How Common Is Hepatitis B
The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Drugs In India
How Do You Test For Hepatitis B
A simple blood test carried out by a healthcare professional will show whether you have the virus. You may also be given extra tests to see if your liver is damaged.
If youve got hepatitis B you should be tested for other STIs. Its important that you tell your recent sexual partner/s so they can also get tested and treated. Many people who have hepatitis B dont notice anything wrong, and by telling them you can help to stop the virus being passed on. This can also stop you from getting the infection again.
What Happens To Your Liver When You Get Hepatitis B
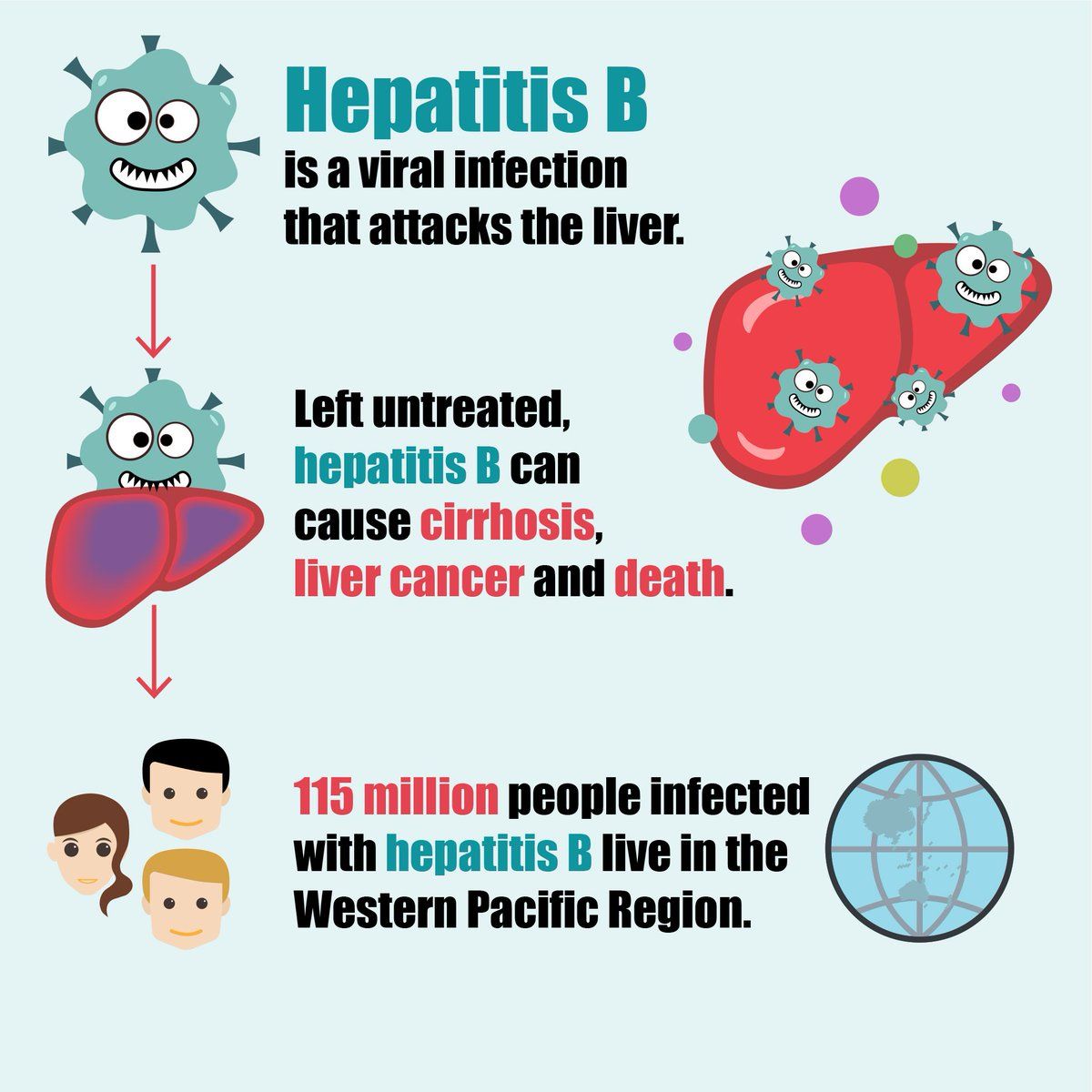
When the hepatitis B virus enters the body, it attacks liver cells. The liver cells then become swollen and inflamed and are unable to work properly.
