What Are Genotypes And Do They Matter
Six different genotypes of hepatitis C have been identified. Genotypes 1 and 3 are the most common causes of hepatitis C in Australia and make up 90 per cent of all cases. They are important because they help determine the treatment you need. Unlike in the past, however, your genotype is not important in terms of the chance of cure. With the treatment drugs, all six genotypes have a very high chance of cure.
How Much Will It Cost Patients To Access The New Drugs
The Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme listing means that hepatitis C patients will only pay the normal co-payment for the new drugs. The co-payment is currently worth $6.20 for patients with concessional healthcare cards and $38.30 for general patients without concessional healthcare cards, per drug, per month. For some patients needing three drugs, for example, the co-payment will therefore be $114.90 per month, or $18.60 per month concession.
More information on co-payment charges can be found on the Commonwealth Department of Healths website
What Does Low Blood Platelets Count Mean
When you receive your blood test results and platelets count comes low in CBC test, that means:You dont have enough platelets in your blood which makes your body to be unable to form clots properly, you will have a tendency of bleeding upon injury more than the healthy person,Mild low platelets count is less significant and means transient state, pre-recovery, or variation of laboratories.However, in severe platelets deficiency you may show superficial bleeding in the skin that appears as a rash of tiny-sized purple spots , usually seen on the lower legs and forearms as well as excessive bruising Low Blood Platelet count doesnt necessarily mean you have a cancer, more blood tests for cancerso that please carefully read the possible reasons to understand your platelets level then you have the right to ask about your results.
purpura looks like on hand foot skin
You May Like: Which Hepatitis Causes Liver Cancer
What Medications Treat Or Cure Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C treatments once involved months of injected interferons with up to 50% cure rates, and serious side effects. With newer medications, hepatitis C can be treated with oral combinations of medicines for several weeks. These are generally well-tolerated and yield sustained cure of virus from the blood in over 90% of cases.
The goal of treating HCV-infected persons is to reduce the risk of death, end-stage liver disease, and other liver-related adverse events by the achievement of a virologic cure which is determined by the sustained virologic response . Sustained virology response means complete disappearance of the HCV for at least 12 weeks after stopping treatment.
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Generally seen as a safe vaccine, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against receiving the HBV vaccine. You shouldnt have the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or to any other vaccine components
- youre experiencing a moderate or severe acute illness
If youre currently experiencing an illness, you should postpone receiving the vaccine until your condition has improved.
Read Also: What Causes The Hepatitis C Virus
Antiviral Treatment In Childhood
In an initial clinical trial, 12 weeks of treatment with sofosbuvir/ledipasvir yielded sustained virus eradication rates of 96% and 100% in patients aged 12 to 17 with chronic HCV infection of genotypes 1 and 4, respectively. The pharmacokinetic parameters of both substances were analogous to those seen in adults . Further cohorts of children aged 611 and 35 are now under evaluation, with drug doses of 33.7545 mg and 150200 mg . The findings are expected to become available in 2017.
Joint And Muscle Pain
A condition called arthralgia causes joint pain and is common in people with hepatitis C. Itâs different from arthritis, which causes pain and swelling in joints. But infected people can also get hepatitis C-related arthritis.
Fibromyalgia, which causes body aches and muscle pain, is also common in people with hepatitis C.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B And C Virus
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Cover Hepatitis B Vaccine
The Increase Of The Platelet Count In Chronic Hepatitis C
Common causes of the increase of the platelet count in chronically HCV-infected patients are splenectomy, ribavirin treatment, and liver transplantation . But clinically evident thrombocytosis, usually defined as > 45×104/mm3, is rare in HCV patients receiving splenectomy or ribavirin monotherapy.
