Hepatitis C Virus Infection In Renal Transplant Recipients
The pretransplantation prevalence of HCV infection is reported to be as high as 40%. Studies have revealed that overall survival and graft survival are significantly lower in HCV-seropositive renal transplant recipients compared to their HCV-seronegative counterparts. A suggested approach for prerenal transplantation screening for HCV-positive recipients is shown in . Use of this algorithm is especially important because it prompts clinicians in evaluating potential renal transplant recipients for evidence of potential portal hypertension, which usually leads to consideration for simultaneous liver-kidney transplantation.
Dr Leonard Seeff Division Of Digestive Diseases And Nutrition Niddk Bethesda Md
Hepatology.N Engl J Med.
- Alter H.J.
- et al.
Hepatology.
- Frosner G.
- et al.
N Engl J Med.N Engl J Med.
- Porst H.
- Oesen U.
Hepatology.N Engl J Med.JAMA.Hepatology.
- Porst H.
- Oesen U.
Hepatology.JAMA.
Hepatology.JAMA.Hepatology.
Hepatology.
N Engl J Med.J Hepatol.Hepatology.
- Alter H.J.
- et al.
Hepatology.Hepatology.
- Frosner G.
- et al.
N Engl J Med.N Engl J Med.
- Porst H.
- Oesen U.
Hepatology.Ann Intern Med.
- Alter H.J.
- et al.
Hepatology.
J Hepatol.Hepatology.J Hepatol.
If I Have Kidney Failure Can I Get Hepatitis C Through My Dialysis Treatment
The chance of getting hepatitis C through your treatment is small because of strict standard health precautions used in dialysis units today. However, there have been some reports that hepatitis C has been spread between patients in hemodialysis units where supplies or equipment may have been shared between patients. If you are a long-term hemodialysis patient, you should be tested for hepatitis C when you have your regular blood tests.
In the unlikely chance that you get hepatitis C for any reason or if you already have it you should discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider. Today, there are treatments that have been shown to be safe and effective for people on dialysis.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis B Mean
Demographic And Clinical Characteristics Of The Study Participants
A total of 2,435 subjects completed the survey and examination in this study. The mean age was 50.3±10.3 years, and 52.5% of patients were women. The study subjects were divided into four groups based on the types of viral hepatitis, according to the following distribution: HCV infection , HBV infection , HBV/HCV co-infection , and uninfected controls . The demographic and clinical characteristics of the study subjects in the four groups are summarized in Table . The HCV infection group had an older mean age , higher rates of diabetes mellitus and CKD , and higher levels of hemoglobin , alanine aminotransferase , total bilirubin , serum urea nitrogen , and serum creatinine compared to the HBV group, which had a mean age of 46.0±10.2 years and CKD prevalence of 19.7%. Notably, the uninfected control group had higher levels of platelets , albumin , triglycerides , and cholesterol compared with the HCV infection, HBV infection, and HBV/HCV co-infection groups.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of chronic hepatitis patients and controls.
Treatment Of Hcv Infection
Greater eradication of HCV infection by antiviral therapy has been documented in hemodialysis patients than in those with normal renal function , possibly reflecting the high antiviral drug plasma levels achieved because of reduced renal clearance. Actually, the clearance of PEG-IFN is reduced by 45% in patients with ESRD , being mainly affected by the permeability and pore size of dialyzers . This accounts for the high incidence of adverse effects in dialysis patients .
A meta-analysis of 24 prospective studies, including 529 HCV-positive patients on dialysis, showed that monotherapy with IFN allowed SVR in 39% of cases, but 19% of patients were withdrawn from treatment because of side effects . Similar efficacy results were reported in 4 trials with 116 patients given PEG-IFN monotherapy but the drop-out rate was 27% . Overall, there was, however, very high between-study variability as far outcomes independent of the antiviral therapy used, possibly because of the fact that only few of them were randomized or had controlled design. This precludes any conclusions about the indication of preferably using IFN or PEG-IFN in hemodialysis patients with HCV infection.
