What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Identification Of The Hepatitis C Virus
HCV was first recognized in 1989 using recombinant technology to create peptides from an infectious serum that were then tested against serum from individuals with non-A, non-B hepatitis. This approach resulted in the isolation of a section of the HCV genome. Subsequently, the entire HCV genome was sequenced. HCV is a member of the family of flaviviridae. Flaviviruses are positive, single-stranded RNA viruses. The HCV genome encodes a gene for production of a single polypeptide chain of approximately 3000 amino acids. This polypeptide gives rise to a number of specific proteins. The Env proteins are among the most variable parts of the peptide chain and are associated with multiple molecular forms in a single infected person. The mutations affecting this portion of the HCV genome seem to be critical for escape of the virus from the host immune response. The HCV protein NS5a contains an interferon-response element. Evidence from several studies suggests that mutational variation in the HCV genome encoding this protein is associated with resistance to interferon, the main antiviral agent used in treatment of HCV. Other proteins encoded by the HCV genome include the NS3 region that codes for a protease and the NS5b region that codes for an RNA polymerase. Drugs that target the HCV protease or polymerase are now undergoing trials as therapeutic agents to treat HCV infection.
P.M. Mulrooney-Cousins, T.I. Michalak, in, 2017
What Does A Reactive Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you currently have hepatitis C and a follow-up test is needed.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis From Donating Plasma
All Adults Pregnant Women And People With Risk Factors Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Most people who get infected with hepatitis C virus develop a chronic, or lifelong, infection. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. People can live without symptoms or feeling sick, so testing is the only way to know if you have hepatitis C. Getting tested is important to find out if you are infected so you can get lifesaving treatment that can cure hepatitis C.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Hcv Infection
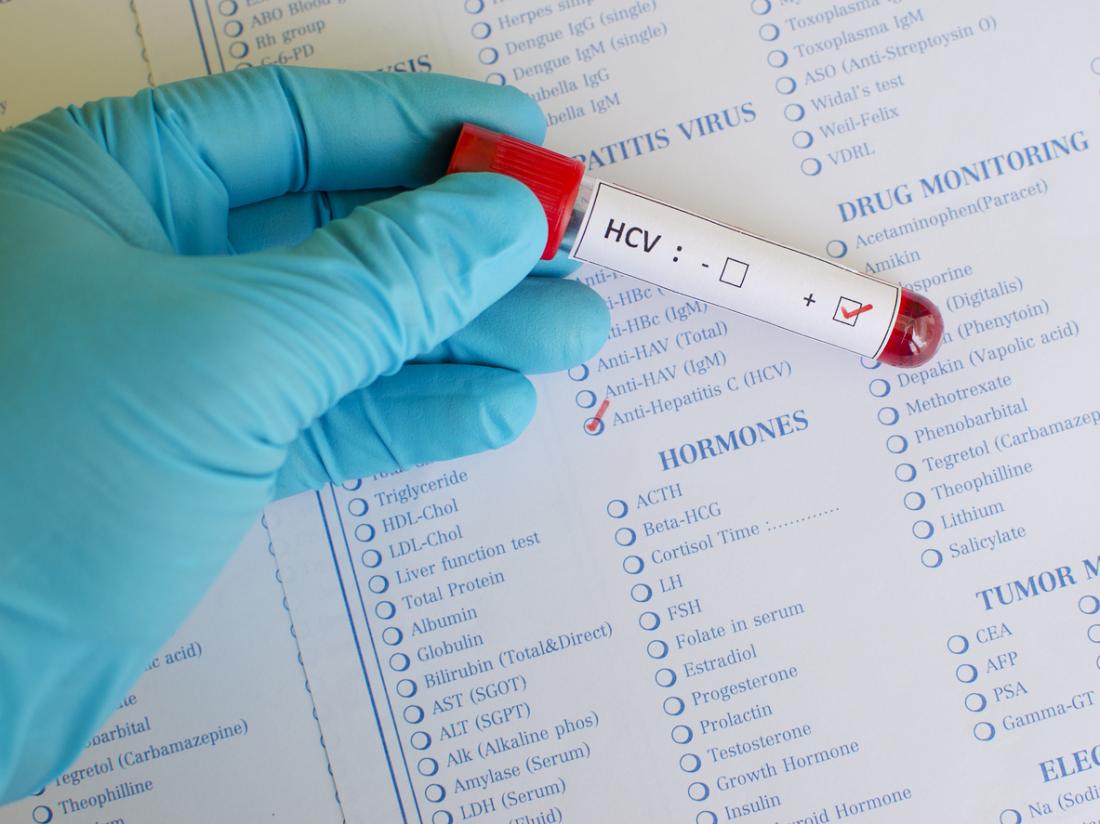
Hepatitis C is rarely diagnosed at the time of infection, since few individuals are symptomatic. Asymptomatic cases may be detected, however, through recommended screening in high-risk populations, such as intravenous drug users and recipients of blood transfusions or organ transplants in which the tissues were not initially tested for HCV. Diagnostic testing and screening for hepatitis C centres on the detection of circulating antibodies and RNA specific to HCV. HCV RNA is detectable within 1 to 3 weeks of infection, and the antibodies are usually detectable within 8 to 12 weeks.
