What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
Significant progress has been made in treating and even curing hepatitis C. Older hepatitis C treatments usually required weekly injections, had serious side effects, and often were not effective.
New and better oral medicines now can cure HCV for many people within 3 months. The new medicines were very expensive at first, but their prices have come down, a trend that health experts hope will continue as the incidence of HCV rises and increased screening brings more cases to light.
These medicines successfully cure about 90% of HCV patients. A new oral medicine under development looks promising for the 10% who don’t respond to the standard treatment. This new antiviral combination pill is currently under review by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
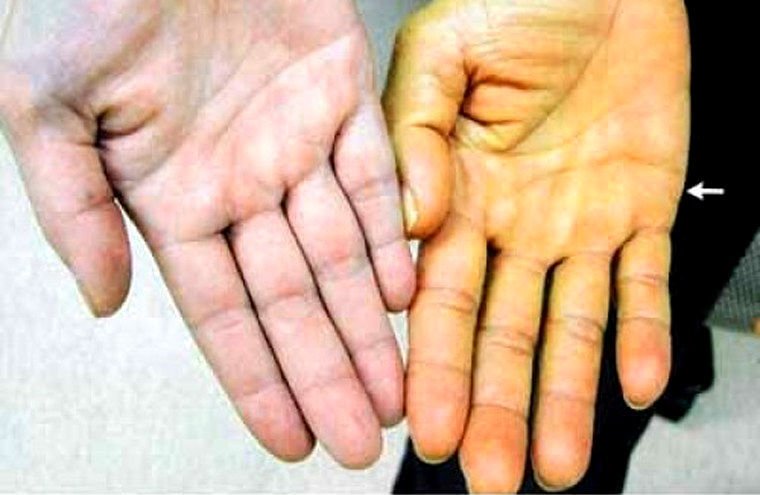
General Symptoms Of Liver Diseases
Liver disease symptoms may be present with hepatitis, cirrhosis, or any other conditions that result in dysfunction of or damage to the liver. These may include:
More symptoms of acute hepatitis are possible, including bleeding gums, edema in your legs, sleep reversal and other sleep disorders, and loss of consciousness.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Liver Failure
Can Cirrhosis Be Reversed
Generally no. If you have been told you have cirrhosis, you have a late-stage liver disease and the damage that is already done is permanent. There are many liver diseases and complications of liver diseases that can lead to cirrhosis. If your liver disease or complication is caught early and successfully managed, it may be possible to slow or stop the progression of disease.
Complications Of Liver Cirrhosis
Without medical treatment, cirrhosis of the liver can lead to a range of potentially life-threatening complications including:
- bleeding from enlarged blood vessels in the oesophagus or stomach
- build-up of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- infection of the fluid found within the abdominal cavity
- liver failure loss of liver cells and disruption of blood flow through the liver by scar tissue can impair liver function
- impaired functioning of the brain caused by toxins that the liver has failed to remove .
- primary liver cancer the most common type of cancer caused by cirrhosis is hepatocellular carcinoma
- osteoporosis
Tests used to diagnose liver cirrhosis may include:
- medical history
- blood tests, including liver function tests
- urine tests
- imaging studies, including ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging
- transient elastography , this test uses an ultrasound-based technique to detect liver cirrhosis. This test is less accurate in people with obesity issues unless specially designed XL probes are used.
- liver biopsy, obtaining liver tissue for laboratory examination.
Recommended Reading: How To Reverse Hepatic Steatosis
Related Conditions And Causes Of Hepatitis C
Other types of viral hepatitis include hepatitis A, B, D, and E.
Hepatitis A and E are generally acquired from contaminated food and drink, while hepatitis B and D are transmitted via bodily fluids. You can only get hepatitis D if you already have hepatitis B.
Though viruses are the most common causes of hepatitis, there are also forms of nonviral hepatitis, including:
- Alcoholic hepatitis caused by prolonged alcohol abuse, per the Mayo Clinic
- Autoimmune hepatitis, in which the immune system attacks healthy liver cells, per the NIDDK
One of the most common reasons for liver transplantation in the United States is organ failure due to hep C. This network serves as a comprehensive resource for those exploring liver transplant options, organ donation, and medical advances. Profiles of people who have had transplants and connections to support groups are available.
What Is Hepatitis C Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, and hepatitis C is liver inflammation caused by the hepatitis C virus .
Journal of Clinical MicrobiologyJournal of Infectious Diseases
Though these genotypes appear to affect people similarly, they respond differently to treatments, and it’s possible to be infected with more than one HCV genotype at the same time.
Whatever the genotype, hepatitis C is considered either acute or chronic .
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Hepatitis B Viral Load Naturally
Are There Stages Of Cirrhosis
If you have been diagnosed with cirrhosis of the liver, you are already beyond the early stages of liver disease. Having cirrhosis means your liver has scar tissue in it because it has been damaged.
