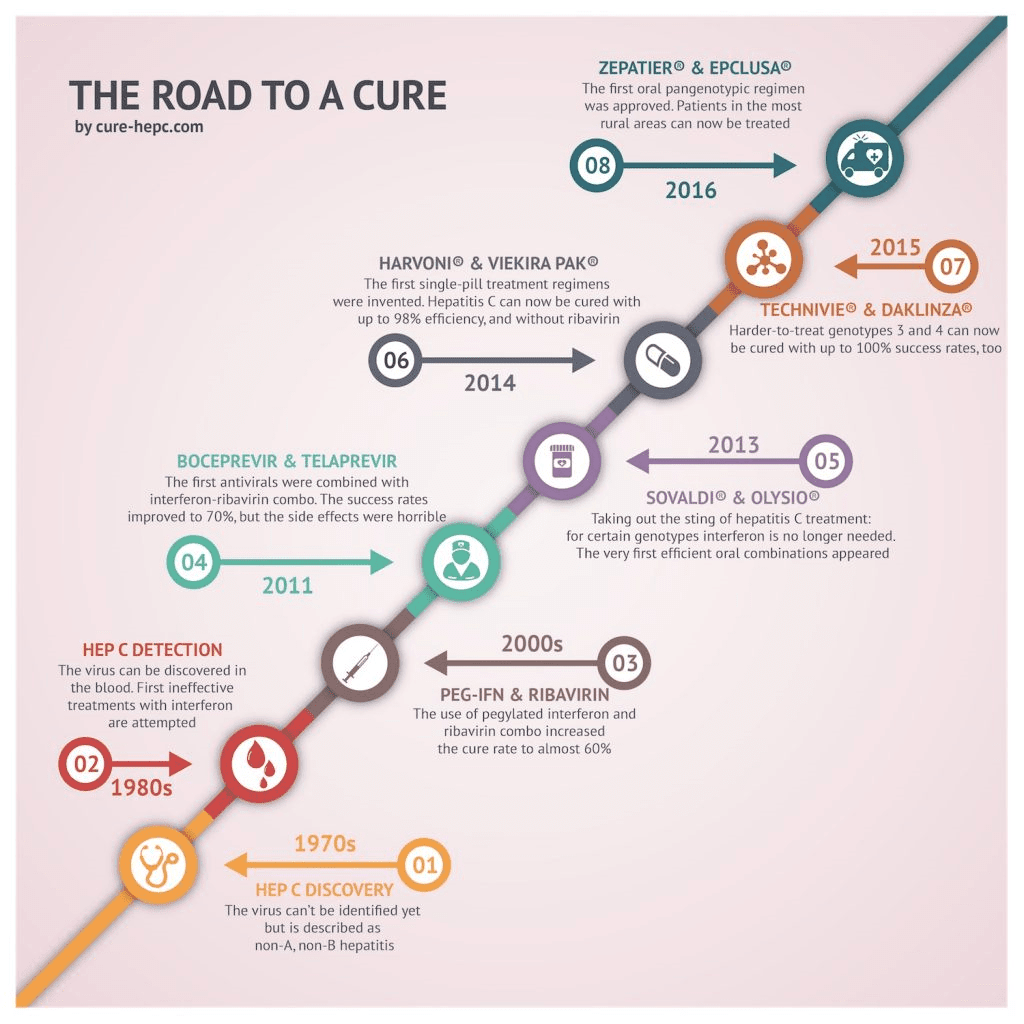
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Barriers To A Cure For Hepatitis C
While a potential cure for hepatitis C exists, it doesn’t mean that the cure is accessible for most people carrying the virus. A number of factors have historically limited access to even the newly improved HCV treatments. One of the biggest is that screening for hepatitis C isn’t universal. Many people don’t know they’re infected. Therefore, they can’t be treated.
Another factor is that it’s really important for people to adhere to their treatment regimen and follow-up plan. If someone’s virus is resistant to a treatment, other options are available. However, healthcare providers don’t want more resistant viruses to develop, and thus they may be reluctant to prescribe these drugs to patients who are unlikely to take them reliably. There are also concerns that high-risk hepatitis C patients, such as those who inject drugs, may be at risk of re-infection.
That said, cost-effectiveness research suggests that hepatitis C treatments are a good deal in the long term. That’s true even when they’re given to people with early, “silent” HCV or those who are at high risk for reinfection. Furthermore, the CDC now recommends all adults born between 1945 and 1965 receive one-time testing for the virus.
Don’t Miss: How Many Types Of Hepatitis C Are There
Can A Transplant Cure Hepatitis C
If you develop chronic hepatitis C and it leads to liver cancer or liver failure, you may need a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is one of the most common reasons for a liver transplant.
A liver transplant removes a damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy one. However, theres a high likelihood that the hepatitis C virus will be transmitted to the new liver in time.
The virus lives in your bloodstream, not just your liver. Removing your liver wont cure the disease.
If you have active hepatitis C, continued damage to your new liver is very likely, especially if hepatitis C remains untreated.
Living With Hepatitis C
Coping with hepatitis C isnt easy. You may feel sad, scared, or angry. You may not believe you have the disease. These feelings are normal, but they shouldnt keep you from living your daily life. If they do or if they last a long time you may be suffering from depression. People who are depressed have most or all of the following symptoms nearly every day, all day, for 2 weeks or longer:
- Feeling sad, hopeless and having frequent crying spells.
- Losing interest or pleasure in things you used to enjoy .
- Feeling guilty, helpless, or worthless.
- Thinking about death or suicide.
- Sleeping too much or having problems sleeping.
- Loss of appetite and unintended weight loss or gain.
- Feeling very tired all the time.
- Having trouble paying attention and making decisions.
- Having aches and pains that dont get better with treatment.
- Feeling restless, irritated, and easily annoyed.
Talk to your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms. Your doctor can help by recommending a support group or a therapist. He or she may also prescribe a medicine for you to take.
Read Also: How Do You Contract Hepatitis A
How Can I Cover Medication Costs
New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are effective and can achieve cures of over 90%. Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Talk with your healthcare provider about financial support that may be available.
Below are useful resources when looking for financial assistance:Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded plansEach provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Programs for Hepatitis C treatment Holkira Pak Maviret
MerckCare Hepatitis C Program 1 872-5773 Zepatier
Who Is At Risk Of Infection
In Québec, most new infections are linked to injectable drug use. More rarely, transmission can occur during sex or from a mother to her fetus. Hepatitis C is more widespread in certain regions outside of Canada where transmission also occurs during non-sterile medical procedures.
The following can increase your risk of exposure to infection:
- sharing non-sterile materials for injection or inhalation
- tattooing, piercing or transfusion with non-sterile materials
- having unprotected sex when there is a high risk of bleeding
- being incarcerated
Public health authorities have also observed high rates of hepatitis C in people born between 1950 and 1969 . It is therefore recommended for people in this age group to be screened once in their life.
You May Like: How Can You Treat Hepatitis C
Chronic Phase Of Hepatitis C
After six months 70% to 85% of those infected will have failed to clear the virus spontaneously. After this period the hepatitis C virus enters what is known as the chronic phase. This is when hepatitis C becomes a chronic or long-term infection. The diagnosis is confirmed when over a six month period hepatitis C RNA viral presence is detectable on at least two occasions.
A diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C means the battle between the virus and the immune system that occurs during the acute stage has finally been won by the virus. It is now highly unlikely that the virus can be cleared without treatment.
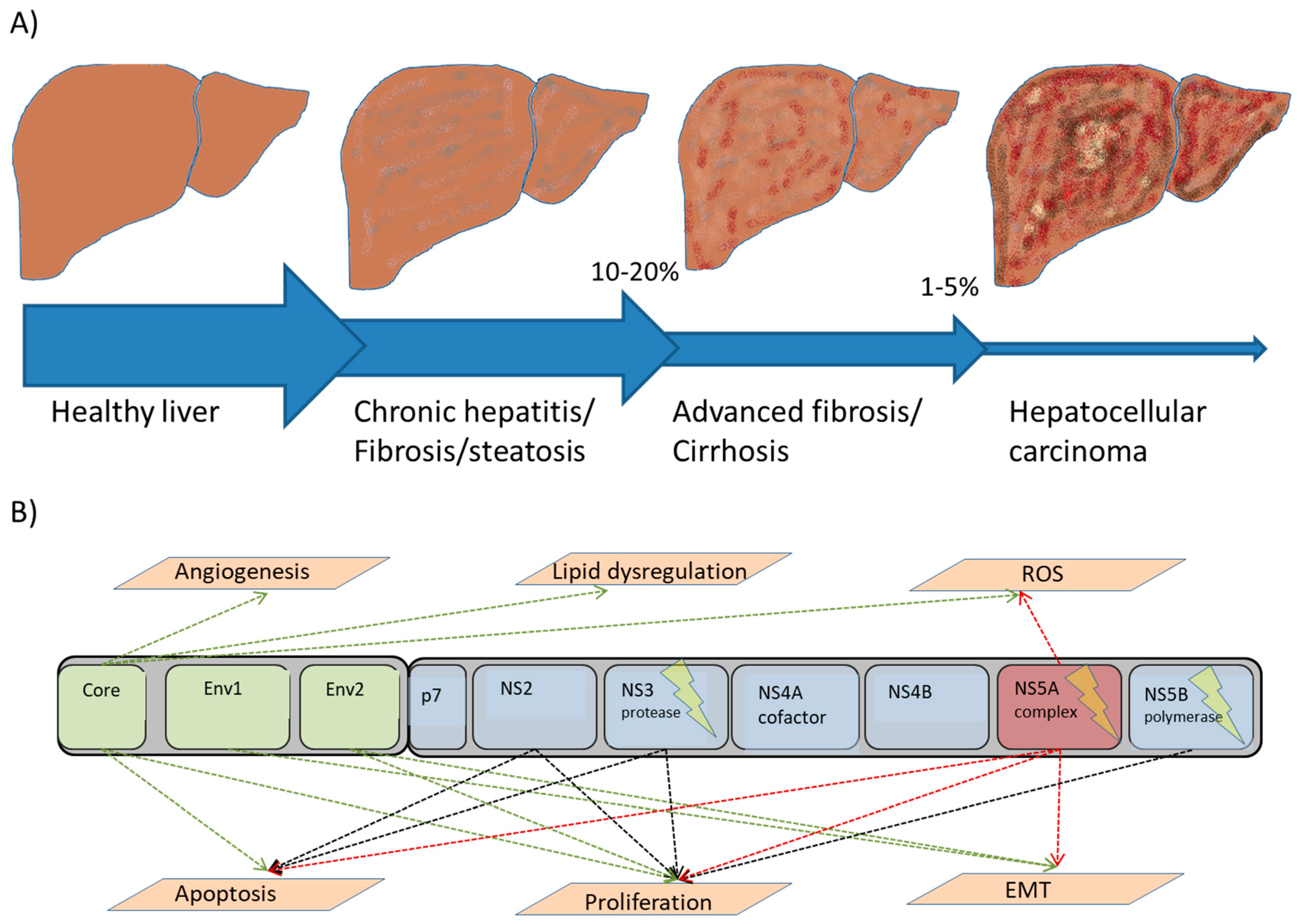
How the disease then progresses varies significantly from person to person. After many years some people will have minimal liver damage with no scarring while others can progress to cirrhosis within less than ten years. On average it takes about twenty years for significant liver scarring to develop. It is still not known whether chronic hepatitis C infection inevitably leads to cirrhosis. At present it is thought that this is a very likely outcome, although for some people it may take at least 50 years or more. They may well die of other unrelated diseases or conditions before cirrhosis develops. The rate of progression of liver damage cannot be accurately determined by liver enzyme levels, viral load or by genotype.
Liver damage and fibrosis during the chronic stage
Free Radicals and Fibrosis
Monitoring While On Treatment
Recommendations
Patients who do not achieve virologic suppression or a 2-log decrease in HCV RNA at 12 weeks may have therapy discontinued, although factors such as degree of fibrosis and tolerability of therapy should be considered.
Patients should have a CBC and chemistry evaluations 2 weeks after initiation of treatment to assess for potential toxicities. CBC, chemistry evaluations, and pregnancy tests in women should be done routinely at each follow-up visit and not less often then every 4-6 weeks during treatment.
Patients who achieve an end-of-treatment virological response should have HCV RNA testing performed 24 weeks after stopping treatment to evaluate for a SVR.
Erythropoetin alfa and granulocyte colony stimulating factor may be used to treat anemia and neutropenia, respectively, in order to maintain the patient on full medication doses.
Providers should reference the full discussion of side effects of hepatitis C treatment in Appendix A.
Pegylated interferon and ribavirin have been found to be safe and effective in HCV mono-infection and in co-infection with HIV.2,61 Safety and efficacy has not been established in patients who have received liver or other organ transplants, in patients who have failed other alpha interferon treatments and in patients under the age of 18.56,57
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Cvs
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
Acute hepatitis C is a short-term illness that can occur within the first six months after being exposed to the virus. The modes of infection are via sexual intercourse, needle stick injury, infected blood transfusion, infected organ transplant, dialysis or a mother to her child during delivery. People are also at risk if they have engaged in high-risk behaviors like intravenous drug use, shared needles or had unprotected sex.
In many cases, early hepatitis C infection can clear on its own without treatment in about one in four individuals. This is especially possible in younger people. The treatment options for hepatitis C include
Antiviral medications
These are the mainstay of treatment against hepatitis C. The treatment aims to have no detected hepatitis C virus in the body at least 12 weeks after treatment.
