Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel
A Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel includes a Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total , Hepatitis B Surface Antigen , Hepatitis B Surface Antibody .
CPT Code: See Individual Tests
Also Known As:
No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results:
2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
CPT Code: See Individual Tests
Also Known As:
No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results:
2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Also Check: How Long Are Hepatitis B Shots Good For
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
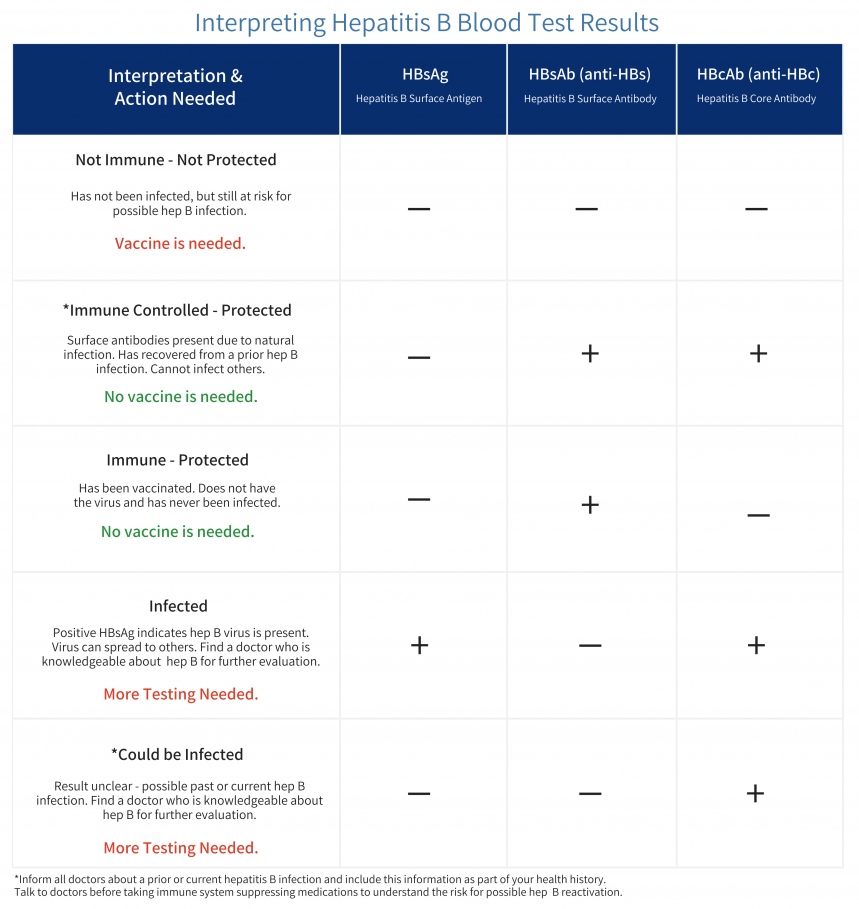
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Fatty Liver
Recommended Tests To Investigate Chronic Hbv Infection And The Interpretation Of Results
Chronic HBV infection is defined by the continued presence of HBsAg in the blood for longer than six months. Figure Figure11 and Table Table22 outline the tests used to diagnose most cases of chronic HBV. Test selection should be based on the person’s risk factors, vaccination history and findings from previous tests .
Diagnostic tests for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection . ALT Alanine aminotransferase Anti-HAV-IgM Immunoglobulin M class antibody to HAV Anti-HCV Antibody to HCV antigens HBsAg Hepatitis B surface antigen
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients may find it helpful to ask questions about their hepatitis B test results. Questions that may be helpful include:
- What was my test result?
- Do I have an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity for hepatitis B?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis B vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis B test results?
You May Like: How Much Does Hepatitis C Treatment Cost
Assessment Of Hbv Immune Status
Immunity to HBV is acquired from a resolved infection or from vaccination .2). The HBV vaccine has been shown to induce protective immunity in 90% to 95% of vaccinees. Most vaccinees will have protective levels of anti-HBs for five to 10 years after vaccination, although the exact duration of immunity remains undefined. When anti-HBs levels have waned below the protective threshold of 10 mIU/mL, a booster dose of HBV vaccine has been shown to induce a strong anamnestic immune response in such individuals. It is therefore probable that protection from chronic HBV infection may last for decades and may well be lifelong .
