History And Physical Exam
To diagnose all forms of hepatitis, your doctor will first take your history to determine any risk factors you may have.
During a physical examination, your doctor may press down gently on your abdomen to see if thereâs pain or tenderness. Your doctor may also check for any swelling of the liver and any yellow discoloration in your eyes or skin.
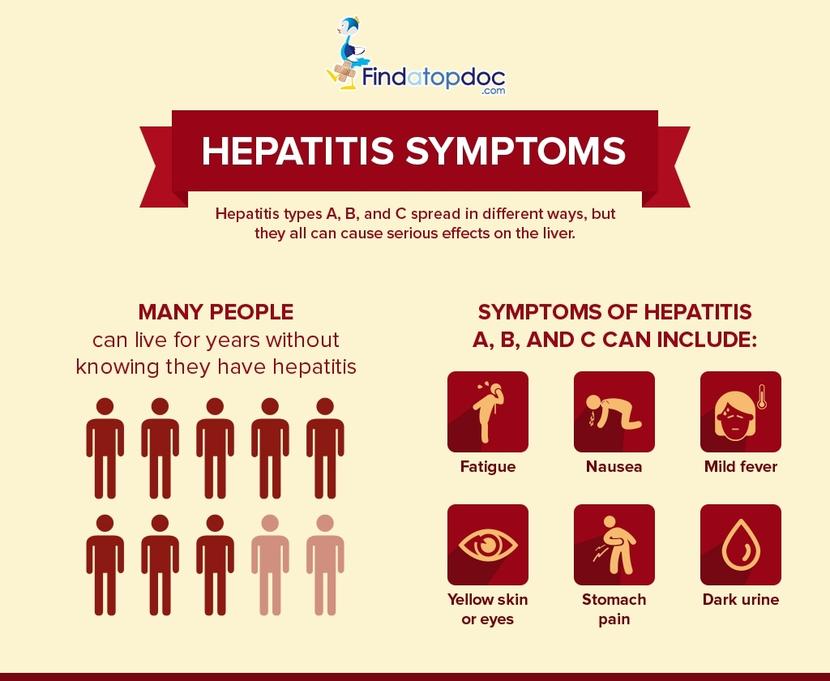
What Are Signs Of Hepatitis B
When you first get hepatitis B, it is called acutehepatitis B. Most adults who have hepatitis B willrecover on their own. However, children and someadults can develop chronic hepatitis B.
Acute hepatitis B: Signs of acute hepatitis B canappear within 3 months after you get the virus.These signs may last from several weeks to 6 months.Up to 50% of adults have signs of acute hepatitis Bvirus infection. Many young children do not show anysigns. Signs include:
- Yellow skin or eyes
- Tiredness
- A longer than normal amount of time for bleedingto stop
What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Doctors refer to hepatitis B infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HBV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HBV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis B infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and causes lifelong illness. An estimated 850,000 to more than 2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HBV.
The younger someone is when infected, the greater the chances for chronic hepatitis B. About 90% of babies with HBV will develop a chronic infection. That risk drops to 6%10% when someone over 5 years old is infected. Because of this, the World Health Organization and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that all babies get the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 1224 hours of birth. They’ll get two more doses later, at 12 months of age and at 618 months of age.
You May Like: What Drug Is Used To Treat Chronic Hepatitis B
Chronic Hepatitis B Symptoms Are Similar To Acute Hepatitis B Symptoms
Like acute hepatitis B, chronic infection usually causes no symptoms in most adults. In fact, people can live for decades with chronic hepatitis B and not know it. If symptoms do develop, they are very similar to the symptoms of acute hepatitis B. Symptoms with chronic infection is often a sign of serious liver disease, such as cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis B will eventually become fatal in about 15% of adults who develop it.
Can The Liver Repair Itself From Hepatitis B
Reversing liver damage Liver Basics Barring complications, the liver can repair itself completely and, within a month, the patient will show no signs of damage. However, sometimes the liver gets overwhelmed and can’t repair itself completely, especially if it’s still under attack from a virus, drug, or alcohol.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Negative Means
Hepatitis B: Symptoms Causes And Treatment Options
Hepatitis B refers to the inflammation of the liver, often caused by a viral infection. However, there are many other possible causes of hepatitis. These include hepatitis caused by secondary results of drugs, medications, alcohol, and toxin. If a person’s body makes antibodies against the liver tissue, it can also lead to autoimmune hepatitis.
According to an estimate by the WHO, over 356 million people worldwide currently live with chronic hepatitis. Most adults suffer from acute hepatitis B, which lasts a short time. However, CDC reveals that about 3-7% of people develop a chronic infection that can cause liver failure, cancer, and scarring of the organ, which can be life-threatening, especially for those with compromised immune systems.
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis has many different types. HBV and the hepatitis C virus have both acute and chronic forms.
The main difference between HBV and HCV is how they spread from person to person. Although HCV is transmissible via sexual activity, this is rare. HCV usually spreads when blood that carries the virus comes into contact with blood that does not.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
How Long Does It Last
According to the World Health Organization , the complete vaccine series induces protective antibody levels in of the infants, children, and adolescents who receive it.
