Treating Acute Hepatitis C
Treatment is usually not necessary for those with acute hepatitis C, as immune responses are generally able to resolve the infection between 2 to 12 weeks. However, the risk comes from the high risk of acute cases becoming chronic . Given how symptoms do not present themselves until much, much later, early screenings can make a difference in what the recommended treatment plan is.
If treatment is considered, 8 to 12 weeks of oral medication therapy is usually prescribed to prevent acute cases from becoming chronic.
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis C Infection
There are two types of hepatitis C infection:
- Acute: a short-term infection that occurs within 6 months after a person is exposed to the virus. However, about 75 to 85 percent of people with the acute form go on to develop the chronic form.
- Chronic: a long-term illness that can continue throughout a persons life. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and other serious problems, such as liver failure or cancer. About 15,000 people a year die from liver disease associated with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C And Blood Spills
When cleaning and removing blood spills, use standard infection control precautions at all times:
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a waterproof dressing.
- Wear single-use gloves and use paper towel to mop up blood spills.
- Clean the area with warm water and detergent, then rinse and dry.
- Place used gloves and paper towels into a plastic bag, then seal and dispose of them in a rubbish bin.
- Wash your hands in warm, soapy water then dry them thoroughly.
- Put bloodstained tissues, sanitary towels or dressings in a plastic bag before throwing them away.
Also Check: Ok Google How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Acute Hepatitis C Vs Chronic Hepatitis C
Acute and chronic hepatitis C are caused by the same virus.
Acute hepatitis C develops after initial infection with the HCV. This stage can last up to 6 months. Many people have no symptoms during the acute stage and never find out that they have the infection.
According to the CDC, of people with acute hepatitis C develop chronic hepatitis C.
The World Health Organization states that 15 to 45 percent of people with acute hepatitis C spontaneously clear the virus within 6 months. This means that the virus goes away even though it hasnt been treated.
The 55 to 85 percent of people who dont clear the virus will develop a chronic HCV infection.
Chronic hepatitis C can be managed with medications and even cured, but its still a serious condition. According to the CDC,
Chiron Recombinant Gpe1/gpe2 Vaccine
A significant limitation to the chimpanzee studies of the gpE1/gpE2 vaccine is the lack of understanding of the significance of protection against an intravenous challenge with 10100 CID50 of virus. Although this has become a standard in the field, it is not clear how it relates to the real-world situation. While a contaminated blood transfusion would provide a challenge many orders of magnitude greater than this, such an event would be very unlikely today because of screening procedures in place to protect the blood supply. The typical inoculum size in the setting of community-acquired infections is not known and can only be guessed at. Nonetheless, the data obtained in these chimpanzee challenge experiments suggest that the gpE1/gpE2 vaccine may be capable of protecting against persistent infection with at least genotype 1a viruses . This is likely to be accomplished this via the induction of neutralizing antibodies, since the existence of sterilizing immunity in some animals correlated at least roughly with the magnitude of the antibody response to E2 as assessed by inhibition of E2 binding to CD81 and neutralization of HCVpp entry .
Read Also: Can Liver Disease Cause Hepatitis C
What Is The Treatment For People With Acute Hepatitis C Infection
When people first get hepatitis C, the infection is said to be acute. Most people with acute hepatitis C do not have symptoms so they are not recognized as being infected. However, some have low-grade fever, fatigue or other symptoms that lead to an early diagnosis. Others who become infected and have a known exposure to an infected source, such as a needlestick injury, are monitored closely.
Treatment decisions should be made on a case-by-case basis. Response to treatment is higher in acute hepatitis infection than chronic infection. However, many experts prefer to hold off treatment for 8-12 weeks to see whether the patient naturally eliminates the virus without treatment. Approaches to treatment are evolving. Patients with acute hepatitis C infection should discuss treatment options with a health care professional who is experienced in treating the disease. There is no established treatment regimen at this time.
How effective is hepatitis C treatment? Is hepatitis C curable?
If the hepatitis C RNA remains undetectable at the end of the treatment and follow-up period, this is called a sustained virologic response and is considered a cure. Over 90% of people treated with DAAs are cured. These people have significantly reduced liver inflammation, and liver scarring may even be reversed.
About 5% of people who are treated for HCV infection are not cured by some of the older regimens. These people may still have options for cure with the newer regimens.
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors
There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
Don’t Miss: Do I Need To Fast For A Hepatitis Blood Test
How Is Monitoring Done After Treatment For Hepatitis C
Once patients successfully complete treatment, the viral load after treatment determines if there is an SVR or cure. If cure is achieved , no further additional testing is recommended unless the patient has cirrhosis. Those who are not cured will need continued monitoring for progression of liver disease and its complications.
While cure eliminates worsening of fibrosis by hepatitis C, complications may still affect those with cirrhosis. These individuals still need regular screening for liver cancer as well as monitoring for esophageal varices that may bleed.
Because hepatitis B co-infection may reactivate or worsen even after treatment for HCV, monitoring for hepatitis symptoms may be needed after the end of therapy.
Hepatitis C Antibody Test
Certain foreign substances that enter your body trigger your immune system to make antibodies. Antibodies are specifically programmed to only target the foreign substance they were made to fight.
If youve ever had a hepatitis C infection, your body will make hepatitis C antibodies as part of its immune response.
Your body only makes these antibodies if you have hepatitis C or had it in the past. So the hepatitis C antibody test can confirm whether you have the virus by testing for these specific antibodies.
It may take 2 to 3 months after exposure for the test to detect antibodies. If needed, your healthcare professional may order an HCV RNA test, which can detect the virus after just 1 or 2 weeks.
If the antibody test is positive, an HCV RNA test can show whether the infection is current.
While people of any gender experience the same hepatitis C symptoms, 2014 research suggested some effects of the virus may differ, depending on the sex you were assigned at birth.
Researchers noted that:
- women have a higher chance of clearing the virus without treatment
- liver disease may progress more rapidly in men
- men have a higher chance of developing cirrhosis
Read Also: Stage 3 Fibrosis Hepatitis C
What Are The Complications Of Undiagnosed Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis C is known to be associated with two skin conditions, lichen planus and porphyria cutanea tarda.
- Diabetes, heart disease, and arterial blockage are more common among patients with chronic hepatitis C infection than in the general population. It may be that liver damage and chronic inflammation caused by hepatitis C may affect the levels of blood fats and blood sugar.
- Low platelet counts may occur as a result of the destruction of platelets by antibodies.
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Diagnosed
Since hepatitis C infection is usually asymptomatic until it gets severe, only a few people are diagnosed with recent infection. In those people who develop chronic hepatitis C infection and symptoms of liver damage have started to appear, two hepatitis C blood tests are done to identify the infection. These are:
- Anti-HCV antibody test to identify the people who have been infected.
- If the anti-HCV test results come out to be positive, an HCV RNA test is needed to confirm the infection as those people also who had an acute infection and have now cleared the virus from the system on their own also test positive for an anti-HCV antibody test.
After HCV infection is confirmed, you should also get a liver function test done to assess the degree of liver damage. It helps in understanding and planning the future course of action.
What are the complications of hepatitis C infection?
Acute hepatitis C infection doesnt cause any complications as your body usually clears it on its own without any external help. But in chronic hepatitis C, complications such as liver cirrhosis or scarring of the liver, liver cancer, and complete liver failure are there. Though it would take years for your liver to reach this state, these complications are long term and can be fatal.
Is there a cure for hepatitis C infection?
Is hepatitis C prevention possible?
Read Also: Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis C
Is Liver Transplantation An Option For A Person With Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is the leading reason for 40% to 45% of liver transplants in the U.S. Hepatitis C usually recurs after transplantation and infects the new liver. Approximately 25% of these patients with recurrent hepatitis will develop cirrhosis within five years of transplantation. Despite this, the five-year survival rate for patients with hepatitis C is similar to that of patients who are transplanted for other types of liver disease.
Most transplant centers delay therapy until recurrent hepatitis C in the transplanted liver is confirmed. Oral, highly effective, direct-acting antivirals have shown encouraging results in patients who have undergone liver transplantation for hepatitis C infection and have recurrent hepatitis C. The choice of therapy needs to be individualized and is rapidly evolving.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C often does not have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged.
This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition.
Symptoms can include:
- stomach ache
- feeling and being sick
The only way to know for certain if these symptoms are caused by hepatitis C is to get tested.
You May Like: Signs N Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
What Medications Cure Hepatitis C Infection
Interferons, for example, Roferon-A and Infergen, and pegylated interferons such as Peg-IntronT, Pegasys, were mainstays of treatment for years. Interferons produced sustained viral response of up to 15%. Later, peglatedll forms produced SVR of 50%-80%. These drugs were injected, had many adverse effects, required frequent monitoring, and were often combined with oral ribavirin, which caused anemia. Treatment durations ranged up to 48 weeks.
