How Can I Cover Medication Costs
New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are effective and can achieve cures of over 90%. Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Talk with your healthcare provider about financial support that may be available.
Below are useful resources when looking for financial assistance:Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded plansEach provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Programs for Hepatitis C treatment Holkira Pak Maviret
MerckCare Hepatitis C Program 1 872-5773 Zepatier
Scar Tissue Accumulates In The Liver
When the liver is injured it forms a scar, the same way your skin does when you cut it, says Ira Jacobson, M.D., a professor of medicine and director of hepatology at New York Universitys Langone Medical Center. In some cases, scar tissue can build up into an extensive network that changes the texture of the organ, giving it a lumpy, bumpy appearance, according to Dr. Jacobson. This advanced stage of liver damage is called cirrhosis, and it means blood can no longer properly flow through your liver.
Myth: Most People Infected With Hepatitis C Contracted The Virus During Unprotected Sex
In most cases hepatitis C is spread when blood from an infected person enters the body of an uninfected person. Before the virus was screened from the nations blood supply, hepatitis C was commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Today most people become infected by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
Only about 1 to 2 percent are infected through unprotected sex, Nguyen said.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A Shots At Costco
Multidisciplinary Care For Patients
The Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center and the Liver Transplant Program receive many referrals for the prevention and management of liver cancer treatment both incident and recurrent cases. Our cancer center is one of just 32 U.S. cancer research centers named by the National Cancer Institute as a National Clinical Trials Network Lead Academic Participating Site.
Only centers that meet rigorous standards for advanced cancer research can become NCI-designated. UT Southwestern is also home to one of the largest and most robust liver transplantation programs. Together, we care for patients awaiting liver transplants as well as those who have complex concurrent conditions such as decompensated cirrhosis from hepatitis C, alcohol-related liver disease, or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
As a multidisciplinary team, we approach patient care holistically with the goal of improving overall patient health along with their emergent liver condition. UT Southwestern continually pushes the boundaries of research in prevention and ongoing care. We anticipate that the profound findings from our research will usher in a new era in the care of patients with liver disease.
Why Does Cirrhosis Sometimes Cause Liver Cancer
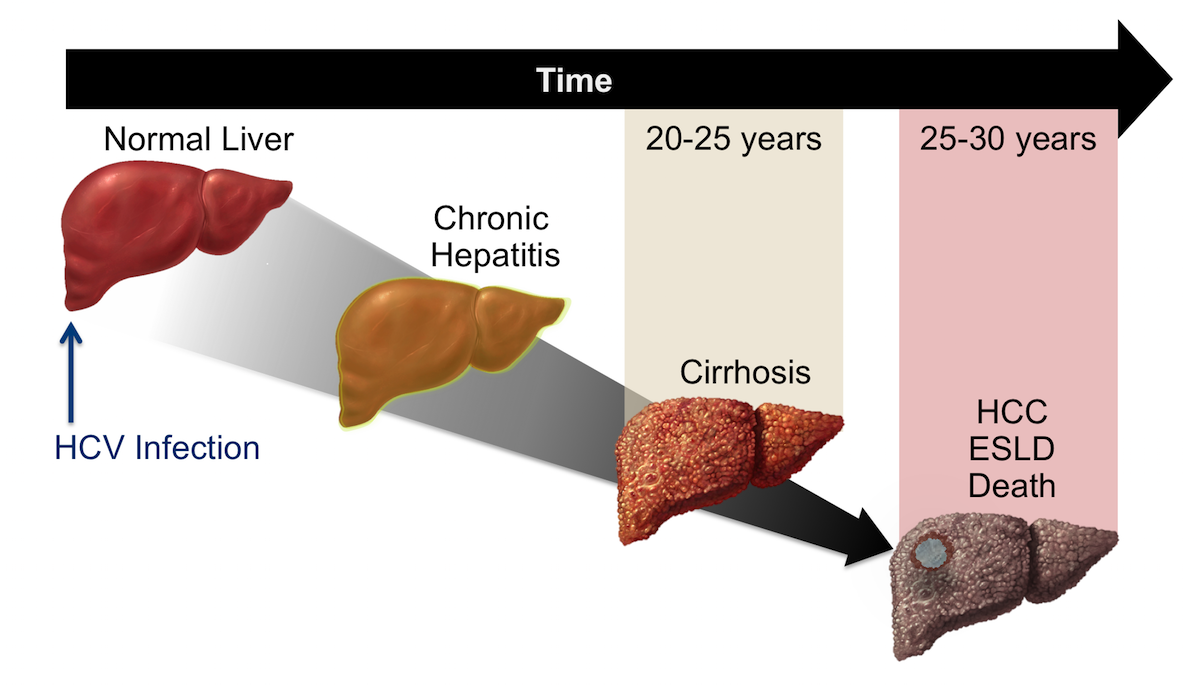
Cirrhosis can take 20 or more years to establish. During that time, the healthy cells in your liver are slowly changed with scar tissue.