Better SVR response to these antiviral agents can be anticipated in dialysis patients if pretreatment viral load is low, the degree of cirrhosis is moderate, and the infection results from HCV genotype other than type 1 .
Table 3.
Results of combined treatment of IFN or PEG-IFN with RBV in dialysis patients
Also Check: How To Treat Alcoholic Hepatitis
Assessment Of Hepatitis C And Liver Disease Status In Renal Patients
The clinical tools used in assessing HCV and the liver disease in non-uremic patients are generally applicable to renal patients apart from a few notable differences. HCV infected patient on hemodialysis tend to have normal alanine transaminase possibly due to high lactate level, which cause rapid consumption of NADH co-enzyme or enzyme during dialysis.
All anti-HCV-positive CKD patients should be assessed for HCV RNA viral load, HCV genotyping as well as liver fibrosis. HCV genotype is a strong predictor of response to anti-HCV treatment. KDIGO recommended special steps in drawing blood sample for HCV RNA tests in hemodialysis patients because heparin is an inhibitor of polymerase chain reaction. In order to avoid contamination with heparin which is used in hemodialysis session, the blood sample for HCV RNA should be taken from a peripheral vein before the dialysis session.
We look into several studies that analysed liver biopsy findings in this group of patients. These studies revealed that about 22%-81% of HCV positive ESRD patients had histological evidence of liver fibrosis on biopsy while a smaller percentage of approximately 13%-25% had biopsy proven cirrhosis.
Patients with clinical or histological evidence of cirrhosis should have further assessments to look for the complications of cirrhosis such as upper endoscopy for varices and liver ultrasound for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance.
Getting A Kidney Transplant From And A Person Who Has Hepatitis C When You Dont Have Hepatitis C
Within the last few years, there have been a few cases where doctors transplant a hepatitis C infected kidney into the body of a person without hepatitis C. This means that when you receive your new kidney, you will probably become infected with hepatitis C. But once you receive your new kidney, you are treated with drugs to cure the hepatitis C.
The health of people who receive a kidney transplant is better than the health of people on long-term dialysis. This makes getting a kidney transplant the top priority. Since hepatitis C can be cured without too many side effects, this is now being considered as an option.
This type of transplant is still being studied by researchers, but has shown very positive results for patients who have had it done so far.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Luciferase Expression
Why A Liver Virus Would Damage The Kidney
Damage to the kidney from hepatitis B virus is not usually a result of direct infection. In fact, the immune system’s abnormal reaction to certain parts of the virus may play a larger role in disease causation.
These viral components will typically get attacked by your antibodies in an attempt to fight the infection. Once this happens, the antibodies will bind with the virus, and the resultant debris will get deposited in the kidney. It can then set off an inflammatory reaction, which could cause kidney damage. Hence, rather than the virus directly affecting the kidney, it is your body’s response to it that determines the nature and extent of kidney injury.
What Does Hepatitis C Do To The Kidneys
Once the above mechanisms have been set in motion, the kidneys begin to get damaged. The most frequent site of damage is the kidney’s filter, called the glomerulus . This happens because the filter is essentially a microscopic ball of tiny blood vessels. As mentioned above, the hepatitis C virus does have a tendency to induce vasculitis, an immune injury to the blood vessels. This conglomeration of blood vessels inside the glomerulus is prone to a major hit.