The “direct-acting” antiviral medications are given over 12 weeks. These are combination medications and will cure early acute hepatitis C in more than 90 percent of people. They are
- Harvoni
- Viekira Pak
The choice of medications and length of treatment depend on the
- Hepatitis C genotype
- Presence of existing liver damage
- Co-existing medical conditions
The Prevalence Of Hepatitis C
2,967 cases of acute hepatitis C were reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2016. However, many people with hepatitis C do not experience symptoms others experience symptoms, but do not know the cause of their illness. In reality, the CDC estimates there were as many as 41,200 cases of hepatitis C in 2016 nearly 14x the number of cases actually reported.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C Virus Caused By
Hepatitis: Which Forms Of This Virus Are Curable
There are several types of hepatitis, some require little to no treatment while others can leave you with more serious conditions such as cirrhosis or cancer of the liver. In this article, we identify the main types, the effect they have on the body, whether they are curable and how to prevent contracting the disease.
Whats in this article
- The facts
- How can I prevent hepatitis?
The factsHepatitis is most often caused by a virus which inflames the liver and can disappear without treatment or progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer. There are three major types of hepatitis: A, B & C. Unlike A and B, a vaccine for hep C is not available. According to the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, in 2009, there were about 16,000 reported cases of acute hepatitis C and approximately 3.2 million people in the United States are living with chronic hepatitis C.
All strains of the disease can be diagnosed through a blood or tissue sample among other methods. Ensure that you consult your doctor if you suspect you have have been infected by one of them.
Types of hepatitis
There are many types of this disease, however, the following are the most common forms:
Is hepatitis curable?In conclusion, we have found that whether this disease is curable greatly depends on what type of the disease you have contracted.
Find out more about the basics of liver health with Dr. Tarek Hassanein, M.D.
How Effective Is Treatment
Direct-acting antivirals cure 9 out of 10 patients with hepatitis C.
Successful treatment does not give you any protection against another hepatitis C infection. You can still catch it again.
There’s no vaccine for hepatitis C.
If treatment does not work, it may be repeated, extended, or a different combination of medicines may be tried.
Your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C Virus Ab
If You Notice Symptoms See A Doctor Right Away
Symptoms of hepatitis C include the following:
- Jaundice a yellowish tone to the eyes and skin
- Mild, chronic right belly pain
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
If you believe you have been exposed to hepatitis C or notice any symptoms, visit your primary care doctor as soon as possible. If you test positive for the virus, your doctor can refer you to a hepatologist to discuss your options.
“I strongly encourage all baby boomers and others who are at high risk to get tested, even if you don’t look or feel sick,” Reau says. “If you do have hepatitis C, the earlier we discover it, the more likely we can prevent it from progressing and causing more serious damage.”
Accessibility And Hbsag Clearance Rate
HBsAg clearance occurs spontaneously or via antiviral treatment in CHB patients. The most commonly used drugs are nucleoside analogue and pegylated interferon . NA drugs include entecavir , tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and tenofovir alafenamide fumarate . The 2018 AASLD guidelines recommend Peg-IFN, ETV, or TDF as the preferred initial therapy for adults with immune-active CHB. It also suggests that alanine transaminase levels be tested at least every 6 months for adults with immune-tolerant CHB to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or immune-inactive CHB . The 2017 EASL guideline recommends ETV, TDF and TAF as the preferred monotherapy regimens, and the extension of the duration of Peg-IFN therapy beyond week 48 may be beneficial in selected HBeAg-negative CHB patients . The potential side effects of NAs include lactic acidosis for ETV and nephropathy, osteomalacia, lactic acidosis for TDF. CHB patients should be clinically monitored. The most frequently reported side effects for Peg-IFN are flu-like syndrome, myalgia, fatigue, mood disturbances, weight loss, hair loss and local reactions at the site of injection, and these side effects may be partially managed with dose reduction . Currently, the clearance of HBsAg is based primarily on sequential or combined treatment with NA and Peg-IFN.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
What Does It Mean To Have A Successful Treatment What Is A Sustained Virologic Response
In an untreated state, the hepatitis C virus infects the cells of the liver and then continuously lives there, making copies of itself that circulate in the bloodstream. Antiviral medications can destroy the ability of the virus to reproduce, so the amount of virus in the bloodstream then decreases. The amount of virus in the blood is measured by aviral load.
Treatment is successful when the viral load drops toundetectablelevels, which means the virus cannot be detected in the bloodstream at all. The viral load becomes undetectable during treatment and remains undetected after treatment has ended. If there is still no detectable virus in the blood 12 weeks after the end of the treatment, the treatment was successful. This is called a Sustained Virologic Response .
A patient who has achieved an SVR is considered to be cured of the hepatitis C virus.
You May Like: What Is Chronic Hepatitis B