Challenges In Implementation Of Birth Dose Vaccination In Low
There are several reasons why many low-resource countries are having difficulty implementing birth dose vaccination within 24 hours of birth. These include:
Of note, HBIG is also not available or feasible in many low-income countries because its storage requires a cold chain and complex production.2
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Symptoms And Disease Progression
The majority of adults with hepatitis B have no symptoms, and infection is often only diagnosed by routine blood tests and monitoring the health of the liver. Among people living with HIV, routine liver function monitoring sometimes shows elevated liver enzymes, which can be a sign of liver inflammation due to hepatitis B.
Some people develop symptoms soon after hepatitis B infection, known as the acute phase. These can include the following:
- fatigue
- pain in the upper abdomen or belly
- muscle or joint aches
- feeling generally unwell
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes .
A minority of people may develop severe symptoms during acute hepatitis B infection, and in rare cases it can lead to death.
After the acute stage , many people with chronic hepatitis B have few or no symptoms. Others may experience ongoing symptoms including fatigue and feeling unwell. Even if you have no symptoms, you can still pass on hepatitis B to others.
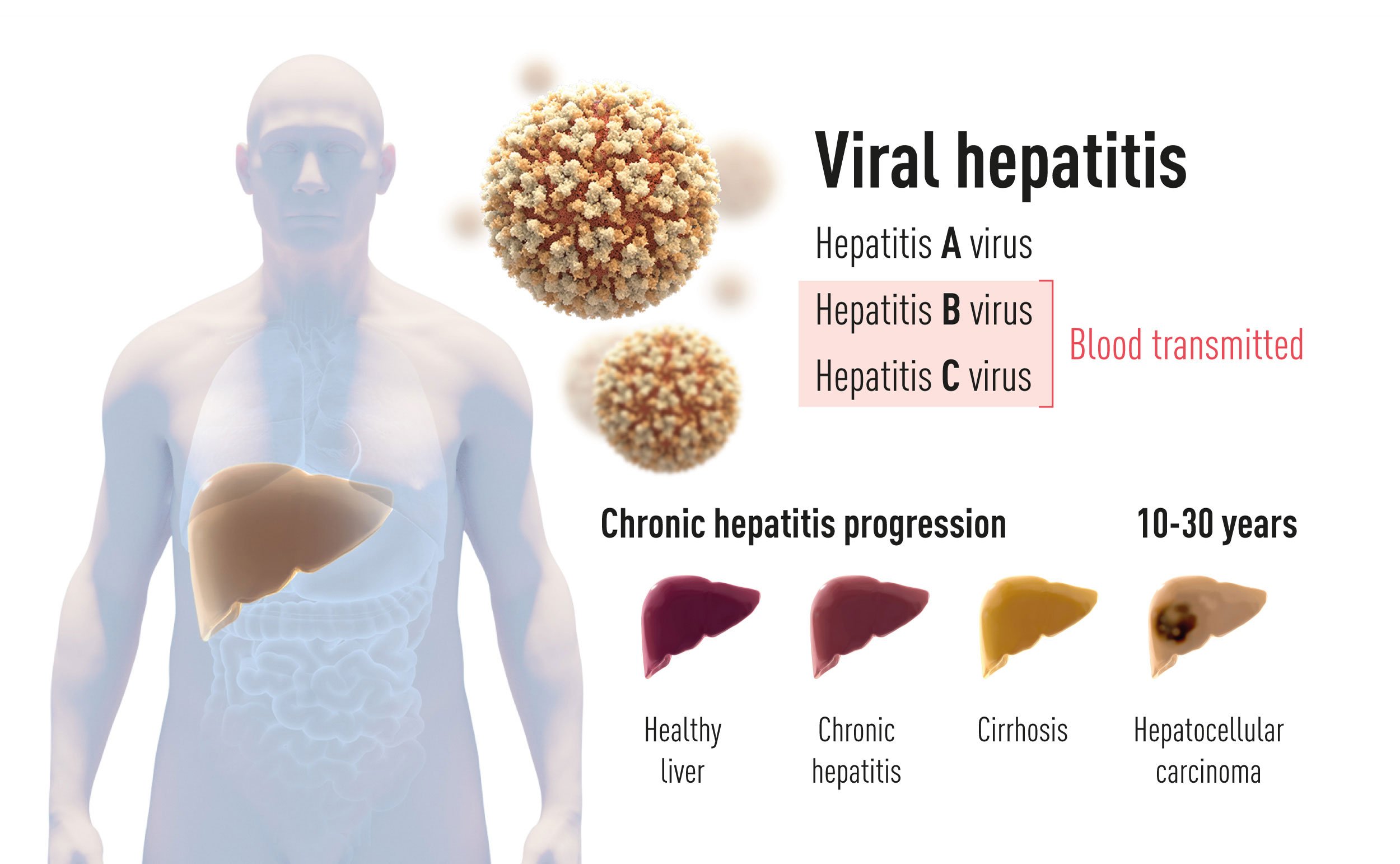
With or without symptoms, chronic hepatitis B infection can lead to serious liver disease over years or decades, including fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
No Fewer Than 20 Million Nigerians Are Living With The Hepatitis B Virus A Gastroenterologist Prof Adamu Samaila Of The Department Of Medicine Bayero University Kano Says
Samaila, who is a professor of Gastroenterology/Hepatology, disclosed this on Friday at the awareness lecture and screening exercise for HBV organised by the Nigerian Air Force for its personnel in Abuja.
He explained that viral hepatitis is an infection of the liver caused by a virus, and the five types of viruses most commonly responsible for viral hepatitis infection are: Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D and Hepatitis E.
Samaila, who noted that hepatitis is a common problem worldwide, said that there were many misconceptions about the ailment.
He said that HBV causes 80 per cent of all liver cancer in human beings, adding that the virus could be transmitted by contaminated blood, semen and risky sex.