Treatment of hepatitis C is focused on the elimination of viral infection, improvement of liver function, and the prevention of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Liver function may be improved with the use of interferon, which reduces HCV replication and stimulates the immune system to fight HCV infection. Interferon is often given in combination with ribavirin, an antiviral drug that mimics nucleosides and thereby interferes with viral reproduction. Ribavirin may also be used in combination with agents known as sofosbuvir and velpatasvir, which inhibit key molecules involved in HCV RNA replication. Treatment of end-stage or advanced liver disease and cirrhosis caused by HCV infection is also possible with liver transplantation, though recurrence of detectable HCV infection is almost universal after transplantation.
Recommended Reading: Anti Hepatitis B Virus Drugs
Genome Structure Of Hcv
The genome of HCV is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA with highly structured elements, which is about 9.6 kb in length . This genomic RNA contains one single open reading frame encoding a polyprotein which can be processed into 10 viral proteins after translation. The HCV genome was flanked by the 5 untranslated- and the 3 untranslated- regions at the 5- and 3 ends, respectively. Both UTRs are highly structured and crucial for the viral translation and proliferation and are well conserved among genotypes or strains of HCV.
FIGURE 1. Depicted secondary structures of 5- and 3 UTRs of HCV genome. The 5 UTR contains four structured domains . The translational start codon is indicated. Two types of conformations for the 3X region within the 3 UTR have been proposed.
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Read Also: How Do Catch Hepatitis B
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Hcv And Hcv Rna Detection Assays
HCV is a positive-strand RNA virus that belongs to the Hepacivirus genus of the family Flaviviridae. Its 9.6-kb-long genome encodes a polyprotein of almost 3000 amino acids flanked by two untranslated regions, that is, 3- and 5-UTR. HCV isolates are categorized into six genotypes with 3035% sequence variability with further variation within subtypes. HCV genotypes are essentially geographically distributed. Approximately 150 million people worldwide suffer from chronic HCV infection, and about 30% of those will develop cirrhosis and potentially HCC . There is no prophylaxic vaccine yet available, which is one of main reasons why HCV infection remains of a global concern.
Figure 6.2. Typical serological and molecular profiles of HCV infection. Acute HCV infection with recovery. After resolution of clinical evident acute hepatitis C, HCV RNA can remain detectable at very low levels for the prolonged period of time. Chronic HCV infection. Colored lines indicate relative levels of anti-HCV antibodies and HCV RNA detected in serum or plasma. The lowest sensitivity limits of HCV RNA detection based on standard clinical or research assays are indicated by dashed black lines.
Table 6.3. Assays for HCV RNA Detection and Quantification
| Assay |
|---|
Stuart C. Ray, David L. Thomas, in, 2015
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A What Is It
Hepatitis C Virus As A Causative Agent Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Log in to MyKarger to check if you already have access to this content.
Buy a Karger Article Bundle and profit from a discount!
If you would like to redeem your KAB credit, please log in.
Save over 20%
- Unlimited fulltext viewing Of this article
- Organize, annotate And mark up articles
- Printing And downloading restrictions apply
- Access to all articles of the subscribed year guaranteed for 5 years
- Unlimited re-access via Subscriber Login or MyKarger
- Unrestricted printing, no saving restrictions for personal use
The final prices may differ from the prices shown due to specifics of VAT rules.
Molecular Basis Of Encapsidation Of Hepatitis C Virus Genome
- 1Antiviral Immunity and Resistance Section, HIV Dynamics and Replication Program, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, Frederick, MD, United States
- 2Department of Virology and Parasitology, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, Hamamatsu, Japan
Hepatitis C virus , a major etiologic agent of human liver diseases, is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus and is classified in the Flaviviridae family. Although research findings for the assembly of HCV particles are accumulating due to development of HCV cell culture system, the mechanism by which the HCV genome becomes encapsidated remains largely unclear. In general, viral RNA represents only a small fraction of the RNA molecules in the cells infected with RNA viruses, but the viral genomic RNA is considered to selectively packaged into virions. It was recently demonstrated that HCV RNAs containing 3 end of the genome are selectively incorporated into virus particles during the assembly process and the 3 untranslated region functions as a cis-acting element for RNA packaging. Here, we discuss the molecular basis of RNA encapsidation of HCV and classical flaviviruses, contrast with the packaging mechanism of HIV-1.
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Is It Spread
History And Physical Exam
To diagnose all forms of hepatitis, your doctor will first take your history to determine any risk factors you may have.
During a physical examination, your doctor may press down gently on your abdomen to see if thereâs pain or tenderness. Your doctor may also check for any swelling of the liver and any yellow discoloration in your eyes or skin.
