What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
What Does It Mean To Have A Successful Treatment What Is A Sustained Virologic Response
In an untreated state, the hepatitis C virus infects the cells of the liver and then continuously lives there, making copies of itself that circulate in the bloodstream. Antiviral medications can destroy the ability of the virus to reproduce, so the amount of virus in the bloodstream then decreases. The amount of virus in the blood is measured by aviral load.
Treatment is successful when the viral load drops toundetectablelevels, which means the virus cannot be detected in the bloodstream at all. The viral load becomes undetectable during treatment and remains undetected after treatment has ended. If there is still no detectable virus in the blood 12 weeks after the end of the treatment, the treatment was successful. This is called a Sustained Virologic Response .
A patient who has achieved an SVR is considered to be cured of the hepatitis C virus.
How Mavyret Treats Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus. Mavyret works to treat hepatitis C by preventing the virus from replicating . When a virus is unable to replicate, it will eventually die and be cleared from your body.
Because Mavyret works on viruses, it belongs to a medication class called direct-acting antivirals. Mavyret contains two active medications: glecaprevir and pibrentasvir.
Recommended Reading: How Did You Get Hepatitis C
What Is The Best Treatment For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C treatment:
Antiviral Medications: Antiviral medication is given during hepatitis C to clean the virus from the body of the person. The main aim of the treatment is to get your body clear from all the virus of Hepatitis C after the 12 weeks. By taking antiviral medications people get better results, fewer side effects, and the treatment can be done in a shorter time.
Liver transplantation: It affects the liver and sometimes damages it completely thus leaving only one option that is liver transplant because it can create more complications in the body of the patient. While doing liver transplant the doctor takes out the damaged liver then it is replaced with a healthy liver.
Vaccination: There are no vaccinations for hepatitis C and the viruses of hepatitis C cannot be cured with hepatitis A and B vaccinations. Therefore one must keep the liver healthy if diagnosed with hepatitis C.
Causes Of Hepatitis C
You can become infected with hepatitis C if you come into contact with the blood of an infected person.
Other bodily fluids can also contain the virus, but blood contains the highest level of it. Just a small trace of blood can cause an infection. At room temperature, it’s thought the virus may be able survive outside the body in patches of dried blood on surfaces for up to several weeks.
The main ways you can become infected with the hepatitis C virus are described below.
Recommended Reading: How To Contract Hepatitis B And C
Articles On Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a sneaky virus. You may not have any symptoms at all. Most people donât. This is one if the reasons, along with treatability now, that all adults are recommended to get tested. Your doctor could check your liver and see only a little damage. You’re usually not diagnosed until they spot a problem with your liver enzymes after a routine blood test.
Is Hepatitis C Curable
Hepatitis c cure:
The cure depends on how well your body reacts to the medicine and how well your liver has fared. After the course of medicines, you can definitely see improvements, and it can be a permanent fixation. However, even after the treatment, you have to go for periodic check-ups to check how well your liver is now faring. The treatment also has its chances that it may not work for everyone.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Advanced Hepatitis C
Testing For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is usually diagnosed using 2 blood tests: the antibody test and the PCR test. These can be as part of a routine blood test or are often combined as a dried blood spot test. The dried blood spot test is similar to a blood sugar test in pricking the finger to get a blood spot that is put on a testing card. This is then sent to a laboratory to be tested.
Another similar test is an antigen test, which if used can often get the results back in 90 minutes. This is very expensive and not many services have access to the machine needed.
Are The Results Of The Treatment Permanent
The permanency depends on how well your body reacts to the medicine and how well your liver has fared. After the course of course of medicines, you can definitely see improvements, and it can be a permanent fixation. However, even after the treatment, you have to go for periodic check-ups to check how well your liver is now faring. The treatment also has its chances that it may not work for everyone.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Reactive
How Hep C Can Impact The Whole Body
To learn more about the symptoms, side effects, and long-term impacts of hep C, check-out these feature articles!