Samaila also said HBV could be transmitted from an infected mother to child, through sharing of needles, syringes or other drug-injection equipment and sharing of personal hygiene items such as razors or toothbrushes.
Health workers can be at risk if they are exposed to unsafe medical practices, such as reusing medical equipment, or not using personal protection.
HBV is not spread through food or water, sharing eating utensils, breastfeeding, hugging, kissing, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or insects that bite.
However, the virus can survive outside the body for at least seven days, during this time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not protected by the vaccine, he said.
Living With Hepatitis B: Your Lifestyle
People living with HIV and hepatitis B can benefit from adopting a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet. Try to maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight is linked to fatty liver disease which can worsen liver damage.
Since people living with HIV and hepatitis may have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes, your clinic should regularly monitor your blood fats or lipids and blood sugar .
People living with hepatitis B should limit how much alcohol they drink, and those with liver damage should avoid alcohol altogether. Not smoking and cutting down or stopping recreational drug use are also important for overall health.
- Eat a balanced diet including vegetables, fruit and wholegrains.
- Get regular moderate exercise.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Contract Hepatitis C
A Liver Disease Progression
Early studies of the natural history of HIV-HBV coinfection demonstrated that liver-related mortality in this population was nineteen times that in HBV infection without HBV, and 8 times higher than in individuals with HIV mono-infection. Mortality rates increased in individuals with lower CD4+ T-cell counts . The NRTIs lamivudine , emtricitabine and tenofovir and alafenamide ) all have dual activity against both HIV and HBV, with TDF and TAF a pivotal therapeutic agent in this setting due to a very high barrier to HBV drug resistance. The inclusion of tenofovir for management of HBV has led to significant improvements in HBV viral control and liver fibrosis and decreased HBV drug resistance . However, recent studies continue to report that overall mortality, liver related mortality and hospital utilization rates and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma remain elevated in HIV-HBV co-infected individuals compared to HIV mono- or HBV mono-infected individuals . Furthermore, liver disease progression continues to occur in 1020% of individuals on tenofovir-containing HBV-active ART .
