What Happens During The Chronic Phase
After six months, most people with hepatitis C go into the chronic phase of the disease. This means their body hasnt been able to fight off the virus and they have developed a long-term infection.
Most people still dont have any symptoms during the chronic phase. Often, people arent diagnosed until they get screened or until their doctor detects high levels of liver enzymes during a routine blood test.
Chronic Phase Of Hepatitis C
When infection with hepatitis C lasts for longer than six months, it is known as chronic hepatitis C infection. The course of the chronic infection varies considerably between people and it is very unpredictable. Of those people who develop chronic infection:
- Some people have mild or no symptoms. However, even if you have no symptoms, you can still pass on HCV to others who may develop problems.
- Some people develop some symptoms due to persistent inflammation of the liver. For example, feeling sick, lack of appetite, intolerance of alcohol, pains over the liver, jaundice and depression. The most common symptoms of chronic hepatitis C are extreme tiredness, poor concentration and memory problems, and muscle and joint aches. There is actually no relationship between the severity of symptoms and the degree of liver damage. This means that some people can have liver inflammation without having any symptoms.
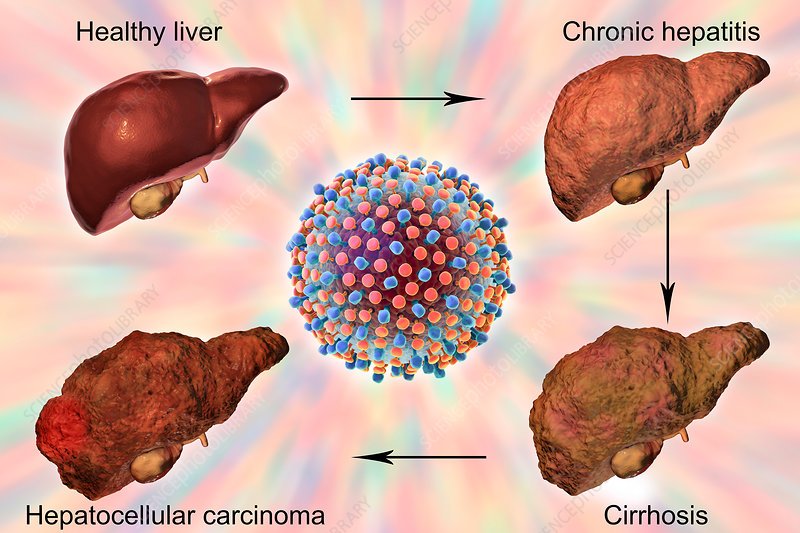
- About one third of people with chronic hepatitis C infection develop cirrhosis over a period of about 20-30 years. Cirrhosis is like a ‘scarring’ of the liver, which can cause serious problems and ‘liver failure’ when it is severe. See the separate leaflet called Cirrhosis. Some people with chronic hepatitis C have no symptoms for many years until they develop cirrhosis. Only when the liver starts to fail with cirrhosis do symptoms appear.
- A small number of people who develop cirrhosis go on to develop liver cancer.
Laboratory Measurements And Other Variables
The following data were extracted from the patients’ electronic medical record: age at time of the first biopsy, sex, race/ethnicity, diagnoses , inflammatory grade and steatosis for each liver biopsy specimen, HCV treatment information , HCV RNA levels, ALT levels, aspartate aminotransferase levels, platelet count, and alkaline phosphatase measurements. We extracted levels of HCV RNA, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and platelets that were measured within 1 year preceding the first liver biopsy, as well as all measurements obtained between biopsies.
Don’t Miss: The Vaccine For Hepatitis B
The Stages Of Liver Disease
There are four main stages of liver disease in hepatitis C infected patients. Staging is determined by liver biopsy or other non-invasive tests such as fibrosure or fibroscan.
Once a person is diagnosed with cirrhosis, monitoring for hepatocellular carcinoma should be done every six months. A blood test called alfa feto protein and imaging with ultrasound and/or MRI, are the tools used. Approximately 20% of cirrhotic patients will eventually develop HCC. The risk falls to about 5% in patients who have successfully treated the virus and have a sustained viral response, better known as a cure.
It is important to determine if a person with cirrhosis has compensated or decompensated disease. In compensated cirrhosis, a persons liver is working well enough to do its many functions and there are often no overt symptoms. When a person starts to decompensate, his prognosis is significantly worsened. Patients with decompensated cirrhosis have complications which may include jaundice, ascites, variceal hemorrhage, and encephalopathy. People with decompensated cirrhosis need to be followed by a hepatologist and evaluated for liver transplant.
The Child-Pugh Score is used along with the MELD score help the physician assess the prognosis of cirrhosis. I will discuss these scoring systems at a later time.1,2,3,4
Peroxisome Proliferator Associated Receptor
Another contributor to HCV-3 steatogenesis is inhibition of the PPAR- pathway involved in metabolic regulation. PPAR- is a transcription factor that induces hepatic fatty acid oxidation and ketogenesis while also up-regulating hepatic glucose production, the primary adaptive response to fasting. PPAR- is the pharmacologic target for the fibrate class of cholesterol lowering medications such as gemfibrozil and fenofibrate which function as PPAR- agonists. Other PPAR agonists are also under current evaluation for cardiometabolic disease and NAFLD . Conversely, inhibition of PPAR- results in decreased triglyceride breakdown and accumulation of intrahepatic fatty acids. HCV-3a core protein has been demonstrated to function as an inhibitor of PPAR- activity in vitro . De Gottardi et al compared the expression of PPAR- in HCV-1b versus HCV-3a infection using liver biopsies of infected patients and in vitro models. This study noted that levels of PPAR- mRNA were significantly decreased in HCV-3a compared to HCV-1b, independent of the extent of liver steatosis. However, inhibition of PPAR- does not appear to be limited to HCV-3. Initial associations of PPAR- inhibition were noted with HCV-1b core protein, although the effect appears less potent compared to that observed with HCV-3a.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Food
Factors Associated With Fibrosis Progression
We first investigated the effect of factors associated with fibrosis progression over the total follow-up period . Based on univariable logistic regression analysis, progression by at least 1 fibrosis stage was significantly associated with mild inflammation and mild fibrosis in the initial biopsy specimen . Additional significant factors on univariable analysis included a longer duration of follow-up , the presence of multiple flares in the ALT level during the entire study period, and HCV treatment during follow-up . On multivariable analysis, fibrosis progression was significantly associated with mild fibrosis at the first biopsy and the presence of at least 1 flare in the ALT level during the follow-up period . In addition, Hispanic patients were more likely to progress than white patients . When we combined Hispanic patients with white patients, we did not see significant differences in fibrosis progression between races. HCV treatment between the biopsies was not significantly associated with fibrosis progression on multivariable analysis.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
You May Like: How Long Does Hepatitis C Take To Show Up
Approach To Choosing Hcv Genotype 3 Treatment Regimen
When considering treatment of persons with chronic HCV genotype 3, five major factors influence the choice and duration of therapy: cirrhosis status, prior treatment experience, coexistent renal disease, drug interactions, and medication cost and/or insurance considerations. With certain regimens for treatment-experienced and/or cirrhotic patients, pretreatment NS5A resistance may also influence both the choice of regimen and duration of therapy. The following treatment recommendations are based on the 2013 AASLD/AST Evaluation for Liver Transplantation Guidelines for initial treatment of adults with HCV genotype 3 and for retreatment of adults in whom prior therapy failed, including those with HCV genotype 3.
What Happens To Your Health When You Arent Treated For Hepatitis C
Although medication can cure hepatitis C, millions of people arent taking it. The problem: Left untreated, the virus can lead to serious health complications.
Theres a reason the hepatitis C virus is called the silent killer. All too often, people dont realize theyve been infected. Out of the estimated 2.4 million people in the United States who have hepatitis C, more than half dont know they have it, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Usually when someone gets infected with hepatitis C, they initially until the disease gets fairly advanced, says Hardeep Singh, MD, a gastroenterologist and hepatologist at St. Joseph Hospital in Orange, California. The median time it takes for symptoms…to develop is 30 years.”
While some people are able to clear the virus on their own, most arent, and more than 50 percent go on to develop long-term, or chronic, hepatitis C, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Over time, untreated hepatitis C can cause hardening and scarring of the liver, which can cause complications that eventually lead to liver failure.
Liver cirrhosis and liver failure usually cannot be reversed sometimes a liver transplant is the only treatment option once advanced liver damage occurs. With hepatitis C, your risk of liver cancer also rises.
Here are a few other conditions that can be caused by untreated hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Cause Cancer
How Can You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne disease. The main source of infection is from blood from an infected person.
- Most cases are caused by using contaminated needles or injecting equipment to inject drugs . Even a tiny amount of an infected person’s blood left on a needle is enough to cause spread to others.
- Some people who received blood transfusions or blood prior to 1991 were infected with hepatitis C from some donor blood. Since 1991 all blood and blood products donated in the UK are screened for HCV.
- There is also a risk of contracting hepatitis C from needlestick accidents, or other injuries involving blood spillage from infected people.
- There is a small risk of contracting the virus from sharing toothbrushes, razors and other such items which may be contaminated with infected blood.
- There is even a small risk from inhaling drugs like cocaine, as these can make the inside of your nose bleed. If that happens, tiny spots of blood can fall on to the note you are using and, if that is used by someone else, your blood can travel up their nose and into their bloodstream.
- There is also a small risk from re-used equipment used for tattooing, body piercing, acupuncture, etc.
- There is a small risk that an infected mother can pass on the infection to her baby.
- There is a small risk that an infected person can pass on the virus whilst having sex.
The virus is not passed on during normal social contact, such as holding hands, hugging, or sharing cups or crockery.
Hepatitis C With Decompensating Cirrhosis
Until recently, doctors considered a liver transplant to be the only effective treatment for decompensating cirrhosis.
However, a recent small-scale study found that a course of direct-acting antiviral medication may improve some peoples liver function enough to take them off the waiting list for a liver transplant. People with liver disease that was less severe had a higher likelihood of removal from the list.
However, recent Canadian guidelines warn that certain antiviral drugs may potentially be dangerous for people with severe decompensating cirrhosis. This is because the liver is less able to filter out toxic waste, meaning that the antiviral drugs could accumulate to toxic levels. Doctors must weigh up the benefits against the risks.
When a person is waiting for a liver transplant, a doctor will assess whether or not to pause antiviral treatment.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C: What Is It
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes inflammation that results in fibrosis, or scar tissue in the liver. This virus not only involves the liver, but it affects the patients entire body and may cause extra-hepatic manifestations such as kidney disease, issues with skin problems, cryoglobulinemia, vascular disease, insulin resistance and many other systemic health conditions.
When a person is exposed to the virus, his body will develop antibodies. Approximately 15-40% of patients have immune systems that fight off the disease in this acute stage without any treatment. The majority, however, progress to chronic hepatitis C which may last a lifetime unless treated. Once exposed, even when cured, the patient will have antibodies for life. Unfortunately these antibodies are not protective and if the person is exposed to the virus again, he may become infected all over again.
What Are The Symptoms And How Does Hepatitis C Progress

Many people with hepatitis C feel entirely well and have few or no symptoms. Any symptoms that may be present are often initially thought to be due to another illness. This may mean that hepatitis C may be diagnosed when you have had the virus for some time. Many people have hepatitis C without knowing it.
It is helpful to think of two phases of infection with HCV. An acute phase when you first become infected and a chronic phase in people where the virus remains long-term.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
When permanent scar tissue replaces healthy liver cells and your liver loses the ability to function, its called cirrhosis. In this condition, your liver can no longer heal itself. This can cause a variety of health concerns, including a buildup of fluid in your abdomen and bleeding from veins in the esophagus.
When the liver fails to filter toxins, they can build up in your bloodstream and impair brain function. Cirrhosis of the liver can sometimes develop into liver cancer. This risk is greater in people who drink excess alcohol. Treatment of cirrhosis depends on the progression of the condition.
Chronic hepatitis C can cause serious long-term health consequences. End-stage hepatitis C occurs when the liver is severely damaged and can no longer function properly.
Symptoms may include:
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Read Also: What Medicine Cures Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver infection that can lead to serious liver damage. Itâs caused by the hepatitis C virus. About 2.4 million people in the U.S. have the disease. But it causes few symptoms, so most of them don’t know. The virus spreads through an infected personâs blood or body fluids.
There are many forms of the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. The most common in the U.S. is type 1. None is more serious than any other, but they respond differently to treatment.
Fibrosis Progression In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection
M. Z. and R. B. D. contributed equally to this work.
Present affiliations: Clinical Directors Network, Inc., 5 West 37th Street, 10th Floor, New York, New York and Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, Maryland .
M. Z. and R. B. D. contributed equally to this work.
Present affiliations: Clinical Directors Network, Inc., 5 West 37th Street, 10th Floor, New York, New York and Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, Maryland .
The Journal of Infectious Diseases
Also Check: Immune To Hepatitis B Means
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
You May Like: How You Get Hepatitis A
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?