Pathogenesis Of Fibrosis With Chronic Hcv Infection
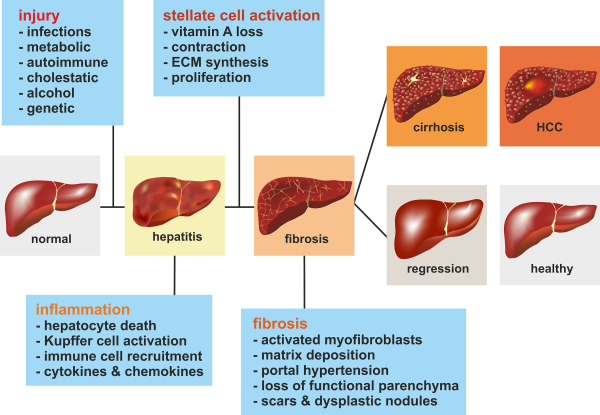
Hepatic fibrosis is a dynamic scarring process in which chronic inflammation stimulates production and accumulation of collagen and extracellular matrix proteins. The hepatic stellate cells are the primary cells responsible for producing these extracellular matrix proteins. Over time, with chronic hepatitis C virus infection, the total extracellular matrix protein content increases and fibrosis can develop, with potential progression to cirrhosis. This dynamic process can also involve remodeling and regression of the fibrous tissue via breakdown of the matrix proteins by the protease enzymes matrix metalloproteinases . Balance of the remodeling process occurs with inhibition of the remodeling by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases .
Direct Markers Of Fibrosis
Direct markers of fibrosis include procollagen type , matrix metalloproteinases, cytokines, and chemokines. The direct markers have shown variable effectiveness in predicting liver fibrosis. Among these markers, those currently used involve matrix metalloproteinases. Liver fibrosis/cirrhosis is characterized by enhanced extracellular matrix synthesis by activated stellate cells. Matrix metalloproteinases are endopeptidases that can degrade collagen and are involved in the tissue remodeling process that takes place with fibrosis. Levels of matrix metalloproteinases are regulated by specific tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase and a mismatch between these inhibitors is associated with extracellular matrix deposition and breakdown. Levels of TIMP-1 significantly correlate with fibrosis, with a sensitivity of 100% in diagnosing cirrhosis, but these tests have low specificity. Hyaluronic acid is a glycosaminoglycan secreted by hepatic stellate cells and is one of the chief components of the extracellular matrix. Extensive fibrosis/cirrhosis has been found to be associated with increased serum levels of hyaluronic acid.
Factors To Consider Prior To Choosing Retreatment Regimen
For retreatment of adults with HCV genotype 3 infection, several factors influence the regimen choice, including the prior regimen used when treatment failure occurred, the presence or absence of cirrhosis, and cost or insurance considerations. It is also worth noting that the clinical data for treatment-experienced individuals with HCV genotype 3 is more limited for the newest DAAs, such as glecaprevir-pibrentasvir, since these individuals have been encountered less frequently in recent years due to the efficacy of earlier DAA regimens. Therefore, the optimal duration of therapy for retreatment of persons with HCV genotype 3 with glecaprevir-pibrentasvir is not well established. The retreatment of individuals with HCV genotype 3 who have decompensated cirrhosis, renal impairment, acute HCV, or post-liver transplantation is not addressed in this lesson.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis B Be Cured Totally
Do All Patients With Liver Disease Need To Have Fibrosis Testing
Fibrosis testing is relevant for the clinical care of patients with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B, hepatitis C , non-alcoholic fatty liver disease , co-infections, primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and other chronic metabolic diseases of the liver.
- Knowing the severity of fibrosis can help with prognosis and understanding the degree of liver damage.
- More rapid development of fibrosis and more advanced stages of fibrosis are more predictive of cirrhosis, and therefore liver-related illnesses and mortality.
- The severity of liver disease is a factor in determining the urgency for HCV treatment and HBV treatment.
- Understanding the fibrosis stage impacts clinical care decisions. Patients with advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis need more frequent follow up visits and labs, avoidance of some medications, and surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma and gastroesophageal varices.
What Fibrosis Score Results Mean
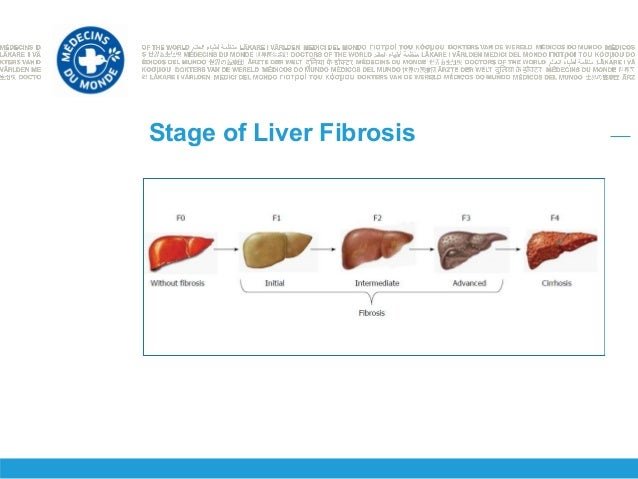
After you have one or more tests, your doctor may tell you how much fibrosis is in your liver by telling you a âstage.â The higher the number, the more fibrosis you have. A fibrosis stage of 2 or higher means thereâs a lot of fibrosis in your liver. If your fibrosis stage is 3 or 4, your fibrosis is advanced. You have cirrhosis if your fibrosis stage is 4.
Your doctor can also use results from your FibroScan test alone or combined with other tests to figure out your fibrosis score. FibroScan fibrosis scores cover five possible stages of liver damage, from none or mild all the way to severe cirrhosis. They are broken down into these groups:
F0 to F1: No scarring in your liver, or just a little.
F2: Some scarring, between a little and a lot.
F3: A lot of scarring.
F4: Cirrhosis.
FibroScan scores are estimates, meaning the measurements are not exact. Other health problems or things you do can make your score less accurate. These include tumors in your liver, heart failure, obesity, or drinking alcohol.
Once your doctor gets your fibrosis test results, they may decide to do more tests to be sure of your diagnosis. Some fibrosis measurements also combine blood test results with a special calculator tool to figure out your risk for fibrosis. These tests are called APRI and FIB-4. But these tests can only tell if you might have fibrosis, not what stage it is.
You May Like: Pro Plan Hepatic Dog Food
What Is Liver Fibrosis
Your liver is one of the biggest internal organs. It has many jobs, including aiding digestion, storing energy, making blood clotting components, and removing waste and microorganisms. The liver is also able to regenerate, or regrow, itself to repair damage.
Normally, the liver can make new cells when something harms it. The new cells replace the old ones that have died. However, this does not work the way it should with a diseased liver or if liver injury is continuous or severe.
Instead, the attempts at repair cause scarring in place of functioning liver cells. Scars are fibrous tissue, hence the name fibrosis. Another name for liver fibrosis is hepatic fibrosis.
In the United States, the most common conditions that result in liver fibrosis are alcohol-related , chronic hepatitis, and nonalcoholic . Having these conditions puts you at risk of developing liver fibrosis.
Blood tests and imaging exams can help find signs of liver fibrosis. When found early, it is possible to cure or reverse liver fibrosis. If liver fibrosis remains undetected and the damage continues, it can progress to cirrhosis.
The difference between liver fibrosis and cirrhosis is that cirrhosis is permanent, irreversible scarring. The liver becomes smaller and mostly consists of hard scar tissue. Once cirrhosis develops, symptoms and problems can appear.
What Are The Stages Of Liver Fibrosis
There are several different scales of liver fibrosis staging, where a doctor determines the degree of liver damage. Since staging can be subjective, each scale has its own limitations. One doctor may think a liver is slightly more scarred than another. However, doctors will usually assign a stage to liver fibrosis because it helps the patient and other doctors understand the degree to which a persons liver is affected.
One of the more popular scoring systems is the METAVIR scoring system. This system assigns a score for activity or the prediction of how fibrosis is progressing, and for the fibrosis level itself. Doctors can usually assign this score only after taking a biopsy or tissue sample of a piece of the liver. The activity grades range from A0 to A3:
- A0: no activity
- F4: cirrhosis
Therefore, a person with the most severe disease form would have an A3, F4 METAVIR score.
Another scoring system is Batts and Ludwig, which grades fibrosis on a scale of grade 1 to grade 4, with grade 4 being the most severe. The International Association of the Study of the Liver also has a scoring system with four categories that range from minimal chronic hepatitis to severe chronic hepatitis.
Doctors dont often diagnose liver fibrosis in its mild to moderate stages. This is because liver fibrosis doesnt usually cause symptoms until more of the liver is damaged.
