Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Causes Of Noninfectious Hepatitis
Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue and liver failure.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. Itâs three times more common in women than in men.
Hepatitis Types Symptoms And Treatments
Hepatitis is a disease that includes any type of inflammation of the liver, the result of a complex process that occurs when the liver suffers an injury. This can be confusing if you have a type of hepatitis that is not an infectious disease. The word hepatitis can simply be broken down into the words “hepa” which refers to the liver, and “itis” which refers to inflammation.
You May Like: A Cure For Hepatitis C
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
Hepatitis B is primarily spread when blood, semen, or certain other body fluids- even in microscopic amounts from a person infected with the hepatitis B virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted from:
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
What Causes Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is caused by infection with the hepatitis A virus. You get the virus when you unknowingly eat a small amount of infected feces. This can happen through person-to-person contact, or through eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
A person can have and spread hepatitis A, even if that person does not have any symptoms. You are most likely to get hepatitis A from another person when:
- A person who has the virus does not wash their hands properly after going to the bathroom
- A parent does not wash their hands properly after changing the diaper of an infected child
- A caregiver does not wash their hands properly after cleaning up the stool of an infected person
- A person has sex with a person who has the virus
You can also get infected with hepatitis A by eating contaminated food or drinking contaminated water. Contaminated food and water are more common in developing countries. When traveling in areas where hepatitis A is common, avoid eating raw fruits and vegetables, shellfish, ice, and untreated water.
Recommended Reading: Blood Test For Hepatitis C Screening
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis B
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis B is to control the virus and keep it from damaging the liver. This begins with regular monitoring for signs of liver disease. Antiviral medications may help, but not everyone can take them or needs to be on medication. Be sure to discuss the risks and benefits of antiviral therapy with your doctor.
You Can Prevent Infection Even After You Have Been Exposed
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis A virus in the last 2 weeks, talk to your doctor about getting vaccinated. A single shot of the hepatitis A vaccine can help prevent hepatitis A if given within 2 weeks of exposure. Depending upon your age and health, your doctor may recommend immune globulin in addition to the hepatitis A vaccine.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis C: What Happens
About 25% of people who get hepatitis C defeat the virus after a short-term infection. The rest will carry the virus in their body for the long term. Chronic hepatitis C can cause very serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer. There are effective treatments for the virus, though.
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
You May Like: How Does Hepatitis C Transmitted
How Long Before I Have Symptoms
Many people have mild symptoms or no symptoms, which is why hepatitis is sometimes called a âsilentâ disease.
Hepatitis A. The symptoms usually show up 2 to 6 weeks after the virus enters your body. They usually last for less than 2 months, though sometimes you can be sick for as long as 6 months.
Some warning signs that you may have hepatitis A are:
Hepatitis B. The symptoms are the same as hepatitis A, and you usually get them 3 months after you’re infected. They could show up, though, anywhere from 6 weeks to 6 months later.
Sometimes the symptoms are mild and last just a few weeks. For some people, the hep B virus stays in the body and leads to long-term liver problems.
Hepatitis C. The early symptoms are the same as hepatitis A and B, and they usually happen 6 to 7 weeks after the virus gets in your body. But you could notice them anywhere from 2 weeks to 6 months later.
For about 25% of people who get hep C, the virus goes away on its own without treatment. In other cases, it sticks around for years. When that happens, your liver might get damaged.
Remember, it’s possible to spread all the types of hepatitis even if you don’t show any signs of being sick.
Hepatitis A: How Does It Spread
It usually spreads through food or water. Food can be tainted when it’s touched by a person with hepatitis who did not wash their hands after using the bathroom. This transfers tiny amounts of infected stool to the food. Raw shellfish, fruits, vegetables, and undercooked foods are common culprits in hepatitis A outbreaks. The virus can also spread in daycare centers if employees aren’t careful about washing hands after changing diapers.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Kissing
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A accounts for 20 percent to 25 percent of hepatitis cases in developed countries. Hepatitis A is usually transmitted through the fecal-oral route, meaning a person somehow ingests contaminated feces from an infected person. If an infected person did not wash his or her hands properly after using the bathroom, the disease may spread from the persons hands. The incubation period is two to six weeks, during which the infected individual is contagious.
Another cause of hepatitis A is eating shellfish harvested from contaminated water. Developing countries experience hepatitis A epidemics caused by drinking water contaminated with raw sewage.
The prognosis for hepatitis A patients is excellent with self-limiting course, and recovery is complete. About 85 percent of people with hepatitis A recover within three months, and almost all recover within six months. The disease does not become chronic, and there are no long-term health implications.
Acute Hepatitis B Infection
There is no specific treatment for acute hepatitis B, and most people recover within one to two months. Usually, you can manage symptoms at home with painkillers if necessary. Your healthcare professional should advise you to have regular blood tests and physical check-ups. Most people make a full recovery from acute hepatitis B.
