Screening Tests For Hepatitis B
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. There are several types of test, but the three generally included are the HBsAg, the antibody to HBsAg , and the antibody to hepatitis B core antigen .
These tests allow the healthcare provider to know whether you could benefit from vaccination, or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care, or treatment.
You may be routinely screened if you are pregnant, are donating blood or tissue, need immunosuppressive therapy, or have end-stage renal disease. You will also be screened if you are in groups that are at higher risk for HBV.
Chronic Hbv Carriers At Greatest Risk Of Hepatic Sequelae
Sustained elevations in ALT, although an imperfect marker for hepatic damage, can help identify chronic HBV carriers at greatest risk of sequelae and those most likely to benefit from current treatments . Chronically infected patients with sustained ALT elevations greater than the upper limit of normal may be candidates for treatment and should undergo additional prognostic hepatitis marker testing as outlined below. Chronic carriers whose ALT is within the normal range should be tested for this marker periodically because ALT levels can fluctuate with this illness. Determination of ALT levels and HBV serological and nucleic acid markers, although valuable in following infection, is not adequate to assess the severity of infection and the resulting liver damage. Before appropriate treatment can be initiated, consultation with a specialist and assessment of the disease through histological examination of a liver biopsy is strongly recommended.
Screening For Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The most important risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma is prolonged chronic HBV infection for decades, particularly in patients with active disease based on elevated ALT levels . The development of cirrhosis in chronic carriers increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma, although in the case of HBV, the latter may occur in the absence of cirrhosis. Although the cost benefit remains to be established, screening for hepatocellular carcinoma is suggested in patients 30 years of age or older with one or more of the following risk factors : infection at birth being male a duration of infection for several decades a family history of hepatocellular carcinoma the presence of HCV co-infection and finally, specific at-high-risk populations . Suggested screening consists of an abdominal ultrasound and serum alpha-fetoprotein at approximately six-month intervals .
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Caused From
Recommended Tests To Investigate Acute Hbv Infection And The Interpretation Of Results
Acute HBV infection generally presents after an incubation period of six weeks to several months with an onset of nonspecific symptoms that may include fever, malaise, anorexia and nausea, followed by the onset of jaundice, dark urine and pale stools. Approximately 25% to 40% of infected adults will be symptomatic, and most will demonstrate elevations in ALT however, infants, toddlers and immunosuppressed individuals may not manifest signs or symptoms of infection. The management of acute infections is largely supportive unless fulminant hepatitis develops, in which case the patient should be referred to a liver specialist. Because the clinical features of acute hepatitis are very similar for HAV, HBV and HCV, testing for all three agents should be performed when working up an acute case. While the sexual transmission of HCV is rare, varying between zero to six cases per 1000 person-years , HAV that is typically spread by the fecal-oral route poses a clear risk to sexual partners. Figure Figure11 and Table Table22 outline the appropriate serological tests to investigate acute hepatitis.
