Question 3 Why Does Quest Diagnostics Also Report Results As Log Iu/ml
This makes it easier to understand whether a change in viral load is clinically meaningful.
Replicate PCR test results using the same specimen can vary analytically by as much as 0.5 log IU/mL thus, only changes greater than 0.5 log IU/mL from one measurement to the next are considered to represent true changes in viral load.3 Reporting the viral load results in log IU/mL units helps the healthcare provider accurately interpret changes in viral load and better assess a patient’s response to antiviral treatment.
What Does A Reactive Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you currently have hepatitis C and a follow-up test is needed.
Understanding Of Lab Tests Results
Please visit the site associated with The American Association for Clinical Chemistry for better understanding of tests. There you will find the most detailed and full information regarding lab tests. In “common questions” tab you will find answers on the most common questions.
In addition, you can use a special form to ask the question. It is useful, if there is no answer on your question on the web site. A laboratory scientist will answer your question. It is a part of voluntary service provided by the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science.
Read Also: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Adults
Determining The Prevalence Threshold For The Recommendations
Although the intent of public health screening is usually to identify undiagnosed disease, many persons previously diagnosed with hepatitis C are not appropriately linked to care and are not cured of their HCV infection, thereby representing an ongoing source of transmission. Therefore, the prevalence threshold of 0.1% should be determined on the basis of estimates of chronic hepatitis C prevalence, regardless of whether hepatitis C has been diagnosed previously.
Clinical Features And Natural History
Persons with acute HCV infection are typically either asymptomatic or have a mild clinical illness like that of other types of viral hepatitis . Jaundice might occur in 20%30% of persons, and nonspecific symptoms might be present in 10%20% of persons. Fulminant hepatic failure following acute hepatitis C is rare. The average time from exposure to symptom onset is 212 weeks . HCV antibodies can be detected 410 weeks after infection and are present in approximately 97% of persons by 6 months after exposure. HCV RNA can be detected as early as 12 weeks after exposure. The presence of HCV RNA indicates current infection .
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
What To Expect During Testing
A healthcare provider will take a blood sample for analysis.
Before the test, let them know if youre uncomfortable with certain needles or if youve ever passed out at the sight of blood. They can give you a snack to reduce your risk of fainting.
The needle may sting a little as it enters your skin, and you may have a bruise on the site of the draw for a few days.
Results are usually available within a few days or a few weeks at most.
The HCV RNA PCR test is conducted through a process called polymerase chain reaction . There are two approaches to this process: qualitative and quantitative.
What To Know About Hepatitis C Testing
The HCV RNA PCR test is a blood test that helps a doctor diagnose hepatitis C. The test measures the level of the hepatitis C virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is an infection that causes scarring in the liver and reduces function in this vital organ. Severe HCV can lead to liver failure. However, early diagnosis can reduce the risk of severe infection.
In this article, we look at how the test works and what the results mean.
The HCV RNA PCR test is a blood test. A lab technician looks for the genetic material of the HCV virus, or its ribonucleic acid . They use a process called a polymerase chain reaction .
The results of the HCV RNA PCR test help a doctor recommend different ways of reducing the viral load. The viral load indicates how many HCV viral particles are in the blood.
If a doctor suspects that a person has HCV, they will recommend this test early on in the diagnostic process, even if it is not the first test they carry out.
The test can detect the presence of the virus itself, rather than the antibodies that the body creates in response to the virus.
This means that a person does not have to wait until symptoms of the infection develop for a diagnosis.
It can take an average of 68 weeks for antibodies to become detectable after an HCV infection begins. However, a doctor can identify the virus itself after about 1-2 weeks by using PCR or another means of direct virus detection.
Doctors use the HCV RNA PCR in one of two ways:
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C Antibody
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis C testing is performed by a doctor. Testing requires a blood sample, which can be collected in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Blood is often drawn from a vein in the arm or, in children, taken by pricking the skin. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Question 5 Which Hcv Genotypes May Be Reported By The Lipa Assay At Quest Diagnostics
The LiPA genotype assay can identify all 6 major HCV genotypes . In many cases, it can also differentiate among HCV subtypes, including 1a, 1b, 2a-c, 3a, 3b, 3c, 3k, 4a/c/d, 4f, 4h, 5a, 6a/b, and 6c-l. However, if the LiPA banding pattern for a patient specimen does not sufficiently differentiate between subtypes, only the genotype may be reported .
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis A
Diagnosis And Hepatitis C Elimination
In one report, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine explored the feasibility of hepatitis C elimination and concluded that hepatitis C could be eliminated as a public health problem in the United States, but that substantial obstacles exist . In another report, specific actions were recommended to achieve elimination considering information, interventions, service delivery, financing, and research . These reports were the culmination of decades of progress in the development of HCV infection diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
In 1990, serologic tests to detect immunoglobulin G anti-HCV by enzyme immunoassay were licensed and became commercially available in the United States, and U.S. blood banks voluntarily began testing donations for anti-HCV . In 1991, U.S. Public Health Service issued interagency guidelines addressing hepatitis C screening of blood, organs, and tissues . These guidelines recommended hepatitis C testing for all donations of whole blood and components for transfusion, as well as testing serum/plasma from donors of organs, tissues, or semen intended for human use .
Hepatitis C Ab With Reflex To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
The Hepatitis C AB with reflex to HCV RNA, QN, PCR test contains 1 test with 2 biomarkers.
Hepatitis C AB with reflex to HCV RNA, QN, PCR
IMPORTANT – THIS IS A REFLEX TEST AND AN ADDITIONAL CHARGE OF $129 WILL BE APPLIED IF THE Hepatitis C Antibody is reactive.
If Hepatitis C Antibody is reactive, then Hepatitis C Viral RNA, Quantitative, Real-Time PCR will be performed at an additional charge of $129.00
For the detection of active HCV infection in HCV antibody positive individuals.
Clinical Significance
Hepatitis C Virus is a major cause of hepatitis. The clinical symptoms of an HCV infection are variable. Infection with HCV results in a chronic infection in 50 to 80% of cases. The “window” between HCV acquisition and seroreactivity is highly variable up to six months.
Read Also: How To Check For Hepatitis
Are Test Results Accurate
Although no test is perfect, hepatitis C testing is an important and accepted method of testing for HCV. In order to reduce the risk of inaccurate results, doctors take steps to verify a patients diagnosis. For example, a positive test result for hepatitis C antibody requires confirmation with HCV RNA testing.
Question 4 What Do These Test Results Mean: < 15 Detected And < 15 Not Detected

A < 15 Detected viral load result means the assay detected HCV RNA in the patients specimen at a very low level , but could not measure the precise level. A < 15 Not Detected viral load result means the assay did not detect HCV RNA in the patients specimen.
This test is performed using a Taqman® assay. The lowest viral load this assay can accurately quantify is 15 IU/mL, but the qualitative limit of detection is in the 10 to 13 IU/mL range. Therefore, even when the viral load is below 15 IU/mL, we can still report qualitative detection of HCV RNA consistent with active infection in some cases.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Contagious Through Urine
Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Pcr
- Hepatitis C Ab w/RFLX PCR
- Lab Code
- Hepatitis C Antibody w/Reflex PCR
- Description
-
The Qualitative detection of Hepatitis C virus IgG and IgM antibodies in human sera by the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT Anti-HCV test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and recombinant HCV antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HCV present in the sample binds to the rHCV coated microparticles. In the second step, anti-human IgG/IgM acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG and IgM anti-HCV. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
The presence or absence of IgG/IgM anti-HCV in the sample is determined by comparing the chemiluminescent signal in the reaction to the cutoff signal determined from an ARCHITECT Anti-HCV calibration. Specimens with signal to cutoff values 1.00 are considered reactive for IgG/IgM anti-HCV. Specimens with S/CO values < 0.79 are considered nonreactive and specimens with S/CO values between 0.80 and 0.99 are Indeterminate.
Reactive anti-HCV will reflex to Hepatitis C RNA, Quantitative for confirmation with an additional charge.
For anti-HCV testing without PCR reflex for REACTIVE results, see Hepatitis C Antibody without PCR reflex on reactive samples .
- Synonyms
Question 2 Why Are Hcv Rna Results Being Reported In Iu/ml
Results are reported in international units per milliliter to facilitate comparisons between results generated by different test methods. This is important because the various methods used by different laboratories are not standardized against each other. Use of IU/mL reporting units helps to make the comparison of viral load results across different methods more reliable.
Also Check: What Is A Hepatic Diet
Results From The Qualitative Test
Doctors use the qualitative HCV RNA PCR test to determine whether or not the hepatitis C virus is present in the blood.
If the virus is present, the test will be positive. If the test does not detect the virus, the result will be negative.
If the result is positive, a person will then need a quantitative HCV RNA PCR test. For this reason, many doctors now prefer to skip the first test and use the quantitative test straight away.
The quantitative test results show how much HCV is in the body. However, whether low or high, the viral load does not reflect levels of damage to the liver.
Other blood tests, ultrasounds, and, rarely, a liver biopsy will help a doctor determine overall liver health.
After using an HCV RNA PCR test to confirm the presence of HCV, doctors will work out which strain of the virus is active in the body. This helps a doctor plan the course of treatment.
The primary goal of treatment is to bring down the viral load in the body until it is entirely free of the virus. Doctors know this as a sustained virologic response .
SVR occurs when the virus is undetectable for 12 weeks or longer after treatment.
Achieving SVR is the best outcome of treatment, as it often means the person is free from hepatitis C, or that treatment has cured hepatitis C.
Doctors will also combine treatments with other tests that monitor for complications of HCV, including cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: This blood test is the first — and sometimes only — one you may get. Also called the ELISA screen, it checks for antibodies that your body releases to fight the virus. These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection. Your test will be either negative or positive for antibodies. It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
What the results mean
Negative . This is when your blood shows no signs of HCV antibodies. Most of the time, thatâs because you never came in contact with the virus and you do not have hep C.