Read Also: How Can You Catch Hepatitis A
How Do You Prevent Hepatitis
Both hepatitis A and hepatitis B can be prevented with a vaccine. There is currently no vaccine available to prevent hepatitis C.
To prevent spreading or getting hepatitis A:
- Wash hands with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds after using the bathroom, changing diapers, touching garbage or dirty clothes, and before preparing food and eating
- Follow guidelines for food safety
- Avoid unpasteurized milk or foods made with it
- Thoroughly wash fruits and vegetables before eating
- Keep the refrigerator colder than 40°F and the freezer below 0°F
- Cook meat and seafood until well done
- Cook egg yolks until firm
- Wash hands, knives, and cutting boards after contact with raw food
To prevent spreading or getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C:
- Practice safe sex and use a latex condom each time you have sex
- Dont share razors, toothbrushes, or any personal objects that might have blood on them
- Dont share needles or syringes
- Cover cuts and open sores with bandages
- Clean blood off of things with a mixture of bleach and water: use 9 parts bleach to one-part water
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
You May Like: What Is Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Can Hepatitis A Be Prevented
Yes. The hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for all children over 1 year old. Having many young kids vaccinated against HAV can limit the spread of the disease in a community.
The vaccine also is recommended for older kids, teens, and adults who have never gotten it.
If you babysit or take care of young kids, be sure to wash your hands well and often, especially after going to the bathroom or changing a diaper, and before preparing or eating food.
You Might Not Know You Have It
Nearly half of people living with hepatitis C dont know they have it. Thats because most people live with the disease for years without feeling sick, or experiencing only minor symptoms such as fatigue. Frequently, the only indication of hepatitis C is an abnormal liver blood test panel. If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis C, be sure to talk to your physician.
Read Also: Best Medication For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
When Should I Contact A Doctor About Hepatitis A
If you have recently been exposed to a source of HAV and are unsure if you are vaccinated, contact your health-care professional, as it is possible to get vaccine or even immunoglobulin treatment to prevent the disease and/or its symptoms.
If you have the disease, contact your health-care professional for symptomatic treatment methods to help prevent HAV spread to family and friends. Some individuals have more severe symptoms and may need to be hospitalized.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Catch Hepatitis C
What If You Test Positive
If a test says you have viral hepatitis, you can take steps to protect the ones you love. For hepatitis A, wash hands frequently. For hepatitis B and C, avoid sharing nail clippers, razors, or toothbrushes. Hepatitis B, and sometimes hepatitis C, can be passed through sexual contact. Make sure everyone in your household gets the hepatitis B vaccine. An important step is to see a specialist to discuss treatment options.
How Do You Get Hepatitis A
The main way you get hepatitis A is when you eat or drink something that has the hep A virus in it. A lot of times this happens in a restaurant. If an infected worker there doesn’t wash their hands well after using the bathroom, and then touches food, they could pass the disease to you.
Food or drinks you buy at the supermarket can sometimes cause the disease, too. The ones most likely to get contaminated are:
- Shellfish
- Ice and water
You could catch or spread it if you’re taking care of a baby and you don’t wash your hands after changing their diaper. This can happen, for example, at a day care center.
Another way you can get hep A is when you have sex with someone who has it.
Also Check: How Many Hepatitis B Shots Are Required
How Long Does The Hepatitis A Vaccine Last
We dont know exactly how long the protection of the vaccine lasts, but studies have indicated that it lasts at least 20 years in some people and it could last as long as 40 years or more. Having only one dose of the recommended two-dose vaccine has shown to provide protection for at least 10 years.
What Causes Hepatitis In A Child
Hepatitis in children can be caused by many things. Your child can get hepatitis by being exposed to a virus that causes it. These viruses can include:
-
Hepatitis viruses. There are 5 main types of the hepatitis virus: A, B, C, D, and E.
-
Cytomegalovirus. This virus is a part of the herpes virus family.
-
Epstein-Barr virus. The virus causes mononucleosis.
-
Herpes simplex virus. Herpes can affect the face, the skin above the waist, or the genitals.
-
Varicella zoster virus . A complication of this virus is hepatitis. But this happens very rarely in children.
-
Enteroviruses. This is a group of viruses often seen in children. They include coxsackie viruses and echoviruses.
-
Rubella. This is a mild disease that causes a rash.
-
Adenovirus. This is a group of viruses that causes colds, tonsillitis, and ear infections in children. They can also cause diarrhea.
-
Parvovirus. This virus causes fifth disease. Symptoms include a slapped-cheek rash on the face.
Conditions can also cause hepatitis in children. These can include autoimmune liver disease. For this disease, your childs immune system makes antibodies that attack the liver. This causes inflammation that leads to hepatitis.
Read Also: Where Can You Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis C: Who Is At Risk
People who have injected illegal drugs at any time, even one time, many years ago, could be walking around with chronic hepatitis C. Because there are often no symptoms, many former drug users may not realize they have the infection. People who received a blood transfusion before 1992 also have a higher risk. Before that year, donated blood was not screened for the hepatitis C virus.
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
Read Also: What Type Of Cirrhosis Is Caused By Hepatitis C
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis A
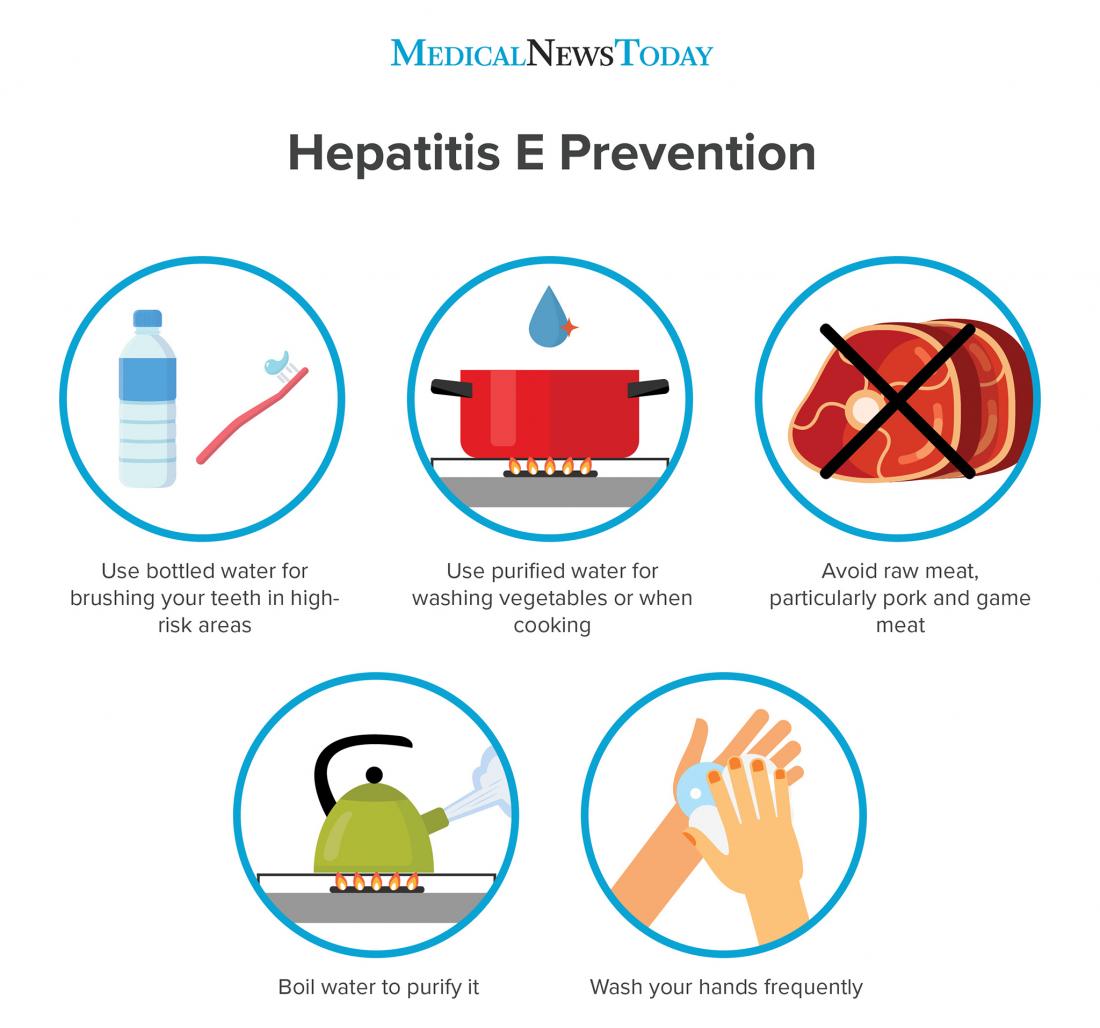
There is a vaccine, made from an inactivateddeadvirus to prevent hepatitis A. If you are not sure you have had the vaccine, you can ask your doctor to test you to see if you have been vaccinated.
You can also practice good hand washing hygiene. Make sure you use soap and warm water to wash your hands for at least 15 to 30 seconds after you use the toilet, change diapers, and before and after touching food.
If you are traveling in another country, especially a developing country, drink only bottled water and use only bottled water to brush your teeth, wash your produce, and freeze for ice cubes.