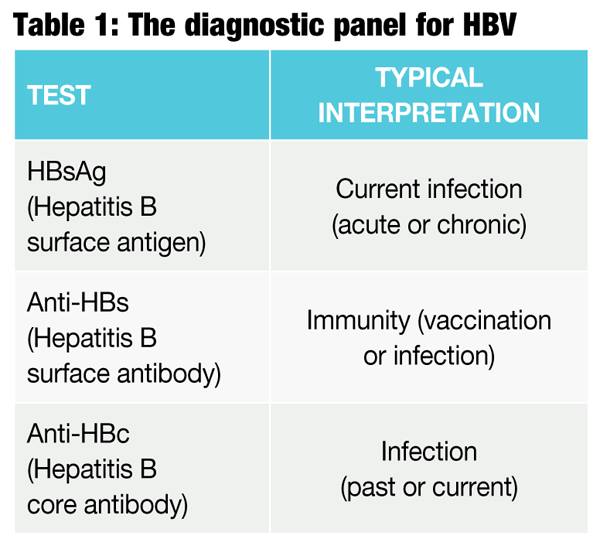
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Declination Form
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Evaluation Of Individuals Suspected Of Having An Hbv Infection
Given the perinatal and childhood vaccination programs already in place in North America, most HBV-infected individuals will likely present with chronic infection. Such individuals are likely to have risk factors that include immigration from high endemicity regions, injection drug use or sexual contact with an infected person 1) . Therefore, the present guideline will provide diagnostic recommendations first for individuals suspected of having chronic HBV infection and, subsequently, for those with acute infection. The diagnosis of HBV infection in any individual has important management implications, including appropriate counselling, monitoring and/or treating and vaccinating family or at-risk contacts.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic
Acceptability Values And Preferences
In a values and preferences survey among 104 respondents from 43 countries, overall, there was strong support from patient groups for simplified testing strategies that would improve access to testing including for high-risk groups. Seventy-seven per cent expressed a strong preference for a one-serological assay testing strategy with same-day results using RDTs to reduce loss to follow up.
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Recommended Reading: What Can Hepatitis C Do To You
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
You May Like: Common Signs Of Hepatitis C
Detection Of Antiviral Resistance
Lamivudine monotherapy has been reported to be associated with the rapid emergence of antiviral resistance in 15% to 60% of treated individuals . Resistant HBV genomes have mutations in codon 552 within the YMDD motif of the reverse transcriptase/polymerase where a valine or isoleucine replaces the methionine. Resistance is typically clinically manifested by significant elevations in ALT after an initial decline in response to treatment. Prolonged treatment after development of the YMDD mutant is controversial, although improvement in liver pathology with decreased fibrosis may occur with continuation of treatment. Concerns about disease flares after stopping lamivudine have been raised . The development of genotypic resistance can be documented by molecular sequencing or by the INNO-LiPA HBV DR assay , which involves hybridization of amplified HBV-DNA fragments onto specific nucleotide probes that have been immobilized on nitrocellulose strips .
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
You May Like: Medicine To Cure Hepatitis C
Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
Doctors must closely monitor pregnant people who have HBV.
There is a risk that the virus can pass from parent to child during delivery without the correct treatment. Therefore, all people should receive hepatitis B testing during pregnancy. A person with chronic hepatitis B should talk with a doctor about the risks and benefits of antiviral treatment while pregnant.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, if someone has HBV, their newborn must immediately receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of birth. The infant should then receive the second and third doses of the vaccine according to the standard childhood immunization schedule.
Pregnant people unsure of their vaccination status can receive the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy and breastfeeding or chestfeeding.
However, there is currently not enough safety information about Heplisav-B and PreHevbrio, so pregnant people
Chronic Hbv Carriers At Greatest Risk Of Hepatic Sequelae
Sustained elevations in ALT, although an imperfect marker for hepatic damage, can help identify chronic HBV carriers at greatest risk of sequelae and those most likely to benefit from current treatments . Chronically infected patients with sustained ALT elevations greater than the upper limit of normal may be candidates for treatment and should undergo additional prognostic hepatitis marker testing as outlined below. Chronic carriers whose ALT is within the normal range should be tested for this marker periodically because ALT levels can fluctuate with this illness. Determination of ALT levels and HBV serological and nucleic acid markers, although valuable in following infection, is not adequate to assess the severity of infection and the resulting liver damage. Before appropriate treatment can be initiated, consultation with a specialist and assessment of the disease through histological examination of a liver biopsy is strongly recommended.
Also Check: Booster For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Which Testing Strategy To Use
No studies were identified that directly compared the diagnostic accuracy of a one- versus two-assay serological testing strategy in high- and low-prevalence settings . A predictive modelling analysis was therefore undertaken, which examined diagnostic accuracy of a one- or two-assay strategy based on a hypothetical population of 1000 individuals across both a range of HBsAg seroprevalence levels and a range of assay performance characteristics (sensitivity of 98% and 90%, and specificity of 99% and 98% derived from the systematic review pooled sensitivity and specificity for HBsAg RDTs.
Prevalence had a strong impact on the PPV and the ratio of true-positive to false-positive results . The introduction of a second assay of similar sensitivity to be applied to all specimens reactive in the initial serological assay provides substantial potential gains in the PPV across all prevalence levels , but particularly at a low prevalence and with an assay that has a lower specificity.
The overall quality of the evidence for the recommendation on use of a one- or two-assay serological testing strategy was rated as low, as this was based on predictive modelling simulation and hypothetical scenarios.
Which Serological Assay To Use
A systematic review compared the diagnostic performance of commercially available serological assays for the detection of HBsAg, when compared to a laboratory-based immunoassay reference standard . The review identified 30 studies from 23 countries with varying prevalence of hepatitis B and evaluated 33 different RDTs. There were five studies of eight different EIAs against an immunoassay reference standard . A mixture of serum, plasma, capillary and venous whole blood specimens were used for RDTs, but only serum or plasma was used for EIAs. Seven studies assessed performance using capillary or venous whole blood . Sample size varied from 25 to 3928, and populations studied included healthy volunteers and blood donors, at-risk populations, pregnant women, incarcerated adults, and patients with confirmed hepatitis B.
RDTs. In 30 studies of 33 different RDTs, the pooled clinical sensitivity of RDTs against different EIA reference standards was 90.0% and pooled specificity was 99.5% .
Summary test accuracy of RDTs and EIAs for HBsAg .
Brands: there was significant variation in performance between RDT brands and within the same brand of RDT, with sensitivity ranging from 50% to 100% and specificity from 69% to 100%.
Specimen type: results for capillary whole blood specimens were comparable to serum but less heterogeneous.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine In Newborns
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
You May Like: Foods To Eat When You Have Hepatitis
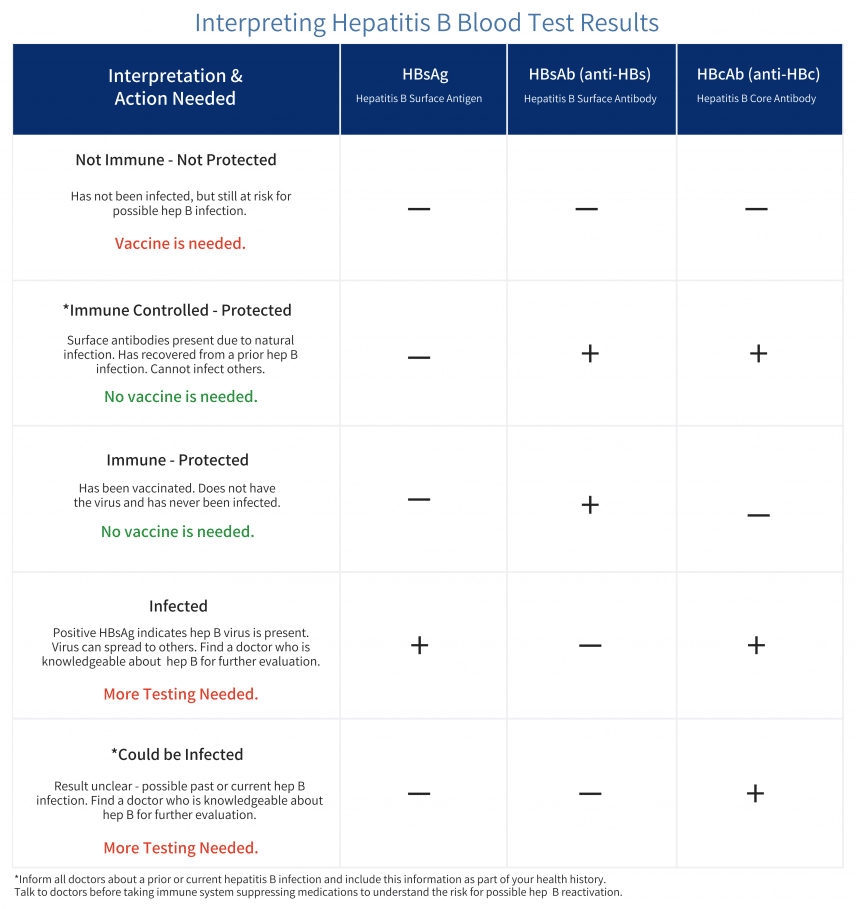
The Hep B Blood Tests
There are 3 hep B tests called HBsAg, anti-HBs, and anti-HBc. You should make sure your doctor does all three hep B tests. Our hep B testing chart can explain each test and help you to make sure your doctor does all the tests you need.
These three tests tell you if you have hep B, if you are protected against hep B , and if you have ever come into contact with hep B. Getting all three tests is important to helps you and our doctor understand your hep B status.
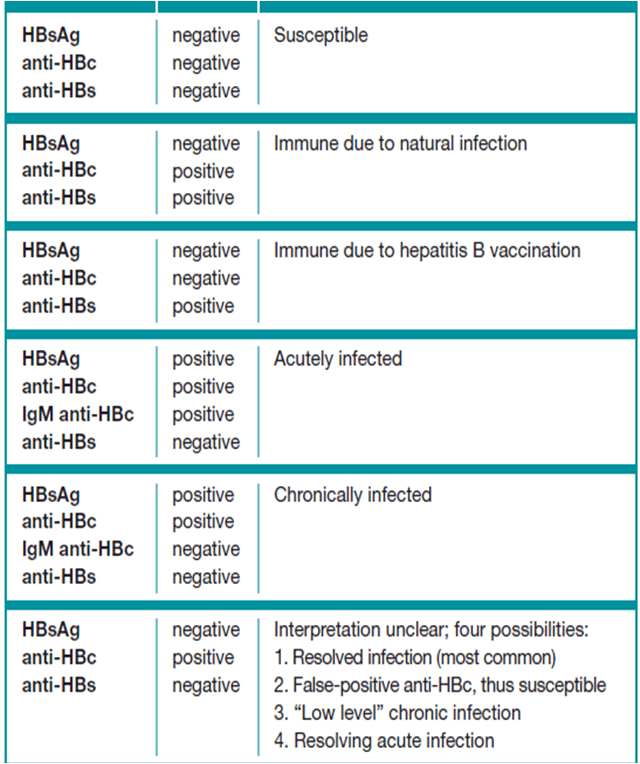
Interpreting Hepatitis B Laboratory Results
Many jurisdictions have regulations requiring laboratories to report all positive HBsAg, HBV DNA, and anti-HBc IgM laboratory results to the HD while a subset might also routinely receive positive total anti-HBc and anti-HBs results.
Additionally, some HDs might receive negative hepatitis B laboratory results, which are useful for determining false-positive results and monitoring patients through their infection and recovery. Table 3-1 shows how to interpret the combinations of laboratory results frequently available in hepatitis B test panels, following the biomarker changes over the course of disease as shown in Figure 3-1.
Table 3-1. Interpretation of hepatitis B laboratory results
| HBsAg |
|---|
- Concurrent ALT and total bilirubin result
- Other hepatitis serological results
- Negative HBsAg and/or negative/undetectable HBV DNA results
Total anti-HBc is detectable, on average, approximately 5 weeks post-HBV exposure, remains detectable indefinitely following exposure, and indicates past or current infection. In the presence of total anti-HBc, a positive HBsAg, HBeAg, or anti-HBc IgM result is a more reliable indication of recent or current infection. Jurisdictions that receive total anti-HBc laboratory results can use these results to clarify a persons HBV infection status.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
Whats The Outlook For People With Chronic Hep B
The majority of people who have hep B as adults fully recover within 1 to 3 months. Children under the age of 5 are at the highest risk of developing chronic hep B infection.
Medications can help manage chronic hep B, but about 15 to 25 percent of people die prematurely from liver cancer, cirrhosis, or liver failure.
More than half of liver cancers are caused by chronic hep B infection. Taking your medications as prescribed and following your healthcare professionals recommendations can help you minimize your chances of complications.
Molecular Methods For Hbv Infection
HBV DNA is a direct measurement of the viral load, which reveals the replication activity of the virus. It is detectable at the early stage of infection and increases up to peak level approximately 3 months after the exposure to HBV and then gradually diminishes in chronic infection or disappears at the recovery from HBV infection.
As the prevalence of serologically negative HBV infection has increased, HBV-DNA detection has obtained more awareness in clinical medicine . The detection of HBV DNA is a reliable marker of replication activity, and higher titers of HBV DNA are related to the more rapid disease progression and higher incidence of HCC . Furthermore, HBV DNA testing is useful in routine clinical setting to determine patients who need antiviral therapy and monitor them for suitable treatment .
There are two principles of techniques to identify and quantify HBV DNA: signal amplification such as hybrid capture and branched DNA technology target amplification such as polymerase chain reaction . Real-time PCR can detect wide dynamic range of viral load . For this reason, it has come to be the standard method to detect and quantify HBV DNA in clinical setting. Furthermore, it can be fully automated and does not generate carry-over contamination . Table 1 displays the comparison of assays for quantitative measurement of HBV DNA.
Table 1
Read Also: All Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.