Direct-acting anti-viral agents are antiviral drugs that act directly on hepatitis C multiplication.
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Symptoms alone generally dont offer enough information for a doctor to diagnose hepatitis C. Whats more, you might not have symptoms or notice any signs of the condition.
Thats why its so important to connect with a doctor or other healthcare professional and ask about getting tested if youve been exposed to the hepatitis C virus.
The also recommend hepatitis C testing for people who have abnormal liver tests, along with those who are:
- pregnant
- on hemodialysis
A healthcare professional can order a few different tests to help diagnose hepatitis C. These include:
- Blood tests. They may order a series of blood tests to check for the virus, starting with a hepatitis C antibody test. A PCR test can tell your healthcare professional whether the virus is currently active, and viral load testing can measure the amount of virus in your blood.
- Genotype test. This test can reveal which hepatitis C genotype you have. This information will help your healthcare professional find an effective treatment approach.
- Liver function test. If blood test results suggest chronic hepatitis C or your healthcare professional believes you could have liver damage, theyll order a liver function test. This test checks your blood for signs of heightened enzymes from your liver.
- Liver biopsy.This procedure can also help check for liver damage. A biopsy involves taking a small piece of tissue from your liver and testing it for cell abnormalities.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Long Term Effects Of Hepatitis C
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Totally
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
What Should People Do If They Think They Have Been Exposed To Hcv
People concerned about being exposed to HCV should consult their health care professional about screening for HCV infection. Common tests include:1,9,10
- Antibody detection tests: The antibody detection test determines the presence of antibodies of the virus, indicating exposure to HCV. An antibody is a substance found in the blood that the body produces in response to a virus. A doctor will likely order a second test to confirm whether the virus is still present in the bloodstream.
- Virus detection tests: The virus detection test identifies whether the virus is still present, indicating an active infection of HCV. This test may also be used after treatment to determine if the virus has been eliminated from the body.
- Liver biopsy: A liver biopsy is a procedure to remove a small piece of the liver so it can be examined with a microscope for signs of damage or disease. A liver biopsy is not necessary for diagnosis but is used to determine the severity of the disease and permanent damage. It is also helpful in determining the cause of the damage.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B How Long Does It Last
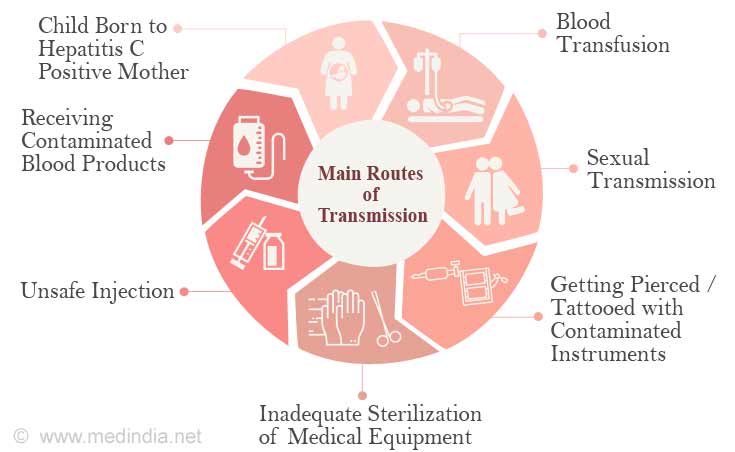
What Causes Hepatitis C Infection
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus. It is spread by contact with an infected person’s blood.
You can get hepatitis C if:
- You share needles and other equipment used to inject illegal drugs. This is the most common way to get hepatitis C in the United States.
- You had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992. As of 1992 in the United States, all donated blood and organs are screened for hepatitis C.
- You get a shot with a needle that has infected blood on it. This happens in some developing countries where they use needles more than once when giving shots.
- You get a tattoo or a piercing with a needle that has infected blood on it. This can happen if equipment isn’t cleaned properly after it is used.
In rare cases, a mother with hepatitis C spreads the virus to her baby at birth, or a health care worker is accidentally exposed to blood that is infected with hepatitis C.
The risk of getting hepatitis C through sexual contact is very small. The risk is higher if you have many sex partners.
If you live with someone who has hepatitis C or you know someone who has hepatitis C, you generally don’t need to worry about getting the disease from that person. You can help protect yourself by not sharing anything that may have blood on it, such as razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers.
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Antibody Test Positive