When a person does progress in their liver disease, they may experience symptoms that include:
- appetite loss
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C And Is It Contagious
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
The only proven treatment for NAFLD is lifestyle modification, including control of the components of metabolic syndrome. Thus, therapy is directed at controlling risk factors such as insulin resistance, decreasing delivery of fatty acids to the liver, and the use of hepatoprotective medications.91 Weight loss improves histologic features of NAFLD, particularly nonalcoholic fatty steatohepatitis . The highest rate of their reduction is seen in those who lose > 10% of bodyweight, with 90% resolution of NASH and 45% regression of fibrosis.92 In a recent study, a text messaging approach encouraging a healthy lifestyle improved weight loss and hepatic function tests in patients with NAFLD.92,93 In another study, some patients with only 3.04.9% weight loss achieved remission of NAFLD at 12 months.94 Previously, NASH was thought to increase the risk of adverse outcomes, but, in a randomised retrospective study of 646 biopsy-proven patients with NAFLD, the stage of fibrosis rather than NASH was determined to predict adverse related events.95 Furthermore, it is suggested that fibrosis stage should be part of predicting all-cause mortality secondary to cardiovascular disease and development of chronic kidney disease.96,97
Disease Progression In Chronic Hepatitis C: Modifiable And Nonmodifiable Factors
- E. Jenny HeathcoteCorrespondenceAddress requests for reprints to: E. Jenny Heathcote, MD, FRCPC, Fell Wing, 6B-154, University Health Network, The Toronto Western Hospital, 399 Bathurst Street, Toronto, Ontario, M5T 2S8 Canada. fax: 603-6281.
Abbreviations used in this paper:
J Viral Hepat.Clin Liver Dis.A Spanish multicentre experience, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
- Delarocque-Astagneau E.
- et al.
J Hepatol.
- Heathcote J.
- et al.
Med Decis Making.Hepatology.Lancet.
- Stravitz R.T.
- et al.
Liver Transpl.
| Nonmodifiable factors | |
|---|---|
|
|
Don’t Miss: What To Do If You Have Hepatitis C
Secondary Analysis: Assessment Of Who Is Left To Be Treated
Based on the eligibility criteria above, we summarized the proportion of participants who initiated treatment and those who remained eligible for treatment, by calendar year, significant fibrosis, and active injection drug use. We then performed a cross-sectional analysis, using a modified Poisson regression model with robust standard errors to assess the predictors of remaining HCV RNA positive at each participants final visit. Predictors included: socio-demographic factors, including age, indigenous ethnicity, women or MSM , income, homelessness, incarceration , and province of residence behavioral factors, including active injection drug and alcohol use clinical factors, including an undetectable HIV RNA level, significant liver fibrosis, HCV genotype, and psychiatric diagnosis and disengagement in care, via being lost to follow-up, which was defined as not having a cohort visit within 18 months of our administrative censoring date .
All analyses were performed using Stata 15/IC .
Approaches To Liver Biopsy
There are three ways to obtain a liver biopsy: percutaneous , transjugular or transfemoral, and laparoscopic. The percutaneous route is the most commonly performed biopsy method in most settings. Specimens are obtained either with a core aspiration needle or sheathed cutting needle that is at least 16-gauge in caliber. The optimum size of a specimen that offers the least risk of understaging fibrosis is 3 cm in length after formalin fixation, and the sample should include at least 11 portal tracts. The number of portal tracts is relative to biopsy size, and, generally, samples greater than 2 cm in length are acceptable. In most circumstances, liver biopsy can be done with minimal side effects, but pain and bleeding can occur.
Also Check: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Evaluation Of Fibrosis Progression Rate
The 378 patients contributed 558 pairs of consecutive biopsies. Fibrosis progression by 1 stage was detected in 203 consecutive biopsies and progression by 2 or 3 stages was observed in 47 consecutive biopsies . We used a multistate Markov model to estimate the progression rates between different fibrosis stages, after accounting for possible misclassification in the assessment of liver fibrosis, based on the observed transition frequencies . The estimated progression rate from stage 0 to stage 1 was the highest, and it was 3.08 times higher than the progression rate from stage 1 to stage 2. The progression rate from stage 2 to stage 3 was the lowest. The estimated sojourn time was the shortest for fibrosis stage 0 and the longest for fibrosis stage 2 . This explains the lower estimated probability for transition from stage 0 to stage 1 after 10 years . Additionally, we conducted a subgroup analysis on the patients who underwent > 2 biopsies. The estimated fibrosis progression rates were 0.34 between stages 0 and 1, 0.09 between stages 1 and 2, 0.07 between stages 2 and 3, and 0.10 between stages 3 and 4 and are consistent with the data obtained on the overall data set.
Probability of remaining at the same fibrosis stage 2, 5, and 10 years after the initial fibrosis assessment.
Can Fibrosis Scores Improve After Successful Hcv Treatment
Fibrosis regression has been demonstrated in certain individuals after HBV treatment, HCV treatment, treatment of iron overload, autoimmune hepatitis, and cessation of alcohol. Elimination of the damaging element often improves inflammation and allows for remodeling of the fibrosis. Our understanding of fibrosis regression is evolving and emerging data is encouraging. Importantly, cirrhosis elevates a patient’s risk for liver cancer, even after improvement in labs, imaging, or evidence of portal hypertension.
