Assessing The Severity Of The Infection
If you are found to have virus present then other tests may be advised to check on the extent of inflammation or damage to the liver. For example:
- Blood tests called liver function tests. These measure the activity of chemicals and other substances made in the liver. This gives a general guide as to whether the liver is inflamed and how well it is working. See the separate leaflet called Liver Function Tests. Other blood tests will also be done for various reasons. For example, tests to check for other illnesses which can be passed on in the same way, such as HIV or hepatitis B. Also tests of other functions of the liver, such as the ability of blood to clot properly, and levels of iron stores.
- An ultrasound scan of the liver.
- Other tests may be done if cirrhosis or other complications develop.
- There are other specialised blood tests being developed which assess the development and severity of cirrhosis.
- A small sample of the liver taken to look at under the microscope used to be recommended before considering treatment. However, this is no longer routine prior to treatment. See the separate leaflet called Liver Biopsy.
Hcv Treatment Goals In Persons With Compensated Cirrhosis
The most important immediate goal of treatment is to achieve a sustained virologic response , which is required before observing the subsequent benefit in liver-related and other outcomes. The next intermediate-term priority with therapy is to decrease the patients risk of developing hepatic decompensation. The long-term goals are to diminish the risk of developing HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma and death.
How Can You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne disease. The main source of infection is from blood from an infected person.
- Most cases are caused by using contaminated needles or injecting equipment to inject drugs . Even a tiny amount of an infected person’s blood left on a needle is enough to cause spread to others.
- Some people who received blood transfusions or blood prior to 1991 were infected with hepatitis C from some donor blood. Since 1991 all blood and blood products donated in the UK are screened for HCV.
- There is also a risk of contracting hepatitis C from needlestick accidents, or other injuries involving blood spillage from infected people.
- There is a small risk of contracting the virus from sharing toothbrushes, razors and other such items which may be contaminated with infected blood.
- There is even a small risk from inhaling drugs like cocaine, as these can make the inside of your nose bleed. If that happens, tiny spots of blood can fall on to the note you are using and, if that is used by someone else, your blood can travel up their nose and into their bloodstream.
- There is also a small risk from re-used equipment used for tattooing, body piercing, acupuncture, etc.
- There is a small risk that an infected mother can pass on the infection to her baby.
- There is a small risk that an infected person can pass on the virus whilst having sex.
The virus is not passed on during normal social contact, such as holding hands, hugging, or sharing cups or crockery.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Related To Aids
Acute Can Lead To Chronic
You may have had some of the symptoms listed above months or even years ago. Then things settled down, and you forgot about them. Remember, if you had a case of acute hep C, there is a great risk that it has turned into chronic hep C. A very small number of people will have what is called a spontaneous remission, but most people with early warning signs will develop chronic hepatitis C.
Medical Help For Treatment
Now that you know what the early warning signs of hepatitis C are, look back at your own health history. If you have been exposed, or have had a period where you had symptoms of hep C, call your doctor. Remember, according to the CDC, 8 out of 10 people with hep C will not experience symptoms. By getting a simple blood test, you can start treatment with the latest medications. Within weeks, you can be hep C free and your body can start healing.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C Virus Caused By
Hcv Treatment Data In Persons With Decompensated Cirrhosis
Limited data exist for hepatitis C treatment in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, primarily because of concerns related to treatment-related toxicity.
Ledipasvir-Sofosbuvir plus Ribavirin
Sofosbuvir-Based Regimens
- Sofosbuvir Plus Ribavirin in Decompensated Cirrhosis: In an open-label, nonrandomized, phase 2 trial, 50 adults with Child-Turcotte-Pugh cirrhosis and portal hypertension were randomized to receive immediate or deferred HCV treatment with sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily plus weight-based ribavirin 1,000 to 1,200 mg divided twice daily. The immediate group received treatment for 48 weeks the deferred group was observed during the first 24 weeks and then received 48 weeks of therapy. Overall, 72% of the participants achieved an SVR12. The results were better in those with Child-Turcotte-Pugh class A than in those with Child-Turcotte-Pugh class B . For the 37 participants who had paired baseline and end-of-treatment hepatic venous gradient measurements, those who achieved an SVR12 had clinically meaningful reductions in portal pressure.
Sofosbuvir-Velpatasvir
Stages Of Infection Flashcards Quizle
The incubation period of an infection is the time between being exposed to it and developing symptoms. There are several challenges with working out the incubation period for coronavirus: It is not always possible to know when people were first infected, especially if they may have received several ‘doses’ of virus Acute HIV infection is the first stage of infection, and the symptoms may last for a few days or up to several weeks. They will then disappear, but the virus will stay in the body. At this point,.. In rapidly progressing acute infections, the incubation may last only hours, while in slow-to-develop chronic diseases, such as HIV, the incubation period may last years. The prodromal phase is the stage of the disease process when symptoms first become apparent
Not all symptoms may be present, and many people with acute HIV infection don’t have any symptoms. However, if a person does experience symptoms, they may last for a few days or up to 4 weeks, then.. Acute HIV infection is the first stage of infection, and the symptoms may last for a few days or up to several weeks. They will then disappear, but the virus will stay in the body. At this point, the person enters stage 2, or chronic HIV infection. Stage 2: Chronic HIV infection. At this stage, there are often no symptoms, but the virus.
Also Check: What Are Some Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
What Are The Symptoms And How Does Hepatitis C Progress
Many people with hepatitis C feel entirely well and have few or no symptoms. Any symptoms that may be present are often initially thought to be due to another illness. This may mean that hepatitis C may be diagnosed when you have had the virus for some time. Many people have hepatitis C without knowing it.
It is helpful to think of two phases of infection with HCV. An acute phase when you first become infected and a chronic phase in people where the virus remains long-term.
Also Check: Signs N Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Are Hepatitis B And C Preventable
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable disease.
There is a three-shot vaccination series that is very effective in protecting people against the virus if theyre exposed. In the United States, all newborns are vaccinated for hepatitis B and all pregnant women are screened for hepatitis B during pregnancy. This way, mothers infected with hepatitis B can take protective steps to decrease the risk of transmission of the virus to the child.
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C With Compensating Cirrhosis
Oral antiviral medications, which remove the virus from a persons blood, are the primary treatment for hepatitis C. The aim is to make the virus undetectable in the blood, which shows that the medication is working. Doctors refer to this as a virologic response.
If this response lasts for 12 weeks or more after finishing treatment, the person has achieved a sustained virologic response . Around 99 percent of people who have an SVR remain virus-free for the rest of their lives.
Although antiviral treatment is generally more successful when liver fibrosis has a METAVIR score of F2 or below, people with stage F3 or even stage F4 fibrosis can reach SVR.
After achieving an SVR, the hepatitis C infection will not cause further liver damage. However, people with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis may continue to experience complications as a result of the existing liver damage.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex
How Common Is Hepatitis C
The exact number of people infected is not known. There are around 200,000 people chronically infected with hepatitis C in the UK. Worldwide, over 180 million people are infected. Rates of infection have been relatively stable in recent years, but deaths from hepatitis C have reduced, thought to be because treatment options have become better.
Most cases are in people who inject illegal drugs. It is estimated that up to half of injecting drug users become infected with hepatitis C.
End Stage Liver Disease And Liver Transplantation
Those patients with cirrhosis who continue to drink have a 5-year life expectancy of less than 70%, although this increases to 90% if they do not consume any more alcohol. For those patients with decompensated cirrhosis who no longer drink alcohol, they have a life expectancy of more than 50%, but this falls to less than 30% if they continue to consume alcohol.
It was recently proved that refraining from drinking alcohol one month after diagnosis is one of the main factors for the survival of patients with cirrhosis for abstainers there is a 72% chance of a 7-year life expectancy, but only 44% for patients who continue to drink. Verrill et al have confirmed through biopsy that it is never too late to stop alcohol consumption, even in the later stages of cirrhosis.
Eighty percent of deaths from liver disease are attributed to alcohol. Deaths from cirrhosis caused by alcohol stand at 44%. ALD is the second most common factor in patients having a LT in the United States and in Europe.
Some data was recently reported supporting LTs in cases of ALD.
Most transplants routinely require 6 mo of zero alcohol consumption before the operation this is known as the 6-mo rule. This rule became a general requirement in 1997, when the United Network for Organ Sharing had a meeting to discuss the criteria as to how adult patients are selected for placement on a liver transplant waiting list.
Recommended Reading: Medication For Hepatitis C Cure
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while they’re very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
Stages Of Infection Nursing Lecture
The prodromal stage The peak stage The recovery stage 21.5K view In the small number of people who get sick during the acute infection, signs and symptoms include: Yellowing of the skin Dark urine. White-colored stool. Nausea. Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen. These signs and symptoms last for two to 12 weeks. Most acute hepatitis C infections today occur in people who share needles to. Names of stages of infection. incubation period. prodromal stage. illness stage. convalescence. Incubation period. Interval between entrance of pathogen into body and appearance of first symptoms . Prodromal stage. Interval from onset of non.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Baby Vaccine Schedule
Note: The Following Is Intended For Use By Broadcast Media
The final stage of Nova Scotia’s hepatitis C risk-notification program is now under way.
The province launched the program two years ago to tryto locate people who may have been exposed to hepatitis Cthrough blood or blood products between 1984 and 1990.
Almost 15-thousand letters have been sent out to peoplewho were patients in Nova Scotia hospitals during thatperiod.
The letters inform people of their potential risk andadvise them to see a doctor about being tested.
The notification program began in June 1997 and costan estimated 500-thousand dollars.
-30-
Chronic Phase Of Hepatitis C
When infection with hepatitis C lasts for longer than six months, it is known as chronic hepatitis C infection. The course of the chronic infection varies considerably between people and it is very unpredictable. Of those people who develop chronic infection:
- Some people have mild or no symptoms. However, even if you have no symptoms, you can still pass on HCV to others who may develop problems.
- Some people develop some symptoms due to persistent inflammation of the liver. For example, feeling sick, lack of appetite, intolerance of alcohol, pains over the liver, jaundice and depression. The most common symptoms of chronic hepatitis C are extreme tiredness, poor concentration and memory problems, and muscle and joint aches. There is actually no relationship between the severity of symptoms and the degree of liver damage. This means that some people can have liver inflammation without having any symptoms.
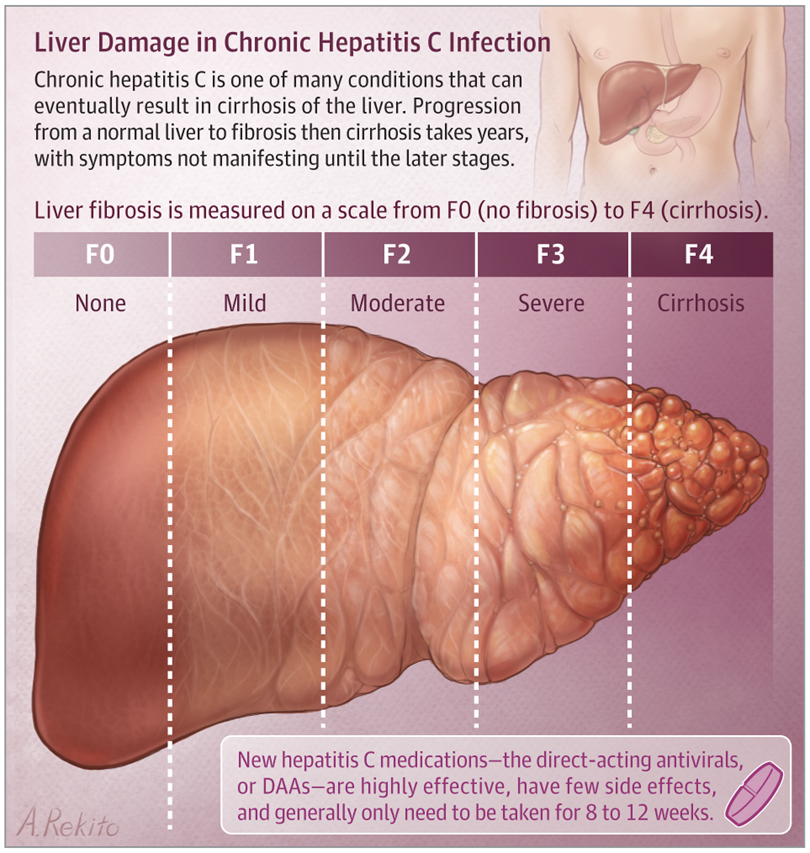
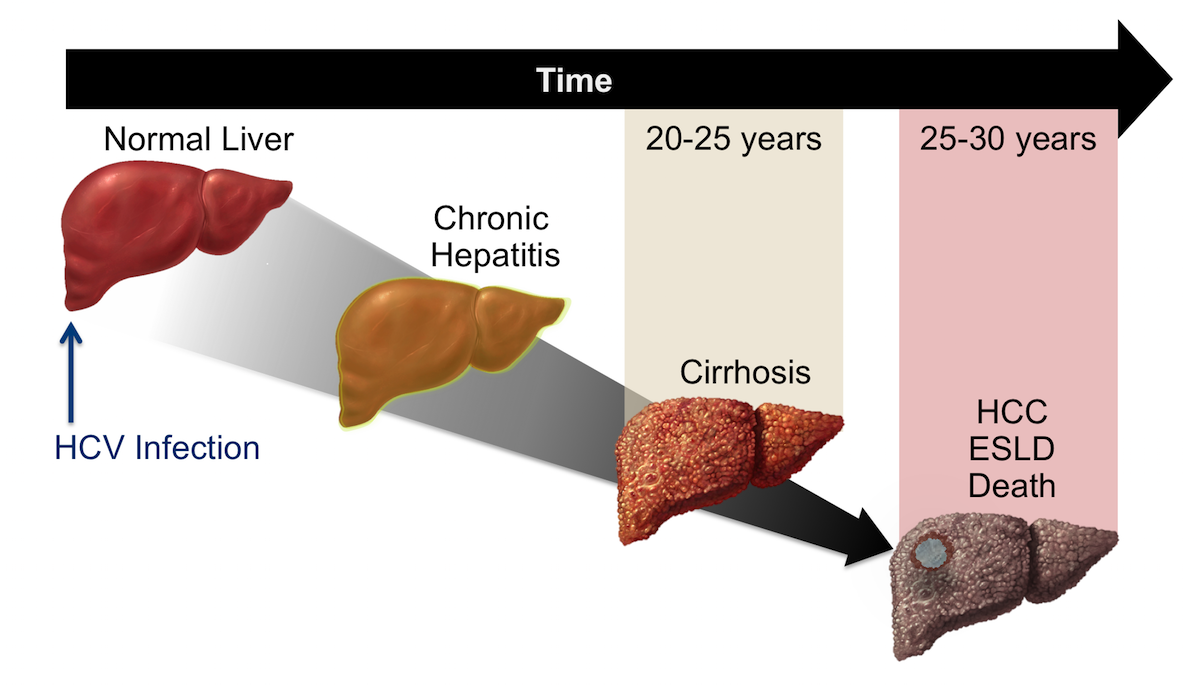
- About one third of people with chronic hepatitis C infection develop cirrhosis over a period of about 20-30 years. Cirrhosis is like a ‘scarring’ of the liver, which can cause serious problems and ‘liver failure’ when it is severe. See the separate leaflet called Cirrhosis. Some people with chronic hepatitis C have no symptoms for many years until they develop cirrhosis. Only when the liver starts to fail with cirrhosis do symptoms appear.
- A small number of people who develop cirrhosis go on to develop liver cancer.
Read Also: Hepatitis B And Hpv Vaccine Together
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Uspstf: Screen Adults 18
September 04, 2019 04:32 pm More than 4 million people in the United States have a past or current hepatitis C virus infection, and it’s the most common cause of death from a reportable infectious disease.
Compounding this, there are now more than three times as many cases of acute HCV infection than there were 10 years ago, and the disease is disproportionately affecting more young people than ever before, especially injection drug users in rural areas.
On the up side, there also now are newer antiviral medications that are safer and more effective in treating patients with HCV infection.
To help address this public health dilemma, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force on Aug. 27 issued a draft recommendation statement and draft evidence review on screening adolescents and adults for HCV infection.
Based on its review of current evidence, the USPSTF recommends screening for HCV infection in adults ages 18-79 — a “B” recommendation.
Story Highlights
In a recently issued draft recommendation, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening adults ages 18-79 for HCV infection — a “B” recommendation.
This draft statement updates a 2013 USPSTF final recommendation, expanding the age range for screening for HCV from adults born in 1945-1965 to all adults.
The task force also suggests in the draft recommendation that clinicians consider screening patients who are younger than 18 and older than 79 if they are at high risk for infection.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C High Viral Load