What Are The Treatment Options For Hcv
Currently, the standard of care for the treatment of HCV is pegylated interferon in combination with ribavirin. This combination therapy is typically a 24-week or 48-week course. Research has shown that combination therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin can result in undetectable levels of HCV in 40-50 percent of people with genotype 1 and 70-80 percent of people with genotypes 2 and 3.11,12,13,14
What Are Some Theories Being Investigated
Health authorities are investigating a number of possible causes for these hepatitis cases. So far, the WHO has ruled out the viruses that cause hepatitis A, B, C, D and E, based on laboratory testing.
While toxin exposure is another consideration, experts believe this is less likely due to the cases being documented in different countries. Health authorities have also not found any links to international travel among the cases either.
Currently, investigations suggest a link to an adenovirus, according to the WHO and ECDC. Adenoviruses make up a large family of viruses that can spread from person to person, causing a range of illnesses including colds, pinkeye and gastroenteritis. Officials say there has been a recent rise in adenovirus infections, particularly in the U.K.
Close to half of the hepatitis cases, including those in Alabama, have been tied to an adenovirus, with lab tests indicating some children were infected with type 41, which is associated with gastroenteritis, causing diarrhea and vomiting. At least 19 cases also involved a SARS-CoV-2 co-infection.
While adenovirus is currently one hypothesis as the underlying cause, it does not fully explain the severity of the clinical picture, the WHO said in its April 23 report. The health agency noted this particular virus has not previously been tied to hepatitis, adding that it is a common pathogen that usually causes self-limited infections.
Human Herpesvirus Type 8
Risk factors and epidemiology
Human herpesvirus 8 is a -herpesvirus, which has potential for malignant transformation. Although primary HHV-8 infection can cause rash and fever in children and immunocompromised individuals, the onset of HHV-8-related diseases usually occurs several years after HHV-8 acquisition: Kaposi sarcoma, body cavity lymphoma, and multicentric Castleman’s disease are the typical presentations of HHV-8 infection but bone marrow aplasia and multiple myeloma has also been described in association with HHV-8 infection .
Clinical presentation
In autopsy studies Kaposi sarcoma involved the liver in approximately 20% of patients with AIDS and was usually part of a widespread cutaneous and visceral disease. Due to highly active antiretroviral combination therapy, Kaposi sarcoma has become a rare complication of HIV infection. However, fulminant hepatic Kaposi sarcoma may occur after organ transplantation . Macroscopically there are dark-red tumors on the skin, the liver capsule and the parenchyma. Under the microscope the typical lesion is a mesh of spindle-cell-like tumor cells and dilated thin-walled vessels .
Kaposi sarcoma after liver transplantation. Brownish nodules appear in the abdominal scars 12 weeks after liver transplantation. Histology reveals a spindle-cell rich tumor confirming the clinical diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma. In situ detection of human herpesvirus 8 in the Kaposi tissue.
Diagnosis
Therapy
Recommended Reading: Is There A Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
Classification Of Chronic Hepatitis
Cases of chronic hepatitis were once classified histologically as chronic persistent, chronic lobular, or chronic active hepatitis. Current classification specifies the following:
-
Etiology
-
Intensity of histologic inflammation and necrosis
Inflammation and necrosis are potentially reversible fibrosis usually is not.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis A Include Fatigue And Tummy Pain
Hepatitis A is a liver infection caused by the highly contagious Hepatitis A virus. Most people are vaccinated against the virus, and don’t need any treatment if they come in contact with it.
The CDC recommends that unvaccinated people who encounter it to get a hepatitis A shot, and possibly an antibody drug, within two weeks of exposure.
Symptoms usually start within 15 to 50 days of coming into contact with the virus.
For most people, symptoms of hepatitis A include fatigue, loss of appetite, tummy pain, nausea, vomiting, yellow skin, dark urine, and pale poop.
Symptoms range in severity and usually last between a few weeks to about two months, without any long-term liver damage.
But in rare cases, the condition can become chronic and lead to liver failure and death. Older people and those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of severe illness.
Kids younger than 6 years old with hepatitis A don’t tend to get symptoms.
You May Like: Hepatitis B E Antibody Positive
What Is Fatty Liver Disease
As the name implies, fatty liver disease occurs when fat deposits build up in your liver. The fat in the liver can damage it, causing inflammation and scarring, explains Rena Fox, M.D., a professor of general internal medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and a UCSF Health hepatitis specialist. Although doctors still arent sure exactly what causes it, NAFLD is linked to obesity, insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and high triglycerides levels.
There are different types of fatty liver disease, but NAFLD is the most common, affecting 30% to 40% of adults in the United States, according to the National Institutes of Health . While some types of fatty liver disease are linked to heavy alcohol use, people with NAFLD are not over-drinkers.
One of the challenging things about this disease is that it can be hard to detect, since it often has no obvious symptoms until the liver damage is already extensive. When someone is at a very advanced stage, they may have some pain in the upper-right part of the abdomen, and they may feel tired, says Dr. Fox. At a very late stage, they could have fluid in the abdomen, and they could develop yellowing of the eyes and skin. We want to help patients avoid getting to this point.
What Is Alcoholic Hepatitis
People who drink alcohol can still develop liver inflammation and injury, even if they never contract HCV. This is because excessive alcohol consumption can lead to alcoholic hepatitis.
Alcoholic hepatitis is a separate condition from HCV it is a severe consequence of long-term alcohol abuse that lasts at least 20 years.
A explains that since the liver is the main site of alcohol breakdown in the body, it is the organ that experiences the most damage from heavy alcohol use.
Alcoholic hepatitis is especially common in those who:
- drink large amounts of alcohol
- drink outside of mealtimes
Also Check: Hepatitis C How You Get It
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while they’re very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
As many as two million people may have hepatitis C and not realize it. Thats because even chronic hepatitis C patients may not have symptoms until late in the disease. You may find out you have the disease accidently through routine screenings for other illnesses.
There are symptoms of hepatitis C that may or may not show up, including:
- Abdominal pain
- Light colored stools
- Loss of appetite
Some patients with hepatitis C can develop a complication called fatty liver disease. Fatty liver disease can also occur as a singular instance of liver illness.
Don’t Miss: How Did You Get Hepatitis C
Cirrhosis And Hepatitis C: Their Connection Prognosis And More
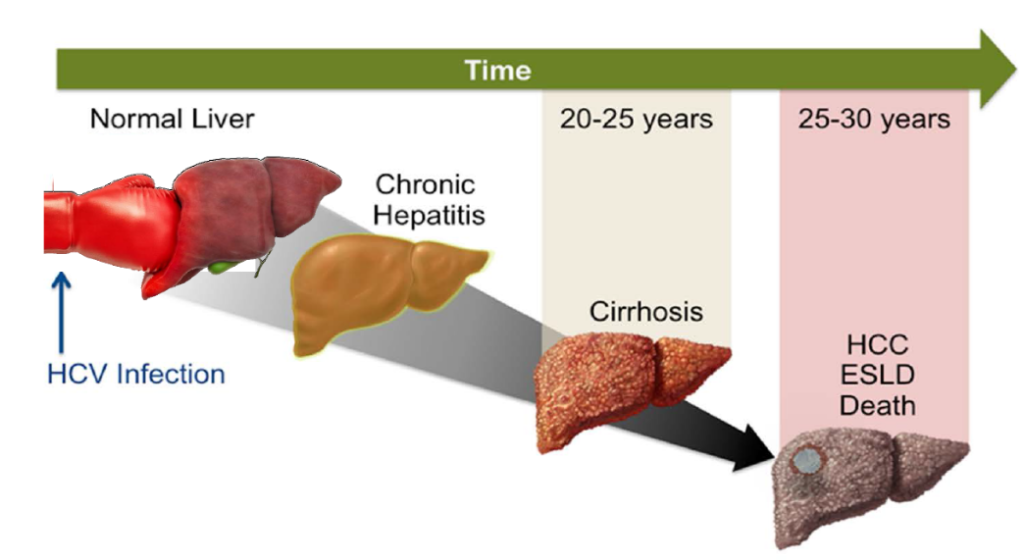
Hepatitis C can lead to cirrhosis
Some 3.5 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C virus . Yet most people infected with HCV dont know they have it.
Over years, HCV infection can cause major damage to the liver. For every 75 to 85 people who have chronic HCV infection, between
Over time, inflammation in the liver causes scarring and permanent damage . At the point of cirrhosis, the liver is unable to heal itself. Cirrhosis can lead to:
- end-stage liver disease
There are two stages of cirrhosis:
- Compensated cirrhosis means the body still functions despite reduced liver function and scarring.
- means that liver functions are breaking down. Serious symptoms may occur, like kidney failure, variceal hemorrhage, and hepatic encephalopathy.
