Determination Of Glucose Metabolism Levels In Other Organs
The left ventricular myocardial ROI was delineated layer by layer on the tomographic PET/CT fusion images. The SUVmean of 18F-FDG in the entire left ventricular myocardium was automatically calculated by Siemens TrueD software. Because the glucose uptake of the myocardium was affected by a variety of metabolic substrates, the value varied greatly. For subjects with low myocardial uptake as a blood pool, an ROI with double U-shaped lines with about 1cm distance was delineated along the border of the left ventricle on the transaxial PET/CT images . The ROI of the mediastinal blood pool was delineated on the continuous layers of the ascending aorta. In the pancreas, three ROIs with a diameter of 1.0cm were delineated in the pancreatic head, body and tail and used to calculate the SUVmean of the pancreas. The ROI of skeletal muscle was delineated on the upper part of the bilateral femur .
What Are The Complications Of Fatty Liver Disease
In many people, fatty liver by itself doesnt cause too many problems. But in some people the fatty liver gets inflamed, causing a more serious condition called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH. Ongoing inflammation may scar the liver, which can lead to cirrhosis. This is a serious illness.
A few people who get cirrhosis of the liver develop liver cancer. Some people who develop severe cirrhosis of the liver need to have a liver transplant.
People with fatty liver have an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Symptoms And Treatments For High Iron
Overview of High Iron High iron, a condition known as hemochromatosis, is when the body absorbs too much iron from the foods. The excess iron usually accumulates in the organs, including the liver, heart, and pancreas. When iron stores overtime in these vital organs, it can lead to life-threatening conditions, …
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Is It Transmitted
Computed Tomography Scan Of Upper Abdomen
A computed tomography scan of the upper abdomen was performed on a Aquillion One scanner using identical scan protocols for the 2 cohorts . Liver attenuation was measured for all CT scans using Vitrea 3.1 imaging software . A region of interest with an area of 1500 mm2 was placed in Coinaud liver segments 5 and 6. The average liver attenuation was calculated from the 2 ROIs, and results were presented in Hounsfield Units . All analyses were performed by trained physicians blinded to clinical and biochemical details of the study participants. A pilot study of 20 participants demonstrated a high interrater correlation with no bias.
