Genotypic Distribution Of Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus infection is distributed worldwide in the form of eight different genotypes . A newly described genotype I is also a pivot of interest for future researchers. There exists at least 8% nucleotide sequence dissimilarity among eight known HBV genotypes. In Pakistan genotype D is most prevalent with estimated prevalence rate of 63.71%. This genotype is usually less responsive towards interferon therapy. The prevalence of genotype A, C, B in Pakistan is 10.036%, 7.550% and 5.335% respectively. The reported prevalence of mixed genotypes and untypable genotypes is 9.93% and 2.37% respectively. According to the most recent study conducted by Awan et al. it has been reported that genotype C is most emerging genotype associated with more severe liver diseases . The approximate prevalence rate of this genotype is 27.7% which represents a major threat to future generations.
How Does Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A is spread from person to person via fecal contamination because the virus is present in the stool. It is spread via contaminated food or water by an infected person who gets small amounts of stool on his or her hands, does not wash his or her hands, and passes the stool onto food that is eaten by others. An example of this is outbreaks of hepatitis A in daycare centers for young children when employees don’t wash their hands after changing diapers, and they then pass the viruses to the next child they feed. In addition, fecal contamination of water in which shellfish live can contaminate the shellfish, and the shellfish can pass the virus to people who eat the shellfish raw.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B Virus
Symptoms for acute hepatitis B virus typically appear about 1 to 4 months after exposure and may resemble the flu. Most people with acute hepatitis B develop no symptoms. Symptoms may include:
- fatigue
Symptoms from liver involvement can include:
- dark urine
- clay-colored stools
- yellow-colored skin or eye sclera
Chronic hepatitis B is a lifelong infection and occurs in about 5% of patients who contract the virus. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic hepatitis B infection, but symptoms may not appear as frequently.
Up to 25% of people who develop chronic infection will develop serious liver conditions, such as cirrhosis , liver failure, or liver cancer.
Those with chronic hepatitis B do not typically have symptoms or feel ill, and can remain symptom free for 30 years or more. If symptoms appear, they are similar to the symptoms of acute infection listed above, but can be at a more advanced stage of liver impairment.
Acquiring hepatitis B during international travel is a possibility in certain regions, so review the CDC guidelines and talk to your doctor for recommendations before travel. If you know you have been exposed to hepatitis B, contact your doctor immediately within 24 hours as you may be able to receive a preventive treatment
Recommended Reading: Where Can You Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Special Considerations And Controversies
Compared to adults with CHC, children have different modes of transmission, spontaneous and treatment rates of clearance, slow progression of fibrosis. The accumulative duration of HCV infection since birth theoretically makes children with vertical transmission of HCV at risk for cirrhosis and HCC by the time of the transition to the adulthood. provides recommendations to pediatricians and pediatric gastroenterologists to monitoring and/or managing children with CHC. As the field of hepatitis C therapy is rapidly progressing, DAAs have proven to be efficient therapy even in HCV-infected adults with compensated cirrhosis. Pretreatment liver histology does not necessarily predict the response. A new IFN-free, DAA-based combination: sofosbuvir plus ledipasvir in one single tablet – was approved in 2014 in the United States for adults clinical trials are ongoing to improve tolerability and compliance in children.
Recommended Approach to Monitoring and/or Managing Children with Chronic Hepatitis C Infection indicated as having HCV infection for greater than 6 months
Hepatitis C: What Happens

About 25% of people who get hepatitis C defeat the virus after a short-term infection. The rest will carry the virus in their body for the long term. Chronic hepatitis C can cause very serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer. There are effective treatments for the virus, though.
Read Also: How Do You Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C: Who Is At Risk
People who have injected illegal drugs at any time, even one time, many years ago, could be walking around with chronic hepatitis C. Because there are often no symptoms, many former drug users may not realize they have the infection. People who received a blood transfusion before 1992 also have a higher risk. Before that year, donated blood was not screened for the hepatitis C virus.
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
- older adults
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Patient Assistance Programs
Hepatitis A: What Happens
Hepatitis A is highly contagious and can spread from person to person in many different settings. It typically causes only a mild illness, and many people who are infected may never realize they’re sick at all. The virus almost always goes away on its own and does not cause long-term liver damage.
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Read Also: Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A And B Vaccines
There are vaccines to protect against hepatitis A and B. The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccination for all children ages 12 to 23 months and for adults who plan to travel or work in areas with hepatitis A outbreaks or who have other risk factors. People with chronic hepatitis B or C should also get the hepatitis A vaccine if they don’t already have immunity to the disease. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants at birth and for adults who have any of the risk factors we discussed earlier. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Just like hepatitis B, you can get this type by sharing needles or having contact with infected blood. You can also catch it by having sex with somebody who’s infected, but that’s less common.
If you had a blood transfusion before new screening rules were put in place in 1992, you are at risk for hepatitis C. If not, the blood used in transfusions today is safe. It gets checked beforehand to make sure it’s free of the virus that causes hepatitis B and C.