Sometimes, your negative result can be false, meaning you have HCV. That may happen if you:
- Took the test too soon after your exposure. This test checks for only HCV antibodies, which can take several months to appear.
- Have HIV, a donated organ, or other conditions that weaken your immune system, which can suppress your antibodies
- Get hemodialysis for kidney problems
If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
Positive . This means youâve been infected with HCV. But false positives are surprisingly common. More than 1 in 5 people who test positive donât actually have hepatitis C. Possible reasons include:
What the results mean
Don’t Miss: How Long Is A Hepatitis C Shot Good For
Summary Of The Literature
For the all-adult review, the initial literature search yielded 4,867 studies. Twenty-nine duplicates were identified. Of 4,838 unique studies, 4,170 were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 668 full texts for review. Among these, 368 studies had data available to extract.
For the pregnancy review, the initial literature search yielded 1,500 studies. Two duplicates were identified. Of 1,498 unique studies, 1,412 were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 86 full texts for review.
The supplementary review yielded an additional 1,038 and 195 studies among all adults and pregnant women, respectively. Of these, 912 and 168 , respectively, were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 126 and 27 , respectively, full texts for review. One study was added to the pregnant women review outside of the formal literature search .
Considering all 104 applicable studies, the median anti-HCV positivity prevalence among all adults was 6.6% . Median anti-HCV positivity prevalence was 1.7% for the general population , 7.5% for ED patients , 3.3% for birth cohort members , 9.3% for others/multiple risk factors , 54.2% for persons who use drugs , 5.2% for persons with HIV or sexual risk , and 4.7% for immigrants . Considering 26 applicable studies among pregnant women, median anti-HCV positivity prevalence was 1.2% .
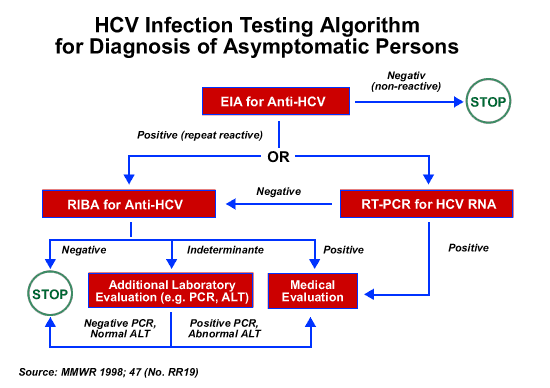
What To Do If The Hcv Antibody Test Is Reactive
If the antibody test is reactive or positive, you need an additional test to see if you currently have hepatitis C. This test is called a nucleic acid test for HCV RNA. Another name used for this test is a PCR test.
If the NAT for HCV RNA is:
- Negative you were infected with hepatitis C virus, but the virus is no longer in your body because you were cured or cleared the virus naturally.
- Positive you now have the virus in your blood.
If you have a reactive antibody test and a positive NAT for HCV RNA, you will need to talk to a doctor about treatment. Treatments are available that can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks.
You May Like: Acute Hepatic Porphyria Treatment Guidelines
When Should I Get Hepatitis C Testing
When used for early detection in patients without symptoms of hepatitis C, screening is recommended at least once for all adults aged 18 years or older, except in locations with very low prevalence of HCV. Screening is also recommended during pregnancy and for patients of any age with risk factors for HCV infection. In patients with risk factors, periodic screening is recommended for as long as risk factors persist.
Risk factors for HCV include:
- Current or past injectable drug use
- Having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Receiving kidney dialysis
- Pain in the abdomen or joints
- Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
- Jaundice or yellowish skin and eyes
Hepatitis C testing may also be performed when liver tests are abnormal or when diagnosing the cause of existing liver damage.
All Adults Pregnant Women And People With Risk Factors Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C

Most people who get infected with hepatitis C virus develop a chronic, or lifelong, infection. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. People can live without symptoms or feeling sick, so testing is the only way to know if you have hepatitis C. Getting tested is important to find out if you are infected so you can get lifesaving treatment that can cure hepatitis C.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Get It
Question 9 How Does The Hcv Genotype Test Differ From The Hcv Ns3 Ns5a And Ns5b Tests For Drug Resistance
The LiPA genotype test is designed to identify all 6 major HCV genotypes. In contrast, the NS3, NS5a, and NS5b drug resistance tests detect mutations associated with drug resistance for a particular HCV genotype. They are not intended for determining HCV genotype and subtype. Separate test codes for drug resistance testing are available, depending on the HCV genotype and the gene of interest:
- Hepatitis C Viral RNA Genotype 1 NS3 Drug Resistance
- Hepatitis C Viral RNA Genotype 1 NS5a Drug Resistance
- Hepatitis C Viral RNA Genotype 1 NS5b Drug Resistance
- Hepatitis C Viral RNA Genotype 3 NS5a Drug Resistance
The HCV genotype test should be performed before ordering an applicable HCV drug resistance test.
References