Hepatitis And Cirrhosis Similarities And Differences
Robert Burakoff, MD, MPH, is board-certified in gastroentrology. He is the vice chair for ambulatory services for the department of medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, where he is also a professor. He was the founding editor and co-editor in chief of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.
Hepatitis and cirrhosis are both diseases that affect the liver. Since hepatitis and cirrhosis are in many ways on a continuum of disease, the symptoms may be very similar. However, there are a number of important differences between the two.
In general, hepatitis may or may not be reversible , whereas cirrhosis refers to permanent scarring of the liver, often as the result of chronic hepatitis. While some forms of hepatitis may come on very rapidly, cirrhosis also tends to develop more gradually.
Lets take a look at the symptoms that may occur with both diseases, review the basics of each disease, and then outline some of their main similarities and differences.
The Best Foods And Drinks For Hepatitis C
Nutritious foods like fruits and vegetables promote liver health when you have hepatitis C. Others, such as alcohol and salt, can make the condition worse.
Although theres no specific diet that will benefit every one of the nearly 4 million people in the United States currently living with hepatitis C, certain foods and drinks may boost liver function. Others, however, may be harmful to the liver.
Whats more: People with hepatitis C have an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease, so making smart choices and maintaining a normal weight can help keep these threats at bay. A healthy diet should be considered an important part of your overall treatment plan.
You May Like: What Are Some Symptoms Of Hepatitis
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
- older adults
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
You May Like: Hepatitis C In Food Service Workers
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be contracted only through direct blood contact. In the U.S., the primary mode of transmission is blood exposure through sharing needles. Mother-to-child transmission is about 5 percent of cases. Hepatitis C infection might also be a risk for people who received a blood transfusion or an organ transplant before 1992, when widespread testing of the blood supply for hepatitis C began.
Three Types Of Hepatitis And What To Do About Them
Contact our practice at 410-224-4887 if you suspect you or a loved one has any form of hepatitis.
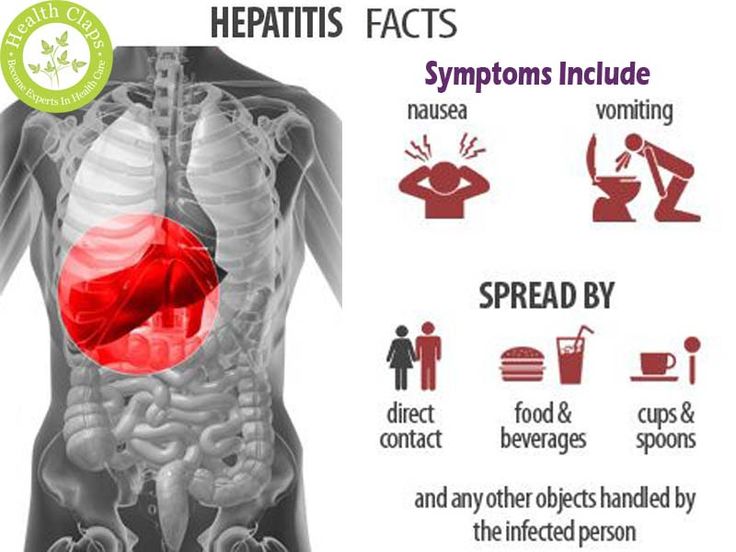
Hepatitis describes inflammation of your liver, the most common types being caused by one of several viruses. Hepatitis symptoms can make you sick for the short term or cause long-term, chronic liver problems.
When you have a form of hepatitis, it affects your livers ability to function. If your body cant clear the virus from your system, you may face long-term liver damage, liver failure, or liver cancer.
At Digestive Disorders Associates in Annapolis, Maryland, the expert team of board-certified gastroenterologists can help you recover from an acute form of hepatitis or manage your long-term infection.
Heres more about the most common forms of viral hepatitis and what you can do to heal.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Totally
Difference Between Hepatitis A B And C
Hepatitis A vs B vs C
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver due to a viral infection. Even though the liver is involved in all types of hepatitis, the virus type, route of transmission, natural history and treatment protocols are different between the types of hepatitis. This article will discuss the virus type, route of transmission, signs and symptoms, investigation and diagnosis, natural history, and treatment protocols of each type of hepatitis and compare them to differentiate one from the other.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a food and water borne infection. Hepatitis A virus is a RNA virus. Usually travelers to tropical countries fall victim to this infection. Children get this infection easily. Virus enters the body via food or water and incubates for 3 to 6 weeks before causing prodromal symptoms like fever, ill health, lethargy, body ache, joint pains. During the active phase, yellowish discoloration of eyes develops with liver, spleen and lymph node enlargement.
Full blood count shows low white blood cell count and low platelets. Serum transaminases rise during the active phase. AST and ALT rise are more than ALP rise. ALT rises more than AST. Serum IgM rises after 25 days of exposure to indicate recent infection. After sero-conversion IgG remains detectable for life.
Hepatitis A is self-limiting but fulminant hepatitis is a rare possibility. Chronic hepatitis does not occur with hepatitis A.
Hepatitis B
Treatment is supportive. Alcohol avoidance is essential.
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Also Check: Hepatic Porphyrias Diagnosis And Management
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Symptoms of hepatitis B are the same as those of hepatitis A: Jaundice, fever, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, joint pain, nausea and vomiting, and weakness and fatigue are common. Some of the more common ways to acquire hepatitis B are through sex with an infected person where sexual body fluids can enter your body, use of IV drugs and/or sharing needles, being born to a hepatitis B positive mother, being a man who has sex with men, traveling to an area such as Africa, Asia or Eastern Europe, and being stuck with a needle in a healthcare setting. Hepatitis B is considered a sexually transmitted infection.
Chronic hepatitis B may lead to cirrhosis, liver cancer, and/or liver failure. Hepatitis B may also lead to kidney disease, and anemia. There are treatments for hepatitis B, but there is no cure, and a liver transplant may be required for the patient to live. There is a preventative vaccine for hepatitis B.
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis B And C Spread
How Do You Get It
HAV can be present in the stool and blood of someone with the virus. Its mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which involves ingesting virus thats present in the stool of someone with hepatitis A.
There are several ways you can get hepatitis A:
- having close person-to-person contact with someone who has hepatitis A, such as:
- taking care of someone whos currently sick
- having sex with someone who has the virus
Read Also: How Do You Cure Hepatitis
Hepatitis Caused By Toxins
- The most common cause is excessive alcohol over a prolonged time. Alcoholic hepatitis is reversible if alcohol is reduced, but can go on to cause longer-term liver damage .
- Medication some medicines can cause liver inflammation as a side-effect.
- Haemochromatosis an unusual condition where the body stores too much iron, can cause hepatitis.
- Wilsons disease an unusual condition where liver damage is caused by copper excess in the body.
Hepatitis A B And C: Whats The Difference
Hepatitis is often caused by a virus that comes in different strains. The most common strains of hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, and C. They all are contagious, but they differ primarily by the way they are spread.
Table: Differences among hepatitis A, B, and C
Table: Differences among hepatitis A, B, and C
Recommended Reading: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis
Acute Vs Chronic Infection
Doctors distinguish between chronic and acute infection with hepatitis viruses. Acute infection is a short-term condition, lasting under six months. Chronic infection is a long-term condition, lasting more than six months.
Hepatitis B infection can be either acute or chronic. Most people who get acute hepatitis B dont end up progressing to chronic hepatitis B. By contrast, acute hepatitis C tends to develop into chronic hepatitis C. Approximately 7585 percent of adults newly infected with hepatitis C develop a chronic infection, according to the CDC . Others clear the infection.
When you get acute hepatitis C you may or may not have symptoms. Most cases of acute hepatitis C are asymptomatic, meaning people dont notice the symptoms. Symptoms are only noticeable in 15 percent of cases of acute hepatitis C.