Immune memory induced by the HBV vaccine can last for in healthy people. That said, studies into the duration of the protection that the vaccine offers are ongoing.
Does Hepatitis B Ever Go Away
In most cases, hepatitis B goes away on its own. You can relieve your symptoms at home by resting, eating healthy foods, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding alcohol and drugs. Also, find out from your doctor what medicines and herbal products to avoid, because some can make liver damage caused by hepatitis B worse.
Also Check: Does Hepatitis A Cause Diarrhea
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B: Diagnosis And Treatment
THAD WILKINS, MD DAVE ZIMMERMAN, MD and ROBERT R. SCHADE, MD, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Apr 15 81:965-972.
Patient information: See related handout on hepatitis B.
Globally, an estimated 350 million persons are chronically infected with hepatitis B virus , resulting in 600,000 deaths annually from cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma.1,2 Approximately 88 percent of the world’s population live in regions where the prevalence of chronic HBV infection among adults is more than 2 percent.3 The prevalence of HBV infection in the United States is 0.4 percent, with an estimated 0.8 to 1.4 million persons chronically infected.3,4 With the implementation of vaccination programs in 1991, the incidence of new infections in the United States has declined from 11.5 cases per 100,000 persons in 1985 to 1.6 cases per 100,000 persons in 2006.3,4
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
High-risk populations should be screened for HBV infection.
HBV = hepatitis B virus.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, go to .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
High-risk populations should be screened for HBV infection.
HBV = hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
If youâre pregnant, you might pass the virus to your baby at birth. Itâs less likely to happen during your pregnancy.
If your baby gets the virus and isnât treated, they could have long-term liver problems. All newborns with infected mothers should get hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine for hepatitis at birth and during their first year of life.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant
Complications Of Hepatitis B
A small proportion of people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection. They may have the virus in their bloodstream for most of their life without realising they are infected.
People with chronic hepatitis B infection may not notice any health problems until they develop liver problems such as liver disease or liver cancer later in life. Treatment for hepatitis B is essential because it is not possible to be a healthy carrier of the hepatitis B virus. Chronic hepatitis B infection occurs more commonly in some communities, including:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
- In people from parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as:
- North-East Asia
Dont Miss: Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
Also Check: Can You Catch Hepatitis C
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
Outlook For Hepatitis B
The vast majority of people infected with hepatitis B in adulthood are able to fight off the virus and fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
Most will then be immune to the infection for life.
Babies and children with hepatitis B are more likely to develop a chronic infection.
Chronic hepatitis B affects around:
- 90% of babies with hepatitis B
- 20% of older children with hepatitis B
- 5% of adults with hepatitis B
Although treatment can help, theres a risk that people with chronic hepatitis B could eventually develop life-threatening problems, such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer.
Page last reviewed: 30 January 2019 Next review due: 30 January 2022
You May Like: Hepatitis B Shot Side Effects
How Is Viral Hepatitis Prevented
Prevention of hepatitis involves measures to avoid exposure to the viruses, using immunoglobulin in the event of exposure, and vaccines. Administration of immunoglobulin is called passive protection because antibodies from patients who have had viral hepatitis are given to the patient. Vaccination is called active protection because killed viruses or non-infectious components of viruses are given to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies.
Avoidance of exposure to viruses
Prevention of viral hepatitis, like any other illness, is preferable to reliance upon treatment. Taking precautions to prevent exposure to another individual’s blood , semen , and other bodily secretions and waste will help prevent the spread of all of these viruses.
Use of immunoglobulins
Immune serum globulin is human serum that contains antibodies to hepatitis A. ISG can be administered to prevent infection in individuals who have been exposed to hepatitis A. ISG works immediately upon administration, and the duration of protection is several months. ISG usually is given to travelers to regions of the world where there are high rates of hepatitis A infection and to close or household contacts of patients with hepatitis A infection. ISG is safe with few side effects.
Hepatitis A
Individuals at increased risk of acquiring hepatitis A are:
Some local health authorities or private companies may require hepatitis A vaccination for food handlers.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for:
What Makes Hepatitis B A Serious Illness
Many people with hepatitis B do not know they are infected since they do not look or feel sick, yet they can still spread the virus to others. Acute infection can lead to chronic infection, which can cause cirrhosis , liver cancer, liver failure, and death. Hepatitis B can be passed from mother to baby during childbirth, and newborns who become infected with hepatitis B virus have a 90 percent chance of developing chronic hepatitis B. Between 4,000 and 5,000 people die each year in the U.S. from hepatitis B-related liver disease.
Also Check: How To Test For Hepatitis B
The Symptoms Are General
Since the liver has a part in so many essential functions, many symptoms are constitutional, meaning they affect the entire body. For example, a sore leg will usually just hurt in and around the leg. With hepatitis, you may feel pain around the liver, but you will also probably have chills and aches in your joints and muscles.