Can Hepatitis Be Prevented
There are different ways to prevent or lower your risk for hepatitis, depending on the type of hepatitis. For example, not drinking too much alcohol can prevent alcoholic hepatitis. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and B. Autoimmune hepatitis cannot be prevented.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
You May Like: At Home Hepatitis C Test
Mode Of Transmission Of Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis C is primarily transmitted by blood-to-blood contact. The risk of transmission is dependent on the mode and status of the source. The average risk is 1.8 per cent via a needlestick or sharps injury from an HCV RNApositive patient, and negligible if the source is HCV RNA negative.
Routes of transmission include:
- use of nonsterile injecting equipment
- needlestick injury or other parenteral inoculation this includes blood and blood product transfusions before blood-bank screening
- some household activities, such as sharing razors or toothbrushes
- invasive procedures with inadequate infection control
- vertical transmission from mother to neonate, around the time of birth .
Rates of sexual transmission of HCV infection are negligible. The risk is increased if the HCV-positive partner is immunocompromised, as the viral blood titre may be increased, or when there is the possibility of blood-to-blood contact for example, sex during menstruation and traumatic sexual practices.
A proportion of HCV-positive individuals do not fall into any known risk subgroup. They may have forgotten that they had exposure to injecting drugs many years ago or may be unwilling to discuss the possibility.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis
Treatment for hepatitis depends on which type you have and whether it is acute or chronic. Acute viral hepatitis often goes away on its own. To feel better, you may just need to rest and get enough fluids. But in some cases, it may be more serious. You might even need treatment in a hospital.
There are different medicines to treat the different chronic types of hepatitis. Possible other treatments may include surgery and other medical procedures. People who have alcoholic hepatitis need to stop drinking. If your chronic hepatitis leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
You May Like: How Hepatitis B And C Are Transmitted
Causes And Risk Factors
HCV causes hepatitis C. People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles, and the virus is not easy to kill.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- having exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offer advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach can kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment can reduce the amount of HCV but might not stop a person from contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so people should make sure they rinse the syringe thoroughly. A person should only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
People who are at risk due to these factors can have screening to rule out HCV.
- peginterferon alfa-2a
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Also Check: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
Symptoms Of Hcv Infection
About 70 to 80 percent of individuals who contract HCV show no symptoms of acute hepatitis. When present, symptoms of acute illness may include fever, malaise, nausea, jaundice, arthralgia , dark urine, pale stools, and abdominal pain. Acute symptoms typically subside within several weeks. In very rare instances, primarily when another chronic liver disease is present, acute illness culminates in fulminant hepatic failure.
In roughly 70 to 90 percent of persons infected with HCV, the virus persists in the liver following the acute phase of infection. In the majority of cases, chronic infection is asymptomatic for decades. The infection may be noticed only after routine blood tests reveal elevated levels of liver enzymes, by which time liver function has begun to decline. Symptomatic patients may experience fatigue, nausea, anorexia, myalgia , arthralgia, weakness, and weight loss. Complications arising from chronic HCV infection include cirrhosis , liver failure, and liver cancer.
Susceptibility And Resistance To Hepatitis C
All nonimmune people are susceptible to infection. The degree of immunity following infection is uncertain. If infection resolves and the virus is cleared, the person can be reinfected with the same and other genotypes. However, there is some evidence from cohort studies that the likelihood of reinfection is reduced after the first HCV infection.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis B
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Find out more on how to prevent hepatitis C.
Noids Causative Agents: Week 40
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/notifiable-diseases-causative-agents-reports-for-2022/noids-causative-agents-week-40-week-ending-9-october-2022
Don’t Miss: What Is The Test For Hepatitis C
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often does not have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged.
This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition.
Symptoms can include:
- feeling and being sick
The only way to know for certain if these symptoms are caused by hepatitis C is to get tested.
Pathogenetic Mechanisms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Roberto Marasca
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus infection is probably the most common chronic viral infection and affects an estimated 180 million people worldwide, accounting for 3% of the global population. Although the liver is considered to be the primary target, extrahepatic manifestations are well recognized among patients with chronic HCV infection. Epidemiological studies have clearly demonstrated a correlation between chronic HCV infection and occurrence of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas . The clinical evidence that antiviral therapy has a significant role in the treatment at least of some HCV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders, especially indolent B-NHL, further supports the existence of an etiopathogenetic link. However, the mechanisms exploited by HCV to induce B-cell lymphoproliferation have so far not completely clarified. It is conceivable that different biological mechanisms, namely, chronic antigen stimulation, high-affinity interaction between HCV-E2 protein and its cellular receptors, direct HCV infection of B-cells, and hit and run transforming events, may be combined themselves and cooperate in a multifactorial model of HCV-associated lymphomagenesis.
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiologic Association of HCV and B-NHL
3. Mechanisms of HCV-Induced Lymphoproliferation
| The different oncogenetic mechanisms are not mutually exclusive, but they may be integrated and cooperate in a multifactorial pathogenetic model of HCV-associated B-cell lymphoproliferation. |
Recommended Reading: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B And C