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Recommended Reading: New Medicine For Hepatitis C
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis
The three most common types of hepatitis in the United States are A, B, and C, but there are five types in total. All of these forms of hepatitis target the livers ability to function. Here are the differences between them:
- Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus, which spreads through the blood and stool of people infected by the virus.
- Hepatitis B is also caused by a virus spread through bodily fluids from an infected person however, it can be prevented through the use of vaccines.
- Hepatitis C is also a viral form of hepatitis. It can be short-term or long-term. As a chronic infection, it can cause life-threatening health issues like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
- Hepatitis D, also known as delta hepatitis, only occurs concurrently within people who also have the hepatitis B virus.
- Hepatitis E,though not particularly common in the United States, can spread from eating raw or undercooked pork, shellfish, or wild game.
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C Antibody
Also Check: Hepatic Steatosis Treatment Step By Step
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A Vaccine San Diego Free
How To Protect Yourself Against Hepatitis C
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine available for hepatitis C, but you can protect yourself by avoiding behaviors such as sharing needles and syringes. In addition, the CDC recommends people born between 1945 and 1965 get tested for hepatitis C. Testing is also recommended for people who were treated for blood-clotting problems before 1987 and recipients of blood transfusions or donated organs before 1992.
The UNC Liver Center has a clinic in Chapel Hill that specializes in hepatitis B and C, incorporating the latest clinical trials and most up-to-date therapies. Treatment for hepatitis is also available at our locations in Asheville, High Point, Raleigh and Wilmington. To learn more, call 966-2516.
Michael Fried, MD, is the director of the UNC Liver Center and a professor of medicine at the UNC School of Medicine.
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
Dont Miss: Can Your Body Heal Itself From Hepatitis C
Read Also: Can You Donate Plasma With Hepatitis C
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has not been vaccinated or previously infected can get infected with the hepatitis A virus. In areas where the virus is widespread , most hepatitis A infections occur during early childhood. Risk factors include:
- poor sanitation
- living in a household with an infected person
- being a sexual partner of someone with acute hepatitis A infection
- use of recreational drugs
- travelling to areas of high endemicity without being immunized.
Deterrence And Patient Education

Patient education is key to preventing and controlling hepatitis, especially viral and alcoholic hepatitis. Patients who have viral hepatitis must obtain education educated regarding the importance of routine follow-up and the importance of monitoring the disease progression and development of complications. They should learn about the importance of personal hygiene, including frequent handwashing. People who are traveling to endemic areas should be advised not to drink untreated water or ingest shellfish or raw seafood, and fruits and veritable should always be eaten after being cooked or after being peeled. Patients who have hepatitis A should not handle food for others until they stop shedding the virus. Patients should receive instruction about not sharing any articles, including toothbrushes, razors, or needles that have the potential for contamination with saliva, semen, or blood. All the patients should avoid using hepatotoxic agents, including alcohol and acetaminophen. Patients who are having a disease progression with liver disease should be referred to a gastroenterologist or hepatologist promptly. Patients with features of liver damage that includes liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and features of portal hypertension should be monitored with routine labs.
Vaccination
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis G
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C Virus
How Do You Get Hepatitis A
The main way you get hepatitis A is when you eat or drink something that has the hep A virus in it. A lot of times this happens in a restaurant. If an infected worker there doesn’t wash their hands well after using the bathroom, and then touches food, they could pass the disease to you.
Food or drinks you buy at the supermarket can sometimes cause the disease, too. The ones most likely to get contaminated are:
- Shellfish
- Ice and water
You could catch or spread it if you’re taking care of a baby and you don’t wash your hands after changing their diaper. This can happen, for example, at a day care center.
Another way you can get hep A is when you have sex with someone who has it.
How Do You Treat Hepatitis C
When Dr. Fried started treating hepatitis C in 1990, the cure rate was 7 percent. Treatments have evolved since then, leading to a 95 percent cure rate. The treatment course includes taking one to a few pills a day for 12 to 24 weeks, and the medicines have few side effects. Hepatitis C is the only chronic viral infection that you can routinely cure, thanks to these new medicines.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Titer Blood Test