The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Can This Test Be Done At My Healthcare Practitioners Office
Maybe. There are rapid HCV antibody tests available that can be done at the point of care , in settings such as your healthcare practitioners office, community health clinics, and emergency rooms. They provide results in about 20 minutes. However, a positive result requires confirmation of active disease with an HCV RNA test, which is performed in a laboratory.
Interpreting Hcv Rna Test Results
It is essential that the provider understands how to interpret HCV RNA test results, especially during the course of HCV treatment.
| Result of HCV RNA Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A quantified viral load — any exact number | Ongoing HCV infection |
| “Detected” | The HCV RNA is detectable but the number of international units is so low that it cannot be quantified accurately. This indicates extremely low level of virus is present. |
| “< 12 IU/mL” or “< 15 IU/mL” or “< 25 IU/mL” All of these are “less than the LLOQ” | HCV RNA is undetectable. No virus is detected at all in the patient’s serum specimen. |
Also Check: Transplanting Hepatitis C Positive Kidneys
What Is Reflex Testing
Reflex testing, also called one-step diagnosis, is a relatively new method of hepatitis C testing in Canada. Reflex testing uses a single blood sample to complete both screening and confirmatory tests. This means that a person does not have to have blood taken a second time if they test positive for hepatitis C antibodies. Instead, some of the original blood sample that tested positive for hepatitis C antibodies is automatically used for confirmatory testing.5 This makes the testing process more convenient for the person being tested and reduces the risk of not completing the testing process.
Reflex testing can also be performed on dried blood spot samples, where a sample of blood drops is collected from a finger prick on a piece of filter paper, dried and transported to a laboratory. This form of sample collection is not yet widely used across Canada for hepatitis C testing. For most regions, reflex testing would require drawing blood from a persons vein for sample collection.
Types of tests used in Canada
A hepatitis C RNA test is the most commonly used test for confirmatory testing in Canada.6 With this test, the current presence of the hepatitis C virus in the blood is confirmed by analyzing the sample for RNA, the genetic material of the virus. Another type of confirmatory test, called a core antigen test, is used in some jurisdictions. This test detects proteins that are part of the hepatitis C virus.
Reliability
Testing For Chronic Hcv Infection
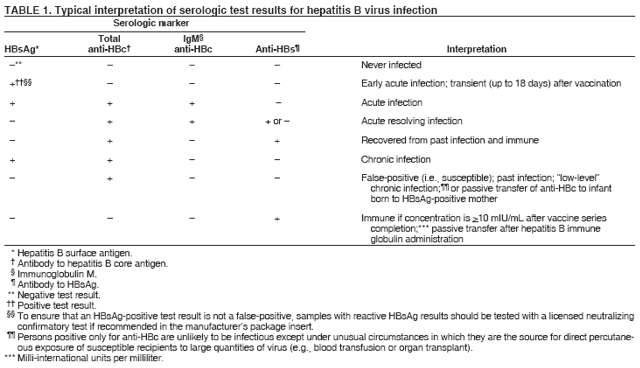
The initial screening test to be used in all circumstances is a test for antibody to hepatitis C viral proteins . These tests become positive as early as 8-10 weeks after infection, will be positive in 97% of patients by 6 months after infection, and probably will persist for life. Presence of anti-HCV does not define activity of infection. Up to 25% of patients will resolve infection spontaneously, but will still have detectable anti-HCV. Antibody tests currently recommended for anti-HCV screening include the EIA test and the more specific RIBA the latter being used to confirm a positive EIA test in some situations . These antibody tests are highly reliable for determining HCV infection at some time in the past.
Detection of HCV RNA in blood is the currently accepted “gold standard” for diagnosis of active HCV infection. Tests for HCV RNA are both qualitative and quantitative, vary in technical aspects, and report values differently.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Flare Up Symptoms
Blood Transfusion Issues And Donor Counseling
Guidelines for donor notification for donors positive for transfusion transmissible infections are outlined in An Action Plan for Blood Safety by National AIDS Control Organization 2004. A blood donor is offered an option to know his TTI status at the time of registration for blood donation after due counseling and give consent for the same.
Notifying donors regarding a single positive screening test is fraught with the risk of causing undue anxiety and stress to a donor. If a screening test is positive, the blood unit should be immediately discarded. Presently there are no guidelines regarding confirming the test results before informing the donor. In case of samples with low S/CO and grey zone samples, a retesting of the donor samples using a different assay would be imperative before notifying the donor. There are clear cut guidelines regarding donor notification and referral for HIV positive blood donors with integrated counseling and testing centers available for the same. Donors who are positive for viral hepatitis markers have to be counseled by blood bank staff. An algorithm for donor counseling for HCV positive donors is outlined in .
Algorithm for donor counseling for HCV positive donors
Recommended Laboratory Evaluation Prior To Referral
All persons referred for further evaluation and management of HCV infection should have a confirmed positive HCV RNA level, preferably a quantitative HCV RNA level and not a qualitative HCV RNA level. It is ideal, but not imperative, that the clinician who makes the diagnosis of HCV infection can perform some preliminary tests to provide advanced information in anticipation of the initial referral visit. These initial preliminary tests include an HCV genotype, tests of synthetic liver function , hepatic inflammation , and assays to detect relevant coinfection . For primary care providers taking on a more comprehensive role for the initial evaluation and management, see Module 2, Lesson 1 for a detailed discussion in the Core Concept Initial Evaluation of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis C.
You May Like: Medications Used For Hepatitis C
Virological Tools For Diagnosis
Virological diagnosis of HCV infection is based on two categories of laboratory tests, namely serologic assays detecting specific antibody to HCV and assays that can detect, quantify, or characterize the components of HCV viral particles, such as HCV RNA and core antigen . Direct and indirect virological tests play a key role in the diagnosis of infection, therapeutic decision-making, and assessment of virological response to therapy.
When Should I Get Hepatitis C Testing
When used for early detection in patients without symptoms of hepatitis C, screening is recommended at least once for all adults aged 18 years or older, except in locations with very low prevalence of HCV. Screening is also recommended during pregnancy and for patients of any age with risk factors for HCV infection. In patients with risk factors, periodic screening is recommended for as long as risk factors persist.
Risk factors for HCV include:
- Current or past injectable drug use
- Having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Receiving kidney dialysis
- Pain in the abdomen or joints
- Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
- Jaundice or yellowish skin and eyes
Hepatitis C testing may also be performed when liver tests are abnormal or when diagnosing the cause of existing liver damage.
Recommended Reading: Early Signs Of Hepatitis C
Specific Hcv Rna Assays And Range Of Detectable Virus
HCV RNA tests use target amplification techniques. Several assays exist for HCV RNA testing. Methods include polymerase chain reaction , transcription mediated amplification , and branched chain DNA tests. Results are expressed as international units/mL . The different methods and different commercial assays each have a lower limit of quantification and lower limit of detection , therefore a patient’s results could be reported differently depending on the assay used. HCV RNA tests must have an LLOQ of 25 IU/mL or lower when used to assess treatment response with DAAs.
LLOQ = the lowest HCV RNA level that is within the linear and analytically acceptable range of the assay.
LLOD = the lowest level of HCV RNA that is detected 95% of the time.
Taking A Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C testing is conducted on a sample of blood. Blood samples can be collected by a doctor, nurse, technician, or other health care provider from an adult patients vein using a small needle or a skin prick on a childs heel.
For an at-home hepatitis C test, patients collect a blood sample according to the manufacturers directions. Instructions provided in the test kit detail the steps to obtain a small sample of blood and mail it for testing.
