History And Physical Exam
To diagnose all forms of hepatitis, your doctor will first take your history to determine any risk factors you may have.
During a physical examination, your doctor may press down gently on your abdomen to see if thereâs pain or tenderness. Your doctor may also check for any swelling of the liver and any yellow discoloration in your eyes or skin.
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Viral Hepatitis
The period of time between exposure to hepatitis and the onset of the illness is called the incubation period. The incubation period varies depending on the specific hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A virus has an incubation period of about 15 to 45 days Hepatitis B virus from 45 to 160 days, and Hepatitis C virus from about 2 weeks to 6 months.
Many patients infected with HAV, HBV, and HCV have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including:
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
Hepatitis B is primarily spread when blood, semen, or certain other body fluids- even in microscopic amounts from a person infected with the hepatitis B virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted from:
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Read Also: Drugs Used For Hepatitis C
How Long Before I Have Symptoms
Many people have mild symptoms or no symptoms, which is why hepatitis is sometimes called a âsilentâ disease.
Hepatitis A. The symptoms usually show up 2 to 6 weeks after the virus enters your body. They usually last for less than 2 months, though sometimes you can be sick for as long as 6 months.
Some warning signs that you may have hepatitis A are:
Hepatitis B. The symptoms are the same as hepatitis A, and you usually get them 3 months after you’re infected. They could show up, though, anywhere from 6 weeks to 6 months later.
Sometimes the symptoms are mild and last just a few weeks. For some people, the hep B virus stays in the body and leads to long-term liver problems.
Hepatitis C. The early symptoms are the same as hepatitis A and B, and they usually happen 6 to 7 weeks after the virus gets in your body. But you could notice them anywhere from 2 weeks to 6 months later.
For about 25% of people who get hep C, the virus goes away on its own without treatment. In other cases, it sticks around for years. When that happens, your liver might get damaged.
Remember, it’s possible to spread all the types of hepatitis even if you don’t show any signs of being sick.
How Is Hepatitis A Diagnosed
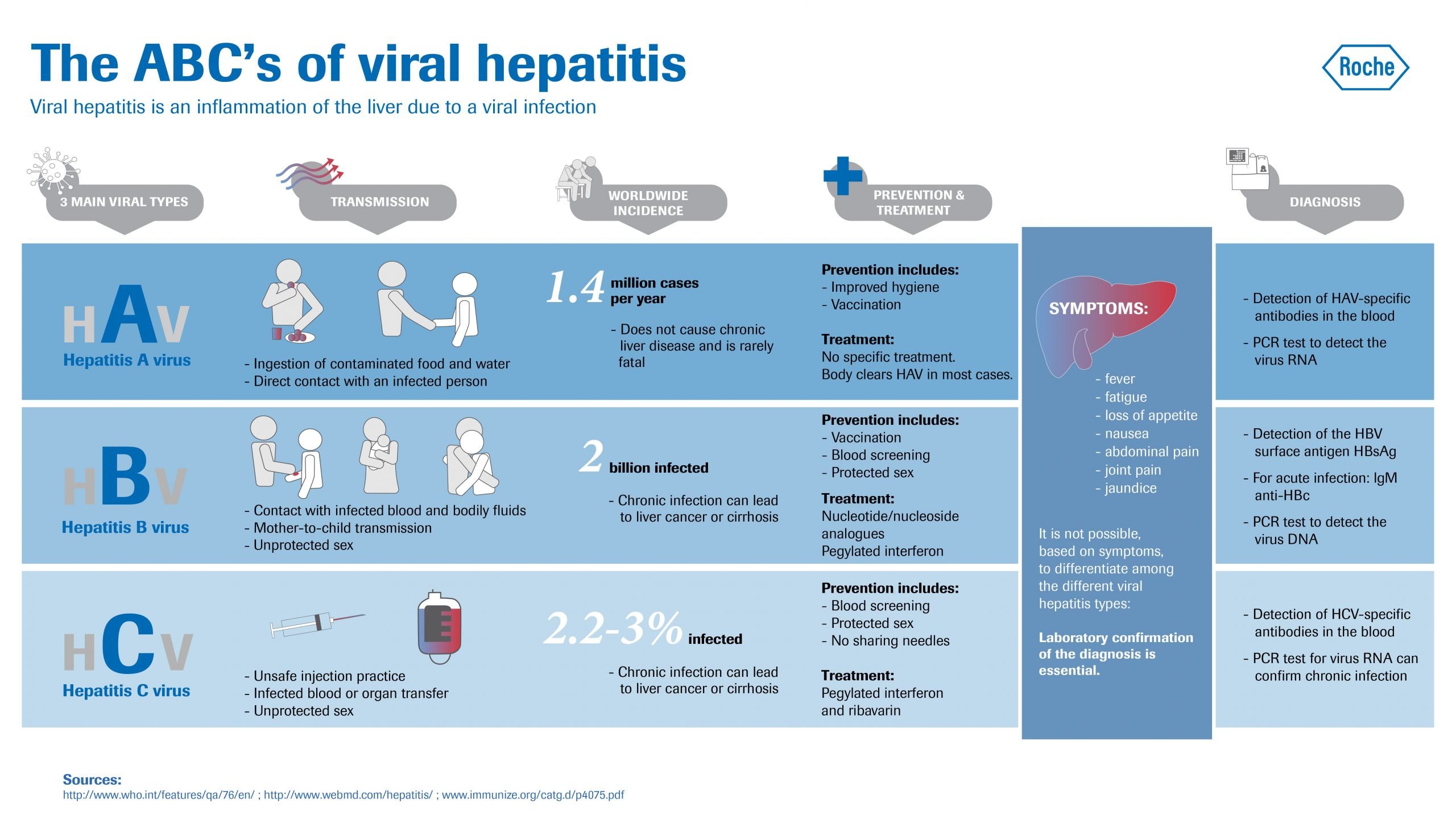
Some people have only a few symptoms and no signs of jaundice. Without visible signs of jaundice, its hard to diagnose any form of hepatitis through a physical examination. When symptoms are minimal, hepatitis A can remain undiagnosed.
After you discuss your symptoms with your doctor, they may order a blood test to check for the presence of a viral or bacterial infection. A blood test will reveal the presence of the hepatitis A virus.
Complications due to a lack of diagnosis are rare.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B And Hiv The Same Thing
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Just like hepatitis B, you can get this type by sharing needles or having contact with infected blood. You can also catch it by having sex with somebody who’s infected, but that’s less common.
If you had a blood transfusion before new screening rules were put in place in 1992, you are at risk for hepatitis C. If not, the blood used in transfusions today is safe. It gets checked beforehand to make sure it’s free of the virus that causes hepatitis B and C.
It’s rare, but if you’re pregnant and have the disease, it’s possible to pass it to your newborn.
There are some myths out there about how you get hepatitis C, so let’s set the record straight. It’s not spread by food and water . And you canât spread it by doing any of these things:
- Joint pain
See your doctor as soon as possible if you have any of these symptoms.
Sometimes, people have no symptoms. To be sure you have hepatitis, youâll need to get tested.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Genotype 1a Treatment
How Serious Is It
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
Hepatitis Testing Prevention And Treatment In Pearland Tx
Prime Urgent Care provides hepatitis testing and treatment to residents in Pearland and the Greater Houston area. We accept most major insurance providers, and we offer low out-of-pocket rates for patients without insurance. To get tested today, book an appointment online or just walk into our clinic for immediate medical care.
You May Like: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma Hcc
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
To diagnose hepatitis, your health care provider:
- Will ask about your symptoms and medical history
- Will do a physical exam
- Will likely do blood tests, including tests for viral hepatitis
- Might do imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI
- May need to do a liver biopsy to get a clear diagnosis and check for liver damage
Doctors Without Waiting Rooms
Health