It’s rare, but if you’re pregnant and have the disease, it’s possible to pass it to your newborn.
There are some myths out there about how you get hepatitis C, so let’s set the record straight. It’s not spread by food and water . And you canât spread it by doing any of these things:
- Joint pain
See your doctor as soon as possible if you have any of these symptoms.
Sometimes, people have no symptoms. To be sure you have hepatitis, youâll need to get tested.
Don’t Miss: Is Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
Hepatitis A: How Does It Spread
It usually spreads through food or water. Food can be tainted when it’s touched by a person with hepatitis who did not wash their hands after using the bathroom. This transfers tiny amounts of infected stool to the food. Raw shellfish, fruits, vegetables, and undercooked foods are common culprits in hepatitis A outbreaks. The virus can also spread in daycare centers if employees aren’t careful about washing hands after changing diapers.
Hepatitis A B And C: Whats The Difference
Hepatitis is often caused by a virus that comes in different strains. The most common strains of hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, and C. They all are contagious, but they differ primarily by the way they are spread.
Table: Differences among hepatitis A, B, and C
Table: Differences among hepatitis A, B, and C
Recommended Reading: Is There An Immunization For Hepatitis C
Keep Personal Items Personal
Any tools or implements that may have a bit of blood on them from infected people are potential sources of hepatitis B or C transmission. Toothbrushes, nail clippers, razors, needles, and washcloths may all contain trace amounts of blood that can transmit infection. Keep personal items such as these to yourself and never use personal items that belong to others.
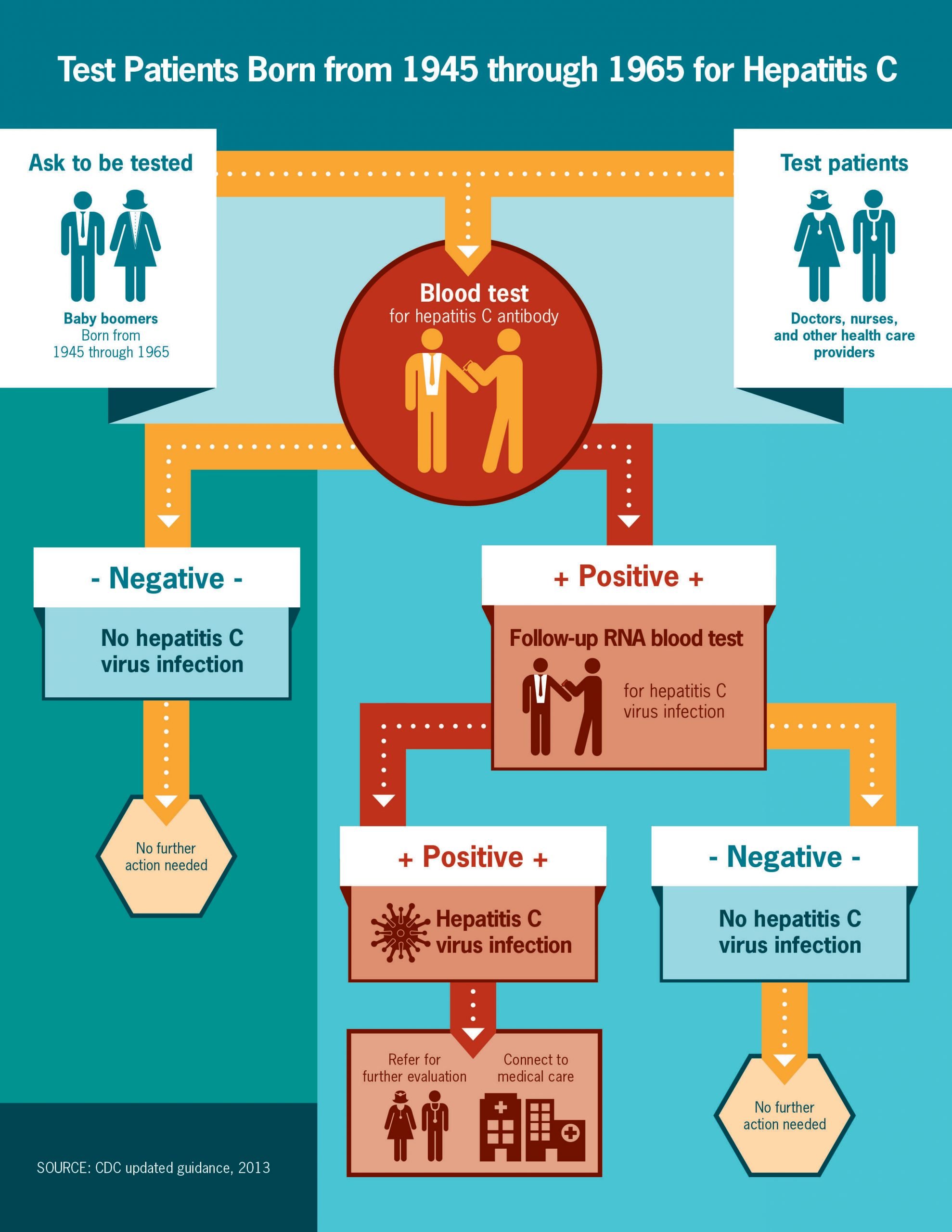
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Recommended Reading: What Medicine Cures Hepatitis C
Global Epidemiology Of Hbv
The epidemiology of chronic HBV infection is distinct and diverse worldwide . Various seroprevalence studies conducted in different areas of world can easily be categorized into three distinct groups of higher, intermediate and lower endemicity. In developing countries with larger population , there is higher prevalence of endemicity with approximately 8% of population as chronic carrier of HBV. In aforementioned areas of world, 70% to 95% of population represents present or past serological markers against HBV. In another study, it has been reported that 60% of world population exist in high endemic zone of HBV infection. The intermediate endemic zone of HBV infection, Middle East, Eastern and Southern Europe, South America and Japan exist. Among these populations the estimated infection is approximately 10-60% and the chronic carrier rate is 2-7%. In the region of intermediate endemicity, majority of infection develop in adults but rate of chronic infection are higher in infants due to early childhood exposure to viral infection. The seroprevalence of HBV infection has been reported 5% in India, while in Italy, Russia and Turkey the prevalence rate ranges from 3%-10%.