All participants in the COCOMO study were invited to a CT scan 921 participants attended. Participants from the CGPS aged 40 years or above were randomly invited to a CT scan 70% accepted the invitation .
Diet With Steatosis Of The Liver
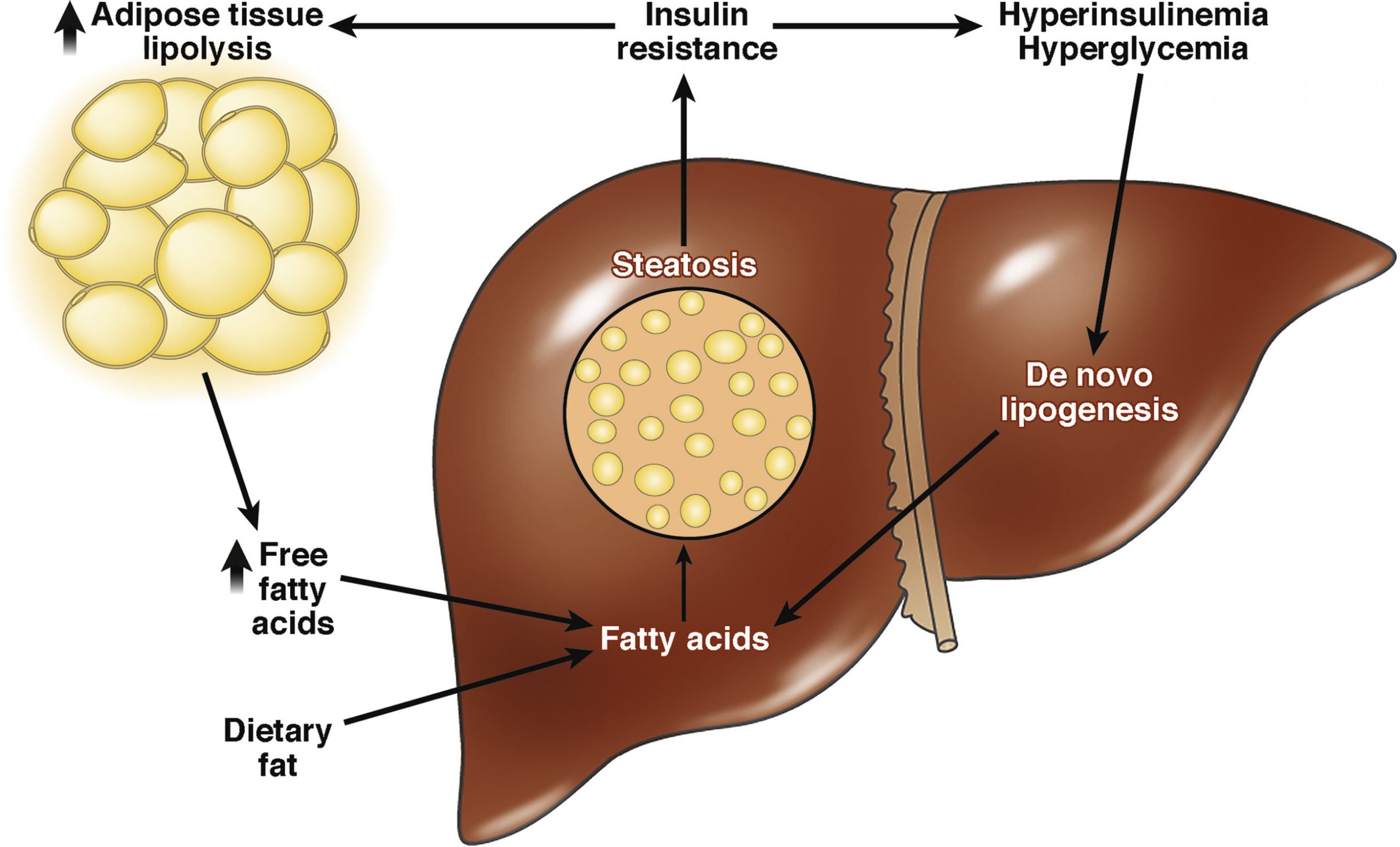
Steatosis of the liver is associated with the accumulation of fat in the body, so an important part of the treatment is a diet with a minimum fat content.
During treatment it is better to use sour-milk and plant products, as well as products containing easily digestible protein.
In the diet can include fresh vegetables, cottage cheese, berries, fruit, tselozernovye porridge, bran, a small amount of vegetable oil.
With steatosis it is necessary to refuse fresh baked goods, fried pies, donuts, etc., fatty meat and fish varieties, broths, okroshki, borsch, salty, acidic, smoked products .
Also, you can not eat fried or hard-boiled eggs, strong tea, coffee, garlic, onions, radish, beans, mayonnaise.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Hepatitis C Infection
Fibrosis Progression In Nash
Progression of fibrosis in NASH has been histologically demonstrated in 32%-37% of the patients. Estimated rates of cirrhosis development over 10 years of 5%-20% have been reported by 3 independent studies . NASH patients with advanced fibrosis are at risk of developing liver complications. Obesity, diabetes, IR and the initial severity of the fibrosis are the factors most conspicuously associated with fibrotic progression.
The mechanisms by which IR promotes fibrosis progression include: steatosis, hyperleptinemia, increased TNF production, impaired expression of PPAR- receptors. Hepatic injury in NASH induces oxidative stress, ROS and peroxidation products which lead to cytotoxic events, release of proinflammatory cytokines that activate hepatic stellate cells and deposition of collagen.
HCC has been detected in several NASH patients, most often at the time of diagnosis, and rarely, during follow up. In the larger Olmsted County Community Study, 2 of 420 NAFLD patients developed HCC during a 7-year follow-up period. The estimated rate of liver-related deaths over 10 years was 12% for NASH patients.