Natural Remedies For Hepatitis B And C
Our natural remedy for hepatitis is much more effective than the drugs commonly used to fight hepatitis. These drugs do not fight hepatitis that caused it. They can only prevent the symptoms of the disease, without destroying the virus.
In addition to being ineffective, these antiviral drugs can have side effects such as anemia, insomnia, suicidal urges, irritability, impaired lung function, pancreatic diabetes, etc.
Our natural treatment is different, it is 100% herbal and it attacks the virus directly. At the end of your treatment, the virus will have definitively disappeared and you will be completely cured. Trust us! This natural remedy is the secret to cure hepatitis B and C by plants.
The natural treatment that we offer to cure hepatitis B, like hepatitis C, is essentially made of natural herbal teas. It is one of the best natural remedies to cure hepatitis. The natural remedy for hepatitis is made up of plants that have been proven to work with dozens of cases resolved.
This natural remedy has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which help in healing and preventing liver problems. It also fights against the viruses responsible for hepatitis and provides the antioxidants that help maintain overall liver health. It helps the body fight viral infections and cleanse the liver.
It is a quick fix for curing hepatitis B or C.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Without Insurance
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
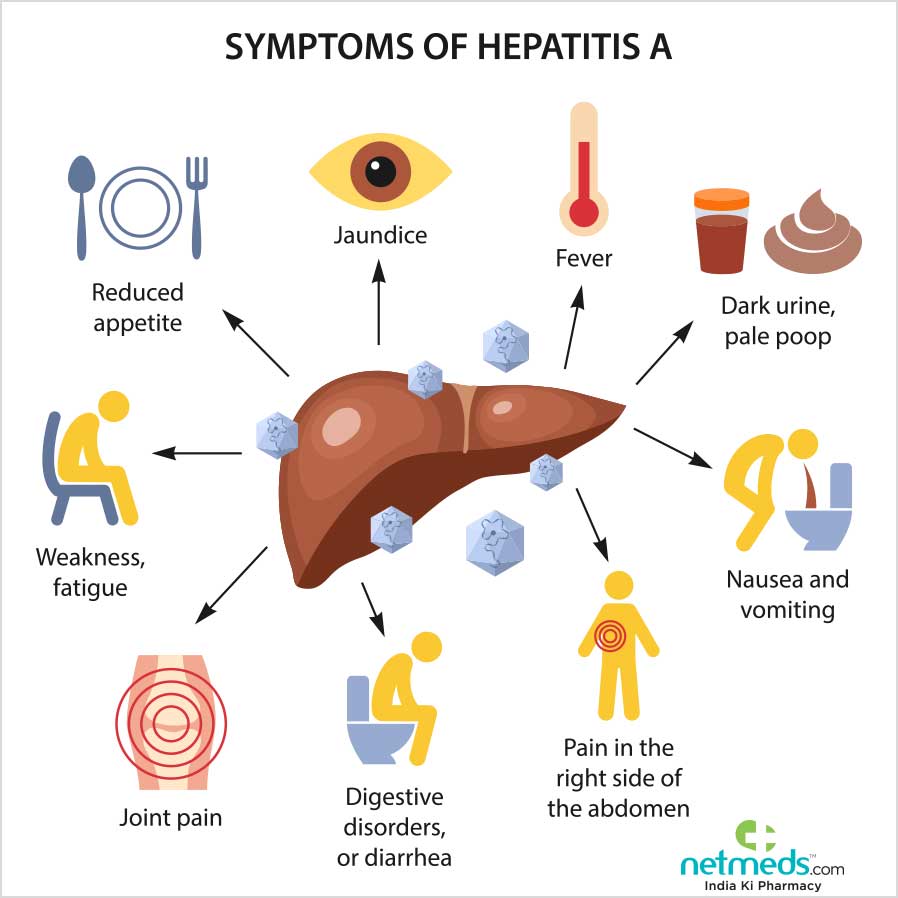
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection
The incubation period for hepatitis B virus is 30-180 days . Patients then enter the prodromal or preicteric phase, characterized by the gradual onset of anorexia, malaise, and fatigue. During this phase, as the liver becomes inflamed, the liver enzymes start to elevate, and the patient may experience right upper quadrant pain. About 15% of patients develop an illness resembling serum sickness. These patients may experience fever, arthritis, arthralgias, or an urticarial rash.
As the disease progresses to the icteric phase, the liver becomes tender, and jaundice develops. Patients may note that their urine darkens and their stools lighten in color. Other symptoms in this stage include nausea, vomiting, and pruritus.
From this point on, the clinical course may be highly variable. Whereas some patients experience fairly rapid improvements in their symptoms, others go on to experience prolonged disease with slow resolution. Still others may have symptoms that periodically improve, only to worsen later . Finally, there is an unfortunate subset of patients in whom the disease rapidly progresses to FHF this may occur over days to weeks.
References
Wasley A, Grytdal S, Gallagher K, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Surveillance for acute viral hepatitisUnited States, 2006. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2008 Mar 21. 57 :1-24. .
Previsani N, Lavanchy D, World Health Organization. Hepatitis B . 2002. .
Also Check: How Do You Transfer Hepatitis C