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Recommended Reading: Can You Heal From Hepatitis C
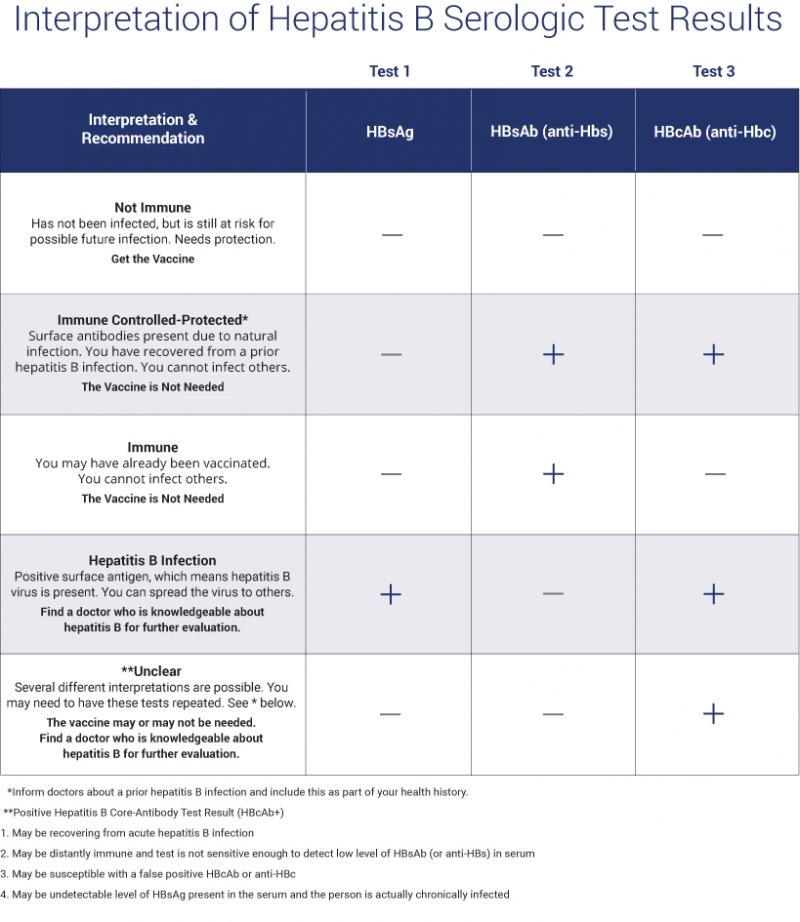
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Specimen Choice Collection And Transport
The specimen of choice for the diagnosis of HBV infection is blood. Serological tests for viral antigens and antibodies are typically used for diagnostic screening and can be performed on either serum or plasma. Both HBV antigens and antibody are stable at room temperature for days, at 4°C for months, and frozen at -20°C to -70°C for many years. Because modern testing involves automated enzyme immunoassays that depend on colourimetic or chemiluminescence signal measurement, care should be taken to avoid hemolysis of the sample because it may interfere with the ability of the assay to accurately detect these markers.
A number of nucleic acid-based tests, which have been the subject of recent reviews , are available to directly detect HBV-DNA in serum or plasma. Care must be taken to avoid the degradation of the viral nucleic acid in the specimen, which can result in falsely low or no measurable viral load. Serum should therefore be removed from clotted blood within 4 h of collection and stored at -20°C to -70°C , and can be subjected to up to eight short-term freeze-thaw cycles without significant loss of detectable HBV-DNA . Alternatively, the presence of EDTA in plasma is known to stabilize viral nucleic acids. EDTA blood can be stored for up to five days at 4°C without affecting the viral load . Polymerase chain reaction-based tests can use either serum or plasma, while hybridization-based assays recommend the use of serum.
You May Like: Google What Is Hepatitis B
Is It Possible To Prevent Hepatitis
Hepatitis prevention is very much a possibility with the right strategies. A vaccine is available for hepatitis A. Healthcare providers recommend this vaccine for all people who are at high risk of exposure to the virus. Children- one year and above, should take this vaccine. Prevention of hepatitis A is possible with good hygiene and sanitation. Washing hands especially after using the toilet and before consumption of food can help with cutting hepatitis A transmission. Hepatitis B vaccine has become the norm in developed nations and most new-borns are given these shots. The hepatitis B shots are recommended for children and adolescents as well as adults in high-risk groups. Hepatitis C vaccine is not developed yet, and efforts are in the process to have a vaccine for this infection. Prevention of hepatitis C is possible by avoiding contact or exposure to blood and bodily fluids. Further, avoiding the sharing of needles or other instruments to inject drugs can cut the rate of transmission of this disease.
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Don’t Miss: How To Live With Hepatitis B
Management Of Pregnant Hbv Carriers
Pregnant HBV carrier mothers present a unique opportunity to prevent transmission of HBV to their neonates. All infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should receive hepatitis B immune globulin and a full course of HBV vaccination . Vaccine failure in the neonate is rare but does occur , and may be accounted for by transplacental transmission before birth. Follow-up testing of the neonate should be performed to confirm vaccination effectiveness. Testing should be performed for HBsAg to detect vaccine failures, anti-HBs to confirm a successful vaccine response and anti-HBc-Total to determine if the anti-HBs response was due to vaccination or resolution of natural infection. While testing for these markers is recommended one to two months after completion of the vaccine series, testing at approximately 18 months would ensure that the anti-HBc-Total test does not represent maternal antibody. This may be important because vaccination failures have occasionally been associated with HBV vaccine escape mutants that may only demonstrate a positive anti-HBc-Total as the sole marker of infection. These mutations occur in the open reading frame of the HBsAg, may not be recognized by antibodies induced by current HBV vaccine, and may not be detected by currently available HBsAg enzyme immunoassays . Clearly, surveillance systems need to be in place to ensure that HBV vaccines remain effective and vaccine escape mutants do not replace current HBV strains.
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients may find it helpful to ask questions about their hepatitis B test results. Questions that may be helpful include:
- What was my test result?
- Do I have an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity for hepatitis B?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis B vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis B test results?
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Related To Aids
Can Hepatitis Patients Spread The Infection To Others
Patients can spread hepatitis infection and the spread depends on the type and stage of the hepatitis infection. Those suffering from viral hepatitis can easily spread the infection even while being asymptomatic. Those with hepatitis A can spread the infection from the time they are infected. Those with hepatitis B are contagious as long as the virus is present in the blood. Those with hepatitis C infection are contagious and can transmit the infection.
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Cdc Fact Sheet
Antibody To Hcv Antigens
- If negative, chronic HCV infection is ruled out in immunocompetent individuals. Because the antibody to HCV antigens response in immunocompromised persons can be blunted, a qualitative test for HCV-RNA may be required to rule out occult infection in such individuals. A new HCV core antigen test, which is currently under evaluation, can also be used to confirm active infection . However, the currently available HCV core antigen test is less sensitive, detecting less than 90% to 95% of HCV-RNA-positive specimens . Therefore, the current HCV core antigen should not be used for definitive exclusion of active infection.
- If found to be anti-HCV positive, the patient has been infected with HCV. Because most HCV infections are chronic , the presence of anti-HCV is correlated with active infection however, a qualitative test for HCV-RNA is currently required to confirm active HCV infection .
Evaluation Of Individuals Suspected Of Having An Hbv Infection
Given the perinatal and childhood vaccination programs already in place in North America, most HBV-infected individuals will likely present with chronic infection. Such individuals are likely to have risk factors that include immigration from high endemicity regions, injection drug use or sexual contact with an infected person 1) . Therefore, the present guideline will provide diagnostic recommendations first for individuals suspected of having chronic HBV infection and, subsequently, for those with acute infection. The diagnosis of HBV infection in any individual has important management implications, including appropriate counselling, monitoring and/or treating and vaccinating family or at-risk contacts.
Also Check: How Much Is A Hepatitis B Shot
What Does The Test Result Mean
The tests for hepatitis B may be ordered individually but are often ordered in some combination, depending on the reason for testing. Results of the tests are typically evaluated together. Sometimes the meaning of one result depends on the result of another test. However, not all tests are performed for all people.
The table below summarizes possible interpretations of some common patterns of results.
| Initial Tests | |
| None detected or detected at very low level | Chronic infection but low risk of liver damage carrier state |
*Note: There are some types of HBV that do not make e-antigen. In areas where these strains of HBV are common , testing for HBeAg is not very useful. In these cases, a negative HbeAg result does not necessarily mean that the person is not infectious it may be that the person is infected with a strain that does not make the e-antigen.
Monitoring treatment of chronic infection: If the results from initial and follow-up testing indicate that a person has chronic hepatitis B, then the individual may be treated with medication and the effectiveness of that treatment may be monitored using the tests for HBe and HBs antigen and antibody and HBV DNA:
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
You can become infected with hepatitis B through exposure to blood, semen and other bodily fluids of an infected person. You can get the infection by:
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
- Breastfeeding.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Normal Range
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
What Happens During A Hepatitis Panel
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
At-home testing kits are available for hepatitis B and C. Usually the test kit will include a sharp device, to prick your finger so you can collect a drop of blood to send to a lab for testing. For more information on at-home testing for hepatitis, talk to your provider.
Read Also: Cvs Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost