Workforce Screening Digitally Delivered
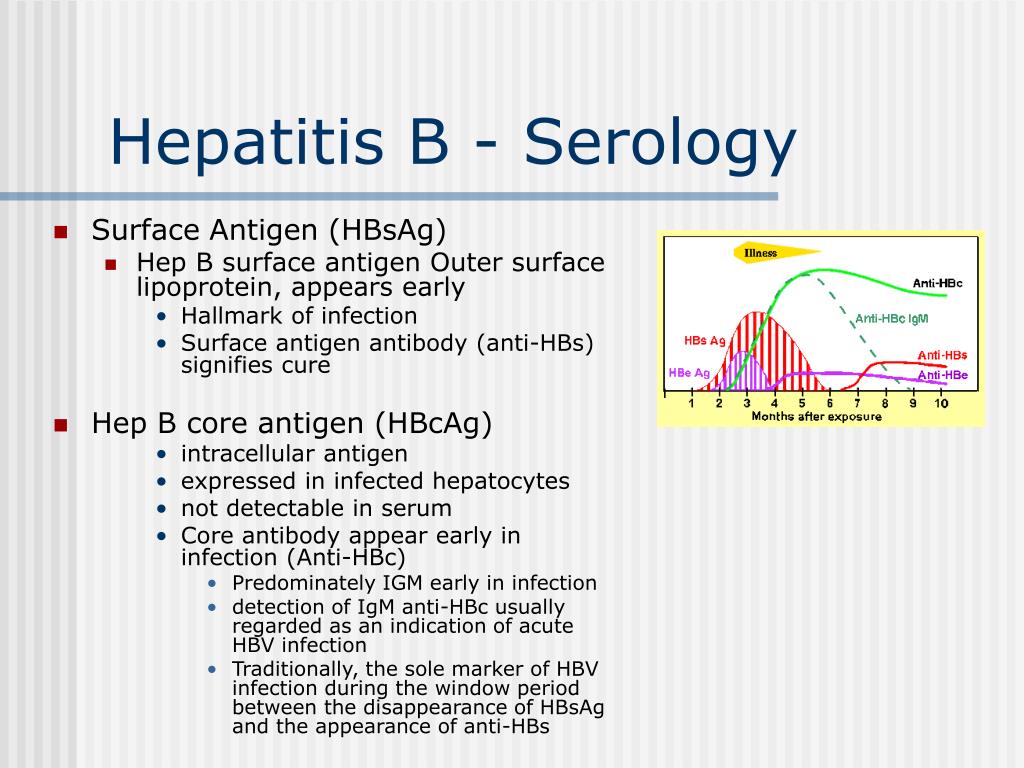
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Options
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Frequently Asked Questions
Quick Links:
bolt
What Is the Difference Between a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test and a Hepatitis B Antibody Test?
The hepatitis B surface antigen test can detect current hepatitis B infection, while the hepatitis B antibody test checks for the antibodies that are presumed to provide immunity to hepatitis B.
expand_less
When Should Someone Get a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test?
If someone is suspected to have hepatitis B, this test is intended to identify a chronic or current infection.
expand_less
What Does a Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test Mean?
A positive test means the person is currently infected or has a chronic infection of hepatitis B. This means that the person has the hepatitis B virus in their blood and can be contagious.
expand_less
About Our Other Services
For industries that require specific occupational health testing, such as healthcare, construction, and manufacturing, Health Street offers quick and easy scheduling. Simply enter your ZIP code and choose the location nearest to you or the person being tested. When the registration process has been completed, we will email you the registration barcode to and a map to the facility.
Why Choose Health Street
Related Services
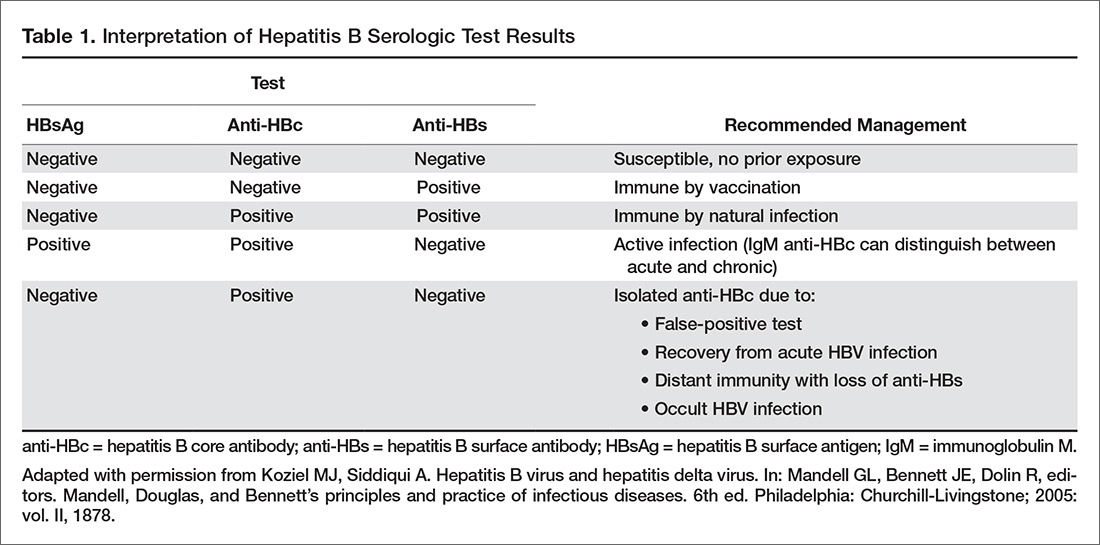
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
What Tests Will You Have To Do
Hepatitis B
You can be tested for hepatitis B at your VA medical center. This test is done by taking a sample of your blood.
Your provider may recommend the following tests:
Hepatitis B surface antibody If this test is positive, it means that:
- you have antibodies against hepatitis B and are safe from getting the disease
- you were either vaccinated against hepatitis B or exposed to it at some point in your lifetime
Hepatitis B core antibody If the test is positive, it means that:
- you have been exposed to hepatitis B and have developed an antibody to only part of the virus
- they will do more tests to find out if you currently have the disease
Hepatitis B surface antigen If the test is positive, it means that:
- you currently have hepatitis B infection
- you can spread the virus to others
Hepatitis B e antigen If the test is positive, it means that:
- you may have active hepatitis B and should be followed closely by your provider and possibly take hepatitis B medications
- you may be very contagious to others
Don’t Miss: What Are The Warning Signs Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is used to determine immune status to HBV or disease progression in individuals infected with HBV. Anti-HBs levels can be measured to determine if vaccination is needed, or following a vaccination regimen, to determine if protective immunity has been achieved.
– Anti-HBs usually can be detected several weeks to several months after HBsAg is no longer found, and it may persist for many years or for life after acute infection has been resolved.
– It may disappear in some patients, with only antibody to core remaining.
– People with this antibody are not overtly infectious.
– Presence of the antibody without the presence of the antigen is evidence for immunity from reinfection, with virus of the same subtype.
What is the Hepatitis B virus?
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days .
What are common symptoms?
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturer’s instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
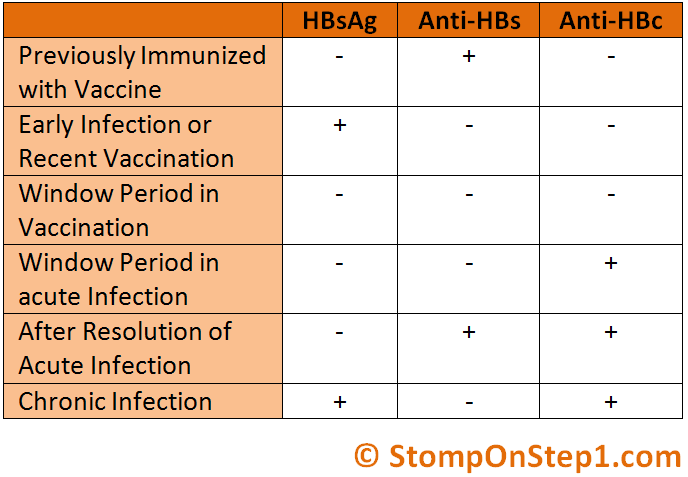
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Treatment Indications And Phases Of Chronic Hbv Infection
Phases of Chronic HBV Infection
| Phase | |
|---|---|
| HBV DNA | Inflammation |
|
May or may not be indicated |
|
|
Immune tolerant |
HBV = hepatitis B virus + = detectable = undetectable +/= may or may not be detectable.
Information from reference 22.
Phases of Chronic HBV Infection
| Phase | |
|---|---|
| HBV DNA | Inflammation |
|
May or may not be indicated |
|
|
Immune tolerant |
HBV = hepatitis B virus + = detectable = undetectable +/= may or may not be detectable.
Information from reference 22.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Cdc Fact Sheet
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Health Streets Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test checks for a current infection of the hepatitis B virus. If the test is positive, then the person can be contagious to others.
Online registration is simple. You choose the lab location based on ZIP code during registration. An authorization barcode is instantly emailed to you and texted directly to the phone of the person being tested. A map of the clinic location will accompany the barcode. The registrant can then walk into the testing facility and show the barcode along with photo ID. Results are fast and stored securely online. Individuals and employers can register online or call to order tests.
Preparing Clients For Screening
Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
Recommended Reading: What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Individuals who have received blood component therapies , plasma, or intravenous immunoglobulin infusion) in the previous 3 to 6 months may have false-positive hepatitis B surface antibody results due to passive transfer of anti-HBs present in these products.
Individuals possessing IgM anti-rubella virus may have falsely high results with the VITROS Anti-HBs quantitative test.
Anti-HBs levels from past hepatitis B or hepatitis B virus vaccination may fall below detectable levels over time.
A positive anti-HBs result does not exclude infection by another hepatitis virus.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
-Grossly lipemic
-Grossly hemolyzed
-Containing particulate matter
You May Like: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
The Frequency And Significance Of Isolated Hepatitis B Core Antibody And The Suggested Management Of Patients
Hepatitis B core antibody is the first antibody to appear following acute hepatitis B infection and will persist in high levels following resolution of infection and in chronically infected patients. Resolved infection is generally recognized by the presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen in the serum, whereas in chronic infection hepatitis B surface antigen itself is typically present.
Isolated HBcAb, which is defined as positive HBcAb with undetectable HBsAg and HBsAb, may occur in any of several clinical situations. It may be the only serum marker of acute hepatitis B infection during the so-called window phase between disappearance of HBsAg and appearance of HBsAb. It may also represent a remote resolved infection with the decline of HBsAb to undetectable levels or ongoing chronic infection with HBsAg that is escaping detection, either because of low levels of HBsAg or because of mutations in the protein that render it undetectable using certain diagnostic assays. It rarely represents a false-positive test. Acute hepatitis B virus infection is often recognized by its clinical presentation, and repeat testing after several weeks will generally detect the appearance of HBsAb. The other clinical possibilities are not easily distinguished on routine serological testing but may have important consequences, particularly in situations of chronic infection with no detection of HBsAg.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Hepatitis A Vaccine Last
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to hepatitis B, your body mounts an immune reaction against it as an invader. This happens whether you are exposed due to blood or sexual contact or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The hepatitis B virus has proteins on its surface that cause your immune system to produce antibodies. With the vaccine, the sample contains the protein only and not the virus itself.
The first response your body will make when exposed to hepatitis B is to manufacture hepatitis B IgM antibodies. These early antibodies are produced to fight against several parts of the virus including its core. These antibodies are seen in the initial response, but they eventually fade away.
Your immune system then begins to produce IgG antibodies. It continues to produce these antibodies for the rest of your life. In this way, your immune system is always ready to attack hepatitis B virus when it is exposed to it.
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C An Std
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patients body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a persons ability to spread HBV to others.
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Also Check: What Hepatitis Is Not Curable
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Recommended Reading: Hep C Without Hepatic Coma