How Are Hepatitis B And C Transmitted
A key difference between hepatitis B and C is the way they are transmitted. Hepatitis B is typically transmitted through the exchange of bodily fluids like blood and semen, while Hepatitis C can only be transmitted through blood-to-blood contact.
This means that needle sharing is a big problem for the spread of both of these viruses, especially since most people are symptomless and dont know that they’re infected.
Hepatitis C is much more limited in how it can be spread. By contrast, hepatitis B can be spread several ways, including:
- Birth: can be transmitted to a newborn during childbirth.
- Sex: can be transmitted to or contracted from a partner through intercourse.
- Sharing Items of Personal Hygiene: can be transmitted to or contracted from anyone through the use of items like razors and toothbrushes.
Hepatitis A: How Does It Spread
It usually spreads through food or water. Food can be tainted when it’s touched by a person with hepatitis who did not wash their hands after using the bathroom. This transfers tiny amounts of infected stool to the food. Raw shellfish, fruits, vegetables, and undercooked foods are common culprits in hepatitis A outbreaks. The virus can also spread in daycare centers if employees aren’t careful about washing hands after changing diapers.
The Abcs Of Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis is an infection or inflammation of the liver. It is most commonly caused by a viral infection. There are 6 types of hepatitis viruses types A, B, C, D, E and G.
Two types, hepatitis B and hepatitis C, are linked to cancer.
Hepatitis B is the most common type of hepatitis virus. It is very infectious and is spread mainly by being exposed to infected blood or other bodily fluids . HBV is more likely to cause symptoms than hepatitis C.
HBV infection can cause flu-like symptoms and yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes . Most people recover completely from HBV infection within a few months and develop lifelong protection against it. Only about 10% of people have an infection that lasts a long time.
You May Like: How Serious Is Hepatitis C
Which Strawberries Are Affected
Fresh, organic H-E-B and FreshKampo-brand strawberries purchased between March 5 and April 25 shouldn’t be eaten, per the FDA. Stores that sold them include :
- Aldi
- Weis Markets
- WinCo Foods
All the investigated strawberries would be past their shelf life and no longer on store shelves. In a statement, FreshKampo said the strawberries included would have had a label that said “Distributed by Meridian Fruits” on the plastic packaging. H-E-B said in a statement that it has not received or sold organic strawberries from the supplier under investigation since April 16.
If you purchased the possibly affected strawberries and became sick within the last two weeks and you haven’t been vaccinated against hepatitis A you should immediately call your doctor or a health clinic, per the FDA.
Postexposure prophylaxis might be given within two weeks of exposure to hepatitis A, but it’s only recommended for people who aren’t vaccinated or those who haven’t previously been infected with hepatitis A, the FDA said.
The hepatitis A vaccine is one example of PEP. The two-dose hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for most US children between their first and second birthdays.
The potentially affected strawberries are now past their shelf life, the FDA said, but make note of the agency’s warning if you freeze fruits.
How To Prevent Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by a virus . It can be serious and theres no cure, but the good news is its easy to prevent. You can protect yourself by getting the hepatitis B vaccine and having safer sex. If you have oral, anal, and vaginal sex, use condoms and dental dams to help stop the spread of hepatitis B and other STDs.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Non Reactive Meaning
Acute Vs Chronic Infection
Doctors distinguish between chronic and acute infection with hepatitis viruses. Acute infection is a short-term condition, lasting under six months. Chronic infection is a long-term condition, lasting more than six months.
Hepatitis B infection can be either acute or chronic. Most people who get acute hepatitis B dont end up progressing to chronic hepatitis B. By contrast, acute hepatitis C tends to develop into chronic hepatitis C. Approximately 7585 percent of adults newly infected with hepatitis C develop a chronic infection, according to the CDC . Others clear the infection.
When you get acute hepatitis C you may or may not have symptoms. Most cases of acute hepatitis C are asymptomatic, meaning people dont notice the symptoms. Symptoms are only noticeable in 15 percent of cases of acute hepatitis C.
In Case Of Contact With An Infected Persons Blood Sperm Or Vaginal Secretions
Consult a health-care professional or call Info-Santé 811 immediately if:
- You have come into contact with the blood, sperm or vaginal secretions of a person who could be infected with the hepatitis B virus. You may have to receive preventive treatment that protects you from catching hepatitis B. This treatment is called post-exposure prophylaxis. It must be administered as soon as possible after contact
Consult a health-care professional if:
- You have come into contact with the blood of someone who could be infected with the hepatitis C virus. You can get tested and receive appropriate care, as needed
You May Like: Immune To Hepatitis B Means
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Also Check: How Often Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Need To Be Given
Hepatitis C: How Does It Spread
It spreads through infected blood. In the U.S., sharing needles or other items used to inject drugs is the most common cause of infection. Getting a tattoo or body piercing with an infected needle is another means of exposure. A mother may pass the virus to their child at birth. In rare cases, unprotected sex spreads hepatitis C, but the risk appears small. Having multiple sex partners, HIV, or rough sex seems to raise risk for spreading hepatitis C.
What Happens With Hepatitis B
A majority of adults who contract hepatitis B have none to mild symptoms, and then the virus resolves spontaneously however, about 5% of people are not able to eliminate the hepatitis B virus and develop chronic infection. If a chronically infected mother gives birth, 90% of the time her infant will be infected and develop chronic hepatitis B, usually for life. This may give rise to serious complications of liver disease later in life such as liver damage, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Read Also: How Can Hepatitis B Be Treated
How Does Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A is spread from person to person via fecal contamination because the virus is present in the stool. It is spread via contaminated food or water by an infected person who gets small amounts of stool on his or her hands, does not wash his or her hands, and passes the stool onto food that is eaten by others. An example of this is outbreaks of hepatitis A in daycare centers for young children when employees don’t wash their hands after changing diapers, and they then pass the viruses to the next child they feed. In addition, fecal contamination of water in which shellfish live can contaminate the shellfish, and the shellfish can pass the virus to people who eat the shellfish raw.
What Happens With Hepatitis A
Viral diseases generally are contagious. Hepatitis A is highly contagious. It usually is spread from person to person via a fecal-oral route, meaning via fecal contamination of food. It usually is a mild hepatitis, and many people do not know they are infected. The virus is eliminated by the body rapidly, and it does not cause long-term damage. Good hand washing hygiene helps prevent hepatitis A.
Also Check: How Often Should You Be Tested For Hepatitis C
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Just like hepatitis B, you can get this type by sharing needles or having contact with infected blood. You can also catch it by having sex with somebody who’s infected, but that’s less common.
If you had a blood transfusion before new screening rules were put in place in 1992, you are at risk for hepatitis C. If not, the blood used in transfusions today is safe. It gets checked beforehand to make sure it’s free of the virus that causes hepatitis B and C.
It’s rare, but if you’re pregnant and have the disease, it’s possible to pass it to your newborn.
There are some myths out there about how you get hepatitis C, so let’s set the record straight. It’s not spread by food and water . And you canât spread it by doing any of these things:
- Joint pain
See your doctor as soon as possible if you have any of these symptoms.
Sometimes, people have no symptoms. To be sure you have hepatitis, youâll need to get tested.
What Happens With Hepatitis C
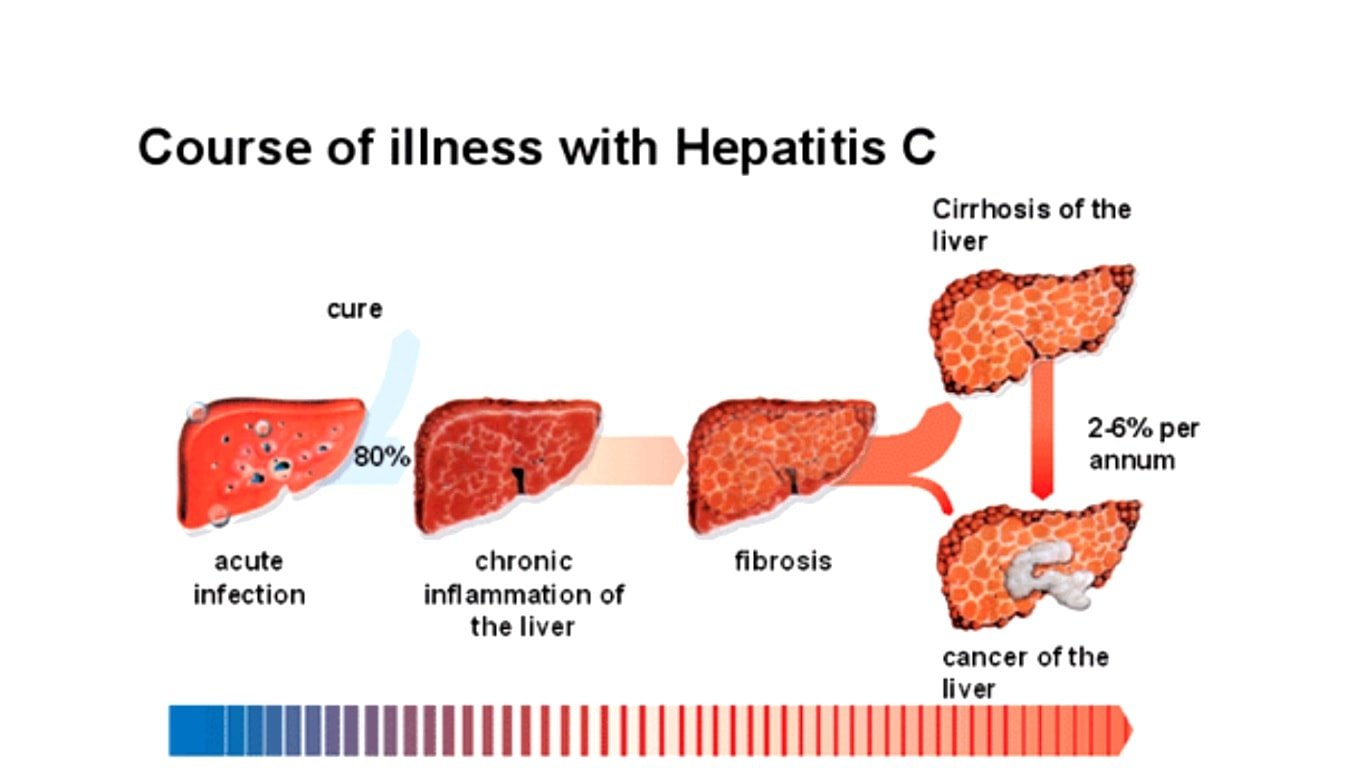
Is hepatitis C a virus? Yes. With acute hepatitis C, the virus is eliminated in 25% of people. The rest of the people become chronically infected and later may develop serious complications such as liver failure and liver cancer. There is treatment, however, for hepatitis C that usually can prevent the complications.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis A Curable Or Treatable
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Symptoms for HCV may not appear for 20 to 30 years, and that is why it is so important to get tested. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control now recommends that all adults 18 years and older are tested at least once for HCV. Some high risk groups may need more frequent testing, and all pregnant women should be tested during every pregnancy.
HCV can actually clear itself from the body in about 15% of people, but most people become infected with the virus chronically.
Early symptoms of acute HCV occur within 1 to 3 months and may last several weeks. These may include:
- yellow-colored skin or eye sclera
- weakness
- nausea and stomach pain
- joint or muscle pain
Chronic, long-term symptoms of HCV can include weight loss, fluid build-up and swelling, poor appetite, fatigue, easy bruising and bleeding, itchy skin, jaundice, dark-colored urine, confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech , and spider-like blood vessels on the skin .
Is Everyone Tested For Both Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B
The US Centers for Disease and Control recommends testing for certain high-risk groups for hepatitis B.
- High-risk groups include people not born in the US, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, and people with hepatitis C, among other groups.
- If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, contact your doctor right away. A treatment is available that may reduce your risk of infection if you receive this medicine within 24 hours of exposure to the virus.
Hepatitis C
The CDC recommends that all adults 18 years and older be tested for hepatitis C at least once. Pregnant women should be tested during each pregnancy. Getting tested for hepatitis C is important, because HCV treatments can cure most people in 8 to 12 weeks. If you are at higher risk for HCV, youll need to be tested more frequently.
Treatments for both hepatitis B and hepatitis C are in a class called antivirals, but the medications that are used are different.
Don’t Miss: Where Can You Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C: What Happens
About 25% of people who get hepatitis C defeat the virus after a short-term infection. The rest will carry the virus in their body for the long term. Chronic hepatitis C can cause very serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer. There are effective treatments for the virus, though.
Epidemiology And Natural History
The number of cases of chronic HBV infection has been estimated at almost 400 million worldwide . HBV has 8 genotypes which are associated with moderate differences in response to therapy. Children with chronic hepatitis B have a high frequency of HBeAg positivity and high HBV DNA levels compared to those with other genotypes and the timing of HBeAg seroconversion in genotype C is more delayed compared to genotype B. Genotype C results in more aggressive hepatitis and is associated with an increased risk of HCC. However the development of HCC was associated with genotype B in a single Taiwanese pediatric study. The prevalence of chronic HBV infection in pregnant women in urban areas of the USA varies by race and ethnicity. While the highest rate was observed in Asian women , the rates in black, white and Hispanic women were 1, 0.6 and 0.14%, respectively.
The spontaneous seroconversion rates of HBeAg for children infected via perinatal transmission are less than 2% per year for those under age 3 years, and 4 5% per year in those older than 3 years, whereas children infected after the perinatal period have higher rates of spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion, up to 70 80% over 20 years. The time to HBeAg clearance for individuals with HBV genotype C is longer than in patients with other genotypes . Since the early 1990s, the incidence of acute HBV in the United States has declined .
Read Also: How Do You Screen For Hepatitis C
Who Should Be Tested
Testing for hepatitis A is not routinely recommended.
CDC recommends hepatitis B testing for:
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household and sexual contacts of people with hepatitis B
- People requiring immunosuppressive therapy
- People with end-stage renal disease
- People with hepatitis C
- People with elevated ALT levels
- Pregnant women
- Infants born to HBV-infected mothers
CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for:
- All adults aged 18 years and older
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy
- About 24,900 new infections each year
- About 22,600 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 862,000 people living with hepatitis B
- About 50,300 new infections in 2018
- Estimated 2.4 million people living with hepatitis C
Hepatitis A And B Vaccines
There are vaccines to protect against hepatitis A and B. The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccination for all children ages 12 to 23 months and for adults who plan to travel or work in areas with hepatitis A outbreaks or who have other risk factors. People with chronic hepatitis B or C should also get the hepatitis A vaccine if they don’t already have immunity to the disease. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants at birth and for adults who have any of the risk factors we discussed earlier. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Also Check: What Form Of Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
Hepatitis A B And C: What Is The Difference
A, B, C D and E.
Aside from the letters associated with it, how much do you know about hepatitis? Whats the difference between the types? And if get a vaccination for hepatitis, which are you protected from?
We spoke with Moises Ilan Nevah, MD, a transplant hepatologist/gastroenterologist and medical director of the Liver Transplant Program at Banner University Medical Center Phoenix, to help better understand the similarities and differences between the various types of hepatitis, who is at risk and when to get vaccinated.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Patient Assistance Programs