Healthcare providers typically divide hepatitis C-related kidney disease into the following categories:
Don’t Miss: How Much Does A Hepatitis A Shot Cost
Management Of Hcv And Ckd
The goal of treatment is to achieve sustained virologic response . Optimal treatment for HCV-infected CKD patients should consider the HCV genotype, extent of liver damage, CKD stage, transplant candidacy, prior HCV treatment, patient comorbidities, and the benefits and risks of antiviral treatment itself.8
Interferon-based therapy was used sparingly in the past as it was limited by low efficacy as well as high toxicity. A meta-analysis of 10 clinical studies by Fabrizi et al studying interferon/ribavirin in HCV-infected patients receiving hemodialysis showed a summary SVR rate of 56% and discontinuation rate of 25%.21
The advent of direct-acting antivirals has dramatically changed the approach to HCV genotype and viral load. For example, SVR rates generally exceed 90% in most subpopulations with DAAs.22,23 These therapies target non-structural parts of the HCV genome and include NS3/4A protease inhibitors, nucleotide analog NS5B polymerase inhibitors, NS5A inhibitors, and multi-class combination antiviral medications. These newer therapies have been the focus of clinical research in recent years for their improved efficacy, compared to interferon-based therapies. Typically, multiple DAAs are used in combination, NS5A or NS5B inhibitor with a protease inhibitor, to target the different aspects of the HCV genome. Multi-class combination antiviral medications for HCV infection are summarized in Figure 2.
NameFigure 2: Multi-Class Combination Direct-Acting Antivirals:
Hepatitis C And Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease is when there is lasting damage to the kidneys that can get worse over time. Sometimes hepatitis C can cause CKD, but this does not happen very often.
Hepatitis C is connected to CKD because:
- Hepatitis C can cause a type of kidney disease called glomerulonephritis. Your kidneys are made up of thousands of tiny filters called glomeruli. Glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of the kidney filters , which causes permanent damage. When your kidney filters are damaged, this can lead to chronic kidney disease.
- When you have hepatitis C, you have a higher chance of getting diabetes. Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney disease and kidney failure.
Since there is a connection between hepatitis C and kidney disease, doctors recommended that patients with hepatitis C be tested for kidney disease every year.
- If you have hepatitis C and kidney disease, your health may be worse than kidney patients without hepatitis C.
- Having hepatitis C can lead to a faster progression of CKD into kidney failure compared to people without hepatitis C.
This is why getting tested and treated for hepatitis C is so important for your health.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hepatitis C Live Outside The Body
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Blood tests are available to check for hepatitis C. People who are at increased risk should be tested. Your healthcare provider may do a combination of tests to make the diagnosis. It is important to see a healthcare provider if you have any of the symptoms listed above or believe you may have been in contact with blood infected with the hepatitis C virus.
How Do You Know You Have Kidney Disease
You might not! Beyond the symptoms of hepatitis C, kidney-specific symptoms may or may not be present and it’s not unusual to have the silent disease, unbeknownst to the patient. As described above, patients could see blood in the urine, but that might not always be the case. Similarly, protein in the urine might not be apparent or be attributed to other ailments that you might have .
Needless to say, none of these findings are enough to confirm or refute hepatitis C-related kidney damage. However, a good healthcare provider will order tests of kidney function in a patient with hepatitis C, while a nephrologist managing a patient with any of the above telltale features should start looking for hepatitis C as a potential cause. Specifically, there are a few other tests which could be helpful:
- Testing for cryoglobulins
- Rheumatoid factor testing
- Testing the Complement levels
Since the disease happens at a microscopic level and can come in different variations, a kidney biopsy is often the only way to confirm what is going on.
