What Are Fatty Liver Disease And Liver Fibrosis
One of the many causes of liver disease is the buildup of too much fat in the organ, called steatosis. The liver normally contains some fat, but more than 5-6 percent of fat is abnormal. The class of liver disease in which liver becomes fatty is called Fatty Liver Disease .
There are two major causes of FLD:
- alcoholic fatty liver disease , which occurs as a result of drinking excessive quantities of alcohol.
- nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , which occurs as a result of abnormal metabolism. It is associated with obesity, high cholesterol and diabetes. NAFLD is the most common liver disease in developed countries, including the United States.
Other causes of FLD include: viral hepatitis, certain medications including steroids and chemotherapy, and pregnancy.
FLD can progress to a condition called steatohepatitis when the accumulation of fat in the liver causes inflammation, cell death, and scarring. Long-standing steatohepatitis leads to liver fibrosis as scar tissue builds up and replaces healthy liver tissue.
Liver fibrosis results in diminished blood flow throughout the liver. As healthy liver tissue is lost, the liver also loses its ability to function. If untreated, liver fibrosis may progress to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Unfortunately, many patients with FLD and liver fibrosis do not realize they have liver disease because the symptoms are often vague, like mild fatigue or abdominal discomfort.
- appetite and weight loss
How Is Fatty Liver Disease Treated
Theres no medication specifically for fatty liver disease. Instead, doctors focus on helping you control factors that contribute to the condition. They also recommend making lifestyle changes that can significantly improve your health. Treatment includes:
- Avoiding alcohol.
- Losing weight.
- Taking medications to control diabetes, cholesterol and triglycerides .
- Taking vitamin E and thiazolidinediones in specific instances .
Natural History Of Chronic Liver Disease
Chronic liver injury leads to initiation and perpetuation of inflammatory processes, which, by a cascade of inter-related processes and pathways, leads to deposition of fibrous tissue .1). By convention, fibrosis has been considered potentially reversible, while the end-stage of the pathological process, cirrhosis, has been considered irreversible. However, with elimination of the cause of liver injury, a number of studies have demonstrated regression of all stages of fibrosis in animal models and in humans. Elucidation of the process of fibrogenesis enables markers of disease severity and potential targets for therapeutic intervention to be developed.
Histology of normal liver, fibrosis and cirrhosis. A: Representative histological images , normal liver B: Mild to moderate fibrosis with portal tract expansion C: Moderate bridging fibrosis D: Cirrhosis .
Don’t Miss: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted
Proton Density Fat Fraction
MRI techniques can also be used to calculate the proton density fat fraction , a marker of hepatic steatosis, using MRS as a reference. PDFF is defined as the ratio of density of mobile protons from triglycerides and the total density of protons from mobile triglycerides and mobile water which then reflects the concentration of fat within that tissue in the absence of confounding factors. PDFF has shown at least equivalence in accuracy for quantifying hepatic steatosis with both 1H MRS and with histological grade, across several studies with various aetiologies of chronic liver disease. Additionally, in a retrospective study of data from 506 adults, PDFF estimation accuracy was not affected by age, sex and BMI with the authors concluding these confounders have a clinically negligible effect. Further validation of these techniques would be of benefit as 1H MRS techniques are not widely available.
Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Score
The enhanced liver fibrosis score score combines three direct markers of fibrosis including hyaluronic acid , TIMP-1 and PIINP . Therefore, the premise of this scoring system is that a higher score will indicate a higher rate of fibrogenesis. ELF® has been shown to have good performance for the detection of significant fibrosis in chronic HCV but also in NAFLD and ALD , although results for the latter two have been less rigorously evaluated. Results also need to be adjusted appropriately as scores can be influenced by gender, age, and sex.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Hepatitis B
Liver Biopsy And Histopathologic Examination
Liver biopsy and histopathologic examination are important components of the diagnostic evaluation in patients with suspected alcoholic liver disease . They are the most sensitive and specific means of evaluating the degree of liver cell injury and hepatic fibrosis. Several reasons justify obtaining a liver biopsy in patients with ALD, including the following:
-
Confirming the diagnosis
-
Excluding other unsuspected causes of liver disease
-
Assessing the extent of liver damage
-
Defining the prognosis
In making the decision on whether to perform a biopsy, it is important to consider the strength of the clinical diagnosis and the role that the biopsy findings would have in guiding therapeutic options. For patients who are unlikely to receive specific treatments or who have conditions that make a biopsy unsafe, the 2018 ALD guideline recommends including procedure risk in the biopsy decision.
A liver biopsy and histopathologic examination are required to establish the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . The diagnosis should be considered in all patients with unexplained elevations in serum aminotransferases . It should also be considered in patients with NAFLD who are at increased risk of having steatohepatitis and/or advanced fibrosis. The Brunt classification is the standard used to report NAFLD and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis biopsy specimens.
Key Mechanisms Of Fibrogenesis
Fibrosis is a dynamic process of hepatic homeostasis mediated by several cellular mediators in response to an inflammatory process. In particular, hepatic stellate cells have a central role in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. These cells comprise 15% of liver cell mass. HSCs are activated following liver injury from a relatively quiescent lipid and vitamin A-storing phenotype to a myofibroblastic phenotype, capable of proliferation, contraction and fibrogenesis. However, other myofibroblastic cell populations have also been shown to be involved in fibrogenesis, including portal fibroblasts .
Read Also: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis C
Does Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms
During the early stages, fatty liver disease often exhibits no symptoms. Or, symptoms are very nonspecific and easy to attribute to other causes. Generally, it takes many years for fatty liver disease to advance and become symptomatic. When fatty liver disease progresses, it may cause symptoms like weakness, fatigue, unintentional weight loss, yellowing of the skin , easily bruising, spider angiomas, ascites, and muscle wasting.
Steatosis And Fibrosis Progression In Hcv
High levels of TNF- have also been observed in human chronic hepatitis C patients. TNF- has been shown to induce IR in experimental animals and cultured cells. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS 1 and 2 may be one of the mechanisms by which a high level of TNF- causes IR. Administration of an anti-TNF- antibody restores insulin sensitivity. These results provide direct experimental evidence for the contribution of HCV in the development of IR. There are experimental arguments for a direct role of insulin in fibrosis progression in HCV infection.
Epidemiological studies indicating that the state of IR now associated with NASH is also associated with an increased risk of HCC. It is worth mentioning that diabetes increases the risk of chronic liver disease and HCC.
You May Like: What Happens When You Get Hepatitis C
Controlled Attenuation Parameter Using Transient Elastography Device
Table 1
| Biopsy* | Deffieux et al 2015 |
AC: attenuation coefficient ASQ: acoustic structure quantification AUC: area under the receiver operating characteristic curve BSC: backscatter coefficient CAP: controlled attenuation parameter CLD: chronic liver disease HRI hepatorenal index MRI: magnetic resonance imaging MRS: magnetic resonance spectroscopy NAFLD: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease PDFF: proton density fat fraction r: Pearson correlation coefficient Sens: sensitivity SoS: speed of sound Spec: specificity SWE: shear wave elastography : Spearman correlation coefficient TE: transient elastography UGAP: ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter US-FLI: ultrasonographic fatty liver indicator.
* S1, S2, and S3: fat accumulation in 5%-33%, 33%-66%, and > 66% of hepatocytes, respectively, based on histologic analysis . For non-biopsy gold standard references, cutoff values are listed in 3rd column diagnostic performance.
Figure 2
Attenuation Coefficient quantitative ultrasound method. Schematic and clinical image of a 55 year old female with fatty liver demonstrating greater ultrasound beam attenuation within the deep aspects of the liver and high attenuation coefficient of 0.87 dB/cm/MHz. Schematic and clinical image of 60 year old male with normal liver demonstrating homogenous attenuation throughout the liver with a low attenuation coefficient of 0.49 dB/cm/MHz.
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Advanced Hepatitis C
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, sometimes called NAFLD, is not connected to alcohol intake. Instead, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease arises from the chronic consumption of unhealthy foods. Conditions like obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension, high triglycerides and cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes are risk factors for developing fatty liver disease.
Eat Lots Of Fruits And Vegetables
Fruits and veggies are a critical component of the fatty liver disease diet plan. Both fruits and vegetables are chock-full of anti-inflammatory components like polyphenols, carotenoids, and other antioxidants that can fight liver damage. Reach for foods like broccoli, spinach, apples, blueberries, and raspberries for a liver-friendly diet.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Caused By
Stay Away From Refined Grains And Added Sugar
Refined grain and added sugar are significant contributory components to fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Refined grain and added sugar are quickly broken down into glucose molecules in the digestive system. These glucose molecules then enter the bloodstream and spike blood sugar. Insulin is released and signals to body tissues to utilize the glucose as energy, but inevitably, there is leftover glucose that must be stored throughout the body, including the liver. Eating too many refined carbs and added sugar could, over time, contribute to fatty liver disease as well as metabolic conditions like insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Steer clear of products that contain added sugar, such as candy, soda, pastries, cookies, cakes, and ice cream. Even products like granola bars, breakfast cereals, salad dressing, and condiments can contain more added sugars than you think.
To avoid refined grains, stay away from foods like white rice, white pasta, and white bread. Just like added sugar, refined grains are broken down into glucose.
Elastography Metrics Such As Elasticity Viscosity And Dispersion
Figure 4
Shear wave elastography quantitative ultrasound method with calculated SWE measurements shown as color-coded scale superimposed on grayscale clinical images. 55 year old female patient with NAFLD and MRI calculated fat fraction of 43 % with SWE measurement of 6.15 kPa and a 60 year old male without history of NAFLD and MRI calculated fat fraction of 1.4 % with SWE measurement of 4.55 kPa. These SWE measurements show no significant differences despite marked variability in MR calculated fat fractions .
Read Also: What Is The Test For Hepatitis C
What Does Mild Heterogeneous Liver Mean
4.9/5liverheterogeneousliverliverheterogeneous
Simply so, what is heterogeneous enhancement of the liver?
Heterogeneous enhancement of liver parenchyma on CT during arterial portography, reflecting heterogeneous portal venous supply, is often observed in patients with cirrhosis . In conclusion, several different types of underlying chronic liver disease were observed in most of the patients with EHE.
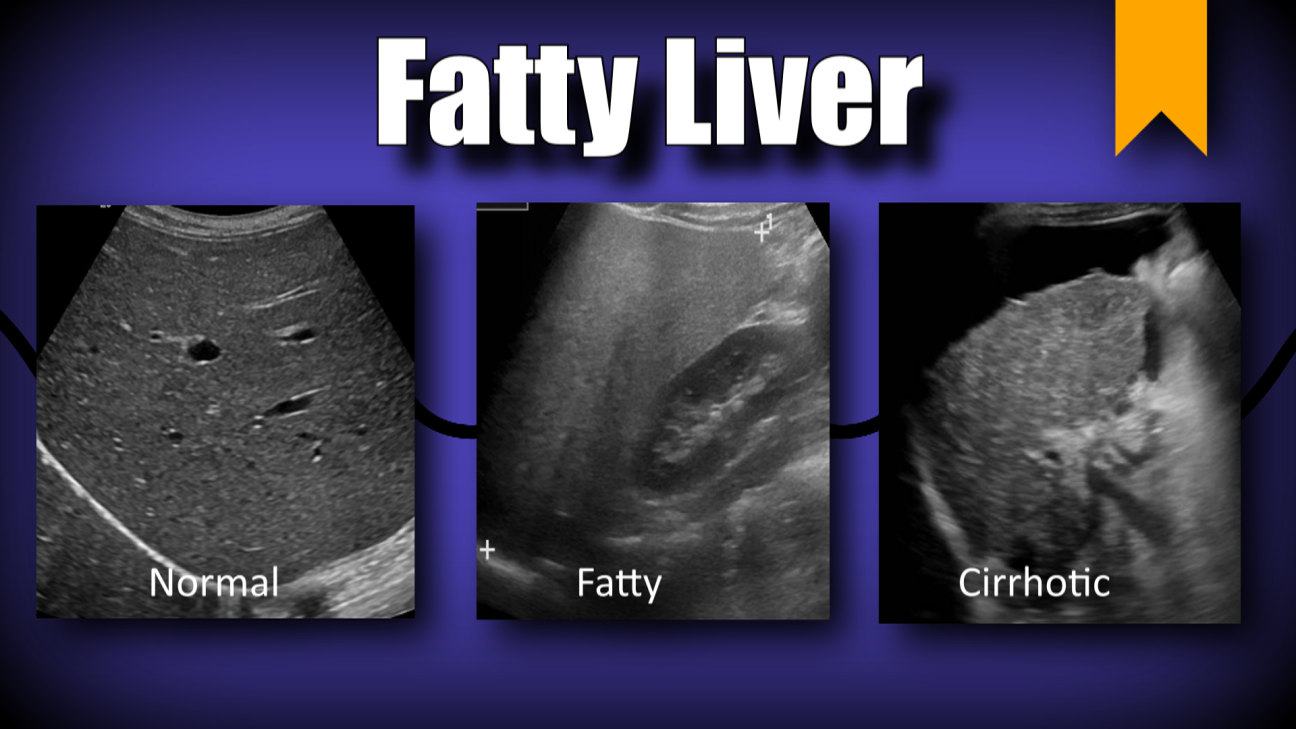
Also Know, is the liver homogeneous? Diffuse fat deposition in the liver is the most frequently encountered pattern. Liver involvement usually is homogeneous, and the image interpretation is straightforward if the rules specified earlier are applied .
Considering this, is mild fatty liver dangerous?
Although it is normal to have a tiny amount of fat in these cells, the liver is considered fatty if more than 5% of it is fat . Over time, NAFL may lead to a more serious liver condition known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH.
What does it mean when your liver is mildly echogenic?
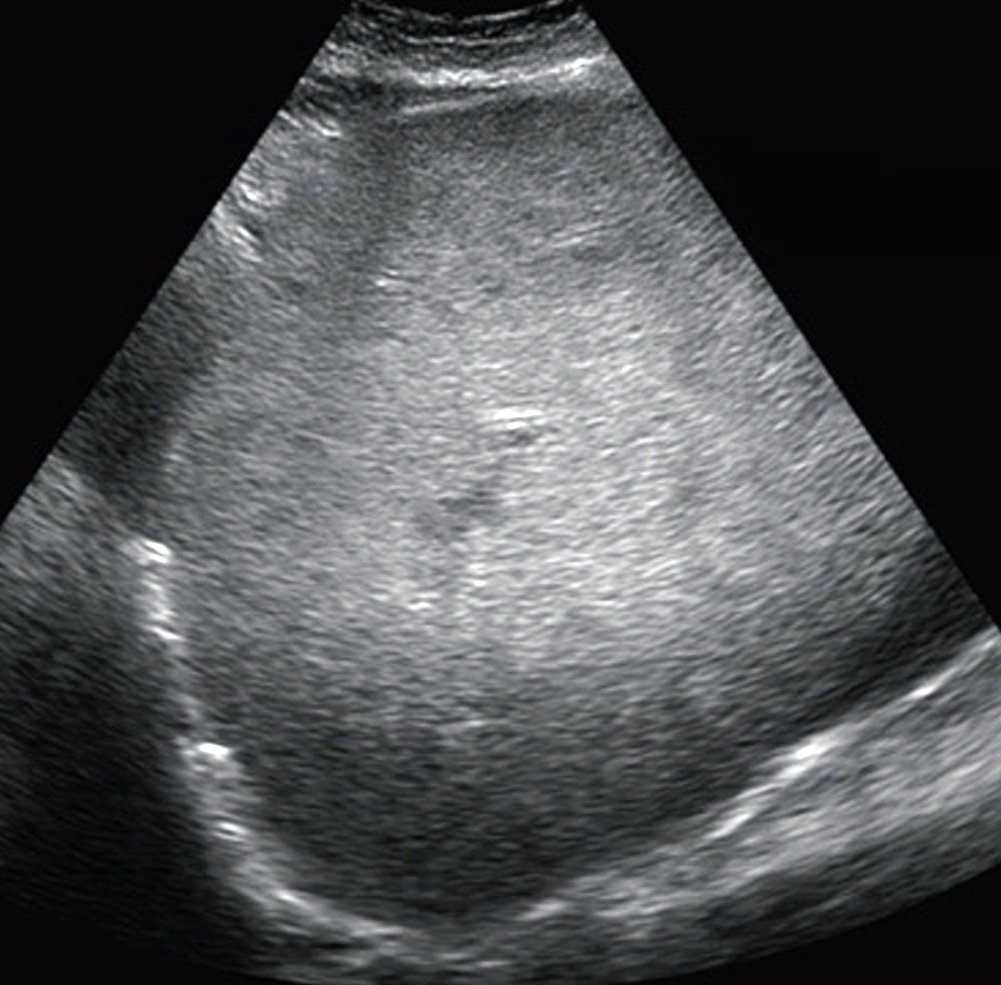
Ultrasound of the abdomen usually shows the liver is echogenic, that is more dense than usual toward sound waves. The liver can also be enlarged due to fat. Ultrasound does not really measure fat, but the great majority of the time an echogenic liver is found, this is related to excess fat.
Inflammation And Cell Turnover
Hepatic inflammation is associated with cellular inflammatory infiltrate, tissue oedema and hepatocyte swelling. Each of these is likely to affect the physical properties of liver tissue and, as such, can be measured by imaging modalities. These properties include: nuclear relaxation , assessed by MR techniques water perfusion and diffusion, as assessed by DWI liver stiffness changes in attenuation, assessed by CT and echogenicity, assessed by B-mode ultrasound.
Also Check: Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Since a Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy spectrum of the liver is dominated by lipid and water resonances, 1H MRS has been used for the assessment of hepatic fat. The percentage liver fat has been estimated from the number of protons in the lipid and water resonances by calibration with hepatic lipid extracts. Such measures have been used to assess racial differences in the prevalence of hepatic steatosis and the technique has also been applied in a population of over 2000 participants. Simpler lipid-to-water resonance ratios have been used to compare hepatic steatosis between obese and lean individuals and have demonstrated a change in intrahepatic lipid in response to dietary intervention. 1H MRS also has also been applied to the assessment of steatosis in living-donor liver transplantation and for quantification of steatosis in HIV mono-infected individuals who are at greater risk of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Key Issues In Pathophysiology
The development of hepatic steatosis occurs when the rate of synthesis or import of fatty acids by hepatocytes exceeds the rate of export or catabolism. Such an imbalance can occur in a number of ways and is summarised in Figure with increased uptake of fatty acids by hepatocytes in obesity, increased hepatic fatty acid triglyceride synthesis, impaired fatty acid mitochondrial -oxidation and reduced VLDL and triglyceride synthesis all being components to consider to a greater or lesser extent. Importantly, with respect to hepatic triglyceride export, HCV core protein has been shown to inhibit this process, providing a direct route to hepatic steatosis in HCV infection.
Summary of metabolic mechanisms leading to hepatic steatosis. Reproduced from Dowman et al with permission from Oxford University Press.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Steatosis In Chronic Hepatitis C
In chronic hepatitis C patients, the prevalence of steatosis ranges from 40% to 86% . The majority of patients with steatosis have mild steatosis affecting less than 30% of hepatocytes. Thus, steatosis occurs more frequently in patients with chronic hepatitis C than in the general population of adults in the Western world. Macrovesicular steatosis is found in the periportal region of the liver-different from the centrilobular distribution characteristic of NASH patients. Mild steatosis had been reported in nearly 40% of patients with HCV genotype 4.
Moderate or severe steatosis is significantly less frequent in genotype 4 than 3 chronic hepatitis C patients and similar between genotype 4 and 1. In non-diabetic, overweight patients, moderate or severe steatosis is present in only 10%-15% of genotype 4 or 1 compared with 40% of genotype 3 patients. Thus, hepatic steatosis in genotype 4 is mostly associated with metabolic factors, similar to those in genotype 1.
What Does Diffusley Increased Echogenicity Of The Liver Mean
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Reading: Should I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Is Increased Echotexture Of The Liver
liverliver’sliverliverincrease
. Accordingly, what does increased Echotexture of the liver mean?
et al. Coarsened hepatic echotexture is a sonographic descriptor where there uniform smooth hepatic echotexture of the liver is lost. This can occur due to number of reasons which include: conditions that cause hepatic fibrosis 1. cirrhosis.
Subsequently, question is, what does Echotexture mean? Noun. echotexture The patterning of echogenicity in a diagnostic image.
Secondly, what is increased echogenicity of the liver?
Increased liver echogenicity at ultrasound examination reflects degree of steatosis but not of fibrosis in asymptomatic patients with mild/moderate abnormalities of liver transaminases. Echogenicity was normal in 5 out of 9 patients with septal fibrosis and in 4 out of 6 patients with cirrhosis.
Is an enlarged liver dangerous?
An enlarged liver on its own may not have any symptoms. But if a medical condition is causing your enlarged liver, you may experience serious symptoms such as: jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes. muscle aches.
Steer Clear Of Added Sugar And Saturated Fat
Both added sugar and saturated fat contribute to fatty liver disease. Consuming large amounts of added sugar and saturated fat are also linked to associated conditions like type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and obesity.
So, what happens when we consume excess sugar? When we eat an abundance of sugar food, glucose travels into the bloodstream and spikes blood sugar. The pancreas then releases insulin, which signals to cells throughout the body to uptake the glucose and use it as energy. However, the body cant use all of the sugar at once. So, leftover sugar is converted into fat and stored throughout the body. Chronic consumption of sugar also causes insulin to function less effectively, worsening metabolic dysfunction.
Saturated fat essentially clogs up insulin receptors, meaning that insulin becomes less effective. Saturated fat negatively impacts metabolism and also increases the risk of heart disease. TO cut down on your saturated fat intake, steer clear of full-fat animal products like whole milk, hard cheese, cream, butter, and animal fat.
Don’t Miss: How To Check For Hepatitis C