Most people exposed to hepatitis B experience an acute hepatitis B infection that causes acute hepatitis. During the acute infection, liver cells are sick and not working properly but the liver is still able to function. Healthcare providers will check blood work called liver function tests to monitor the livers progress. For most people, the liver will start to heal on its own over a period of months, and liver function tests will return to normal.
For some people, damage to liver cells will continue. This damage is part of a chronic hepatitis B infection. When damage to the liver continues, a person can develop liver cancer as well as scarring of the liver, which is called cirrhosis.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice is attributed to a pathological increase in bilirubin production. The pathophysiology is quite simple an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis increased bilirubin production increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissue appearance of yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant damage to liver function hepatic cell death and necrosis occur impaired bilirubin transport across hepatocytes. Bilirubin transport across may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism uptake, conjugation, and excretion usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
How Can I Avoid Getting Hepatitis B
There is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect you from getting hepatitis B. The vaccine is usually given in three doses over a six month period. The vaccine will give you long-lasting protection. A combined vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B is also available.
Other ways to protect yourself or your loved ones include:
- Adopt safe sex practices.
- Avoid sharing personal hygiene items
- If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus , an injection of hepatitis B immune globulin may help protect you.
- If you are pregnant, make sure you are screened for hepatitis B. If the test result shows that you have the virus, make sure your baby receives the free hepatitis B vaccine. If you have hepatitis B, breastfeeding is safe if the baby has received both protective antibody called immune globulin, and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within the first 12 hours of life. Talk to your doctor about having your newborn immunized .
- If you decide to have a tattoo, piercing, manicure or pedicure, ensure that the facility uses single-use needles and inks and/or follows proper sterilization procedures.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Turn Into Hiv
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can get hepatitis B, but the risk is higher in:
- Infants born to mothers who have hepatitis B
- People who inject drugs or share needles, syringes, and other types of drug equipment
- Sex partners of people with hepatitis B, especially if they are not using latex or polyurethane condoms during sex
- Men who have sex with men
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B, especially if they use the same razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- Health care and public-safety workers who are exposed to blood on the job
- Abdominal pain
- Yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you may not have symptoms until complications develop. This could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis B screening is important, even if you have no symptoms. Screening means that you are tested for a disease even though you don’t have symptoms. If you are at high risk, your health care provider may suggest screening.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Symptoms of hepatitis B can range from mild to severe. If you have a mild case of hepatitis, you may not even realize that you have it. It may not cause any symptoms, or may only cause symptoms similar to the stomach flu. The symptoms of hepatitis B may include:
- Loss of appetite.
- Jaundice .