While these scars grow, your liver aims to recover itself by producing brand-new cells. However this procedure has a disadvantage. It can raise your odds of getting liver cancer. The more cells your liver develops, the higher the chances that a change, or anomaly, will occur. And thats what causes cancerous tumors.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Can You Get It From Intercourse
Chronic Hepatitis Cirrhosis Adenoma Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocyte necrosis and mitosis of chronic hepatitis favor nodular regeneration, which in appropriate circumstances, is followed by hepatocyte dysplasia and carcinoma.
In many parts of the world HCC is among the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, and the third most common cause of cancer death in the world. Japan, for example, unlike other Asian countries, also has a high proportion of HCC caused by HCV infection accounting for 80 to 90% of all cases, while in the western world hepatocellular carcinoma is known to complicate cirrhosis secondary to hepatitis C in 2-6% per year.
There is currently no evidence that HCV by itself is oncogenic however, HCC may rarely develop in non-cirrhotic HCV-infected individuals, so a direct oncogenic effect cannot be excluded. However, in the pathogenesis of HCC associated with HCV, it remains controversial whether the virus plays a direct or indirect role. Recent studies using transgenic mouse models, in which the core protein of HCV has an oncogenic potential, indicate that HCV is directly involved in hepatocarcinogenesis, albeit other factors such as continued cell death and regeneration associated with inflammation would also play a role.
Almost all HCC occurs in the liver of patients with chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis, caused by HBV and HCV. Consequently, eradication of these hepatitis viruses with anti-viral agents and chemoprevention methods may decrease the risk of HCC.
What Increases A Persons Risk Of Getting Liver Cancer
Other factors besides hepatitis C and cirrhosis can also increase a persons chance of getting liver cancer. These include conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes, as well as behaviors like using alcohol and tobacco.5
Gender and race/ethnicity are also risk factors for liver cancer. Liver cancer occurs more often in men and in racial/ethnic minorities. In 2017, men had 3 times as many cases of liver cancer than women. Hispanic people had more new cases of liver cancer than any other race in 2017.2,5
Age can also play a role when it comes to liver cancer and hepatitis C. In 2017, people between the ages of 60 and 69 had more new cases of liver cancer than any other age group. This age group is also more likely to have had hepatitis C for a greater length of time than younger age groups.2
Read Also: What Is The New Drug For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Linked To Increased Risk Of Liver Cancer Other Cancers
Researchers have long known that patients with hepatitis C are at increased risk of liver cancer. But a new study recently presented at the European Association for the Study of the Livers 50th International Liver Congress in Vienna, Austria, finds hepatitis C may also raise the risk of developing other cancers.
Hepatitis C is a condition characterized by inflammation of the liver, resulting from infection with the hepatitis C virus . It is estimated that in the US, around 3.2 million people have chronic HCV, although 70-80% of these are unaware they are infected as the condition may not present any symptoms.
Hepatitis C is primarily spread through contact with the blood of an infected person. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , most people become infected with HCV by sharing needles or other drug-injecting equipment.
Though less common, HCV can also be spread through having sexual contact with an infected person, sharing personal care items such as toothbrushes and razors that may have come into contact with the blood of an infected individual, or being born to a mother with hepatitis C.
It is well established that infection with HCV can increase a persons risk of liver cancer. The CDC state that 1-5 in every 100 people with HCV die from liver cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Functions Of The Liver
The liver is considered the largest internal organ. It has the ability to execute a wide variety of jobs and functions, such as changing food into energy and cleaning out poisons and alcohol from the blood.
- The liver is also responsible for making bile, which is a yellowish-green liquid that helps with digestion.
- The liver produces blood clotting factors and proteins that your body needs.
- The liver regulates glucose or sugar in your blood and stores additional sugar.
- The liver works with your intestines and stomach to easily and quickly digest food.
- The liver stores minerals and vitamins.
- The liver removes toxic or poisonous substances from your blood.
Don’t Miss: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C Sexually
Treatment For Liver Cancer
There have been many reports of effective drug therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma , but so far most have only been tested in small samples of patients. At present, no drug or combination drugs have resulted in an effective cure.
Currently treatments such as chemoembolisation, injecting alcohol into the tumour or radiofrequency ablation may be helpful as palliative treatments. Palliative treatments are those that provide relief or remission from the cancer but are not cures.
Curative Treatments
Surgical removal of the tumour
Liver resection aims to remove the tumour and the surrounding liver tissue without leaving any tumour behind. As this option is usually limited to those people with excellent liver function, ideally without cirrhosis, there are very few people eligible for it. This is usually because the remaining portion of the liver is incapable of providing the necessary support for life. For patients whose tumours are successfully removed the five year survival rate is between 21% and 57% .
Liver transplants
For people who have cirrhosis and HCC, an early liver transplant may be effective. If a transplant is available it is probably the best option. This is particularly true for people with tumours less than 5cm in size who also show signs of liver failure.
A transplant may be suggested if: a single liver tumour is less than 5cm across up to three tumours are all less than 3cm across a single tumour 5-7cm in size has not grown for at least six months.
Hepatitis C Virus Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress And Oxidative Stress
Hepatitis C virus and other flaviviruses have been shown to induce ER stress . Endoplasmic reticulum stress is a homeostatic mechanism that regulates cellular metabolism and protein synthesis in response to perturbations in protein folding and biosynthesis . Mild ER stress modulates protein synthesis initiation and causes a reduction in cell growth, whereas extreme or prolonged ER stress leads to apoptosis mediated by the activation of the ER-associated caspase 12 . Although the long-term consequences of low-level ER stress signaling in the pathogenesis of HCV infection are not well understood, it has been hypothesized that persistent ER stress induction results in intra- and extracellular accumulation of DNA-damaging factors that could predispose a cell to mutagenesis. Indeed, ER stress signaling is intimately linked to changes in the intracellular redox state. Markers of acute intracellular oxidative stress are elevated in patients with chronic HCV and they accumulate the DNA adduct 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine . Transgenic mice expressing HCV core protein show an increased accumulation of ROS that correlates with HCC development . Transient expression of HCV NS5A alters intracellular calcium levels, induces oxidative stress and activates STAT-3 and NF-B . Oxidative stress activates intracellular signaling pathways, including the MAPKs that can have profound effects on cell growth regulation and may also promote transformation.
You May Like: How To Cure Hepatic Encephalopathy
Who Is At Risk For Liver Cancer After Hepatitis C Treatment
Hepatocellular carcinoma can still occur after hepatitis C is cured, and risk factors differ for people with and without cirrhosis.
Some people with liver cirrhosis remain at risk for developing liver cancer even after hepatitis C treatment, according to study results presented at the AASLD Liver Meeting. Unsuccessful treatment that did not lead to a cure is the biggest risk factor. A related study found that among people who were cured, risk factors differ for people with and without cirrhosis.
Over years or decades, chronic hepatitis C virus infection can lead to the development of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma , the most common type of liver cancer. People who are successfully treated for hepatitis C are less likely to develop HCC, but some risk remains, especially for those who have already progressed to advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis. Liver cancer is often diagnosed late, when it is more difficult to treat, and being able to predict who is at risk could enable targeted surveillance and prompt treatment.
Liver Cancer and Cirrhosis
In the first study, Loreta Kondili, MD, PhD, of Istituto Superiore Di Sanità in Rome, and colleagues evaluated the medium- to long-term impact of direct-acting antiviral treatment on the development of liver cancer in hepatitis C patients with cirrhosis.
Liver Cancer After SVR
The researchers found that liver cancer risk factors differed according to cirrhosis status.
Uncovering The Myths And Facts About Hepatitis C And Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C is a serious disease that can cause severe damage to the liver and trigger cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancer. Yet most people who have hepatitis C dont know they are infected.
Its a silent disease, said Minhhuyen T. Nguyen, MD, AGAF, a hepatologist and Director of Clinical Gastroenterology at Fox Chase Cancer Center. The virus slips past the surveillance of our immune defenses. You might not know you have it for 20 or 30 years.
Hepatitis C affects an estimated 3.9 million people in the U.S., and infection with this virus is an all too common yet preventable cause of liver cancer.
Here, Nguyen offered some need-to-know facts about hepatitis C and dispelled some common myths.
You May Like: New Medicine For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis And Liver Cancer
Institute of Medicine Committee on the Prevention and Control of Viral Hepatitis Infection Editors: Heather M. Colvin and Abigail E. Mitchell.
The global epidemic of hepatitis B and C is a serious public health problem. Hepatitis B and C are the major causes of chronic liver disease and liver cancer in the world. In the next 10 years, 150,000 people in the United States will die from liver disease or liver cancer associated with chronic hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus infections. Today, between 800,000 and 1.4 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis B and between 2.7 and 3.9 million have chronic hepatitis C. People most at risk for hepatitis B and C often are the least likely to have access to medical services. Reducing the rates of illness and death associated with these diseases will require greater awareness and knowledge among health care workers, improved identification of at-risk people, and improved access to medical care.
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable disease. Although federal public health officials recommend that all newborns, children, and at-risk adults receive the vaccine, about 46,000 new acute cases of the HBV infection emerge each year, including 1,000 in infants who acquire the infection during birth from their HBV-positive mothers. Unfortunately, there is no vaccine for hepatitis C, which is transmitted by direct exposure to infectious blood.
Cirrhosis And Liver Cancer
When people have cirrhosis of the liver, theyre more likely to develop a type of liver cancer called hepatocellular carcinoma. Researchers dont fully understand the link between the two conditions, but one explanation is that the buildup of scar tissue and ongoing inflammation creates an environment where cancerous tumors are more likely to grow. Regardless of exactly why scarring of the liver is linked to cancer, anyone with cirrhosis should be screened regularly for liver cancer, says Dr. Jacobson.
Read Also: Difference Between Hepatitis A And B
Local Impact Of Hepatitis C And Chronic Liver Disease
Hepatitis C is one of the most common liverdiseases in the U.S. and the Western world. An estimated 2.4 million peoplelive with the disease, and approximately 70% to 85% of cases are consideredchronic. The World Health Organization estimates that nearly 400,000 patientsdied from hepatitis C in 2016, mostly due to cirrhosis and HCC.
Texas has a high volume of aging patientswho are living with hepatitis C. Many were infected in the 1980s or 1990s, andthe infection can lie dormant for 25 years or longer before it begins to damagethe liver. Texas is home to many people of Hispanicdescent. Individuals with this ethnicity are at up to double the risk of developing infection-related cancers, such as livercancer. Other factors for the high rates ofliver cancer in Texas include a prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and a highrate of alcohol use.
‘At UT Southwestern, we are well equipped to treat the potential complications of Hepatitis C including cirrhosis or liver cancer. We have a multidisciplinary liver cancer program that offers cutting edge treatment options and compassionate care as well as a large and robust liver transplantation program.’
Amit G. Singal, M.D.
Hepatitis C And Cancer: What To Know
Hepatitis C is one of the leading causes of liver cancer. Its also linked to non-Hodgkins lymphoma, cancer in the bile ducts, and possibly pancreatic and head and neck cancers. And if you already have any other type of cancer, it can cause additional complications. Thats why MD Anderson tests all new patients for hepatitis C.
The good news is that if its found early and treated, hepatitis C can be cured, reducing your risk for cancer and other complications. Thats why hepatitis C screening and treatment is so important.
Unfortunately, an estimated 3.2 million people in the U.S. living with a chronic hepatitis C infection and dont know theyre infected. In many cases, thats because chronic hepatitis C doesnt any symptoms until the liver shows signs of damage.
We talked to Harrys Torres, M.D., associate professor of Infection Diseases and founding director of the hepatitis C clinic at MD Anderson, about what you should know about hepatitis C. Heres what he had to say.
Whats the link between hepatitis C and cancer?
There are two types of hepatitis C:
- acute or short-term hepatitis C, which goes away on its own in less than six months
- chronic hepatitis C, which requires treatment
The reason chronic hepatitis C causes multiple types of cancer is complex and not fully understood. The good news is that in most cases, hepatitis C infection can be cured with medication, and treatment can prevent many associated cancers.
Who is at risk for hepatitis C?
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Totally