Corticosteroid Therapy Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Willis C. MaddreyCorrespondenceAddress requests for reprints to: Willis C. Maddrey, M.D., Associate Professor of Medicine, The Johns Hopkins Hospital, 601 North Broadway, Baltimore, Maryland 21205.AffiliationsDepartments of Medicine, Pathology and Radiology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
- John K. BoitnottAffiliationsDepartments of Medicine, Pathology and Radiology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
- Fredrick L. Weber Jr.AffiliationsDepartments of Medicine, Pathology and Radiology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
- Esteban MezeyAffiliationsDepartments of Medicine, Pathology and Radiology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
- Robert I. White Jr.AffiliationsDepartments of Medicine, Pathology and Radiology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
Protein Restriction Vs Normal Protein Intake
Except in patients with severe encephalopathy, protein restriction is unnecessary and should be avoided because a protein-deficient diet impairs liver regeneration and worsens liver function. Even in the presence of hepatic encephalopathy, patients are usually able to ingest a minimum of 60-100 g/d of dietary protein if other measures to control encephalopathy have been aggressively pursued. In rare instances, restricting dietary proteins may be necessary. In these cases, alternatives include provision of high-quality protein via the parenteral route or provision of oral amino acid supplements that are selectively enriched with branched-chain amino acids.
What Are Possible Risk Factors For Alcoholic Hepatitis
Because alcoholic hepatitis doesnt occur in all people who excessively use alcohol, other factors may influence the development of this condition. These include:
- genetic factors that affect how the body processes alcohol
- the presence of liver infections or other liver disorders, such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and hemochromatosis
- lowers the risk of developing alcoholic hepatitis)
Women are at a greater risk of developing alcoholic hepatitis. This may be due to the differences in how the bodies of men and women absorb and break down alcohol.
Also Check: How Do People Catch Hepatitis B
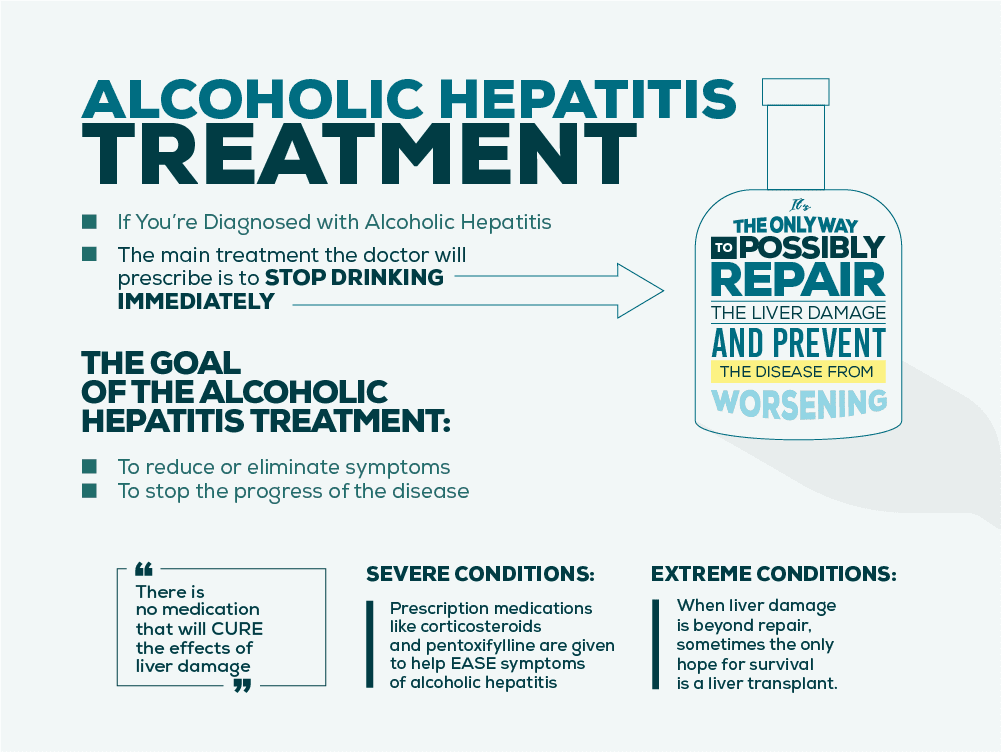
Treatment For Alcoholic Liver Disease
Treatment strategies for ALD include lifestyle changes to reduce alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, and obesity nutritional therapy pharmacological therapy and possibly liver transplantation .
