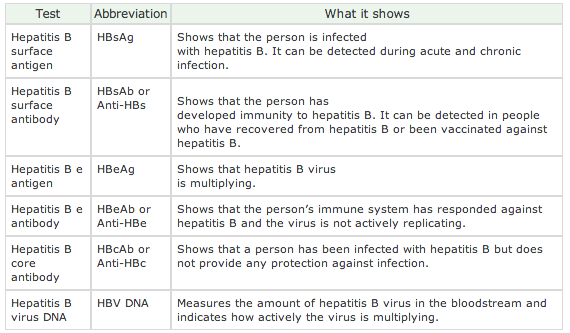
Virological Tools For Diagnosis
Virological diagnosis of HCV infection is based on two categories of laboratory tests, namely serologic assays detecting specific antibody to HCV and assays that can detect, quantify, or characterize the components of HCV viral particles, such as HCV RNA and core antigen . Direct and indirect virological tests play a key role in the diagnosis of infection, therapeutic decision-making, and assessment of virological response to therapy.
Risk Of Hcv Infection In Recipients Of Blood Transfusion
Prior to 1992, blood transfusions carried a high risk of HCV infection, approximately 15-20% with each unit transfused. In 1988, 90% of cases of posttransfusion hepatitis were due to NANBH viruses which was later found out to be due to HCV. The move to all-volunteer blood donors instead of paid donors had significantly reduced the risk of posttransfusion hepatitis to 10%. Screening of blood further reduced the rate of posttransfusion hepatitis C by a factor of about 10,000 to a current rate of 1 per million transfusions. The few cases that still occur are due to newly infected people donating blood before they have developed antibodies to the virus, which can take up to 6-8 weeks.
Recommended Laboratory Evaluation Prior To Referral
All persons referred for further evaluation and management of HCV infection should have a confirmed positive HCV RNA level, preferably a quantitative HCV RNA level and not a qualitative HCV RNA level. It is ideal, but not imperative, that the clinician who makes the diagnosis of HCV infection can perform some preliminary tests to provide advanced information in anticipation of the initial referral visit. These initial preliminary tests include an HCV genotype, tests of synthetic liver function , hepatic inflammation , and assays to detect relevant coinfection . For primary care providers taking on a more comprehensive role for the initial evaluation and management, see Module 2, Lesson 1 for a detailed discussion in the Core Concept Initial Evaluation of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis C.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Hepatitis B In Males
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients receiving hepatitis C testing may find it helpful to ask questions about their test results. Questions to consider include:
- What type of hepatitis C test did I receive?
- What was my test result?
- How do you interpret the results of the hepatitis C tests that I had?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my test result?
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Also Check: How Much Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
Testing Procedures And Costs
The test for HCV antibodies, as well as follow-up blood tests, can be done in most labs that perform routine blood work.
A regular blood sample will be taken and analyzed. No special steps, such as fasting, are needed on your part.
Many insurance companies cover hepatitis C testing, but check with your insurer first to be sure.
Many communities offer free or low-cost testing, too. Check with your doctors office or local hospital to find out whats available near you.
Testing for hepatitis C is simple and no more painful than any other blood test.
But if youre at risk for the disease or think you may have been exposed to the virus, getting tested and starting treatment if necessary can help prevent serious health problems for years to come.
CDC recommends that all adults ages 18 years and older should be screened for hepatitis C except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%.
Also, all pregnant women should be screened during each pregnancy, except in setting where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%.
Hepatitis C is often associated with sharing needles . But there are other methods of transmission.
For example, healthcare workers who are regularly exposed to other peoples blood are at higher risk for contracting the virus.
Getting a tattoo from an unlicensed tattoo artist or facility where needles may not be properly sterilized also increases the risk of transmission.
Strategies For Improving Linkage To Care
Attempts at the public health level to implement an HCV testing and linkage-to-care program have shown that additional funds can be used to leverage existing program and provider networks. The CDC and other organizations are actively working to explore strategies, such as the Hepatitis Testing and Linkage to Care initiative, to enhance linkage to care for persons infected with HCV. It should also be noted that patients who have been previously diagnosed many years ago in the interferon era may have been counseled to not seek treatment given the relatively poor efficacy, long duration, and high rate of adverse effects associated with interferon-based therapy. These patients may require more intensive outreach efforts to educate and update on new greatly improved medications that are now available.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative
Does It Matter Which Test I Get
It depends. While both tests give an accurate result as to whether a person has been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, the type of test may matter to some patients. If a patient has a fear of needles or pain, a rapid test may be better since there is less exposure to needles and the process is faster. If a patient struggles with anxiety, a rapid test may be beneficial as the results are known quicker, causing less time to wonder or worry for the patient. However, different tests may be covered differently by insurance companies.
A traditional test is known to insurance companies and is likely to be covered, whereas the new rapid testing may not be because it is so new. It is important to check with your insurance company before agreeing to this test if the cost is a concern for you. In addition, if a rapid hepatitis C test is performed outside of your normal physicians office, it is vital that the patient brings all written records to their physician in order to make sure that all information in the patient chart is included and updated. Those who are tested at their doctors office will not need to worry about this, which may matter to some patients.
Why Do I Need This Test
Every adult who is 18 years of age or older should have this test at least once to screen for HCV. You may also need this test if your healthcare provider suspects that you have HCV. If you are infected with HCV, you probably won’t have any symptoms at first. Consequently, the CDC recommends having the test if you:
-
Ever injected illegal drugs
-
Had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
-
Received clotting factor concentrates for hemophilia before 1987
-
Are the child of a mother with HCV
-
Have been a sexual partner of someone with HCV
-
Have HIV
-
Are a healthcare worker who may have been exposed to HCV
HCV can lead to liver disease, which has these symptoms:
-
Nausea
-
Frequent bruising
-
Belly pain
Symptoms of severe liver disease include mental confusion and swelling of your feet, ankles, and belly.
You May Like: How Does Someone Contract Hepatitis C
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Hep C Antibodies Do Not Prevent Re
What does it mean, in any real terms? Well, in terms of my status as being cured, it means nothing at all, because we do believe, as a fact, that antibodies for hep C offer no protection and so have no real value. It is interesting to me, and that is only because of my interest in the science of why and how things work, and there is some science that points to diminished antibody presence over time, and is it the same with all treatments? We dont know, and no need to be concerned, unless you too have a mildly science and nerdy side like me.
You May Like: Can You Catch Hepatitis C
What Do The Results Mean
There are two results from a hepatitis C antibody test.
- A non-reactive or negative test result means that the person does not have the virus. The exception is if someone has come into contact with the virus recently, such as through contaminated blood. If this is the case, they will need to have another test.
- A reactive or positive test result means that the person has had the virus at some point but does not mean that they still have it. Further tests will be needed to check whether the virus is still active in the body and if treatment will be required.
Once diagnosed with hepatitis C, a person will need to undergo a series of different tests to see how the virus has affected their body.
These tests will check for any liver damage, identify how well the liver is working, and help a healthcare professional to decide on treatment.
Hepatitis C is treated with medication known as an antiviral. It gets this name because it aims to clear the virus out of the body.
Another aim of the medication is to slow down damage to the liver. It may also reduce the chance of a person getting liver cancer or developing serious liver scarring, known as cirrhosis.
A person with hepatitis C will require regular testing during treatment to see how well the medication is working. Keeping healthy, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can help treatment to work.
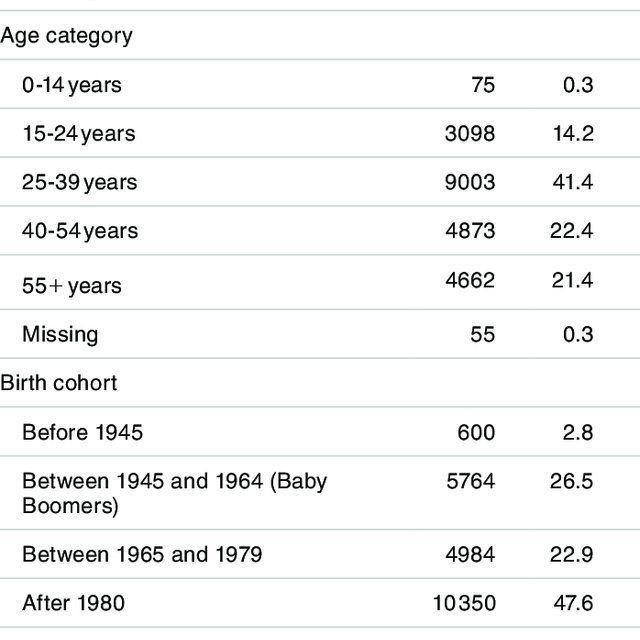
Definition And Statistical Analysis
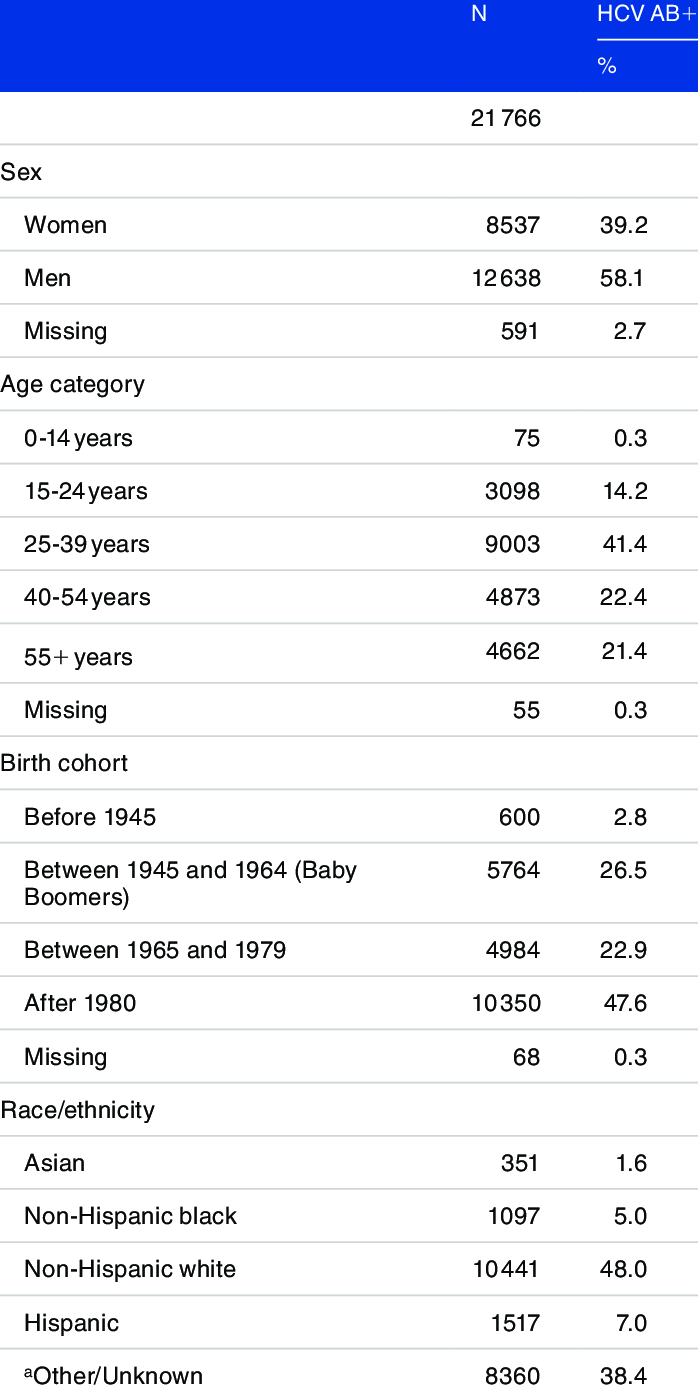
Individuals with HCV-positive RNA were considered viremic. Samples with a positive RIBA result and negative HCV RNA were recorded as true antibody positive, nonviremic. Samples with reactive anti-HCV screening test results but negative HCV RNA results and negative or indeterminate RIBA results were categorized as falsely positive .
ROC curves were constructed by plotting sensitivity versus 1 specificity, using HCV RNA and the third-generation RIBA test as gold standards, respectively. We determined the diagnostic sensitivity, diagnostic specificity, positive predictive value , NPV, and their respective exact 95% CI to predict HCV viremia and RIBA status at S/Co ratios of 3.0, 8.0, and 20.0, according to previously published methods . Optimal S/Co ratios were identified from the analysis of ROC curves and associated data . We performed ROC analysis using Graphpad Prism 6 statistical software.
You May Like: How To Prevent Hepatitis B
Adverse Effects Of Treatment
Adherence to treatment remains a major factor influencing the rates of sustained virologic response.33,42 Discontinuation of therapy because of adverse events is common and has been reported in up to one third of patients. Approximately 50 to 60 percent of patients may exhibit self-limited influenza-like symptoms with interferon-based therapy.2 Effective management of treatment-related adverse events is essential to improve adherence to treatment therefore, patients should be monitored closely for hematologic, renal, and thyroid abnormalities. Approximately 30 percent of patients undergoing treatment for HCV infection experience depression, emotional lability, or anger, but treatment is rarely associated with suicidal ideation or hallucinations.43 Treatment for HCV infection is contraindicated in persons with uncontrolled major depression.32 A recent randomized trial found that the overall adverse effects of pegylated interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin and pegylated interferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin were similar.40 Adverse effects of pegylated interferon and ribavirin for the treatment of HCV infection are listed in Table 8.32
Adverse Effects of Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Information from reference 32.
Adverse Effects of Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Information from reference 32.
What Is A Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical procedure. A tiny piece of liver is removed and examined to find out the extent of damage. It involves a large needle and local anesthetic, as well as some risk of bleeding. A pathologist looks at the piece of liver under microscopes to determine how much damage has occurred in the liver. This is a very useful test and used to be done very commonly. However, the procedure is done much less frequently than in the past. For most patients with hepatitis B and C, liver biopsy is not required. Today, other tests can be used to try to estimate the fibrosis in the liver.
Read Also: How Do You Cure Hepatitis A
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis B
Diagnosis And Hepatitis C Elimination
In one report, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine explored the feasibility of hepatitis C elimination and concluded that hepatitis C could be eliminated as a public health problem in the United States, but that substantial obstacles exist . In another report, specific actions were recommended to achieve elimination considering information, interventions, service delivery, financing, and research . These reports were the culmination of decades of progress in the development of HCV infection diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
In 1990, serologic tests to detect immunoglobulin G anti-HCV by enzyme immunoassay were licensed and became commercially available in the United States, and U.S. blood banks voluntarily began testing donations for anti-HCV . In 1991, U.S. Public Health Service issued interagency guidelines addressing hepatitis C screening of blood, organs, and tissues . These guidelines recommended hepatitis C testing for all donations of whole blood and components for transfusion, as well as testing serum/plasma from donors of organs, tissues, or semen intended for human use .
Tests After The Diagnosis
Once the doctor knows you have hep C, theyâll do tests to find out more about your condition. This will help determine your treatment. They could include:
- Genotype tests to find out which of the six kinds of hepatitis C you have.
- Liver function tests. They measure proteins and enzymes levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C.
- Tests to check for liver damage. You might get:
- Elastography. Doctors use a special ultrasound machine to feel how stiff your liver is.
- Liver biopsy. The doctor inserts a needle into your liver to take a tiny piece to examine in the lab.
- Imaging tests. These use various methods to take pictures or show images of your insides. They include:
Also Check: Can Hepatitis A Be Cured
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis C testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patients health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with their insurance company. In addition to the cost of testing, there may be other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance, or for whom insurance doesnt cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
At-home hepatitis C testing starts around $49. Some at-home kits test for multiple types of viral hepatitis at once, with the cost of these panels starting around $80.
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home hepatitis C tests are available that allow patients to collect a blood sample at home and mail it to a laboratory for testing. Test samples are collected through pricking a finger with a sharp object, called a lancet, thats included in the test kit.
At-home HCV testing is a form of hepatitis C antibody testing and does not test for hepatitis C RNA or the strains genotype. Testing for hepatitis C at home is not a substitute for testing performed by a health care professional, and positive test results may need to be confirmed by laboratory-based testing.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Is Caused By
How Is The Hbcab Test Done
This is a blood test. A clinician will fill a tube with blood taken from a vein in your arm through which a needle is inserted. If you are giving blood, a sample will be taken from the blood youre donating. The blood is sent to a lab, where it is tested. Sometimes HBcAb will be added on to lab orders when results from other tests indicate there may be a hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis C Is Often Asymptomatic
Offer testing to anyone with a risk factor or clinical indication.
Risk factors:
- shared drug-use equipment, even once
- received personal services , with nonsterile equipment
- exposed to blood during sexual activity
- received blood, blood products, or organ transplant before 1992
- received medical care where non-sterile equipment may have been used
- born, travelled, or lived in a region where hepatitis C is common
- born to a mother with hepatitis C
- diagnosis of HIV or hepatitis B
- clinical clues or symptoms of liver disease
- occupational exposure
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva