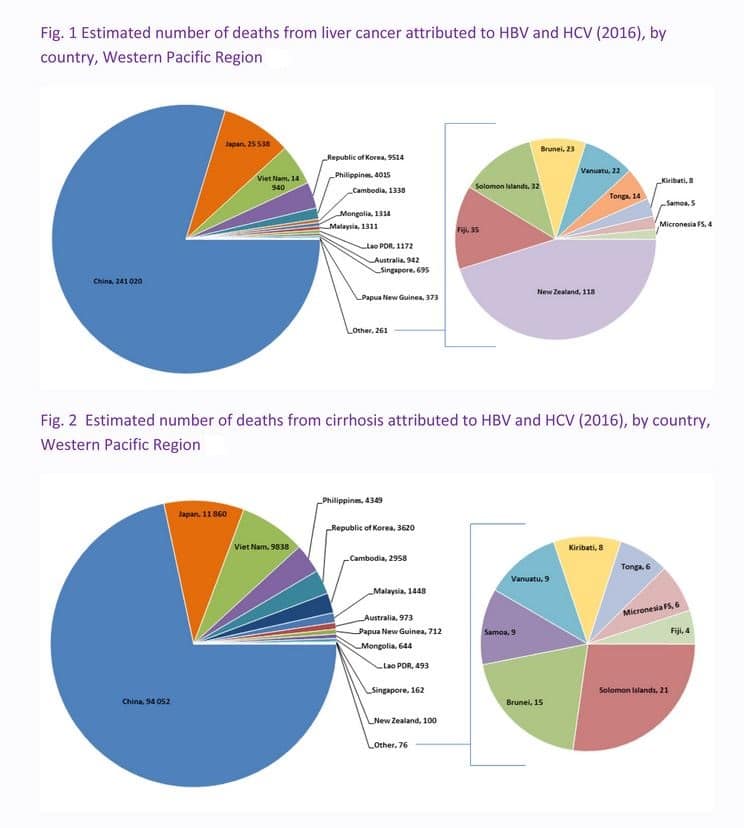
Among the causes attributed to deaths due to hepatitis in 2019, acute hepatitis caused nearly 1% of deaths while 99% were attributed to cirrhosis and liver cancer . Most acute hepatitis deaths were due to hepatitis B. Hepatitis B and C are the major causes of liver cirrhosis in the Western Pacific region .
What Is Already Known On This Subject
- Since viral hepatitis is an important global public health problem, there are international commitments that have prioritized the elimination of hepatitis.
- Chronic viral hepatitis can lead to significant morbidity and mortality, but early detection through screening can help mitigate the risk of clinical deterioration.
- Canada receives over 350,000 immigrants each year, with the numbers expected to grow.
- Patterns of migration have changed over time.
- For admissibility purposes, Canadian immigrants are medically screened for selected diseases to mitigate impacts on Canadian health and social services.
Also Check: How To Get Hepatitis B And C
What Countries Are Affected By Hepatitis B
North America, Northern Europe and Australia have a low incidence of hepatitis B. Countries in the Mediterranean, parts of Eastern Europe, Africa, Central and South America have higher rates. The highest rates of hepatitis B exist in sub-Saharan Africa, South East Asia and the Pacific Islands.
If you are travelling to countries with higher incidences of hepatitis B or those which may not screen their blood supply in case of a blood transfusion, there are several precautions you can take:
- Get immunised before you travel
- Practise safe sex use condoms correctly
- Do not share drug-injecting equipment
- Limit alcohol consumption as people tend to take more risks when intoxicated
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors, piercings or needles
- Avoid tattoos and acupuncture unless you are sure they equipment is appropriately sterilised
- Before any medical or dental procedures, ensure equipment used is sterilised appropriately.