How To Prevent Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by a virus . It can be serious and theres no cure, but the good news is its easy to prevent. You can protect yourself by getting the hepatitis B vaccine and having safer sex. If you have oral, anal, and vaginal sex, use condoms and dental dams to help stop the spread of hepatitis B and other STDs.
You May Like: How Soon Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Recommended Reading: Blood Test For Hepatitis C Virus
Is Hepatitis B Worse Than Hepatitis C
Michael says, At the end of the day, its not which ones worsetheyre both bad. He points out that both can lead to liver cancer if left untreated.
Together, hepatitis B and C account for more than 80% of all liver cancers in the world. However, hepatitis B does seem to be more dangerous in some ways than hepatitis C for several reasons:
- Hepatitis B is certainly more virulent and contagious than hepatitis C.
- Hepatitis B is prevalent around the world and it causes more liver cancer than hepatitis C.
- People with hepatitis B are more likely to die from complications to their liver than people with any of the other hepatitis infections.
When comparing hepatitis B and C, we should note that these viruses attack our cells in completely different ways. Hepatitis C operates in the standard virus way, by invading our cells and reproducing copy after copy of itself until it overwhelms the healthy cells. Hepatitis B, however, goes beyond cloning itself to reproduce and instead inserts itself into the healthy cells DNA. This is a more ominous process because it is much harder to destroy the hepatitis B cell when it takes root at the DNA level.
Additionally, hepatitis C typically causes cirrhosis, which is scarring of the liver that interferes with its function, leading to liver cancer. However, in some cases, hepatitis B can cause liver cancer without any signs of cirrhosis. That can make liver cancer itself difficult to diagnose.
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
Recommended Reading: What Happens When You Have Hepatitis B
Chronic Hepatitis C Treatment
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C has evolved, rendering many earlier drugs obsolete. The drugs currently used include pegylated interferon, ribavirin, elbasvir, grazoprevir, ledipasvir, sofosbuvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir, ombitasvir, dasabuvir, simeprevir, daclatasvir. These are always used in various combinations, never alone. Interferon is given by injection while the other medications are pills. Studies have shown that combinations of these drugs can cure all but a small proportion of patients however, serious side effects of treatment can occur.
Treatment options need to be discussed with a knowledgeable physician, as the appropriate combination is dependent upon multiple factors. These include genotype , prior treatment and results, drug intolerances, presence of compensated liver disease or uncompensated cirrhosis, presence of HIV co-infection, other complicating conditions and liver transplantation.
How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Because HCV is primarily spread through contact with infected blood, people who inject drugs are at increased risk for HCV infection. HCV can also be transmitted from an infected mother to child at the time of birth, from unregulated tattoos or body piercings, and from sharing personal items that may be contaminated with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see. Much less often, HCV transmission occurs through sexual contact with an HCV-infected partner, especially among people with multiple sex partners and men who have sex with men. Currently in the United States, health care related transmission of HCV is rare, but people can become infected from accidental needle sticks and from breaches in infection control practices in health care facilities.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Blood Test Results
What Is Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is a condition that causes inflammation of your liver. When a hepatitis virus enters your body, it travels to the liver. It can then enter liver cells and begin to replicate, making more of itself.
The activity of the virus can cause damage to your liver cells. Immune cells begin to travel to your liver to fight the infection. This can also contribute to inflammation.
Liver damage and inflammation can affect your livers ability to function, which can in turn affect your overall health. This is because your liver has several important functions for your body, including:
- breaking down or filtering various substances in the body, such as drugs and toxins
- producing bile, which is important for digestion
- making important blood proteins, including those that help your blood to clot
- storing additional blood sugar as glycogen, which can be used for energy later
- synthesizing immune system factors that are important for fighting infections
- Eastern Europe