Also Check: Hepatic Steatosis Versus Hepatocellular Disease
Testing For Acute Hepatitis C
Between 1-8 weeks after transmission of hepatitis C, HCV RNA becomes detectable by PCR testing. Although most patients will have some liver function test abnormalities from 6-12 weeks after transmission, only about a quarter will have the syndrome of malaise, abdominal pain, and jaundice that characterizes acute hepatitis C disease. By 12 weeks after development of hepatitis C viremia, up to 25% of patients will spontaneously and permanently clear the virus.40 Spontaneous clearance appears to be much more common in those with the syndrome of acute hepatitis C than in those with asymptomatic viremia.41 Development of hepatitis C antibodies occurs as early as 8-10 weeks after transmission.42 Some immunosuppressed individuals may not develop hepatitis C antibodies despite the presence of viremia.43
| COBAS Amplicor HCV test 2.0 | PCR Roche |
| qPCR Abbott | 25 – 5 x 108 |
| *Results may vary at the lower limit of detection depending on the laboratory performing the test§Research Use Only – Not approved for patient usebDNA: branched chain DNAqPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reactionTMA: transcription mediated assayThe use of proprietary names does not constitute endorsement by the NYS DOH. |
The Hepatitis C Testing Process
In the case of a suspected new infection, two test results are usually required to confirm if someone currently has hepatitis C.
Screening test
The first test is a screening test, which is an antibody test. This test detects antibodies in the blood to determine if a person has ever had a hepatitis C infection.
- A non-reactive screening test result indicates that the person does not have hepatitis C antibodies and has never had a hepatitis C infection. No further testing is usually performed.
- If the antibody test is reactive , this means that the person has antibodies to hepatitis C and therefore has had a hepatitis C infection at some point in their life.
The antibody test alone cannot tell whether the person has a current hepatitis C infection. A person will test positive for hepatitis C antibodies if they have hepatitis C at present, but also if they had a hepatitis C infection in the past. In other words, people will still have hepatitis C antibodies even if they spontaneously cleared the virus in the past or if they were treated and cured.
Confirmatory test
The second test is a confirmatory test, which detects the hepatitis C virus itself. This test detects genetic material of the virus to determine if a person currently has a hepatitis C infection.
Reinfection
If a person has had a positive antibody test result in the past, they will test positive for hepatitis C antibodies every time they have another screening or antibody test.
You May Like: How Much Is A Hepatitis A Shot
Are Test Results Accurate
Although no test is perfect, hepatitis C testing is an important and accepted method of testing for HCV. In order to reduce the risk of inaccurate results, doctors take steps to verify a patients diagnosis. For example, a positive test result for hepatitis C antibody requires confirmation with HCV RNA testing.
Positive Hcv Antibody And Positive Hcv Rna
Individuals with a positive HCV EIA and positive HCV RNA should be told they have evidence of active hepatitis C infection and they should clearly understand they need medical follow-up evaluation and potential treatment of liver disease. A single positive HCV RNA value indicates infection, but must be interpreted in the context of clinical history to determine whether the individual has acute or chronic infection. For persons with a positive HCV EIA and positive HCV RNA, the CDC has generated counseling messages that focus on four areas: contacting a health care provider for further evaluation and management of their HCV infection, protecting their liver from further harm, addressing weight management in overweight and obese persons, and minimizing transmission of their HCV to others . In addition, the CDC recommends performing alcohol screening and brief intervention, which consists of screening for excessive alcohol consumption, brief counseling for individuals who screen positive, and referral to a specialized alcohol treatment program for individuals with possible alcohol dependence.
You May Like: Long Term Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Immunoassays For Hcv Core Antigen
As an HCV diagnostic marker, HCV core antigen has been studied, either alone or as an HCV antibody-HCV antigen combination assay. Some experts have proposed use of an HCV core antigen test as a less expensive option than HCV RNA testing, but there are no HCV antigen assays that are FDA-approved for use in the United States at this time.
Looking Further: Hcv Vaccines
Vaccine development for HCV is currently one of the most challenging fields in virology today. Various obstacles that hinder the development of an effective preventive or therapeutic vaccine for HCV include:
Considerable genetic heterogeneity of isolates within and between geographic locales .
Evolution and existence of quasispecies in an individual .
Poorly defined immunological correlates of protection.
Lack of efficient in vitro propagation to isolate the virus.
