Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Finding Help For Hepatitis
If youve been diagnosed with viral hepatitis, there are a variety of resources that are available to help you. Lets explore a few of them below:
- Your doctor. Your doctor is a great first point of contact for questions and concerns. They can help you to better understand the type of hepatitis you have, as well as how it will be treated.
- American Liver Foundation . ALF is dedicated to ending liver disease through education, research, and advocacy. Their site has educational material about viral hepatitis, as well as ways to find doctors, support groups, and clinical trials in your area.
- Patient assistance programs. If you have hepatitis C, the cost of antiviral drugs can be high. The good news is that many drug manufacturers have patient assistance programs that can help you pay for these medications.
The chart below is an at-a-glance summary of some of the key differences between hepatitis A, B, and C.
| Hepatitis A |
|---|
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis Spread From Person To Person
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
Is Antiviral Therapy Recommended For Acute Hepatitis B
No. Acute hepatitis B, defined as a positive test for hepatitis B surface antigen and the presence of hepatitis B core antibodyimmunoglobulin M , is a self-limited disease in 90% to 95% of adults and resolves without specific antiviral therapy within 3 to 6 months after the onset of clinical symptoms. For this reason, only supportive care is offered to patients with acute hepatitis B infection. Antiviral therapy is considered only for patients with chronic hepatitis B . For patients with severe acute hepatitis B with evidence of liver dysfunction such as coagulopathy or encephalopathy, antiviral therapy may be considered in this situation, expert consultation is advised.
Prodromos Hytiroglou MD, in, 2018
You May Like: Best Diet For Hepatic Steatosis
How Is The Hepatitis B Virus Spread
The Hepatitis B virus can live in all body fluids, but its mostly spread through contact with blood, semen, and vaginal fluids. HBV is most often spread through sharing needles and through sexual contact. Pregnant women with Hepatitis B can pass the infection to their baby. Babies can receive special medical treatment and the vaccination right after birth to help prevent infection.
You can get infected by:
- Having sex with an infected person
- Sharing razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers with someone who is infected
- Sharing needles to inject drugs with an infected person
- Sharing glucose monitoring devices with an infected person
- Using non-sterile needles or equipment to do tattooing, ear piercing, or acupuncture
HBV cannot be spread through food, water, breastfeeding, kissing, or handholding.
When Will Symptoms Appear After You Have Been Exposed To Hav
It generally takes about 4 weeks for symptoms to appear, but they can start at 2 weeks or they can start up to 8 weeks after you have been exposed. You probably wont get every symptom immediately, but they tend to emerge over days.
Also, you can have no symptoms and have the virus and be contagious. Children especially may be free of symptoms despite being infected.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Read Also: Hepatitis B And Ivf Treatment
Introduction To Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver disease which is a result of the infection caused by the Hepatitis virus also known as HBV.
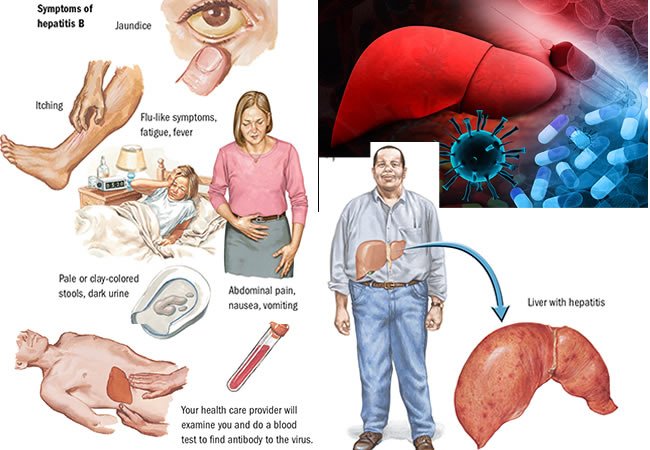
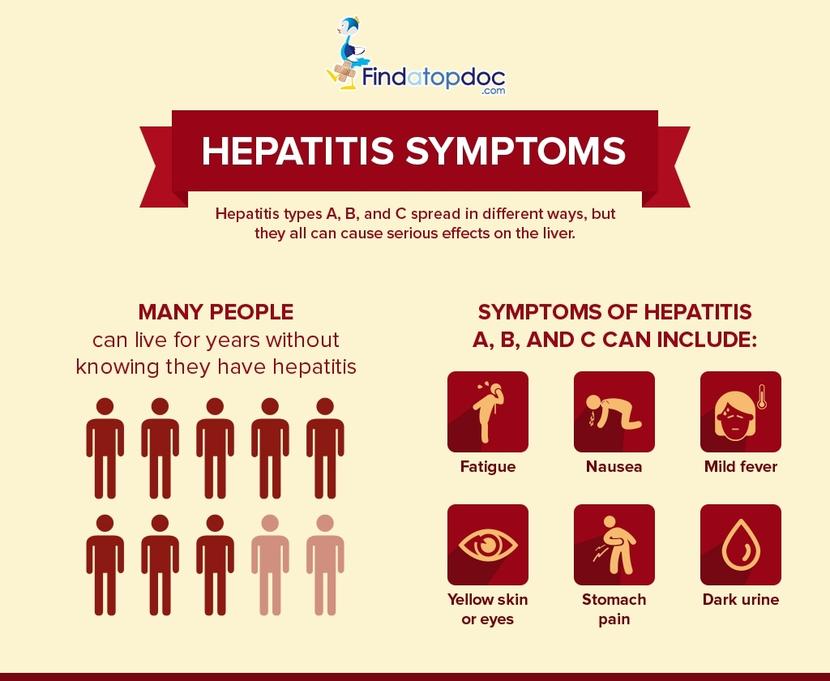
Hepatitis B symptoms in women and men includes yellowing of the eyes, joint and muscle pain, loss of appetite, fever, fatigue, abdominal discomfort etc.
Since the primary cause of Hepatitis B is transmission of contaminated body fluids, Hepatitis B can easily spread and turn into a chronic condition soon enough.
Majority of cases reported last year in New York were of Hepatitis B which signals a bad lifestyle, careless sexual activities and more than one sexual partner. Heres what all you should know about Hepatitis B:
On an average 0.5 people out of 1,00,000 in New York are affected by Hepatitis B.
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
You can become infected with hepatitis B through exposure to blood, semen and other bodily fluids of an infected person. You can get the infection by:
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
You May Like: How To Know If I Have Hepatitis
The Symptoms Are General
Since the liver has a part in so many essential functions, many symptoms are constitutional, meaning they affect the entire body. For example, a sore leg will usually just hurt in and around the leg. With hepatitis, you may feel pain around the liver, but you will also probably have chills and aches in your joints and muscles.
Read Also: Causes Of Hepatitis C Virus
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
FAST FACTS
- Hepatitis B is a virus found in infected blood, semen and vaginal fluids.
- Its a sexually transmitted infection that can be passed on through unprotected sex. You can also get it from contaminated needles and syringes. Its also commonly passed on from a mother to her baby during birth.
- There is a vaccine to prevent hepatitis B, which is routinely offered to infants as well as at-risk groups.
- You can prevent hepatitis B by practising safer sex, never sharing needles and syringes, and avoiding unlicensed tattoo parlours and acupuncturists.
- Most people dont need treatment for acute hepatitis B. If the infection becomes chronic, there is no cure, but it can be managed with treatment.
Recommended Reading: After Being Cured Of Hepatitis C
What Are The Potential Complications Of Hepatitis B
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to serious complications. Ongoing inflammation in the liver can cause cirrhosis, which is scarring in the liver. This condition prevents the liver from functioning normally.
If the damage continues, end stage liver disease and liver failure can occur. A liver transplant is the only effective treatment for liver failure.
Another possible complication of chronic hepatitis B is that it puts you at risk of developing hepatitis D. Hepatitis D can only develop in someone with hepatitis B, and it can cause any symptoms and liver disease to get worse.
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Recommended Reading: Natural Treatment For Hepatitis C
Can You Die From An Std
When untreated, some treatable STDs can spread throughout the body, causing serious consequences.
- Gonorrhea and syphilis are examples of treatable conditions that can cause serious consequences if not treated.
- HIV infection causes immune suppression that can lead to death from cancers or rare infections, although treatments are available to postpone or delay the immunosuppressive actions of the virus.
- Both hepatitis B and C can cause liver damage however, it may cause liver damage that sometimes progresses to liver failure.
- Herpes infection persists throughout life, with the possibility of future outbreaks of the illness however, there is no cure.
- Herpes infection persists throughout life. There is no cure.
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
You May Like: What To Do If You Have Hepatitis C
What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
Key Facts About Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B is a liver infection capable of causing both short-term and long-term disease.
- The virus is contracted through blood or body fluids of someone who is infected.
- The virus is up to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
- Two thirds of people who have caught Hepatitis B virus remain unaware of their infection.
- Every year more than 780,000 fatalities are registered due to complications caused by hepatitis B such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Hepatitis B is a major occupational hazard for health care professionals.
- It is possible to prevent the disease by taking a safe and effective vaccine.
Recommended Reading: How Did I Get Hepatitis C
Who Is Likely To Be Affected By Hepatitis A
Certain people are more at risk than others for hepatitis A. These include:
- People who use recreational drugs, both injected and non-injected types.
- Men who have sex with men.
- People who have close contact with someone who already is infected.
- People who have close contact with someone adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common, or people who travel to countries where hepatitis A is common.
- People who work with non-human primates.
- People who have clotting factor issues, including hemophilia.
- People who work in child care, or children who are in childcare.
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
Also Check: How Did Hepatitis C Start
What Happens After A Hepatitis B Infection
Some people carry the virus in their bodies and are contagious for the rest of their lives. They should not drink alcohol, and should check with their doctor before taking any medicines to make sure these won’t cause more liver damage.
Anyone who has ever tested positive for hepatitis B cannot be a blood donor.
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Booster For Healthcare Workers
What Precautions Should Hepatitis B Carriers Take
Chronic hepatitis B carriers should follow standard hygienic practices to ensure that close contacts are not directly contaminated by his or her blood or other body fluids. Carriers must not share razors, toothbrushes or any other object that may become contaminated with blood. In addition, susceptible household members, particularly sexual partners, should be immunized with hepatitis B vaccine. It is important for carriers to inform their dentist and health care providers.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Baby