Viral hepatitis is an infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs. Researchers have discovered several different viruses link that cause hepatitis, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E.
Recommended Reading: How You Get Hepatitis B And C
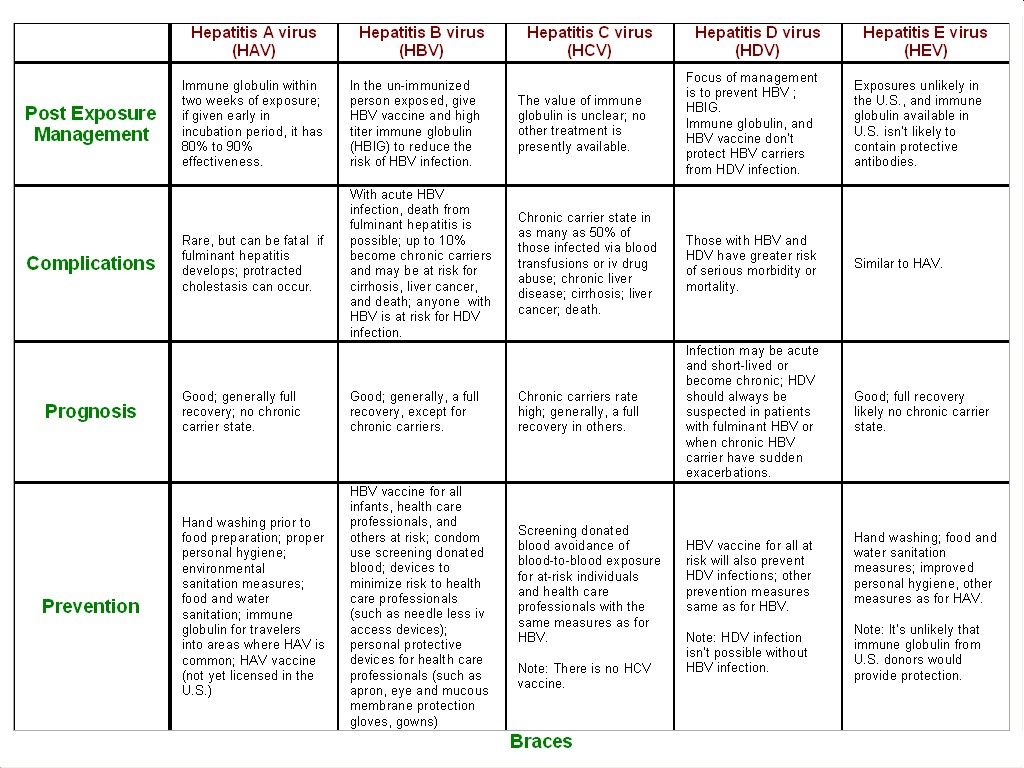
What Is Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, also called enteric hepatitis , is similar to hepatitis A, and more prevalent in Asia and Africa. It is also transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It is generally not fatal, though it is more serious in women during pregnancy and can cause fetal complications. Most patients with hepatitis E recover completely.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Some people with hepatitis do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Joint pain
- Jaundice, yellowing of your skin and eyes
If you have an acute infection, your symptoms can start anywhere between 2 weeks to 6 months after you got infected. If you have a chronic infection, you may not have symptoms until many years later.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Home Test Kit
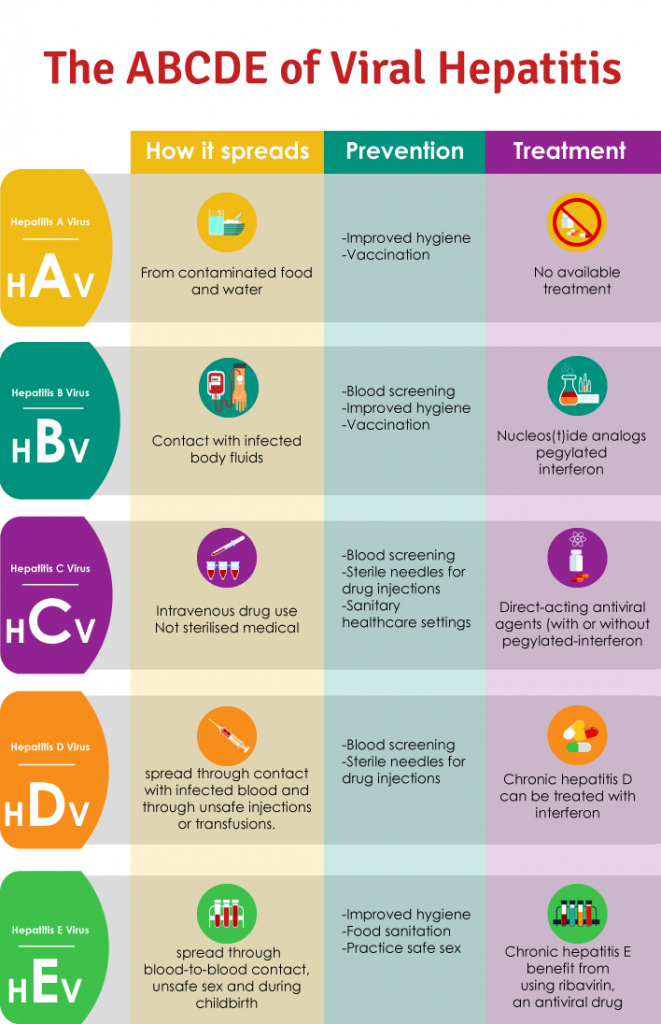
How Do You Get Hepatitis A
The main way you get hepatitis A is when you eat or drink something that has the hep A virus in it. A lot of times this happens in a restaurant. If an infected worker there doesn’t wash their hands well after using the bathroom, and then touches food, they could pass the disease to you.
Food or drinks you buy at the supermarket can sometimes cause the disease, too. The ones most likely to get contaminated are:
- Shellfish
- Ice and water
You could catch or spread it if you’re taking care of a baby and you don’t wash your hands after changing their diaper. This can happen, for example, at a day care center.
Another way you can get hep A is when you have sex with someone who has it.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- alcohol
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Does It Spread
What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis
The liver is a large organ that sits up under your ribs on the right side of your belly . It helps filter waste from your body, makes bile to help digest food, and stores sugar that your body uses for energy. Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when your bodys infection-fighting system attacks your liver cells. This causes swelling, inflammation and liver damage.
It is a long-term or chronic inflammatory liver disease.