Investigation of hepatitis B virus immunity. Anti-HBc-Total Total antibody to hepatitis B core protein Anti-HBs/HBsAb Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen
The HBV immune status can be determined using the tests outlined below, but testing for vaccine immunity in the general population is not indicated unless the individual is at high risk of infection .3). Nonimmune individuals should be offered HBV vaccination where clinically appropriate.
Specimen Choice Collection And Transport
The specimen of choice for the diagnosis of HBV infection is blood. Serological tests for viral antigens and antibodies are typically used for diagnostic screening and can be performed on either serum or plasma. Both HBV antigens and antibody are stable at room temperature for days, at 4°C for months, and frozen at -20°C to -70°C for many years. Because modern testing involves automated enzyme immunoassays that depend on colourimetic or chemiluminescence signal measurement, care should be taken to avoid hemolysis of the sample because it may interfere with the ability of the assay to accurately detect these markers.
A number of nucleic acid-based tests, which have been the subject of recent reviews , are available to directly detect HBV-DNA in serum or plasma. Care must be taken to avoid the degradation of the viral nucleic acid in the specimen, which can result in falsely low or no measurable viral load. Serum should therefore be removed from clotted blood within 4 h of collection and stored at -20°C to -70°C , and can be subjected to up to eight short-term freeze-thaw cycles without significant loss of detectable HBV-DNA . Alternatively, the presence of EDTA in plasma is known to stabilize viral nucleic acids. EDTA blood can be stored for up to five days at 4°C without affecting the viral load . Polymerase chain reaction-based tests can use either serum or plasma, while hybridization-based assays recommend the use of serum.
Read Also: How To Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Blood Tests And Diagnosis For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is diagnosed with a simple blood test that can be done at your doctors office or local health clinic. There are 3 parts to the hepatitis B panel of blood tests, so understanding your test results can be confusing. Are you infected with hepatitis B? Are you protected from hepatitis B because you were vaccinated or have recovered from a past infection? Are you at risk of being infected with hepatitis B? It is very important to understand your hepatitis B blood test results so that you receive the right kind of care and follow-up.
The hepatitis B blood test requires only one sample of blood and your health care provider should order the Hepatitis B Panel, which includes three parts. You and your health care provider will need to know all three test results in order to fully understand whether you are infected, protected or still at risk for a hepatitis B infection. Your health care provider may ask to check your blood again in six months after your first visit to confirm your hepatitis B status. Remember to ask for a copy of your hepatitis B blood test results so that you fully understand which tests are positive or negative.
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Recommended Reading: How You Get Hepatitis A
Igm Class Antibody To Hav
- If the IgM class antibody to HAV is negative, HAV infection is ruled out in immunocompetent patients .
- If positive, acute HAV infection is likely. As the anti-HAV-IgM may remain detectable for up to two years after infection in a small subset of patients, the history and clinical presentation must be considered in making an accurate diagnosis .
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Also Check: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis B
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patientâs body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a personâs ability to spread HBV to others.
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel Includes:
Anti-Hepatitis B Core Antigen is an antibody to the hepatitis B core antigen. The core antigen is found on virus particles but will disappear early in the course of infection. This antibody is produced during and after an acute HBV infection and is normally found in chronic HBV carriers and those who have cleared the virus, and usually persists for life. Anti-HBc testing is either specific for the IgM antibody, anti-HBc, IgM, which will indicate acute infection, or measures total antibody, anti-HBC, which will indicate a past infection, either acute or chronic.
The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody is the most common test. Its presence will indicate previous exposure to HBV, but the virus is no longer present and the person cannot pass the virus on to others. The antibody will also protect the body from future HBV infection. In addition to exposure to HBV, these antibodies can also be acquired from successful vaccination. This test is performed to determine the need for vaccination , or following the completion of vaccination against the disease, or following an active infection.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen is a protein antigen produced by HBV. This antigen is the earliest indicator of acute hepatitis B and often identifies infected people before symptoms appear. HBsAg will disappear from the blood during the recovery period. In some people , chronic infection with HBV may occur and HBsAg will remain positive.
Management Of Pregnant Hbv Carriers
Pregnant HBV carrier mothers present a unique opportunity to prevent transmission of HBV to their neonates. All infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should receive hepatitis B immune globulin and a full course of HBV vaccination . Vaccine failure in the neonate is rare but does occur , and may be accounted for by transplacental transmission before birth. Follow-up testing of the neonate should be performed to confirm vaccination effectiveness. Testing should be performed for HBsAg to detect vaccine failures, anti-HBs to confirm a successful vaccine response and anti-HBc-Total to determine if the anti-HBs response was due to vaccination or resolution of natural infection. While testing for these markers is recommended one to two months after completion of the vaccine series, testing at approximately 18 months would ensure that the anti-HBc-Total test does not represent maternal antibody. This may be important because vaccination failures have occasionally been associated with HBV vaccine escape mutants that may only demonstrate a positive anti-HBc-Total as the sole marker of infection. These mutations occur in the open reading frame of the HBsAg, may not be recognized by antibodies induced by current HBV vaccine, and may not be detected by currently available HBsAg enzyme immunoassays . Clearly, surveillance systems need to be in place to ensure that HBV vaccines remain effective and vaccine escape mutants do not replace current HBV strains.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Can You Get Rid Of It
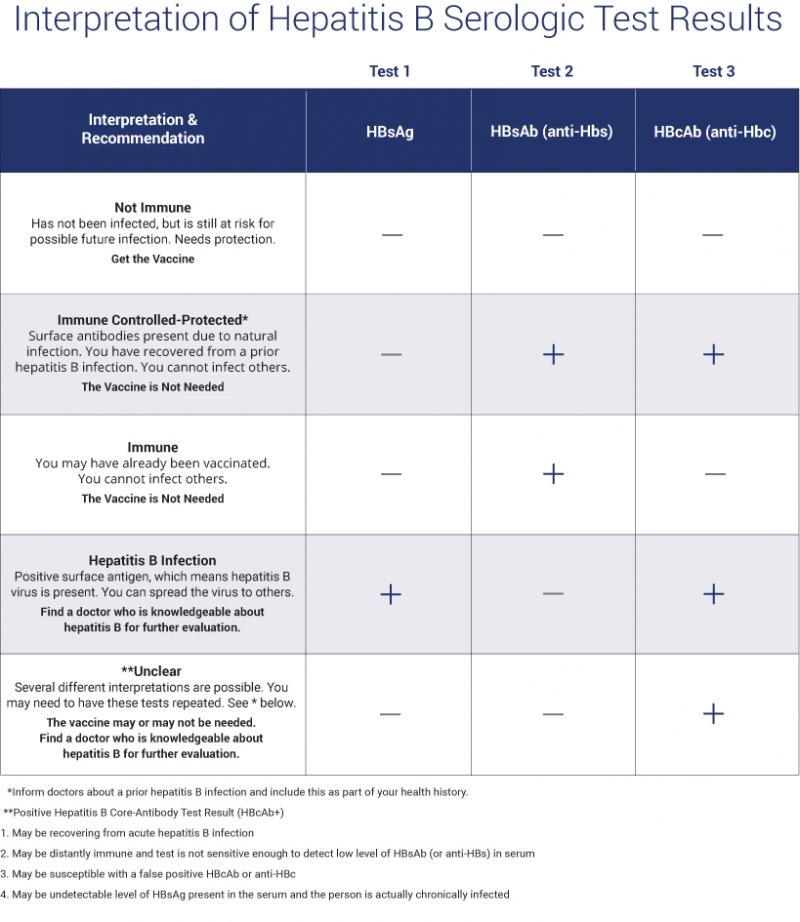
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
Your health care provider will ask about your medical history and symptoms. Especially important is your history of Hepatitis B risk factors such as IV drug abuse.Your provider will examine your skin and eyes for signs of Hepatitis B. Your provider will check your abdomen to see if the liver is enlarged or tender.You will have blood tests. If blood tests show that your liver is not working normally, your provider will do tests to see if you are infected with the Hepatitis B virus.
Questions about online blood testing or how to order a lab test?
Also Check: What Is The Worst Hepatitis Ab Or C