Estimation Of Hepatic Steatosis Severity
Ultrasonographically diagnosed NAFLD was defined according to ultrasonographic findings such as echogenic or bright liver on imaging consistent with fatty infiltration.21 The severity of hepatic steatosis was evaluated using the HSI, which was calculated as follows: HSI=8Ã+BMI .17 In addition, hepatic steatosis was also assessed using MRI-PDFF and a diagnosis of hepatic steatosis was made when the PDFF exceeded 5%.22
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Kidney Failure
Tests Of Inflammation And Iron Studies
There is a need for biomarkers that reliably discriminate NASH from bland steatosis. An earlier suggestion that highly specific C-reactive protein may be valuable has not been confirmed., Serum ferritin is elevated in approximately 60% of patients with NASH,, probably reflecting hepatocyte injury and liver inflammation rather than an increase in hepatic iron stores. Thus, although a possible role for iron in exacerbating NAFLD has been debated,, , , – the weight of evidence is against this some studies do show a weak association with C282Y.,
Exercise Diet And Prevention Of Hepatic Steatosis
Low levels of habitual physical activity and/or poor fitness are routinely linked to increased NAFLD prevalence.81–83 NAFLD patients are known to have lower amounts of daily physical activity than patients without fatty liver disease.84 Less physically active individuals also exhibit higher rates of hepatic FFA uptake compared with more active individuals, a factor known to significantly contribute to hepatic steatosis.34,85 In addition, a recent study in monozygotic twin pigs found that the more active pig in each pair had 18% greater maximal oxygen uptake and approximately 25% less hepatic fat content than the less active animal.86 Furthermore, a recent retrospective cross-sectional study suggests that meeting the recommendations for vigorous physical activity is associated with a significant reduction in the odds of hepatic steatosis progressing to NASH and that exceeding the vigorous activity guidelines is associated with decreased odds of having fibrosis.87 Interestingly, meeting or exceeding the recommendations for moderate intensity activity was not associated with a reduced incidence of NASH or fibrosis. This retrospective analysis points to the potential clinical utility of vigorous, high-intensity exercise training in the management of NASH, but randomized clinical trials are necessary.
Also Check: How Long Hepatitis C Live Outside Body
How Does Nash Develop
One of the primary functions of the liver is to process fat whether breaking down carbohydrates and proteins for use by the body, or synthesizing other fats, like cholesterol, either for use in the body or removal .
But the liver isnt meant to store fat. When there is too much buildup of fat in the liver , this is called steatosis. As a means to protect the liver, inflammation and scarring starts to occur, and can negatively impact the livers primary jobs if it continues to progress without intervention, mainly through lifestyle changes.
When this happens in someone who is not a heavy drinker, it is referred to as Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis, or NASH.
Treatment Of Steatosis Of The Liver With Drugs
Steatosis of the liver is a pathology that develops for various reasons, in connection with this, drug treatment is prescribed in each individual case, taking into account the patient’s condition, the degree of organ damage, the survey data.
Appointed drugs to improve fat metabolism .
As part of complex therapy, hepatoprotectors are prescribed .
Patients with steatosis are recommended to run, swim or exercise, especially with obesity or diabetes.
With alcoholic steatosis of the liver at the heart of treatment is the absolute refusal of alcohol, after which you can take medications.
At the first stage of the treatment, the treatment shows good results, usually on the background of treatment, the baking function is completely restored, the fatty inclusions disappear.
In the second stage of the disease, when all the prescriptions prescribed by the doctor are performed, the therapy also shows good results.
Steatosis of the liver of the third stage is characterized by the most severe organ damage, in this case irreversible processes are already beginning. Treatment in this case is based on the prevention of further decay of liver cells.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis A And B And C
Symptoms Of Steatosis Of The Liver
Steatosis of the liver, in the initial stages is almost asymptomatic, often the disease has a chronic form. Steatosis may not manifest itself for a long time, and a person learns about the disease after a medical examination.
Among the main symptoms of the disease can be identified weakness, nausea, pain in the right upper quadrant, increased liver, decreased immunity .
With steatosis, the outflow of bile is broken, bile stagnation may occur, while the skin becomes yellowish, itching, pain, nausea, vomiting.
What Are The Causes Of Fatty Liver Disease
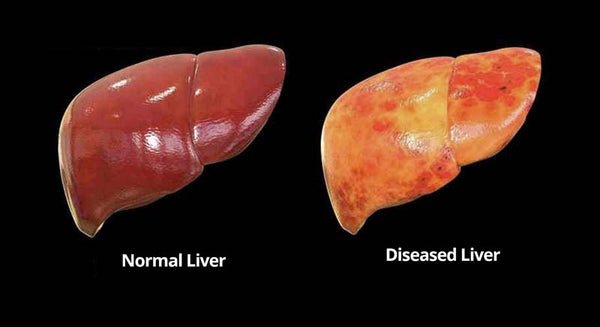
In fatty liver disease, excess fat is stored in liver cells, where it accumulates. A variety of factors can cause this fat buildup.
Drinking too much alcohol can cause AFLD. Heavy alcohol use can alter certain metabolic processes in the liver. Some of these metabolic products can combine with fatty acids, leading to the formation of types of fat that can accumulate in the liver.
In people who dont drink a lot of alcohol, the cause of fatty liver disease is less clear. For these people, its possible their body produces too much fat or doesnt metabolize fat efficiently enough.
One or more of the following factors may play a role in people who dont consume much alcohol and develop fatty liver disease:
- rapid weight loss
- rare genetic conditions, like Wilson disease or hypobetalipoproteinemia
Remember that having risk factors means youre at an increased risk of fatty liver disease compared with people who dont have risk factors. It does not mean youll certainly develop it in the future.
If you have one or more risk factors for fatty liver disease, talk with your doctor about prevention strategies.
To diagnose fatty liver, your doctor will take your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more tests.
If your doctor suspects that you might have fatty liver, they will likely ask you questions about:
Let you doctor know if youve been experiencing fatigue, loss of appetite, or other unexplained symptoms.
You May Like: Pro Plan Hepatic Dog Food
Types And Symptoms Of Alcohol
The symptoms of ARLD depend on the stage of the disease. There are three stages:
Some people with ARLD dont have symptoms until the disease is advanced. Others start showing signs earlier. Symptoms of ARLD include:
- nausea
- swelling in the legs and abdomen
- weight loss
- darkening or lightening of the skin
- red hands or feet
ARLD treatment has two goals. The first is to help you stop drinking. This can prevent further liver damage and encourage healing. The second is to improve your liver health.
If you have ARLD, your doctor may recommend:
Its important to note that taking vitamin A and alcohol together can be deadly. Only people who have stopped drinking can take these supplements. Supplements will not cure liver disease, but they can prevent complications like malnutrition.
Complications of ARLD may include:
Treatment For Fatty Liver Disease
There are no medications approved for NAFLD, though some are in clinical trials.
Usually the first line of treatment is to lose weight. It helps reduce fat, inflammation, and scarring in your liver. Losing just 3% to 5% of your body weight can cut down on how much fat is in your liver. Weight loss surgery is also an option if you have a lot to lose.
Youâll also need to quit drinking. Itâs the only way you can keep liver damage from getting worse. You may even be able to undo some of the liver damage thatâs already happened. Talk to your doctor about how you can get help. You may need a medically supervised detox program to safely quit drinking and manage withdrawal symptoms.
If you have complications due to NASH, such as cirrhosis or liver failure, you may need to have a liver transplant. In general, people with NASH who get a liver transplant do very well.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Cause Low Platelets
Molecular Sieves And Desiccants
Apart from distillation, ethanol may be dried by addition of a , such as , , or . The desiccants can be dried and reused. can be used to selectively absorb the water from the 95.6% ethanol solution. Molecular sieves of pore-size 3 , a type of , effectively sequester water molecules while excluding ethanol molecules. Heating the wet sieves drives out the water, allowing regeneration of their dessicant capability.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B The Same As Hiv
How Nafld Is Diagnosed
NAFLD usually has no symptoms. The condition is typically diagnosed after a blood test finds higher-than-normal levels of liver enzymes. A standard blood test could reveal this result.
High levels of liver enzymes could also suggest other liver diseases. Your doctor will need to rule out other conditions before diagnosing NAFLD.
If NAFLD is suspected, your doctor may look for physical symptoms like signs of insulin resistance , and signs of cirrhosis .
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted Sexually
What Does Diagnosis Look Like
Hepatic steatosis can often be diagnosed by imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, computed tomography scan, or magnetic resonance imaging . All types of medical imaging can reveal diffuse fat content in the liver. This finding may also be described as lower liver attenuation, which means that healthy tissue is interrupted by fatty deposits. Imaging tests are performed by radiology specialists and interpreted by radiologists.
Ultrasound imaging is a type of sonography that is useful for detecting fat within the liver. Ultrasound technology utilizes sound waves to detect variations in structures and composition within body tissues. A higher measure of echogenicity will also accompany fat deposits in the liver parenchyma, which is the part of the liver responsible for carrying out the organs processes. Higher echogenicity means that sound waves more readily bounce off fat tissue and echo back to their source. An MRI might reveal a chemical shift that signifies the presence of fat within the liver.
Another type of imaging is called elastography. Elastography can reveal if soft tissue has hardened, indicating damage. For example, normally functioning liver tissue is soft in texture. Scarred or damaged liver becomes harder in texture.
One of the most definitive ways to detect and diagnose fatty liver disease is through a liver biopsy. A liver biopsy requires taking a tiny sample of your liver and analyzing it for the presence of fat cells, lesions, and other abnormalities.
Predictors Of The Presence Of Fatty Liver
In entire study population, a higher platelet count and higher HSI predicted the presence of fatty liver .
In patients with NAFLD, age, hypertension, and liver cirrhosis were negatively associated with the presence of fatty liver, whereas serum albumin level, platelet count, and HSI were positively associated with the presence of fatty liver in univariate analysis . No predictor of fatty liver was identified in multivariate analysis .
In all patients with CHB, a higher platelet count and a higher HSI independently predicted the presence of fatty liver . When patients with CHB were stratified into two groups with and without AVT, a higher HSI was the only predictor of fatty liver in CHB patients without AVT , whereas a higher platelet count and a higher HSI independently predicted the presence of fatty liver in CHB patients receiving AVT .
You May Like: Primary Biliary Cirrhosis And Autoimmune Hepatitis
Can Fatty Liver Disease Be Prevented
The way to prevent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is to follow the same lifestyle advice given to people who already have the condition, including:
- eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruit and vegetables, whole grains and healthy fats
- maintaining a healthy weight
- being physically active on most days of the week check with your GP first if you havent been exercising regularly
Fatty Liver Disease Has A Genetic Component
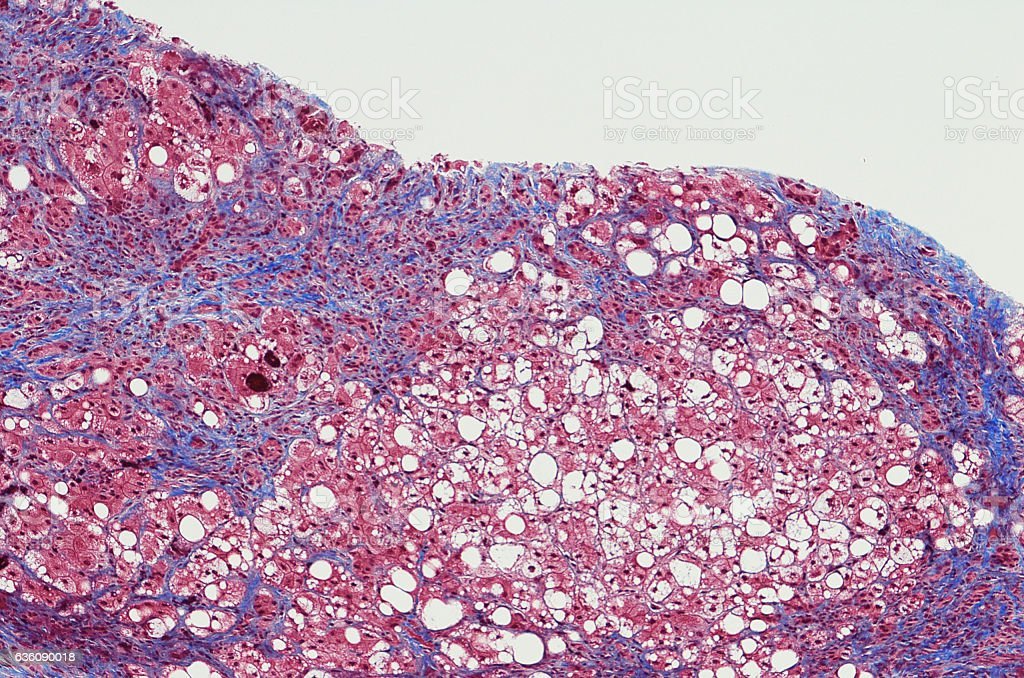
The likelihood of developing fatty liver disease is influenced in part by genetics. But the heritability of fatty liver is not so simple to determine. Research has shown that there is not just one gene that determines the risk of developing fatty liver disease, but rather an interaction of many genes in your DNA.
Research published in Clinical and Molecular Hepatology describes three genes PNPLA2, GCKR, and TM6SF2 that may influence the likelihood of fat accumulation in the liver. Specific variants of each gene are associated with increased risk of conditions associated with fatty liver disease, such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Of the three genes, PNPLA3 is the most well-studied gene and directly plays a role in liver metabolic processes. Moreover, a certain variant of the PNPLA3 gene is associated with a higher risk of fatty liver disease progression to NASH, fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Luciferase Expression