Also Check: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis
Hepatitis C Resulting In Kidney Disease
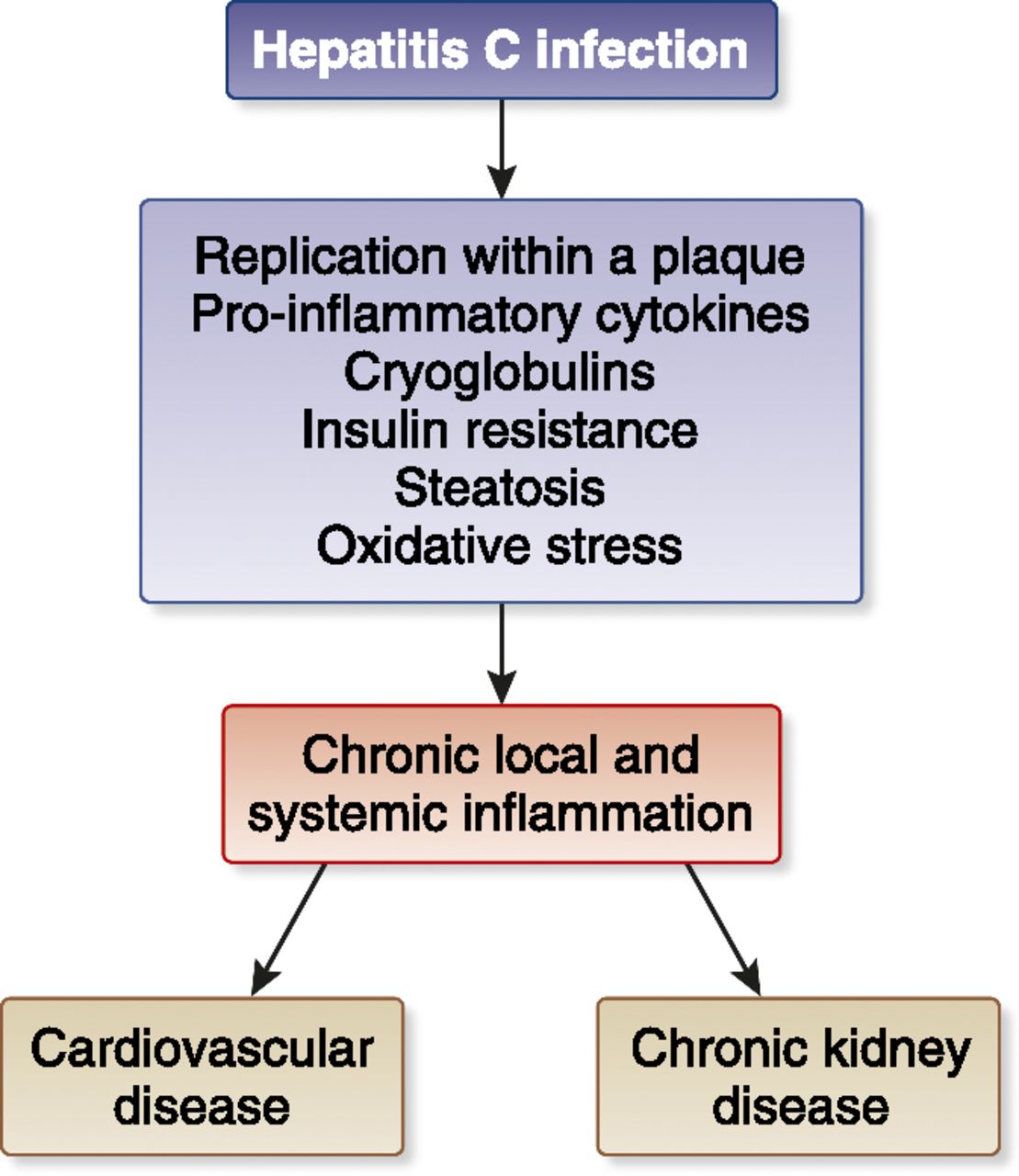
HCV primarily affects the liver causing hepatitis chronic hepatitis may progress to liver fibrosis and subsequently cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, which are the major burden of disease in people living with chronic hepatitis C. However, there are also extra-hepatic manifestations of HCV which include glomerulonephritis, thyroiditis, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, porphyria cutanea tarda, lichen planus, vitiligo, seronegative arthritis, cryoglobulinemia and lymphoproliferative disorders. It has been reported that approximately 40% of the HCV infected patients have at least one extra-hepatic manifestation.