Screening And Vaccination Top Of Page
All HIV-positive patients should be screened for HBV with HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antibody and total hepatitis B core antibody . If these tests are negative, the patient should receive HBV vaccination, though HIV-infected patients do not respond as well to HBV vaccination as HIV-uninfected patients, and the persistence of protective surface antibody is short-lived . The response is poorer in patients with CD4 cell counts between 200 and 500 cells/L compared with patients with CD4 cell counts above 500 cells/L, with response rates of 33% and 87.5%, respectively . Patients who fail to respond to a conventional course of vaccine should receive booster doses or a repeat cycle with the 40-g dose .
If any of these tests are positive, HBV DNA should be measured, since atypical serologies occur in HIV coinfection . Household and sexual contacts should also be screened and vaccinated if not already immune.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Caused By Alcohol
Future Goals In Prevention Of Mother
Some of the key strategies to address current barriers to implementation of the birth dose include the following 49:
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Good For You
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
Everyone should be tested for hepatitis B soon after their HIV diagnosis to see if they have been infected with the hepatitis B virus as well. This is done through a blood test.
In the UK, pregnant women are screened for hepatitis B. Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B can also be vaccinated soon after birth to prevent the infection being passed on to them.
Hepatitis B Virus Is Considered As One Of The Most Infectious Disease And People With Hiv Are Also Infected With Hepatitis Virus
Recent data shows that one out of 20 people in the United States will get infected with hepatitis B some time during their lives. Hepatitis B is 100 times more infectious than HIV.
So what is HBV and how can you get it? What are the symptoms and how can you make sure that youll be treated if you are infected?
First seen on:
Don’t Miss: How To Know If You Have Hepatitis
Use Of Antiviral Therapy In Women With High Viral Loads
Despite timely administration of HBIG and hepatitis B vaccine starting immediately after birth, 5% to 10% of newborns whose mothers have very high levels of HBV DNA can still acquire HBV infection and develop chronic HBV.71 Recently, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases conducted a systemic review of the evidence that administering antiviral therapy in the third trimester reduces the incidence of HBV transmission to women with very high levels of HBV DNA.72 From this review, the AASLD, in their updated guideline that used the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation approach, recommended that antiviral therapy be administered to HBsAg-positive pregnant mothers in the third trimester whose levels of HBV DNA exceed 200,000 IU/mL73 but WHO HBV guidelines have not yet included such a recommendation on use of antiviral therapy.67 Although lamivudine and telbivudine are both efficacious and considered safe in pregnancy , tenofovir is the drug of choice based on both its potency and high barrier to resistance.
Hepatitis: How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus . The virus interferes with the functions of the liver and causes pathological damage. A small percentage of infected people cannot get rid of the virus and become chronically infected these people are at higher risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
HBV is spread by contact with blood or body fluids of an infected person the same way as the human immunodeficiency virus . However, HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
The main ways of getting infected with HBV are:
- from mother to baby at the birth
- from child-to-child
- unsafe injections and transfusions
- unprotected sexual contact.
Worldwide, most infections occur from mother-to-child, from child-to-child , and from reuse of unsterilized needles and syringes. Before the widespread use of the hepatitis B vaccine, almost all children in developing countries used to become infected with the virus.
Don’t Miss: How Does One Get Hepatitis B And C
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Viral Hepatitis is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. The most common types areHepatitis A , Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C . If untreated, hepatitis can cause liver damage, liver failure or liver cancer.
Hepatitis is a serious liver disease that can be spread through sex with an infected person. Men who have sexual contact with other men are at increased risk for both Hepatitis A and B. But protecting yourself is easy. Get vaccinated against Hepatitis A and B. Call your local health department for more information.
Did you know
- Hepatitis is called the silent killer because a person may carry the virus in their body for up to 6 months without having any symptoms.
- CDC estimates that 4.4 million Americans are living with chronic hepatitis most dont know theyre infected.
- According to the CDC, HBV is 50-100 times more infectious than HIV and can be passed through sexual intercourse.
Are you at risk?