Despite these obstacles, both preventive as well as therapeutic vaccines for HCV are under development and also under various phases of vaccine trials, but a successful vaccine remains to be developed.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Signal To Cut Off
When To Get Tested
For screening: at least once when you are age 18 years or older when you are pregnant when you have risk factors for HCV infection, regardless of age
For diagnosis: when you may have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, such as through injection drug use, or when you have signs and symptoms associated with liver disease
For monitoring: before, during, and after hepatitis C treatment
Hcv Core Antigen Detection
During the past decade, several assays for the detection of the core antigen of HCV by ELISA or CLIA have been developed. These assays were envisioned as alternatives to NAT to be used in resource-limited settings, where molecular laboratory services are either not available or not widely utilized owing to cost issues. Since these assays are either ELISA or CLIA based, they are user friendly, require less technical expertise and are less expensive compared to molecular techniques. Evaluations in transfusion settings have shown that the HCVcore Ag assay detects HCV infection as effective as NAT, about 40-50 days earlier than the current third generation anti-HCV screening assays. HCV core antigen levels closely follow HCV RNA dynamics, and allow clinical monitoring of a patient’s therapy, independently of HCV genotype. The major limitation of the HCV core Ag assay is its lower sensitivity limiting its utility. A new generation CLIA based quantitative test with sensitivity comparable to that of end point PCR but less than that of real time RT-PCR has been reported.
Also Check: How Common Is Hepatitis B
Rapid Hiv Antibody Testing
Rapid HIV antibody tests can provide results in less than 30 min and can be adopted in point of care settings. These tests are also based on either immunochromatography or immunoconcentration techniques. Since 2002 the FDA has approved six rapid HIV tests . Most of these tests can utilize whole blood, thus avoiding the need to centrifuge specimens to obtain serum. However, OraQuick Advanced HIV1/2 assay can use whole blood, serum, or oral fluid. The FDA has recently approved the OraQuick for Home HIV test, a rapid home-use HIV kit that uses oral fluid test results can be obtained in 2040 min. Most rapid HIV tests are based on the principles of enzyme immunoassays that are utilized in clinical laboratories and use automated or semi-automated analyzers. Most tests detect HIV antibodies by incorporating HIV envelop-region antigens in the test methodology. However, both false positive and false negative results can occur with rapid HIV tests, and it is important to confirm initial findings with a laboratory-based HIV assay. These tests are used for rapid screening only. Delaney et al. evaluated six rapid HIV antibody tests and observed sensitivities over 95% and specificity over 99% for all rapid tests. However, false negative and false positive results were observed in all rapid HIV assays . Facente et al. observed that false positive rates for oral fluid HIV tests increase near the expiration date of the kit .
Table 23.3. Examples of Available Rapid HIV Tests
| Rapid Test |
|---|
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis C testing is performed by a doctor. Testing requires a blood sample, which can be collected in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Blood is often drawn from a vein in the arm or, in children, taken by pricking the skin. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Also Check: How Do You Spread Hepatitis C
Noninvasive Testing To Assess Liver Fibrosis
Recommendation
The use of non-invasive tests to assess liver fibrosis is not yet recommended.
Various non-invasive tests are being investigated for staging degree of liver fibrosis. These tests may be used in decisions regarding whether or not to initiate antiviral therapy and to monitor the effects of such therapy. 44 An array of such tests would be highly desirable if adequately validated, since liver biopsy may not be readily available in view of the large number of affected patients with hepatitis C, the risks involved in performing liver biopsies, and the problem of sampling error on biopsy that can underestimate cirrhosis in 10-30% of cases.
Standard liver biochemical tests, measures of liver function such as coagulation studies, and radiological imaging of the liver may be sufficiently sensitive to diagnose advanced cirrhosis but have not been accurate in defining evolving hepatic fibrosis and early stages of cirrhosis.44 A number of studies have been published employing a variety of indirect markers of liver fibrosis including standard liver chemistries, platelet count, prothrombin index, and lipoprotein A1 concentrations. These tests have gained acceptance in Europe as alternatives to liver biopsy.45, 46 However, the utility of these tests requires further validation in prospective studies.