What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C Test Done
How Can I Prevent Hepatitis C
Since there is no vaccine for hepatitis C, the best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to avoid contact with the blood of infected people. This includes:
- If you shoot drugs, never share works with anyone. This includes all drug injection equipment that can get blood on or in it . Sterile syringes can be purchased over the counter in most pharmacies in Massachusetts by anyone 18 years of age or older. Find out about drug treatment programs that can help you stop using drugs.
- Only get tattoos or body piercings at places using sterile equipment and supplies.
- Never share razors, toothbrushes, or nail clippers
- The risk of sexual transmission is low, but use of latex condoms during vaginal or anal sex will reduce the risk even more
National Trends For Acute Hepatitis B
The trends in reported cases of acute HBV infection between 2009 and 2018 are presented below. Ten out of 13 P/Ts reported on acute HBV infection in 2018.
3.1.1 Overall trends over time
In 2018, 189 cases of acute HBV were reported in Canada, corresponding to a national rate of 0.52 per 100,000 population. While there was some fluctuation in rates between 2009 and 2013, the overall rate of reported acute HBV infection has remained relatively stable over the past ten years .
Figure 1. Number of reported cases and rates of acute HBV infection by sex in CanadaFigurenote *, CNDSS, 2009 to 2018
This graph displays the overall number of reported cases, as well as the overall and sex-specific rates of reported acute hepatitis B cases, between 2009 and 2018 in Canada. The horizontal axis shows the calendar years from 2009 to 2018. The vertical axis shows the rate of reported acute hepatitis B cases per 100,000 population for male, female, and overall, as well as the total number of reported cases of acute hepatitis B.
| Year |
|---|
3.1.2 Rates of acute hepatitis B infection by province/territory
In 2018, four P/Ts reported rates of acute HBV higher than the national rate of 0.52 per 100,000 population. These included Manitoba , New Brunswick , Ontario and Nova Scotia .
Figure 2. Geographical distribution of rates of reported cases of acute HBV infection across provinces and territories in Canada, CNDSS, 2018Figurenote 2 *
| Jurisdiction |
|---|
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Reactive
Also Check: Ways To Contract Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C, also known as hep C or HCV, is a virus that is associated with liver problems and chronic liver disease. Hepatitis C can be a mild illness that presents no real complications and lasts just a few weeks or months, but the infection can also present with more chronic forms that can last your entire life. Chronic forms of hepatitis C can lead to severe liver issues, including liver cancer and cirrhosis of the liver.
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Cover Hepatitis C Screening
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Women
Many women dont have symptoms until the disease is in a later stage. Women who have signs of the disease in the earliest stage may brush off symptoms or attribute them to other factors, such as anemia, depression, or menopause.
Early symptoms of hepatitis C in women can include:
- fatigue
- muscle and joint pain
- poor appetite
Some hepatitis C infections are acute and the infection clears or improves on its own without treatment within a few months. Acute infections are more common in women .
Hepatitis C can also be chronic, meaning the infection doesnt clear on its own, but rather progresses and damages the liver. Symptoms of chronic hepatitis and liver damage include:
- bruising or bleeding
- spider veins
- confusion
The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C occur in both men and women, but the disease can progress slower in women. However, some women experience rapid progression of the disease and liver damage after menopause.
Having these symptoms doesnt mean you have hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C spreads from person-to-person through contact with infected blood. If you work in an industry where you might come in contact with blood, theres a slight risk of exposure. This includes personal care such as:
- manicurists
- housekeeping
- nursing
Hepatitis C can also be spread to a sexual partner during a menstrual cycle.
Not Only Does The Stage Tell You How Serious The Disease Is But It Can Help You And
Although it is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in american women, breast cancer can impact people of all genders. When malignant cancer cells form and grow within a persons breast tissue, breast cancer occurs. Although screenings for prostate cancer are one tool for early detecti. Prostate cancer is a common type of cancer in men, according to the mayo clinic. Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer diagnosed in men. Although the percentage of cases in men is much lower than in women, male breast cancer accounts for a por. A cancer diagnosis can leave you unable to comprehend anything else your doctor says, but its important to pay attention to what stage of cancer you have. There are a number of different treatments doctors recommend. Here are 10 more facts about prostate cancer. Adenocarcinoma cancers being usually in one of the following organs: Of course, your specialist is the main person whose advice you should follow but it doesnt do anyone harm. Not only does the stage tell you how serious the disease is, but it can help you and. Being armed with information is vital to begin the fight.
Don’t Miss: What Virus Causes Hepatitis A
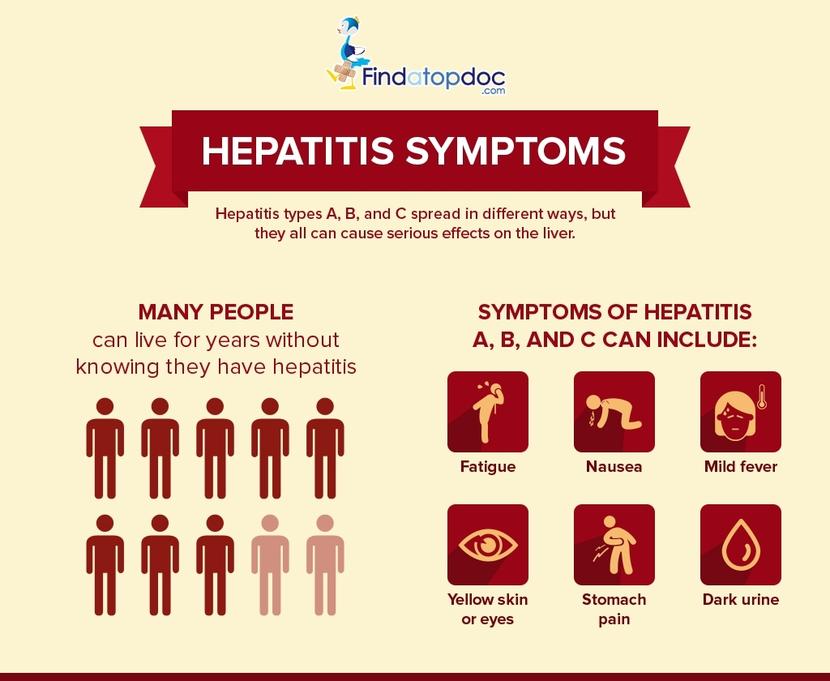
Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis C
Acute Hepatitis C Recognition and Transmission
Since the symptoms of acute Hepatitis C are so vague, more information is needed to suspect this virus as the cause of fatigue and bellyache.
The following information is important regarding acute Hepatitis C:
- Symptom time frame In those individuals who develop symptoms from acute Hepatitis C infection, the average time from exposure to symptoms ranges from 2 to 12 weeks.
- Contagious Even if a person with Hepatitis C has no symptoms, he or she can still spread the Hepatitis C virus to others.
- How you get it The Hepatitis C virus is blood-borne, meaning contaminated blood must enter your bloodstream for infection to occur.
It is important to understand how the virus is transmitted to be able to recognize what early symptoms of Hepatitis C could be.
The Hepatitis C virus itself is small and resilient. A microscopic amount of blood can transmit the virus and it can live outside of your body in open air for at least four days. Inside of a syringe, the virus can live for several weeks. As such, sharing injection drug equipment presents the highest risk for Hepatitis C transmission.
Hepatitis C transmission should be suspected if:
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But its important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Fatty Liver
What Type Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated by either a gastroenterologist, a hepatologist , or an infectious disease specialist. The treatment team may include more than one specialist, depending on the extent of liver damage.Surgeons who specialize in surgery of the liver, including liver transplantation, are part of the medical team and should see patients with advanced disease early, before the patient needs a liver transplant. They may be able to identify issues that need to be addressed before surgery can be considered. Other persons who can be helpful in managing patients include dietitians to consult on nutritional issues and pharmacists to assist with management of drugs.
Can I Breastfeed My Baby If I Have Viral Hepatitis

Yes, you can breastfeed your baby if you have viral hepatitis. You cannot pass viral hepatitis through breastmilk.
But, if you have hepatitis C and your nipple or the surrounding skin is cracked or bleeding, stop nursing your baby on that breast until the sores heal. You can pump or hand-express your milk from that breast until it heals. Throw any breastmilk from that breast away, because it might have been contaminated with hepatitis C from the cracked or bleeding skin.
Pumping the breast that is cracked or bleeding will help keep up your milk supply and prevent the breast from getting overly full and painful. You can feed your baby your milk from your healthy breast.24
Read Also: How Many Hepatitis C Genotypes Are There
What Medications Cure Hepatitis C Infection
Interferons, for example, Roferon-A and Infergen, and pegylated interferons such as Peg-IntronT, Pegasys, were mainstays of treatment for years. Interferons produced sustained viral response of up to 15%. Later, peglatedll forms produced SVR of 50%-80%. These drugs were injected, had many adverse effects, required frequent monitoring, and were often combined with oral ribavirin, which caused anemia. Treatment durations ranged up to 48 weeks.
Direct-acting anti-viral agents are antiviral drugs that act directly on hepatitis C multiplication.
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
Recommended Reading: What Medicine Cures Hepatitis C
Also Check: Home Remedies For Hepatitis B
Is Liver Transplantation An Option For A Person With Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is the leading reason for 40% to 45% of liver transplants in the U.S. Hepatitis C usually recurs after transplantation and infects the new liver. Approximately 25% of these patients with recurrent hepatitis will develop cirrhosis within five years of transplantation. Despite this, the five-year survival rate for patients with hepatitis C is similar to that of patients who are transplanted for other types of liver disease.
Most transplant centers delay therapy until recurrent hepatitis C in the transplanted liver is confirmed. Oral, highly effective, direct-acting antivirals have shown encouraging results in patients who have undergone liver transplantation for hepatitis C infection and have recurrent hepatitis C. The choice of therapy needs to be individualized and is rapidly evolving.
Who Are At Risk Of Hepatitis A
- People who have oral-sex and anal sex on a regular basis with random partners.
- People who are habitual of illegal drugs.
- People who are already having chronic liver disease.
- People who have blood clots or are continuously suffering from it.
- People who are having HIV or have recovered from cancer. Since both HIV and cancer weaken the immunity system, the risk of opportune diseases like Hepatitis A increases.
- People who are in direct contact with chronically or terminally ill patients.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis C Through Saliva
Hepatitis C And Injecting Drugs
If you inject drugs, avoid sharing needles, syringes or other equipment such as tourniquets, spoons, swabs or water.
Where possible, always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available free of charge from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. To find out where you can obtain free needles, syringes and other injecting equipment, contact DirectLine
Try to wash your hands before and after injecting. If you cant do this, use hand sanitiser or alcohol swabs from a needle and syringe program service.
Notable Ways This Liver Disease Affects Women Differently
Robert Burakoff, MD, MPH, is board-certified in gastroentrology. He is the vice chair for ambulatory services for the department of medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, where he is also a professor. He was the founding editor and co-editor in chief of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.
Hepatitis C is a potentially fatal viral infection that can cause long-term damage to the liver. Although the symptoms of hepatitis C are similar in women and men, the disease can progress differently in females. Women also face unique challenges, including the risk of mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Cause Liver Cancer
Acute Hepatitis C: What Are The Signs And Symptoms
For acute hepatitis C, the incubation period is two weeks to three months after exposure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
Most people who contract acute hepatitis C do not show any symptoms, the CDC notes. And because there are no symptoms, they never receive a diagnosis. But others with acute hepatitis C have the following symptoms:
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or clay-colored feces
- Joint pain
- Jaundice
For reasons that arent well understood, a small percentage of individuals exposed to HCV about 15 to 25 percent only develop an acute infection that clears out of the body spontaneously, says Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease physician and senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Pittsburgh. The infection usually clears from the body within six months. The remaining 75 to 85 percent of those exposed to HCV develop chronic hepatitis C.
Among those who develop an acute infection with symptoms, symptoms typically last only 2 to 12 weeks.
You May Like: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B