Lifestyle Changes
Abstinence from alcohol is vital to prevent further liver injury, scarring, and possibly liver cancer it appears to benefit patients at each stage of the disease. Although only a few studies have looked specifically at the effects of abstinence on the progression of ALD, virtually every one has shown that abstaining from alcohol is beneficial.
Many people who drink alcohol also smoke cigarettes, and European studies have found scarring of the liver occurs more rapidly in ALD patients who smoked. Obesity is another factor associated with liver disease-specifically, the development of fatty liver and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, a disorder similar to alcoholic hepatitis. Thus, stopping smoking and maintaining a healthy weight are two more measures patients can take to reduce or prevent further liver injury.
Nutritional Treatment
Although alcoholic beverages contain calories, research suggests that under certain conditions these calories do not have as much value for the body as those derived from other nutrients. In addition, many alcoholics suffer from malnutrition, which can lead to liver damage and impaired liver function. Many drinkers take in less than the recommended daily amount of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins , and minerals .
Symptoms Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Patients who are affected by this syndrome, mainly found with the most common symptoms are yellowing of the skin and whitish of eyes.
Apart from these, a few more symptoms are present in the patient such as,
- subsequently, the onset of low-grade fever
- leukocytosis
- vomiting of blood
- unwanted fluid accumulation
If you develop these symptoms, you should avoid drinking alcohol. Carry on with regular drinking can lead to more health problems, such as liver failure, kidney failure, and cirrhosis, and excessive bleeding in the esophagus.
Apart from these, it can suppress the appetite and cause of deficiency of essential nutrients. A heavy drinker absorbs a more required quantity of calories, which further develops fatty liver.
Read Also: How Does One Get Hepatitis B And C
Liver Disease & Pancreatitis
Along with looking at the impact of alcohol on the liver, its also relevant to consider how alcoholism causes pancreatitis. There is acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis.
The pancreas is a gland behind the stomach responsible for releasing digestive enzymes and works with the liver to process substances. An inflamed pancreas is called pancreatitis.
Acute pancreatitis is sudden onset inflammation thats short-lived. The results of the condition range significantly, from being mildly uncomfortable to fatal, but most people recover. Chronic pancreatitis has symptoms similar to acute, but theres frequent pain, weight loss and the potential for diabetes to develop.
In the majority of cases, alcohol causes acute pancreatitis, although other causes may include trauma, metabolic conditions or infections. Heavy, long-time alcohol use accounts for about 60-90% of chronic pancreatitis cases.
Having chronic pancreatitis puts you at risk for other serious illnesses, including cancer and diabetes. Stopping alcohol use significantly increases your chances of recovering from pancreatitis.
What Are The Symptoms Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
The symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis vary depending on the amount of damage to the liver. If you have a mild case of the disease, you may not experience any symptoms. However, as more damage occurs, you may begin to experience:
- pain or swelling in the abdomen
- jaundice, or yellowing of the skin or eyes
- fatigue
- easy bleeding or bruising
The symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis are similar to those caused by other health conditions. If you develop any of these symptoms, you should contact your doctor to get a proper diagnosis and begin treatment.
You May Like: How Hepatitis C Virus Spread
The Role Of Inflammation In Ah
AH is by its definition an inflammatory condition that is often accompanied by features of SIRS: tachycardia, tachypnea, fever and leukocytosis. Infections are common and must be identified and treated in patients with AH, but SIRS may develop in the absence of infection. The presence of SIRS increases the risk of developing MOF that predicts high mortality in AH . Numerous basic and translational studies have identified high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients with AH that may be linked to an increased risk of mortality.
Importance Of Alcoholic Hepatitis In Clinical Practice
Acute alcoholic hepatitis is a serious form of acute decompensation of alcoholic liver disease that develops in heavy drinkers and is characterized by rapid onset of jaundice, malaise, anorexia, tender hepatomegaly, and features of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome . Two recent studies suggest the number of patients hospitalized in the U.S. with AH increased during the first decade of the 21st century . Although in its most severe form, AH has a high short-term mortality rate if untreated, in 2011, only 28% of more than 1,600 patients admitted to U.S. hospitals were treated with glucocorticoids and 17% with pentoxifylline , suggesting a lack of widespread confidence in the 2 most frequently used therapies for AH . Patients with AH are systemically ill with a high risk of nutritional deficiency, infection, acute kidney injury , and development of multiorgan failure syndrome. Recognition of the possible complications and improved understanding of the basic mechanisms of liver injury from alcohol is essential to improve clinical outcomes for patients with severe AH.