Autoimmune hepatitis:
- May occur at any age
- Affects women more than men
- Is often linked to other diseases where the body attacks itself
How Is Hepatitis Treated In A Child
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Your childs treatment will depend on whats causing his or her hepatitis. The goal of treatment is to stop damage to your childs liver. Its also to help ease symptoms. Your childs treatment may include:
-
Medicines. These can control itching, treat the virus, or control an autoimmune disease.
-
Supportive care. This includes eating a healthy diet and getting enough rest.
-
Reducing risk. Not using alcohol or illegal drugs.
-
Blood testing. This can tell if the disease is progressing.
-
Hospital stay. This is done in severe cases.
-
Liver transplant. This is done for end-stage liver failure.
-
Helping to prevent the spread of viral hepatitis. Having good personal health habits, such as handwashing.
Don’t Miss: Genotype 4 Hepatitis C Treatment
What Causes Alcoholic Hepatitis
When alcohol gets processed in the liver, it produces highly toxic chemicals. These chemicals can injure the liver cells. This injury can lead to inflammation and, eventually, alcoholic hepatitis.
Although heavy alcohol use can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, experts arent entirely sure why the condition develops in some people but not in others.
Alcoholic hepatitis develops in a minority of people who heavily use alcohol no more than 35 percent, according to the American Liver Foundation. It can also develop in people who use alcohol only moderately.
Because alcoholic hepatitis doesnt occur in all people who heavily use alcohol, other factors may influence the development of this condition.
Risk factors include:
- having genetic factors that affect how the body processes alcohol
- living with liver infections or other liver disorders, such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and hemochromatosis
- abdominal CT scan
- ultrasound of the liver
Your doctor may order a liver biopsy to confirm a diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis. A liver biopsy requires your doctor to remove a tissue sample from the liver. Its an invasive procedure with certain inherent risks, but biopsy results can show the severity and type of liver condition.
What Causes Hepatitis In A Child
Hepatitis in children can be caused by many things. Your child can get hepatitis by being exposed to a virus that causes it. These viruses can include:
-
Hepatitis viruses. There are 5 main types of the hepatitis virus: A, B, C, D, and E.
-
Cytomegalovirus. This virus is a part of the herpes virus family.
-
Epstein-Barr virus. The virus causes mononucleosis.
-
Herpes simplex virus. Herpes can affect the face, the skin above the waist, or the genitals.
-
Varicella zoster virus . A complication of this virus is hepatitis. But this happens very rarely in children.
-
Enteroviruses. This is a group of viruses often seen in children. They include coxsackie viruses and echoviruses.
-
Rubella. This is a mild disease that causes a rash.
-
Adenovirus. This is a group of viruses that causes colds, tonsillitis, and ear infections in children. They can also cause diarrhea.
-
Parvovirus. This virus causes fifth disease. Symptoms include a slapped-cheek rash on the face.
Conditions can also cause hepatitis in children. These can include autoimmune liver disease. For this disease, your childs immune system makes antibodies that attack the liver. This causes inflammation that leads to hepatitis.
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis C
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated
Treatment works best when autoimmune hepatitis is found early. The goal of treatment is to control the disease and to reduce or get rid of any symptoms .
To do this, medicines are used to help slow down or suppress your overactive immune system. They also stop your body from attacking your liver.
Once you have started treatment, it can take 6 months to a few years for the disease to go into remission. Some people can stop taking medicine, but often the disease comes back. You may need treatment now and then for the rest of your life. Some people need to remain on treatment if they have relapsed many times or if their disease is severe.
In some cases autoimmune hepatitis may go away without taking any medicines. But for most people, autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease.
It can lead to scarring of the liver . The liver can become so badly damaged that it no longer works. This is called liver failure.
If you have liver failure, a liver transplant may be needed.
Be sure to ask your healthcare provider about recommended vaccines. These include vaccines for viruses that can cause liver disease.
What Is Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is an inflammatory condition of the liver caused by heavy alcohol consumption over an extended period of time. Ongoing alcohol use and binge drinking can both aggravate this condition.
If you develop this condition, its important that you consider stopping alcohol use gradually. Continued drinking can lead to additional health conditions, such as cirrhosis, excessive bleeding, or even liver failure.
Read Also: How Us Hepatitis C Transmitted
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatitis A And E Symptoms
Hepatitis A and hepatitis E present with similar symptoms. The diseases may develop without any signs or symptoms, or symptoms may be nonspecific. If you experience any of the symptoms below for more than two weeks, make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
There are three phases of hepatitis A and E, and symptoms may differ depending on the stage. Early in the disease, called the prodromal phase, symptoms may include:
- Fever
Also Check: Where Can I Get My Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Medications for chronic hepatitis B infection include:
- oral entecavir
- oral tenofovir
Fulminant hepatitis