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
You May Like: Royal Canin Hepatic Dog Food Reviews
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
How Are Fatty Liver Disease And Hepatitis C Connected
Recent research has begun to define the connection between fatty liver disease and hepatitis C. You can have fatty liver disease on its own, or it can accompany a hepatitis C infection. If you have hepatitis C your chances of developing fatty liver disease is higher than developing the disease by itself. According to the data, about 50% of people with hepatitis C also have fatty liver disease.
Typically, we see two types of fatty liver disease in people with hepatitis C:
- Metabolic fatty liver caused by obesity, type 2 diabetes, raised blood fat levels, or insulin resistance
- Hepatitis-C induced fatty liver disease is caused by the HCV virus itself
You can actually have both forms of fatty liver disease simultaneously. Both forms of the disease have a negative effect on hepatitis C symptoms. How are these diseases treated and when should you see a doctor?
You May Like: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
How Many Global Cases And How Serious Are They
Based on numbers compiled by the ECDC in a report on and the WHO on April 23, there are at least 194 cases so far of hepatitis with no known cause in countries including the U.K., Spain, Israel, the U.S., Denmark, Ireland, the Netherlands, Italy, Norway and France.
As of April 21, 114 cases were from the U.K., according to the WHO. As of April 27, there were approximately 55 probable and confirmed cases from a dozen countries within the European Union and European Economic Area, 12 cases from the U.S., and another 12 out of Israel, the ECDC said. Japan has reported one case.
The severe hepatitis for which there is no cause, we rarely see more than about 20, 25 max in the whole year. And weve seen 114 in the first three to four months of this year, Kelly said.
These are perfectly normal children. Theyve got no comorbidities and no other infections and theyre developing severe hepatitis, of which 10 per cent have required liver transplantation.
The 10 per cent figure is based on an earlier tally of cases from the WHO on April 23 that found 17 children required a liver transplant. One child in Britain reportedly died.
The hepatitis cases involve children between the ages of one month and 16 years, health agencies have said, with the majority occurring in young children between the ages of two and five.
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Drinking After Someone
What Is Hepatitis C
- It is a contagious liver disease that damages the liver.
- It can be acute, lasting only a few weeks, in 15-25% of individuals, resulting in a mild illness.
- It can be chronic unless successfully treated, resulting in liver damage, cirrhosis , and liver cancer.
- It is spread through contact with the blood of an infected person.
People who have chronic HCV often have no symptoms and can live for many years without feeling sick.
Symptoms of acute HCV include fever, fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, dark urine, jaundice , and joint pain.
Symptoms of chronic HCV include jaundice, gastrointestinal bleeding, ascites , and mental changes .
What Are The Symptoms
Medical officials have said that a number of cases began with gastrointestinal symptoms such as stomach pains, diarrhea and vomiting. The children later exhibited signs of jaundice, where the skin and whites around the eyes turn yellow. Jaundice is an indication that something is wrong with the liver, and medical advice should be sought immediately.
Other common symptoms of hepatitis include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, dark urine, light-coloured stools and joint pain.
Dr. Deirdre Kelly, professor of paediatric hepatology at the University of Birmingham, told CTV News on Tuesday that the majority of children have spontaneously recovered.
While this is a serious disease if their child develops it, the chances are they will recover on their own, she said.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C Caused From
Human Herpesviruses Types 6 And 7
Risk factors and epidemiology
HHV-6 exists in two variants, HHV6-A and HHV-6B, which infect T cells and various other cells types expressing the CD46 receptor . Although genetically clearly distinct from HHV-6, HHV-7 is another -herpesvirus that shares many features with HHV-6. Primary infection with either virus commonly occurs at young age and can lead to a febrile illness known as exanthema subitum or roseola infantum . Pityriasis rosea reflects primary infection with HHV-7. HVV-6 also integrates into the host’s genome and is transmitted via the germline. HHV6 and HHV-7 can reactivate each other as well as cytomegalovirus leading to symptomatic CMV-disease in liver transplantation .
Clinical presentation
The full spectrum of diseases caused by chronic HHV-6 and -7 infection is still unclear, but these viruses are putatively involved in a variety of different syndromes such as encephalitis, multiple sclerosis, pneumonitis, an infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome, postinfectious drug hypersensitivity as well as lymphoproliferative disorders and systemic disease in immunocompromised patients . HHV-6 can cause severe and fatal hepatitis in neonates, children and adults . Hepatitis due to infection and reactivation of HHV-6 and HHV-7 can also complicate organ transplantation . In addition, HHV-6 has been associated with autoimmunity and giant-cell hepatitis and giant-cell transformation of bile duct cells .
Diagnosis
Therapy
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.