You May Like: How Often Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Need To Be Given
Alcoholic Hepatitis: Symptoms Causes And Treatments
09 August, 2020
Alcohol is a legal drug in most countries and also the most consumed drug worldwide. Often, we tend to underestimate the negative impact it has on the body, or we might not even realize. For example, few people know about alcoholic hepatitis.
Alcoholic hepatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the liver as a result of drinking alcohol. Its an injury thats asymptomatic but, in the long run, can cause irreversible damage to the liver and is even associated with liver cancer.
The fact that its asymptomatic makes it almost impossible to calculate the prevalence of this disease. However, we do know that almost 35% of people with alcohol dependence suffer from it. In this article, well explain everything you need to know about alcoholic hepatitis.
Other Factors Influencing Ald Development
Other factors besides alcohol also may influence ALD development, including demographic and biological factors such as ethnic and racial background, gender, age, education, income, employment, and a family history of drinking problems.
Women are at higher risk than men for developing cirrhosis. This higher risk may be the result of differences in the way alcohol is absorbed and broken down. When a woman drinks, the alcohol in her bloodstream reaches a higher level than a man’s even if both are drinking the same amount. The chemicals involved in breaking down alcohol also differ between men and women.
For example, women’s stomachs may contain less of a key enzyme needed for the initial breakdown of alcohol. This means that a woman breaks down alcohol at a slower rate, exposing her liver to higher blood alcohol concentrations for longer periods of time-a situation that is potentially toxic to the liver. Differences in how a woman’s body breaks down and removes alcohol also may be linked to how much and how often she drinks, the fact that estrogen is present in her body, and even her liver size.
Don’t Miss: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
Who Is At Risk For Developing An Alcoholic Liver Disease
The longer a person drinks alcohol and the more they consume, the higher the chances of them developing alcoholic liver disease.4 While it does not develop in all heavy drinkers, it is common in people between ages 40-50.4 Men are also more likely to develop the disease than women, but women can develop it after less exposure to alcohol.4
According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, a woman consuming up to 1 drink per day and up to 2 drinks per day for men is considered moderate drinking.7 The National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism defines binge drinking as a pattern of drinking that raises blood alcohol concentration levels to 0.08 g/dL. In about a 2-hour time period, this is around 4 drinks for women and 5 drinks for men.7
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration defines heavy alcohol use as the occurrence of 5 or more days of binge drinking episodes within the past month.7
From Steatosis To Cirrhosis

Alcoholic Liver Disease includes three conditions: Fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Heavy drinking for as little as a few days can lead to “fatty” liver, or steatosis-the earliest stage of alcoholic liver disease and the most common alcohol-induced liver disorder.
Steatosis is marked by an excessive buildup of fat inside liver cells. This condition can be reversed, however, when drinking stops.
Drinking heavily for longer periods may lead to a more severe, and potentially fatal condition, alcoholic hepatitis-an inflammation of the liver. Symptoms include nausea, lack of appetite, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain and tenderness, jaundice, and, sometimes, mental confusion. Scientists believe that if drinking continues, in some patients this inflammation eventually leads to alcoholic cirrhosis, in which healthy liver cells are replaced by scar tissue , leaving the liver unable to perform its vital functions.
The presence of alcoholic hepatitis is a red flag that cirrhosis may soon follow: Up to 70 percent of all alcoholic hepatitis patients eventually may go on to develop cirrhosis. Patients with alcoholic hepatitis who stop drinking may have a complete recovery from liver disease, or they still may develop cirrhosis.
Read Also: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis C
Predicting Prognosis In Ah
In 1977, Maddrey and colleagues used the serum bilirubin and prothrombin time to define a group of patients with AH that had a 28-day mortality rate above 50%. This formula, known as the Maddrey Discriminant Function , was subsequently used to stratify subjects for inclusion into clinical trials . Early trials and a subsequent randomized multicenter trial indicated that only those patients with more severe manifestations of AH and an MDF > 32 benefited from treatment with glucocorticoids . The MELD score was also shown to predict 28-day and 90-day mortality, and the ABIC score and the Glasgow AH Score also predict 90-day mortality . All of these scoring systems have been validated to predict severe outcomes with a high degree of reliability.
Although an MDF > 32 initially defined a group of patients with a 28-day mortality rate > 50%, the short-term mortality in the placebo group in recent studies is much better than the mortality rate in the U.S. multicenter trial , likely because of improvements in best supportive care . Importantly, improved outcome with BSC alone makes direct comparisons with historical data from trials more difficult since the time when the trials were completed must be considered.
Signs & Symptoms Of Afld
Unfortunately, AFLD itself has very few symptoms. The main AFLD symptoms include:
- Feeling tired
- Having discomfort in your upper right abdomen
- Yellow coloration of the skin or whites of the eyes
Because there are so few symptoms, it can be hard for doctors to make a diagnosis for AFLD in the early stages. The disease is often found if you need to have imaging done, or if you have a blood test that comes back showing problems with the chemicals in your liver. Sometimes, doctors are not able to find alcoholic fatty liver disease until it progresses into a more dangerous condition like cirrhosis.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Signs And Symptoms Cdc
Nutrition Services And Gastroenterology/hepatology
Adequate nutritional support is of paramount importance for the survival and recovery of patients with alcoholic hepatitis. The complexity of the disease and the wide variation in nutritional regimens and modalities mandate consultation with a nutritionist. Customarily, the gastroenterology service of the hospital should be able to handle this issue and should be instrumental in treatment.
In patients with alcoholic hepatitis who have developed cirrhosis, especially those with coexistent chronic viral hepatitis B or C, consider periodic surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma. A common algorithm includes the determination of serum alpha-fetoprotein levels at 6-month intervals along with annual diagnostic ultrasonography. The finding of a liver nodule or an elevated AFP level should lead to referral to a liver specialist and additional diagnostic studies.
In general, for patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis, observation by a gastroenterologist or a hepatologist is desirable, particularly if the illness is of sufficient severity or complexity to require intensive care.
Alcoholic Hepatitis: Pathogenesis Diagnosis And Treatment
, Department of Health Sciences, University “Magna Græcia”, Viale Europa – Germaneto, 88100 Catanzaro, Italy., Italy, , , , ,
Affiliation:
Journal Name: Reviews on Recent Clinical Trials
Volume 11 , Issue 3 , 2016
Abstract:
Alcohol represents the oldest substance of abuse known and Alcoholic Liver Disease is the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. The ALD includes a widespectrum of injury and may lead progressively from simple steatosis to frank cirrhosis. The ALDdiagnosis may be hard and it is mainly defined by the history of chronic alcohol intake, physical andlaboratory abnormalities suggestive of liver disease. Abstinence is the cornerstone of ALD therapy.Although the burden on health of ALD is not negligible, in the last decades few therapeutic advances have been made.Because of the complex pathogenetic mechanisms, the therapy of ALD and especially of severe Alcoholic Hepatitis ,represents a thorny problem in the clinical practice. In severe forms of acute AH, some specific drug treatments, includingglucorticoids or pentoxifylline, have been defined and are, at the moment, recommended by international guidelines. Onthe contrary, specific long-term treatments of ALD, aimed at stopping the progression of fibrosis, are not yet approved.
Reviews on Recent Clinical Trials
Title:Alcoholic Hepatitis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment
VOLUME: 11ISSUE: 3
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted Disease
Causes & Symptoms Of Alcoholic Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis can lead to several symptoms that can range from irritating to potentially deadly. The most serious of these symptoms are yellowing of the skin and eyes, increased bleeding and swelling.
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes: Increased yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes is a serious symptom of alcoholic cirrhosis. Jaundice indicates a malfunctioning liver, leading to a buildup of toxins that could eventually become deadly. Someone who experiences jaundice should seek emergency medical help.
- Increased bruising or bleeding: Increased bleeding occurs because the liver stops making enough of the components needed for blood clotting. It can also cause a person to bruise easier than they used to. This side effect is dangerous: even a minor source of bleeding can cause significant blood loss because the bleeding cannot be stopped easily. If you notice that you have increased bleeding, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
- Swelling in the abdomen, feet, legs or ankles: The last important symptom of alcoholic cirrhosis is swelling, especially within the abdomen. This swelling, also called ascites, occurs when the liver no longer makes proteins that keep water within the veins. This indicates that the liver is not functioning as it should. The buildup of fluid in the abdomen can lead to serious health problems.
Alcoholic Hepatitis Vs Cirrhosis
scope of the problem
- Epidemiology, signs, symptoms, and lab abnormalities are extremely similar between alcoholic cirrhosis and alcoholic hepatitis.
- Alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis overlap to a large extent .
therapeutic implications
- The management of both conditions is overall extremely similar , consisting primarily of supportive care.
- The only major difference between the acute management of alcoholic hepatitis versus cirrhosis is the use of steroid. The benefit of steroid in alcoholic hepatitis is controversial, so when in doubt omission of steroid may often be reasonable.
features to help sort out alcoholic hepatitis vs. cirrhosis
Read Also: How Often Should You Be Tested For Hepatitis C