The Cycle of Fatigue with Hepatitis C“When you get the cycle of fatigue with hepatitis C, its easy to feel useless. You might not take good care of yourself because youre so tired. Have you felt the cycle of fatigue with hep C? Before I treated for the hep C virus, my whole life was spent trying to feel better and get out of the cycle of fatigue with hepatitis C.” Read more.
How Hepatitis C Affects the Brain“Hepatitis C is a disease caused by a virus that infects the liver. In addition to damaging the liver, research also shows that hepatitis C can cause other symptoms. Some people with hepatitis C may have problems with their skin, joints, or kidneys. Now, doctors are studying how hepatitis C affects the brain.” Read more.
Managing Chronic Pain After A Hepatitis C Diagnosis“Many people who have been diagnosed with hepatitis C also experience chronic pain . Sadly, many patients also experience hepatitis C stigma, and stigma around pain and medications. In this article, we share options for managing chronic pain caused by hep C, seeing a pain management specialist, and more.” Read more.
Symptoms of Hepatitis C“Early symptoms of hep C can often mask as flu or a general un-wellness. Many of these symptoms are discounted until chronic fatigue appears, as well as other hep C symptoms such as fatigue, itchy skin, fever, dark urine, and nausea.” Read more.
How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
Depending on the drug combination, the specific genotype of hepatitis C that is to be treated, any prior treatment, and whether the person has cirrhosis, the duration of medical therapy may be as few as 8 weeks, or up to 24 weeks. Most regimens are for 12 consecutive weeks. This is much shorter than the interferon-based treatments years ago that lasted up to 48 weeks. Generally, a person is not considered “cured” until the “RNA viral load” is undetectable for 24 weeks after therapy is stopped. This is called “sustained virologic response” or SVR.
The presence of cirrhosis or liver fibrosis is determined by liver biopsy, noninvasive fibrosis scans, or formulas that estimate liver fibrosis based on blood tests, such as AST-to-platelet Ratio Index or Fibrosis-4 Index.3
A very important aspect of treatment is the elimination of all alcohol consumption. Alcohol adds fuel to the fire when it comes to chronic hepatitis. Drinking alcohol greatly worsens liver fibrosis and speeds progression to cirrhosis, and there is no “safe” amount to drink for someone with chronic hepatitis. Drinking alcohol also makes it harder for the medications to be effective and may interfere with proper dosing.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis Feel Like
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
How Do You Get Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms To Hepatitis C
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Transmission Routes Cdc
Boxed Warning: Reactivation Of Hepatitis B Virus
Epclusa has a boxed warning . This is the most serious warning from the Food and Drug Administration . A boxed warning alerts doctors and patients about drug effects that may be dangerous.
Taking Epclusa has caused reactivation of the hepatitis B virus in people with both HBV and hepatitis C. Reactivation of HBV can cause liver failure and, in rare cases, death. HBV reactivation may occur while youre taking Epclusa or after you finish treatment.
Before you begin taking Epclusa, your doctor will typically order blood tests to check for hepatitis B . If you have HBV or have had it in the past, you may need to be treated before its safe for you to take Epclusa.
Side Effects And Complications
Severe side effects may reduce adherence to therapy and may result in dose modifications which will result in less response. Both IFN and ribavirin induce side effects that have to be considered in the management of patients with chronic hepatitis C .). IFN related side effects can be divided into IFN induced bone marrow depression, flulike symptoms, neuropsychiatric disorders, and autoimmune syndromes. The main problem with ribavirin is haemolytic anaemia. Overall, side effects result in 1020% premature withdrawals from therapy and an additional 2030% of patients require dose modifications. These numbers are lower in recent than in earlier studies, suggesting improved understanding and management of adverse events, potentially also leading to higher SVR .). However, these percentages were recorded from registration trials using careful selection of patients. This may differ in general clinical practice where patients with, for example, a history of depression, low platelets, or thyroid disease are being treated.
Table 4Common side effects recorded in major pegylated interferon /ribavirin trials,,
| Side effect | Incidence with PEGIFN alpha and ribavirin,, |
|---|---|
| Headache |
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis B Contracted
Treatment Of Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis
Treatment of patients with decompensated cirrhosis ) is limited to regimens containing sofosbuvir and NS5A inhibitors. Protease inhibitors are not recommended due to the hepatic metabolization and subsequently significantly higher drug exposure in this group of patients. Thus, grazoprevir/elbasvir, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir or SOF/VEL/VOX should not be administered. To improve efficacy the remaining combination of sofosbuvir and NS5A inhibitor should be combined with RBV . Many studies and real-world data have shown that IFN-free antiviral therapy is safe in patients with advanced liver disease. However, patients are still at risk of hospitalization during therapy, mainly because of complications from liver disease . The efficacy of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir plus RBV was studied in the SOLAR-1 and -2 study. In GT 1 patients, SVR rates ranged between 87 and 96% and between 72 and 85% in CPS B and CPS C patients, respectively . The ASTRAL-4 study evaluated the use of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir in patients with CPS B, but not CPS C. Treatment duration of 12 weeks showed high rates of SVR for patients with GT 1, 2, 4 and 6 infection. SVR rates of GT 3 were low at 50% but could be increased to 85% by the addition of RBV . Even though the rate of treatment discontinuations is higher in patients treated with RBV, the additional antiviral substance significantly increases SVR rates .
Daa Treatment And Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The impact of DAA treatment on hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, recurrence and tumor aggressiveness in patients with chronic HCV infection has been intensively discussed over the last 2 years. Shortly after DAA approval, an observed increase in early occurrence or recurrence of HCC after HCV eradication with DAA has been reported .
However, the higher incidence of de novo HCC compared to historical data was most likely related to a significantly higher proportion of older patients as well as those with end-stage liver disease certainly ineligible for IFN-based regimens. Later on, further data analysis revealed that HCV eradication due to DAA treatment reduces the risk of HCC development to a comparable level as with IFN-based therapies . These findings were supported by results from prospective studies showing a reduction of HCC incidence in patients with HCV-related liver cirrhosis . Nevertheless, the absolute risk of HCC development remains high in patients with established cirrhosis. Ongoing HCC surveillance is mandatory despite HCV clearance .
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
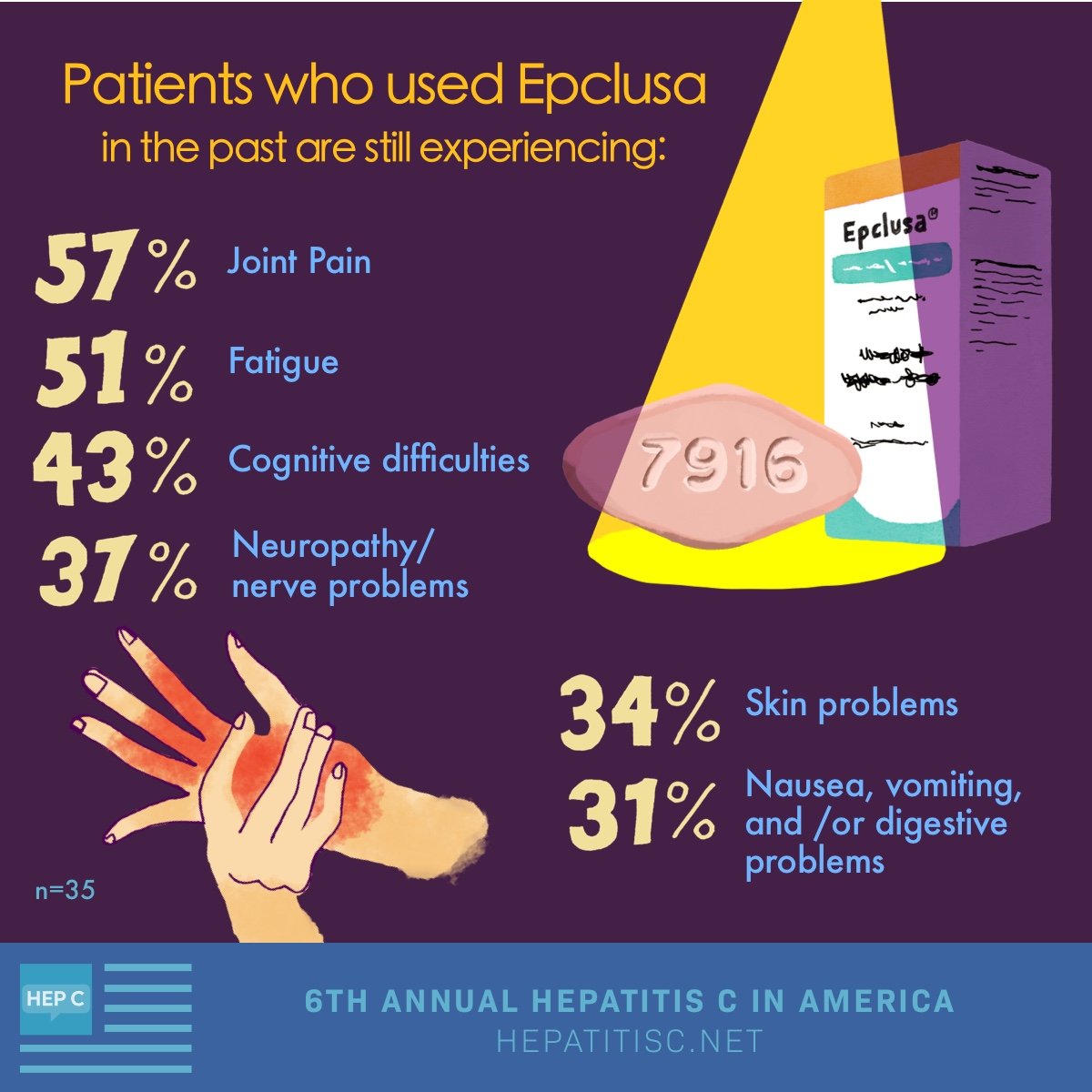
The Way Epclusa Works

Epclusa belongs to a medication class called direct-acting antivirals. Epclusa contains two active medications: sofosbuvir and velpatasvir.
Epclusa works to treat hepatitis C by preventing the virus from replicating . When a virus is unable to replicate, it will eventually die and be cleared from your body.
Its possible for Epclusa to cure hepatitis C. When blood tests can no longer detect the virus in your body, youre considered cured. In clinical studies, whether or not people were cured depended on certain factors. These included their previous hepatitis C treatment, liver function, and hepatitis C genotype.
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C
What Are The Side Effects Of Boceprevir
Side effects of boceprevir include hair loss, dry skin, diarrhea, loss of appetite, nausea, altered taste senses, sleeplessness, irritability, fatigue, shivering, anemia, and low white blood cell count.
Boceprevir can cause serious skin reactions, including urticaria, angioedema, Stevens Johnson syndrome , drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms , and exfoliative dermatitis. Boceprevir should be discontinued if serious skin reactions occur.
Chronic Hepatitis C Symptoms
If you donât get diagnosed and treated, you could have the disease for years and not know it. Doctors call this the chronic form, because it lasts a long time. Some people who’ve had it for a while get scarring of the liver, which is called cirrhosis. or liver cancer.
In addition to the above symptoms, signs that your liver isnât working the way it should include:
- Ascites — fluid buildup in your belly
- Easy bleeding
- Hepatic encephalopathy — confusion, drowsiness, and slurred speech
- Jaundice of the skin
Recommended Reading: How To Catch Hepatitis C