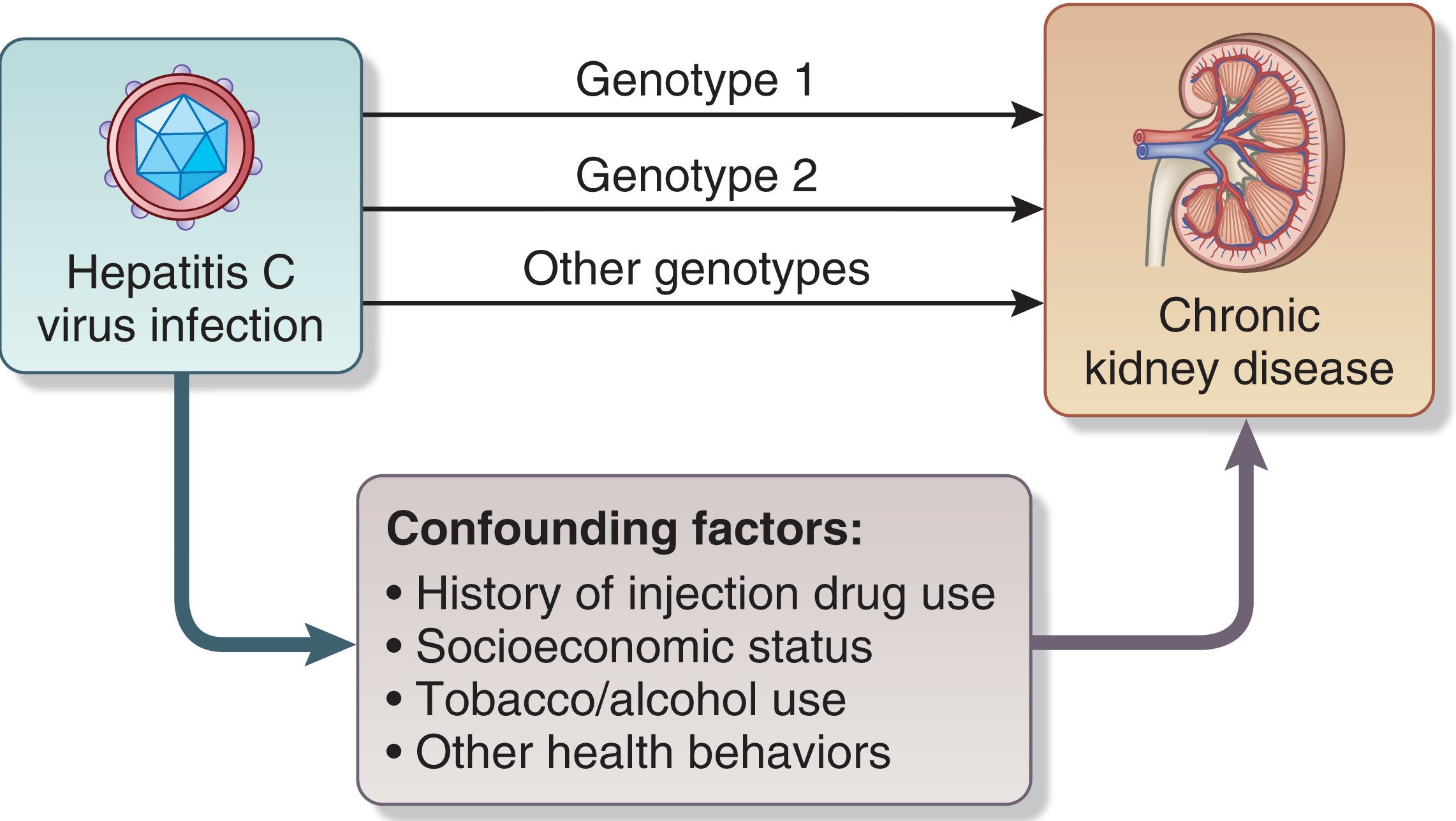
Large-scale community observational studies and others showed that HCV infection carries a risk for CKD and end stage renal disease . Similarly in CKD patients, HCV infection increases the risk of developing ESRD with an estimated 5-year cumulative incidence rate of 52.6% compared to 38.4% in those without HCV infection. This study also reported that HCV infection is an independent risk factor for developing ESRD. The risk for CKD is higher in HCV patients with other co-morbidities such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, cirrhosis, male gender, age < 50 years, and those on more than 6 years follow-up for HCV.
Hcv Diagnosis In Ckd Patients
HCV infection results in an increase in serum alanine aminotransferase , a nonspecific marker of liver damage. The diagnostic value of ALT measurement to assess acute or chronic HCV infection is, however, rather weak in CKD patients, particularly in those on renal replacement therapy with hemodialysis or kidney transplant, since normal aminotransferase levels have been often reported in this patient population . This inconsistency has been ascribed to vitamin B6 deficiency, presence of uremic toxins, or UV-absorbing components in the blood that could alter the transaminase detection . Moreover, serum ALT level does not correlate with the viral load or with tissue liver injury, further indicating the shortcoming of this tool to monitor HCV infection.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis A
Treatment For Hepatitis C Related Glomerulonephritis
In the current understanding of HCV related glomerulonephritis , HCV is the infectious agent which cause GN. The renal disease shows injury from immune complex deposition and cryoglobulins. According to the recent AASLD/IDSA/IAS-USA hepatitis C guideline, HCV patients with type 2 or 3 essential mixed cryoglobulinemia and end-organ manifestations , proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, or membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis are included in the highest priority for anti-HCV treatment due to the high risk for severe complications. Progressive renal disease, proteinuria to the extent of nephrotic syndrome and hypertension are the main manifestations of GN. Therefore a multi-prong approach to the management of HCV related GN involves controlling the clinical manifestations and protecting the kidneys, eradicating HCV, and also reducing the formation and deposition of HCV containing immune complexes in the glomeruli. Anti-hypertensive and anti-proteinuric medications are reno-protective agents, which will delay progression of renal disease while anti-hyperlipidemic therapy may also be required. Diuretics administered together with angiotensin converting enzymes inhibitors and/or angiotensin receptor blockers were proven to be effective.
How Can I Prevent Hepatitis C
Right now, there is no vaccine available for hepatitis C. However, researchers are working to develop a vaccine, and it may be available in the future. In the meantime, the following steps can help to prevent hepatitis C:
- Do not inject illegal drugs
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors or other personal care articles that might have infected blood on them
- Follow safe sex guidelines
- If you are considering getting tattoos or body piercing, make sure the tattoo artist or piercer follows good health practices such as washing hands and using disposable gloves
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B
It is important to remember the sooner you find that you have hepatitis C, the easier it will be for your healthcare provider to treat it. It is important to limit your exposure to the hepatitis C virus and to get checked for the virus during your regular visits with your healthcare provider. If you are told you have hepatitis C it is important to talk with your healthcare provider about your chances of developing kidney disease.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Can You Catch It From Saliva
Hepatitis C And Kidney Disease
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that affects the liver. The liver is an organ in the human body that converts everything you eat or drink into nutrients and gets rid of toxins. There is a connection between hepatitis C and kidney disease. Hepatitis C can cause kidney disease, and sometimes kidney patients can get hepatitis C from hemodialysis, a treatment for kidney failure, if a medical facility does not carefully follow guidelines for infection control.
Can A Person Get Hepatitis C From Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, also called dialysis, is the process of allowing a machine to clean the blood. A persons blood travels into the dialysis machine through an IV line, where the machine cleans it by removing waste products from it. It then travels back into their body through the same or another IV line.
It is possible to acquire the HCV infection from hemodialysis, although improved infection control methods have greatly reduced the possibility of this occurring. Because a person comes into contact with needles during the process, there is always the possibility of even a very small amount of cross-contamination occurring.
Additionally, there may be contamination of:
- medications
1,000 otherwise healthy kidneys from transplantation because they have come from people who were infected with hepatitis C when they died. Early research indicates that by providing follow-up antiviral therapy, it may be possible to transplant these HCV-positive kidneys into recipients who do not have hepatitis C.
A person can be eligible for a kidney transplant if they have HCV. Their medical team will consider the condition of their liver when making the decision. If the liver is not in good condition and the persons overall health is poor, their doctors may deny them a kidney transplant. If their liver is not in good condition, but their overall health is good, they may be eligible for a dual liver and kidney transplant.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis B