Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
How Is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on symptoms and physical findings as well as blood tests for liver enzymes, viral antibodies, and viral genetic materials.
Symptoms and physical findings
Diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis often is easy, but the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis can be difficult. When a patient reports symptoms of fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, darkening of urine, and then develops jaundice, the diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis is likely and can be confirmed by blood tests. On the other hand, patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HCV often have no symptoms or only mild nonspecific symptoms such as chronic fatigue. Typically, these patients do not have jaundice until the liver damage is far advanced. Therefore, these patients can remain undiagnosed for years to decades.
Blood tests
There are three types of blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis: liver enzymes, antibodies to the hepatitis viruses, and viral proteins or genetic material .
Liver enzymes: Among the most sensitive and widely used blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis are liver enzymes, called aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . These enzymes normally are contained within liver cells. If the liver is injured , the liver cells spill the enzymes into the blood, raising the enzyme levels in the blood and signaling that the liver is damaged.
Examples of tests for viral antibodies are:
Dermatologic Manifestations Of Hcv Infection
Primary dermatologic disorders associated with chronic hepatitis C infection
Lichen planus
References
Sterling RK, Bralow S. Extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis C virus. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2006 Feb. 8:53-9. .
Metts J, Carmichael L, Kokor W, Scharffenberg R. Hepatitis C: extrahepatic manifestations. FP Essent. 2014 Dec. 427:32-5. .
Kolopp-Sarda MN, Miossec P. Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis: pathophysiological mechanisms and diagnosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2021 Jan. 33 :1-7. .
Fachinelli LR, Silva EC, Figueiredo MG, Possa MS, Pelegrinelli FF, Molina RJ. Hepatitis C and cutaneous alterations. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2012 Dec. 45:770-3. .
Akhter A, Said A. Cutaneous manifestations of viral hepatitis. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2015 Feb. 17:452. .
Handler NS, Handler MZ, Stephany MP, Handler GA, Schwartz RA. Porphyria cutanea tarda: an intriguing genetic disease and marker. Int J Dermatol. 2017 Mar 21. .
Satta R, Pes GM, Quarta Colosso BM, Dore MP. Skin manifestations in patients with hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver disease. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Feb 8. .
Maticic M. Lichen planus in hepatitis C virus infection: an early marker that may save lives. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat. 2007 Mar. 16:3-6. .
Halawani MR. Dermatological manifestations of hepatitis C virus infection in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2014 Jun. 35:531-7. .
Walczak-Koszela I, Sysa-Jdrzejowska A, Woniacka A. . Postepy Hig Med Dosw . 2015 Dec 9. 69:1325-30. .
Read Also: What Are Some Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C
Researchers have yet to develop a vaccine that prevents hepatitis C .
Just as you might not know you have hepatitis C, other people with the condition may not know they have it, either. But you can take a few key precautions to avoid contracting it:
- Avoid sharing needles.
- When getting piercings or tattoos, check to make sure the piercer or tattoo artist uses only sterile, unopened needles and ink.
- Avoid sharing nail clippers, razors, and toothbrushes.
- Use sterile gloves when caring for someone elses wound.
Since hepatitis C is transmitted through blood, you wont get it by sharing food and drinks with someone who has the condition or by hugging, touching, or holding hands.
Hepatitis C is not commonly transmitted through sexual contact. But using a condom or another barrier method when having sex can always help lower your chances of contracting a sexually transmitted infection.
Keep in mind that you can contract hepatitis C again, even if youve had it already.
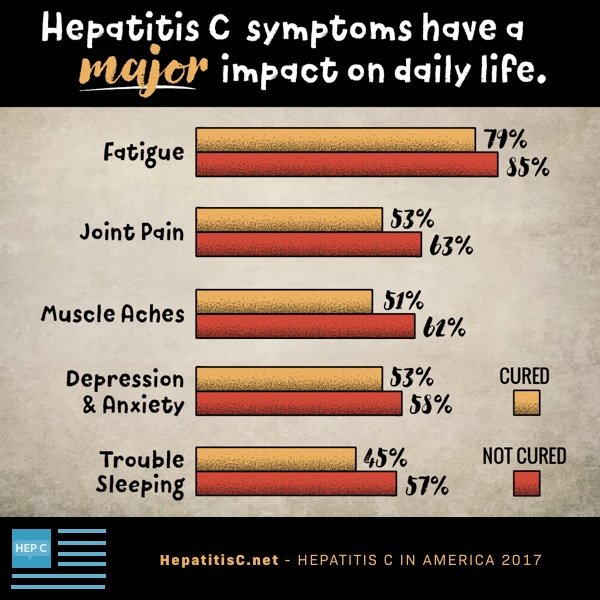
Symptoms Of Infection With Hepatitis C
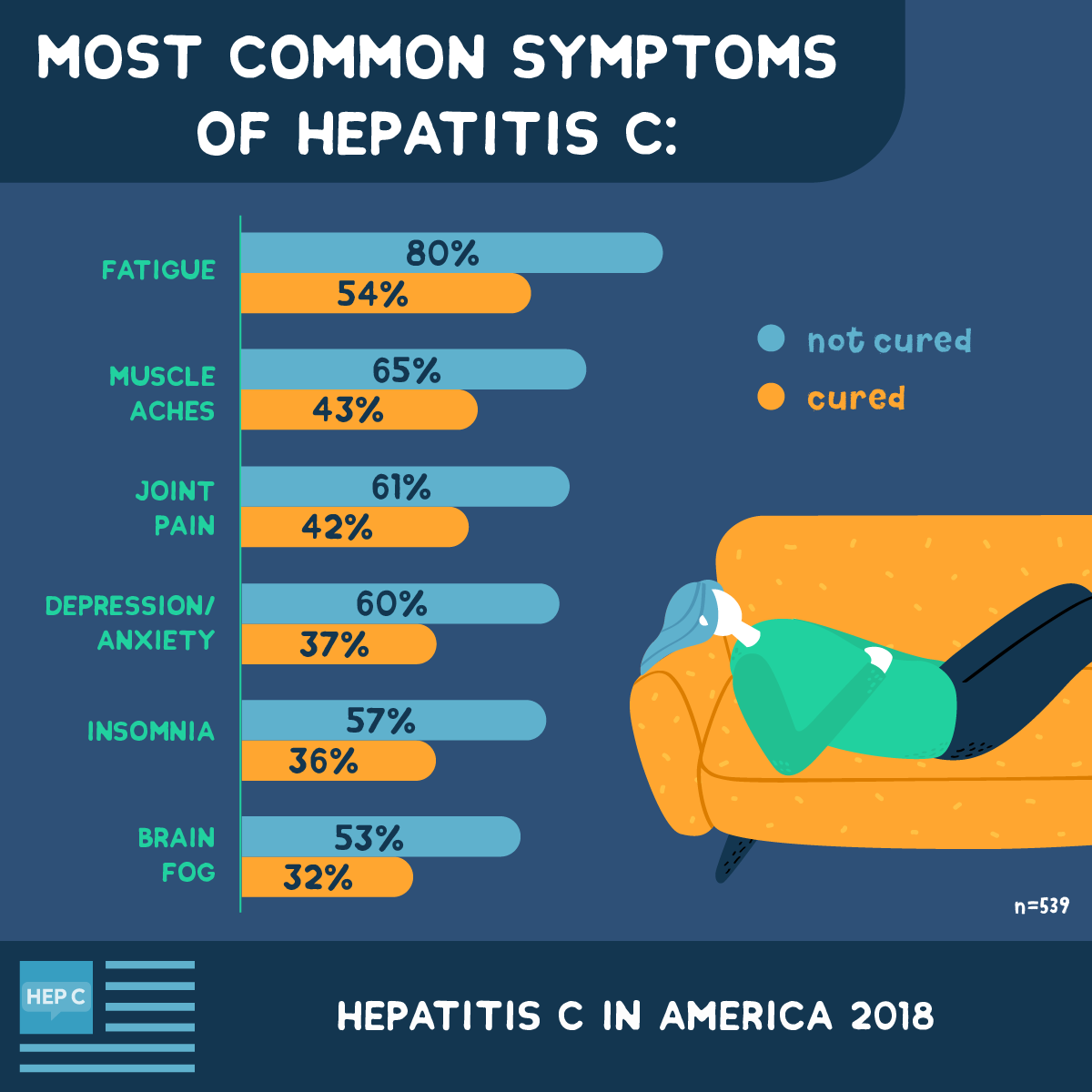
Symptoms of acute infection with hepatitis C
Acute infection is the period when you first contract the virus, during this period most people do not seem to experience any noticeable symptoms.
For the 25-35% of people who do, the symptoms are normally vague and non-specific.They can include: Abdominal pain Nausea and vomiting
About 20% of the people who develop symptoms experience jaundice. This can be seen in the yellowing of the skin and eyes. This is a sign of the livers functions being affected as bilirubin begins to build up in the body. Jaundice is a recognised sign of liver problems and may lead to a test for hepatitis C being suggested.The problem for most people is that they are unaware that they have been infected because of the lack of symptoms. As these symptoms are similar to many other short term infections most people are unlikely to seek medical attention.
And even when they do, most doctors will not necessarily suspect or test for hepatitis C.
Symptoms of chronic infection with hepatitis C
Chronic infection doesn’t mean that you have symptoms, chronic means that the infection is ongoing, that you are living with the virus.
The hepatitis C virus is associated with a wide spectrum of liver disease. This ranges from minor inflammation to cirrhosis, and in certain cases liver cancer.
Chronic fatigue
Pains in the upper part of the abdomen
Dry eyes, irritable bowel and irritable bladder
Do not assume that all of your aches and pains are related to hepatitis.
Read Also: Where Can You Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Preventing The Spread Of Hepatitis C
There is no vaccine available to prevent a person from being infected with hepatitis C. Recommended behaviours to prevent the spread of the virus include:
- Always use sterile injecting equipment. This can be accessed from your local needle and syringe program service.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as toothbrushes, razors, nail files or nail scissors, which can draw blood.
- If you are involved in body piercing, tattooing, electrolysis or acupuncture, always ensure that any instrument that pierces the skin is either single use or has been cleaned, disinfected and sterilised since it was last used.
- If you are a healthcare worker, follow standard precautions at all times.
- Wherever possible, wear single-use gloves if you give someone first aid or clean up blood or body fluids.
- Although hepatitis C is not generally considered to be a sexually transmissible infection in Australia, you may wish to consider safe sex practices if blood is going to be present, or if your partner has HIV infection. You may wish to further discuss this issue and personal risks with your doctor.
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and “tranquilizers” are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Medications for chronic hepatitis B infection include:
- oral entecavir
- oral tenofovir
Fulminant hepatitis
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Untreated
The Symptoms Are Variable
Though doctors can list common symptoms of hepatitis, not everyone will have these symptoms. Some people may have only one or two common symptoms. Others may have all of the symptoms. People experience viral hepatitis in different ways. These symptoms are known to exist in people with viral hepatitis. Your situation might be different.
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- HIV patients
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Recommended Reading: Does Hepatitis C Cause Itching
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
How Is Viral Hepatitis Prevented
Prevention of hepatitis involves measures to avoid exposure to the viruses, using immunoglobulin in the event of exposure, and vaccines. Administration of immunoglobulin is called passive protection because antibodies from patients who have had viral hepatitis are given to the patient. Vaccination is called active protection because killed viruses or non-infectious components of viruses are given to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies.
Avoidance of exposure to viruses
Prevention of viral hepatitis, like any other illness, is preferable to reliance upon treatment. Taking precautions to prevent exposure to another individual’s blood , semen , and other bodily secretions and waste will help prevent the spread of all of these viruses.
Use of immunoglobulins
Immune serum globulin is human serum that contains antibodies to hepatitis A. ISG can be administered to prevent infection in individuals who have been exposed to hepatitis A. ISG works immediately upon administration, and the duration of protection is several months. ISG usually is given to travelers to regions of the world where there are high rates of hepatitis A infection and to close or household contacts of patients with hepatitis A infection. ISG is safe with few side effects.
Hepatitis A
Individuals at increased risk of acquiring hepatitis A are:
Some local health authorities or private companies may require hepatitis A vaccination for food handlers.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for:
Recommended Reading: Chronic Viral Hepatitis B Without Delta Agent
What Is The Treatment For People With Acute Hepatitis C Infection
When people first get hepatitis C, the infection is said to be acute. Most people with acute hepatitis C do not have symptoms so they are not recognized as being infected. However, some have low-grade fever, fatigue or other symptoms that lead to an early diagnosis. Others who become infected and have a known exposure to an infected source, such as a needlestick injury, are monitored closely.
Treatment decisions should be made on a case-by-case basis. Response to treatment is higher in acute hepatitis infection than chronic infection. However, many experts prefer to hold off treatment for 8-12 weeks to see whether the patient naturally eliminates the virus without treatment. Approaches to treatment are evolving. Patients with acute hepatitis C infection should discuss treatment options with a health care professional who is experienced in treating the disease. There is no established treatment regimen at this time.
How effective is hepatitis C treatment? Is hepatitis C curable?
If the hepatitis C RNA remains undetectable at the end of the treatment and follow-up period, this is called a sustained virologic response and is considered a cure. Over 90% of people treated with DAAs are cured. These people have significantly reduced liver inflammation, and liver scarring may even be reversed.
About 5% of people who are treated for HCV infection are not cured by some of the older regimens. These people may still have options for cure with the newer regimens.
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Don’t Miss: What Happens To Your Body When You Have Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
What Are The Complications Of Undiagnosed Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis C is known to be associated with two skin conditions, lichen planus and porphyria cutanea tarda.
- Diabetes, heart disease, and arterial blockage are more common among patients with chronic hepatitis C infection than in the general population. It may be that liver damage and chronic inflammation caused by hepatitis C may affect the levels of blood fats and blood sugar.
- Low platelet counts may occur as a result of the destruction of platelets by antibodies.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Viral Load Quantitative
Hepatitis C And Blood Spills
When cleaning and removing blood spills, use standard infection control precautions at all times:
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a waterproof dressing.
- Wear single-use gloves and use paper towel to mop up blood spills.
- Clean the area with warm water and detergent, then rinse and dry.
- Place used gloves and paper towels into a plastic bag, then seal and dispose of them in a rubbish bin.
- Wash your hands in warm, soapy water then dry them thoroughly.
- Put bloodstained tissues, sanitary towels or dressings in a plastic bag before throwing them away.
How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis C Infection
If you dont have hepatitis C, you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
Hepatitis C can spread from person to person during sex, but the chances are low. People who have multiple sex partners, have HIV or other sexually transmitted diseases, or who engage in rough or anal sex have a higher chance of getting hepatitis C. Talk with your doctor about your risk of getting hepatitis C through sex and about safe sex practices, such as using a latex or polyurethane condom to help prevent the spread of hepatitis C.
If you had hepatitis C in the past and your body fought off the infection or medicines cured the infection, you can get hepatitis C again. Follow the steps above, and talk with your doctor about how to protect yourself from another hepatitis C infection.
If you think you may have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, see your doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent liver damage.
Also Check: Side Effects Of Autoimmune Hepatitis