Don’t Miss: How Does One Contract Hepatitis B
Fibrosis Progression Over The Total Study Period
Our data comprised findings from 936 liver biopsies, with a range of 2 to 5 biopsies per person: 240 patients underwent 2 biopsies, 98 underwent 3 biopsies, 38 underwent 4 biopsies, and 2 underwent 5 biopsies . Thus, we had 558 consecutive biopsy pairs that were used to analyze stage-specific fibrosis progression as described below. The mean duration between the first and the last biopsy was 6.5 ± 3.1 years, while the mean duration between paired biopsies was 4.4 ± 1.9 years.
During the total follow-up period, defined as the interval between the first and the last biopsy, 217 patients progressed by at least 1 fibrosis stage, 61 had more-severe fibrosis progression of at least 2 fibrosis stages, and 40 developed stage 4 fibrosis . A total of 22 patients progressed to cirrhosis during the total study period.
Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Historically, HCV infection was treated with interferon and ribavirin. Interferon-derived therapy resulted in a 50% regression in cirrhosis in the 30% who achieved a sustained virologic response . However, in those with advanced cirrhosis, only 5% saw regression of their liver disease over a 10 year period.62 Lower baseline stage of fibrosis, sustained viral response, age < 40 years, BMI < 27, and viral load < 3.5 million copies per mL were independently associated with regression of fibrosis after treatment.82
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
Factors Associated With Progression To Cirrhosis
Twenty-two patients progressed to cirrhosis over the total follow-up period. The mean duration from biopsy 1 to development of cirrhosis was 7.6 ± 3.6 years. From multivariable logistic regression modeling, progression to cirrhosis was associated with genotype 3 and with area under the ALT level curve . A trend for association was found with higher stage of fibrosis at the first biopsy and lower baseline platelet levels .
Learning Objective Performance Indicators
- Explain the indications, risks, and histologic assessment for liver biopsy in persons with chronic HCV infection
- Discuss noninvasive Indirect and direct tests of liver fibrosis and examine the potential clinical utility of these tests
- Summarize key radiologic methods that can estimate hepatic fibrosis
Paula P. Cox-North, PhD, MN, ARNPDisclosuresReviewer:Disclosures
Read Also: What Kind Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis B
Indications For Liver Biopsy
Prior to the development of widely used noninvasive tests that estimate hepatic fibrosis, such as aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index , FibroSure, FibroTest, and transient elastography , liver biopsy was used to estimate liver fibrosis. Traditionally, the primary reasons for doing a liver biopsy have been to provide information on fibrosis stage which can help guide therapeutic HCV management decisions, diagnose coexisting liver diseases, and help identify cirrhosis that would necessitate routine cancer surveillance. In the current era, liver biopsy is used less frequently. The following outlines certain circumstances that may warrant consideration of liver biopsy when evaluating a person with chronic HCV.
- Two indirect markers show discordant results. For example, when an APRI score is in the 0.5 to 1.5 range and the FibroSure/FibroTest is less than 0.48, then a liver biopsy is warranted to determine the presence or absence of advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis and the need for routine hepatocellular cancer surveillance and follow-up.
- There is a second cause of liver disease is suspected.
- Indirect, direct, and transient elastography tests are unavailable, or not advisable for specific reasons.
How To Prevent Cirrhosis
The best way to prevent alcohol-related cirrhosis is to drink within the recommended limits.
The guidelines recommend:
- men and women should not regularly drink more than 14 units of alcohol a week
- you should spread your drinking over 3 days, or more, if you drink as much as 14 units a week
Stop drinking alcohol immediately if you have alcohol-related cirrhosis. Drinking alcohol speeds up the rate at which cirrhosis progresses, regardless of the cause.
A GP can offer help and advice if you’re finding it difficult to cut down the amount you drink.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis B
What Are The Risk Factors For Liver Fibrosis
A number of factors increase the risk of developing liver fibrosis, including:
- having certain hereditary conditions, such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, , and Wilson disease
- having certain medical conditions, including chronic hepatitis C and
- having obesity with fat distribution mainly in the abdomen
- drinking alcohol in excess
- taking certain drugs, such as amiodarone, corticosteroids, isoniazid, methotrexate, and methyldopa
You may be able to lower your risk of liver fibrosis by:
- controlling blood sugar levels and blood pressure
- limiting or stopping alcohol consumption and getting help for alcohol use disorder
- losing weight, which is the most effective treatment for NAFLD
- maintaining a moderate body weight through a healthy diet and exercise
Seeing your doctor regularly will help identify liver fibrosis in the early stages. In general, the earlier you find potential liver problems, the more likely it will be that you can reverse any damage.