- Joint pain.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
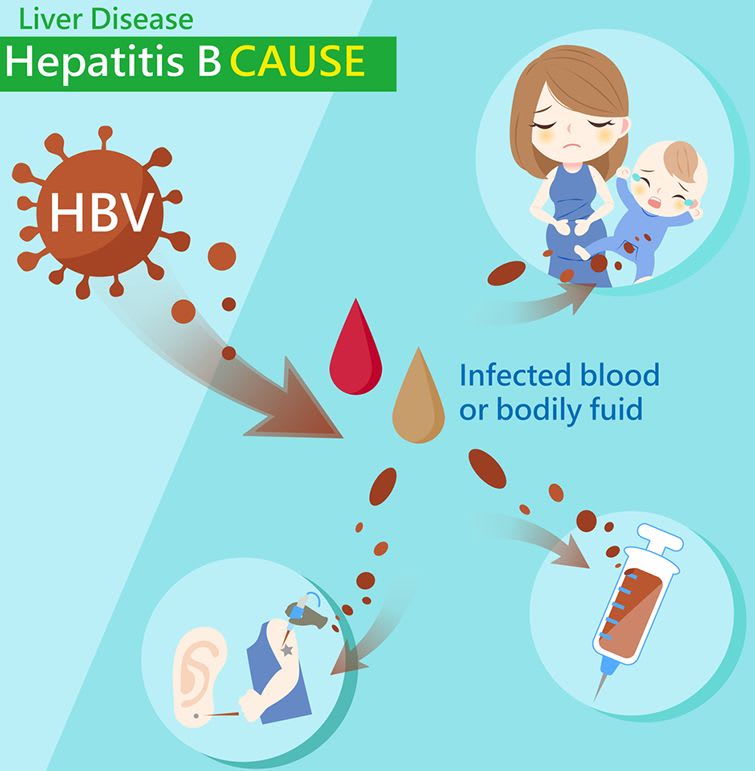
How Hepatitis B Is Spread
Hepatitis B can be spread by:
- a mother to her newborn baby, particularly in countries where the infection is common all pregnant women in the UK are offered screening for hepatitis B babies of infected mothers are vaccinated immediately after birth to help prevent infection
- injecting drugs and sharing needles and other drug equipment, such as spoons and filters
- having sex with an infected person without using a condom
- having a tattoo, body piercing, or medical or dental treatment in an unhygienic environment with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country where blood is not tested for hepatitis B all blood donations in the UK are now tested for the infection
- sharing toothbrushes or razors contaminated with infected blood
- the skin being accidentally punctured by a used needle this is mainly a risk for healthcare workers
- the blood of someone with hepatitis B getting into an open wound, cut or scratch in rare cases, being bitten by someone with hepatitis B can also spread the infection
Hepatitis B is not spread by kissing, holding hands, hugging, coughing, sneezing or sharing crockery and utensils.
You May Like: How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Prevention And Vaccination
Hepatitis B infection is vaccine-preventable. An effective and safe vaccine is used to protect children and adults from the disease. In addition, the implementation of safe injection procedures, blood safety strategies and safer sex practices can protect against HBV transmission. There are simple and effective ways to prevent the spread of Hepatitis B:
- Practice safe sex using protective measures
- Avoid direct contact with bodily fluids and blood
- Wash your hands carefully after any potential exposure
- Clean up blood spills with a disinfecting solution
- Avoid sharing sharp personal items such as nail clippers, razors or toothbrushes
- Cover all wounds and cuts carefully
- Avoid street drugs
- Make sure sterile needles are used for tattoos, piercing, and acupuncture
- Moreover, all blood and blood components used for blood transfusions should undergo quality-assured screening to reduce the chance of getting HBV.
Hepatitis B virus vaccine
What Are The Complications Of Hepatitis B
The course of hepatitis B infection depends mostly on the age at which a person is infected.
People infected as infants are likely to develop long term infection and can get complications such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer. Infants have a 9 in 10 chance and children have a 3 in 10 chance of developing a chronic, lifelong infection.
People infected as teenagers or adults are likely to become unwell with symptoms , but have a smaller chance of developing a chronic infection. Others develop a silent infection, without any symptoms.
Most people infected as adults clear the virus from the body within 6 months. They develop immunity to future hepatitis B infections and do not develop long-term liver damage.
However, approximately 1 in 20 adults cannot clear the virus and develop chronic hepatitis B. They are at risk of developing complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer in the longer term.
Read Also: How Much Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
Hepatitis B Testing And Diagnosis
Its essential to receive a laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis. A number of effective tests are available to diagnose hepatitis B and monitor the condition of infected people. The tests can be used to distinguish chronic and acute infections.
Detection of Anti-HBs by using test cassette, the result showed positive
They involve blood or serum tests that detect either antibodies or vial antigens. Laboratory diagnosis of the infection screens the detection of the surface antigen HBsAg. Acute hepatitis B infection is characterized by the presence of this surface antigen and immunoglobulin M antibody to the core antigen. Chronic infection is diagnosed if HBsAg persists for 6 months. Persistence of the surface antigen HBsAg is the major marker of risk for liver cancer and a chronic disease later in life. Follow-up tests are necessary to detect if the disease has gone. Interpretation of the tests for detection of HBV is complex. The results need to be carefully discussed with health care professionals.
Living With Hepatitis B
Risk of chronic infection caused by hepatitis B is related to your age, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Protection . Approximately 90% of infected infants become chronically infected compared with 2%-6% of adult, reports the CDC.
Chronic hepatitis B infection can lead to serious health issues. If you have it, you should be monitored regularly by a doctor. This means you should check in with your doctor at least once or twice a year. Some people who have chronic hepatitis B infection require medicine, but others do not. Your doctor can discuss treatment options with you.
If you have chronic hepatitis B infection, it will likely stay in your blood and liver for a lifetime, according to The Hepatitis B Foundation. This means that you could pass the virus to others, even if you dont feel sick.
The most important thing to remember is that hepatitis B is a chronic medical condition that can be successfully managed if you take good care of your health and your liver, reports the Hepatitis B Foundation. You should expect to live a long, full life.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
Prevent Hepatitis B Infections In Newborns
If you are pregnant and have hepatitis B, talk with your doctor about lowering the risk that the infection will spread to your baby. Your doctor will check your virus levels during pregnancy. If virus levels are high, your doctor may recommend treatment during pregnancy to lower virus levels and reduce the chance that hepatitis B will spread to your baby. Your doctor may refer you to a liver specialist to find out if you need hepatitis B treatment and to check for liver damage.
When it is time to give birth, tell the doctor and staff who deliver your baby that you have hepatitis B. A health care professional should give your baby the hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG right after birth. The vaccine and HBIG will greatly reduce the chance of your baby getting the infection.
Where Can I Get More Detailed Information On How To Live With Hepatitis B
More detailed information can be found in the Canadian Liver Foundations Healthy Living with Viral Hepatitis booklet, including:
- What to expect if you have hepatitis B
- The different types of blood tests and what they measure
- How to prepare for an appointment with your doctor
- What choices to make to prevent additional damage to your liver
- Who needs to know if you have hepatitis B and how to tell them
- How to recognize and deal with symptoms
- How to find financial assistance
- What questions to ask when considering alternative therapies.
Read Also: Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis B is highly infectious, and is spread from one person to another through exposure to infected blood and body fluids . It can be spread through:
- blood transfusions or organ transplantation in countries where blood or blood products have not been properly screened for hepatitis B and other viruses transmitted through blood
- unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing needles or equipment for injecting drugs
- unsterilized medical/dental equipment and shared/contaminated materials or equipment used for tattooing, body piercing or acupuncture
- sharing toothbrushes or razors
- childbirth
- household contact between family members
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Liver Damage
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B
Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Important Questions And Needs For Future Research
How does HBV establish productive infection in vivo and what is the host response early during the infection? Despite well-described information on the clinical manifestations and natural history of acute HBV infection, detailed knowledge of the virus-host interaction during this stage remains poorly defined. Advances in this area would offer a better understanding of the pathogenesis of HBV infection and its associated disease.
What is the immunologic basis of chronic infection and hepatocellular injury? There have been great strides in understanding the virology and immune response of HBV infection, but the molecular mechanisms whereby the host fails to clear the virus and develops chronic infection remain largely unknown. In addition, the adaptive evolution of virus under host immune pressure remains to be elucidated. Finally, the pathogenesis of various extra-hepatic manifestations associated with HBV infection is poorly understood. Further research in these areas is crucial not only in better understanding the natural history and disease progression but also in improving treatment for chronic hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: The Effects Of Hepatitis C