Liver specialists and researchers have developed many different scoring systems to predict outcome and to guide treatment for chronic liver disease. Some specific liver diseases also have their own scoring systems. However, not every liver disease has a scoring system and theres no scoring system if you happen to have more than one liver disease at the same time.
For these reasons, perhaps its easier to talk about cirrhosis according to a classification system you are more likely to hear from your healthcare provider. He or she may refer to you having either compensated cirrhosis or decompensated cirrhosis.
Compensated cirrhosis means you have cirrhosis but you dont yet have noticeable symptoms . Your lab work and imaging findings may not be abnormal. A liver biopsy may be the only way to confirm a diagnosis of cirrhosis. Median survival in patients with compensated cirrhosis is approximately nine to 12 years.
Primary Goals In Management Ofdecompensated Cirrhosis
- Treatment of etiology of the underlying liver disease
- Antiviral treatment of HCV or HBV is more complicated
- Abstinence from alcohol
- Prevention of further decompensation and death
- Prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage: beta-blockers + ligation, TIPS if recurrent
- Alcohol use: complete abstinence
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Active Hepatitis C
Differences Between Hepatitis And Cirrhosis
There are many important differences between hepatitis and cirrhosis, even when they may have the same cause.
- Reversibility. By definition, cirrhosis is irreversible, whereas hepatitis may be completely reversible depending on the cause.
- Blood tests.Liver enzymes are often very elevated with hepatitis, especially acute hepatitis. With cirrhosis, however, at least in the early stages, liver function tests may be only slightly abnormal.
- Conditions other than hepatitis can lead to cirrhosis. For example, hemochromatosis, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, and more can lead to cirrhosis.
- Treatments. With hepatitis, the goal is usually to alleviate the diseasefor example, treat the infection, remove a drug causing drug-related hepatitis, or decrease weight and increase metabolism with NASH. With cirrhosis, the scarring is permanent and cannot be treated. Therefore, the goal is to treat symptoms related to cirrhosis and to prevent any further liver injury.
- Symptoms. Portal hypertension leading to esophageal varices, an enlarged spleen, a low platelet count, and a low protein level in the blood are more common with cirrhosis than with hepatitis.
Cirrhosis And Hepatitis Are Liver Diseases
Chronic
Both cirrhosis and hepatitis cause inflammation of the liver and damage the organ. Both can cause bad complications, such as causing permanent injury to the liver, leading to liver cancer.
When viewed from the cause of occurrence, these two diseases can occur due to the same thing, for example, long-term drug consumption and excessive alcohol consumption.
When viewed from the cause of occurrence, these two diseases can occur due to the same thing, for example, long-term drug consumption and excessive alcohol consumption.
Symptoms and signs are also almost difficult to distinguish, such as jaundice, itching on the surface of the skin, accumulation of fluid that causes the stomach to become distended, swelling of the legs, vomiting blood, difficulty sleeping, prolonged fatigue, and loss of consciousness.
Difference between Cirrhosis and Hepatitis
The difference between cirrhosis and hepatitis that you need to know is the chance of recovery. In most cases, hepatitis can be cured, especially if the symptoms are detected early. In contrast to cirrhosis, it is more difficult to cure, because it is a chronic infection that causes many wounds to the liver.
The next difference is the treatment carried out. Hepatitis will be cured with some drugs and balanced with enough rest. However, the treatment given depends on the type of hepatitis experienced. Meanwhile, treatment for cirrhosis is in the form of surgery or liver transplantation.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Drug Card
Making The Diagnosis Of Compensated Vs Decompensated Cirrhosis
- Cirrhosis can be diagnosed with clinical, laboratory, radiologic, elastographic, or biopsy findings
- The diagnosis of compensated cirrhosis is more challenging since patients may lack clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings and may require biopsy for diagnosis
- The diagnosis of decompensated cirrhosis is easier as the patient history, physical exam, and laboratory findings are usually more evident
Child-Turcotte-Pugh score
- TheChild-Turcotte-Pugh score is used as a prognostic scoring system in cirrhosis based on 2 clinical and 3 laboratory parameters:
- Ascites: none diuretic-sensitive or mild/moderate diuretic-refractory or tense
- Encephalopathy: none episodic or overt grade 2 recurrent/chronic or grade 3-4
- Albumin in g/dL:> 3.5 3.4-2.8 < 2.8
- Bilirubin in mg/dL:< 2 2-3 > 3
- INR:< 1.7 1.7-2.3 > 2.3
Smv Plus Sof: Cosmos Trial
The COSMOS study evaluated the efficacy of combined SOF plus SMV in patients with HCV genotype 1 infection who had previously not responded to peg IFN and ribavirin or were treatment naïve. Patients in this study were assigned in a 2:2:1:1 ratio to receive 150 mg SMV and 400 mg SOF orally and once daily for 12 or 24 wk with ribavirin or without ribavirin in two cohorts – Cohort 1 and Cohort 2 . Table shows the results of the COSMOS study demonstrating SVR in patients in each cohort. The most common side effects in the pooled groups were fatigue , headache , and nausea . This study also showed that the combination of SOF plus SMV achieved excellent SVR rates in all subgroups regardless of duration of therapy or co-administration of ribavirin in difficult to treat patients. Although, it should be noted that this study was not powered to show non-inferiority of ribavirin -free regimens and hence benefit from RBV is not apparent from the results of the study.