Although anyone can contract Hepatitis, some people are at greater risk, such as those who:
- Have sexual contact with an infected person
- Have multiple sex partners
- Have a sexually transmitted disease
- Are men who have sexual encounters with other men
- Inject drugs or share needles, syringes, or other injection equipment
- Live with a person who has Hepatitis
- Are on hemodialysis
- Are exposed to blood on the job
- Are infants born to infected mothers
Click here to take the online assessment quiz to see if youre at risk.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Prevention
Where Is Hbv Most Common
Hepatitis B is endemic in China and other parts of Asia. Most people in the region become infected with HBV during childhood.
In these regions, 8% to 10% of the adult population are chronically infected. Liver cancer caused by HBV is among the first three causes of death from cancer in men, and a major cause of cancer in women. High rates of chronic infections are also found in the Amazon and the southern parts of eastern and central Europe. In the Middle East and Indian sub-continent, an estimated 2% to 5% of the general population is chronically infected. Less than 1% of the population in western Europe and North American is chronically infected.
Recommended Reading: How To Live With Hepatitis C
Natural History Top Of Page
After acute infection, there is an early replicative phase of HBV. It is during this phase that patients are most infectious and at greatest risk for development of progressive liver disease . The risk of developing chronic HBV following infection varies with age of HBV acquisition . Perinatal acquisition and infection in children younger than 1 year leads to chronic infection in 90% to 100% of cases, whereas less than 5% of adults who acquire HBV develop chronic infection . Individuals with HIV are at significantly higher risk of developing chronic HBV, with a risk of 21% in unvaccinated persons .
In chronic infection, HBV DNA titers decline over time, though HBsAg remains detectable. There is a spontaneous loss of HBeAg and anti-HBe seroconversion at a rate of about 5% to 10% per year, leading to a phase of nonreplication or low-level replication . A flare, or transient rise in alanine aminotransferase levels, often accompanies this seroconversion . What follows is a period of low HBV DNA levels, detectable only by polymerase chain reaction, and normal ALT levels . Spontaneous loss of HBsAg and anti-HBs seroconversion is less common, with an annual incidence below 1% .
| Table 2. Risk of Chronic HBV by Age of Acquisition and Immune Status. |
| Neonates |
| < 5% |
| hbv, hepatitis B virus hiv, human immunodeficiency virus |
Hepatitis B More Infectious Than Hiv Expert
Dr. Bello Kumo, a consultant Gastroenterologist with Ahmadu Bello University Teaching Hospital, Zaria, says Hepatitis B Virus is more infectious than HIV.
Kumo stated this in a paper entitled Face to Face with Hepatitis B: Cost and Burden, presented at a public lecture organised by Kashim Ibrahim Fellows in Kaduna on Thursday.
The consultant, who expressed concern that not many people have knowledge about the disease, added that multitude of patients were not identified early enough and managed.
He explained that the virus could be transmitted through contact with blood and body fluid, adding that it could infect nearly everyone that came into contact with anyone suffering from it through sharp objects and open wounds.
According to him, there is no known cure for chronic HBV, stressing that prevention remains the best option.
He added that but to prevent, people must first know their status so that if they are negative, they can be vaccinated, which gives up to 95 per cent prevention.
And those who tested positive can begin treatment and managing the virus to avoid its spread.
Dr. Muhammad Saleh, a medical doctor, described HBV as a silent killer, stressing the need for massive awareness campaign.
Saleh said in his lecture on Hepatitis B: Finding the Missing Millions, that not much would be achieved if infected persons were not located and placed on treatment.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic Formula Dry Dog Food
How Is Hbv Spread
HBV is more contagious than HIV. It is spread through infected bodily fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk. HBV can be spread through:
- Unprotected sexual contact with exchange of genital fluids
- Sharing injection needles or ‘works’
- Sharing needles that are used to apply tattoos
- Sharing toothbrushes or razors with a person living with HBV
- Receiving a transfusion of blood, blood products, or organs before 1975
- Open sores
- Mother-to-child transmission
Pregnant women who have HBV can pass HBV on to their babies fairly easily . Similarly, up to nine out of every ten infants who become infected with HBV will develop chronic HBV . The good news is that infants can be given immune treatments at birth to greatly reduce the chances that they will become chronically infected or suffer any liver damage.