Read Also: How To Cure Hepatitis A Fast
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Read Also: Royal Canin Hepatic Dog Food
Hepatitis C And Liver Cancer: What To Know
Several viruses besides HPV have been linked to cancer, includinghepatitis C, which is linked to liver cancer.
If you think HPV is the only virus that causes cancer, think again. Several other viruses have been linked to cancer, including hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is the most common blood-borne infection in the United States. Its also the leading cause of liver cancer.
About 30 percent of people who get exposed to the hepatitis C virus will clear it on their own. The rest will go on to have chronic hepatitis C.
This ongoing infection causes inflammation in the liver. This extended inflammation can cause scarring, called cirrhosis, and can ultimately lead to liver cancer.
Chronic hepatitis C also increases the risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and head and neck cancers.
Unlike hepatitis A and B, there is no vaccine against hepatitis C, and there are few if any symptoms, says Harrys Torres, M.D., associate professor of Infectious Diseases.
Its a silent infection, he says. And its a very clever virus that mutates very fast, so it has been difficult to develop a vaccine.
Knowing the risk factors and getting screened are your best defenses against cancers caused by hepatitis C. Treatment of this virus can reduce your risk of liver cancer by 75%.
Risk factors
About 75% of those infected with hepatitis C in the United States are baby boomers people born between 1945 and 1965.
Other risk factors for hepatitis C infection include:
Chronic Hepatitis Cirrhosis Adenoma Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocyte necrosis and mitosis of chronic hepatitis favor nodular regeneration, which in appropriate circumstances, is followed by hepatocyte dysplasia and carcinoma.
In many parts of the world HCC is among the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, and the third most common cause of cancer death in the world. Japan, for example, unlike other Asian countries, also has a high proportion of HCC caused by HCV infection accounting for 80 to 90% of all cases, while in the western world hepatocellular carcinoma is known to complicate cirrhosis secondary to hepatitis C in 2-6% per year.
There is currently no evidence that HCV by itself is oncogenic however, HCC may rarely develop in non-cirrhotic HCV-infected individuals, so a direct oncogenic effect cannot be excluded. However, in the pathogenesis of HCC associated with HCV, it remains controversial whether the virus plays a direct or indirect role. Recent studies using transgenic mouse models, in which the core protein of HCV has an oncogenic potential, indicate that HCV is directly involved in hepatocarcinogenesis, albeit other factors such as continued cell death and regeneration associated with inflammation would also play a role.
Almost all HCC occurs in the liver of patients with chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis, caused by HBV and HCV. Consequently, eradication of these hepatitis viruses with anti-viral agents and chemoprevention methods may decrease the risk of HCC.
Don’t Miss: Is There A Home Test For Hepatitis C
Recommended Hcv Treatment With Compensated Cirrhosis
For individuals with compensated cirrhosis , including those with hepatocellular carcinoma, the AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance provides recommendations for initial treatment and retreatment . Although the treatment recommendations for persons with and without cirrhosis have significant overlap, there are, in some instances, key differences in the recommended regimens, duration of therapy, or inclusion of ribavirin. Thus, when treating HCV in persons with compensated cirrhosis, it should not be assumed the treatment is the same as those without cirrhosis and AASLD-IDSA treatment guidelines should be closely checked and followed.
Relation Between Hepatitis C And Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma accounts for 85 to 90% of the cases of primary liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis constitute the major preneoplastic conditions in the majority of HCC. The risk of developing HCC for a patient with HCV-related cirrhosis is approximately 2-6% per year. HCC risk increases to 17-fold in HCV-infected patients compared to HCV-negative subjects. In general, HCC develops only after two or more decades of HCV infection and the increased risk is restricted largely to patients with cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis.
Multiple steps are required in the induction of all cancers it would be mandatory for hepatocarcinogenesis that genetic mutations accumulate in the hepatocytes. In HCV infection, however, some of these steps might be skipped in the development of HCC, in presence of the core protein. The overall effects achieved by the expression of the core protein would be the induction of HCC, even in the absence of a complete set of genetic aberrations, required for carcinogenesis. By considering such a non-Vogelstein type process for the induction of HCC, a plausible explanation might be given for many unusual events happening in HCV carriers.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis Do To The Body