A platelet count augmentation can be observed after splenectomy in HCV-chronic infected patients and this increase persists for a long time.27 An increase of platelet count can be found in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with ribavirin, which induces haemolytic anaemia followed by a rise in serum erythropoietin. A higher endogenous erythropoietin stimulates not only the erythrocytes production but also that of platelets. Such an augmentation was shown after 4 weeks of ribavirin monotherapy while TPO did not increase.28 IFN-related thrombocytopenia diminished in patients treated not only with IFN, but also with ribavirin, due to its thrombocytotic response.29 It was shown that rs1127354 and rs7270101 produce ITPase deficiency and defend against ribavirin-induced haemolytic anaemia. However, a platelet count reduction appeared in these patients.29 A reactive thrombocytosis , which begins within 8 weeks after LT, was observed especially when LT was made after a seronegative fulminant hepatic failure and was negatively associated with HCV-related liver cirrhosis. This thrombocytosis had a median duration of 25 days and did not raise the hepatic artery thrombotic risk.30
Proinflammatory Cytokines Induce Depression
Mercifully, for patients with hepatitis C, treatment with the cytokine interferon IFN-alpha has been supplanted by more effective and tolerable treatment options. But during the years of its clinical hegemony, IFN-alpha provided a unique model system for understanding behavioral and biological responses to chronic inflammation relevant to depression. Results from many studies have been quite consistent in demonstrating that IFN-alpha exposure produces a widespread increase in depressive and anxious symptoms, with a sizable minority of patients meeting full criteria for major depressive disorder within a month of commencing treatment. As reviewed in Miller and Raison , IFN-alpha treatment also produces all known biological changes associated with MDD more generally, including increased circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines, disruption of the diurnal cortisol rhythm and induction of glucocorticoid resistance, altered sleep physiology, and changes in monoamine metabolism, with many of these changes associating with increased depression during treatment . Supporting these findings are studies showing that even a single exposure to inflammatory stimuli induces depressive symptoms and depressive-style social cognitions in healthy volunteers, with these effects being strongest in women .
Anton Pozniak, in, 2010
Dont Miss: Tenofovir Alafenamide Vs Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Can Be Cured
What Is Hepatitis C Again
Hepatitis C is a viral liver infection thats classified into six strains known as genotypes. Each can help predict distinctly different treatment outcomes. Genotype 1 is the most prevalent in the United States followed by types 2, 3, and 4. Type 5 is almost always found in South Africa, while type 6 is commonly found in Southeast Asia.
If you have been diagnosed with hepatitis C, know that youre far from alone. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, anywhere from 2 million to 2.8 million people in America currently live with chronic hepatitis C. The tricky part in estimating how many people have it is that many are asymptomatic and unaware that they are even infected. In fact, the Health and Human Services estimates 40% of Americans living with hep C dont know they have it.
Hep C is blood-borne, which means in order to contract it, your blood needs to come in direct contact with blood tainted with the virus. The risk factors for getting hep C include being over age 50 sharing needles and, less frequently, through having sex with an infected individual. Most patients with an acute hepatitis C infection are asymptomatic. However, between 50% and 85% of these acutely infected patients progress to chronic hepatitis C, meaning that the virus has been present for more than six months. Individuals that have additional diseases such as diabetes, alcoholism, HIV, and obesity, have an increased risk of liver damage.
-
joint pain
Why Are The New Hepatitis C Treatments Better
The new treatments are highly effective with a cure rate of 95-97 per cent. Treatment time is reduced to 12 weeks, drugs are tablets and there are very few side effects.
This is a major change from just a few years ago, when hepatitis C treatment time was from six to twelve months, with toxic side effects, and only a 50 percent chance of being cured.
This means that people newly diagnosed with hepatitis C, as well as those who have been living with chronic hepatitis C for many years, will now have access to a fast, effective and well-tolerated cure.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Dog Food
How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
Depending on the drug combination, the specific genotype of hepatitis C that is to be treated, any prior treatment, and whether the person has cirrhosis, the duration of medical therapy may be as few as 8 weeks, or up to 24 weeks. Most regimens are for 12 consecutive weeks. This is much shorter than the interferon-based treatments years ago that lasted up to 48 weeks. Generally, a person is not considered âcuredâ until the âRNA viral loadâ is undetectable for 24 weeks after therapy is stopped. This is called âsustained virologic responseâ or SVR.
The presence of cirrhosis or liver fibrosis is determined by liver biopsy, noninvasive fibrosis scans, or formulas that estimate liver fibrosis based on blood tests, such as AST-to-platelet Ratio Index or Fibrosis-4 Index.3
A very important aspect of treatment is the elimination of all alcohol consumption. Alcohol adds fuel to the fire when it comes to chronic hepatitis. Drinking alcohol greatly worsens liver fibrosis and speeds progression to cirrhosis, and there is no âsafeâ amount to drink for someone with chronic hepatitis. Drinking alcohol also makes it harder for the medications to be effective and may interfere with proper dosing.
How Much Does Hepatitis C Treatment Cost
It is impossible to say what the exact cost is for the various regimens, but it is in the tens of thousands of dollars. In general, out of pocket cost would be very high for the average person, and most people are treated through a health insurer, federal health benefits, or veterans benefits. The cost of hepatitis C and the care of its complications, however, is much higher over a persons lifetime, and the roughly estimated savings is believed to make treatment a good health and financial investment. Liver transplantation alone may cost several hundred thousand dollars for the procedure alone, followed by several hundred thousand for the medications needed in the first 6 months afterward.2 This does not include the many complications of liver transplantation.
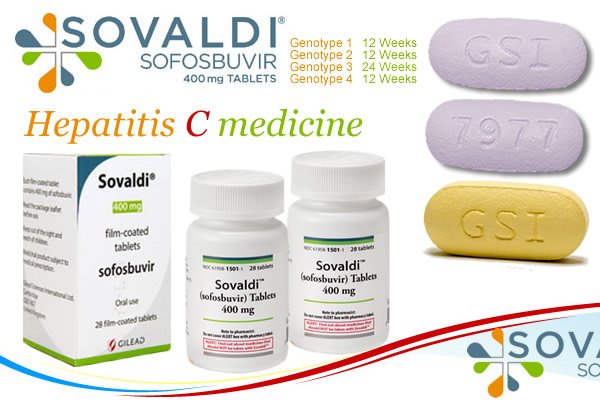
Because negotiations are confidential business contracts, little is known about how much is actually paid for medical treatments by these drugs. One example is the medication sofosbuvir. Estimated costs for a standard 12-week treatment with sosobuvir was $84,000 in the US. Actual costs to individuals depend upon price contracts between pharmaceutical companies and health insurers, as well as government and private organizations. Thus, an individual with healthcare coverage may only pay a monthly co-pay.4
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody Reactive Meaning
Interferons And Pegylated Interferons
The two most frequently used recombinant interferon preparations in clinical trials have been IFN alfa-2b and IFN alfa-2a , which differ from each other by only a single amino acid residue. IFN alfacon-1 , or consensus IFN, is a genetically engineered compound synthesized by combining the most common amino acid sequences from all 12 naturally occurring IFNs. Roferon-A was discontinued from the market in 2007 and Infergen was discontinued from the market in 2013.
The addition of propylene glycol molecules to IFN has led to the development of long-lasting IFNs that have better sustained absorption, a slower rate of clearance, and a longer half-life than unmodified IFN, which permits more convenient once-weekly dosing. The FDA has approved PEG-IFNs for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C.
Two PEG-IFN preparations are available for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. PEG-IFN alfa-2b consists of IFN alfa-2b attached to a single 12-kd PEG chain it is excreted by the kidneys. PEG-IFN alfa-2a consists of IFN alfa-2a attached to a 40-kd branched PEG molecule it is metabolized predominantly by the liver.
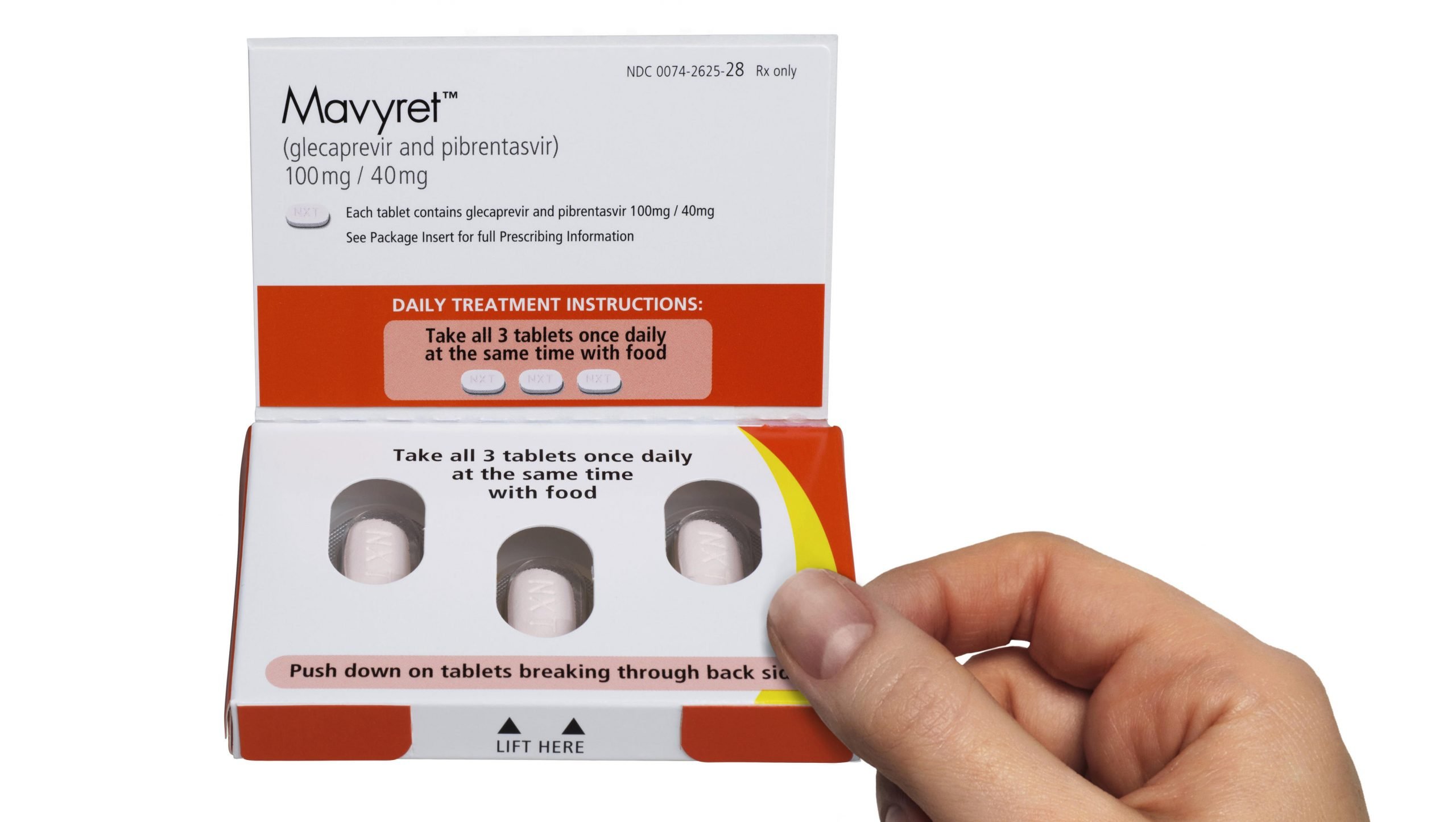
New Drugs Cure Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a that can cause serious and permanent liver damage. The goal of treatment is to clear the virus from the body and stop, slow and prevent liver problems. Until recently, doing that involved inconvenient and painful injections of interferon and a pill called ribavirin. That therapy is known for its toxic side effects and has been compared to low-grade chemo. Worse, it doesnt always work that well. These traditional drugs offer a 50% cure rate at best.
But today, were witnessing a revolution in hepatitis C treatment, as more and more medications that directly target the virus gain approval. These medications offer a cure, instead of a partial clearing of the virus. And, as a bonus, most come in the form of a pill. They have fewer side effects and work much fasterwhich means you dont have to stay on treatment as long as compared to interferon and other drugs.
The rapidly-evolving hep C medication list is giving new hope for the 3.2 million Americans living with the chronic form of the disease. Antiviral therapy for hep C continues to rapidly evolve with the introduction of new drugs and treatment regimens that vary based on hep C genotype, previous treatments, and the presence of cirrhosis. Heres a closer look at some of the currently prescribed interferon-free medicines for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Where To Get Hepatitis B Vaccine In Nigeria
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus . It is a blood-borne virus, most commonly spread through sharing drug using paraphernalia. Hep C is far more infectious than HIV. If left untreated, Hep C can result in serious health implications such a cirrhosis or liver cancer. Almost 40% of living with Hep C are unaware, which is why screening is critical. Knowing your Hep C status will help to eliminate the spread of the virus, and identify those who need treatment. Current treatments for Hep C are over 95% effective, take only 8-12 weeks, and cause very few side-effects. HCV or Hep C is one of the few chronic conditions that can be cured!
Direct Acting Antiviral Agents
This is the class of drugs acting against viral and host proteins involved in HCV life cycle. The major inhibitors of NS3 viral protein are telaprevir and boceprevir. Telaprevir was approved and recommended for use with PegIFN- and ribavirin in genotype-1 patients. This was classified as triple therapy. Since telaprevir treatment is reported to be effective against the resistant mutants in the short term duration, it was decided to use it for long-term and subsequently approved for the treatment. It is important to note here that the long term use of these drugs often leads to drug resistance including T54A/S, R155K/T, V36A/M, V55A, and A156/S/T/V, etc. Simeprevir is another NS3 protease inhibitor classified as second generation drug. This drug is a reversible inhibitor of NS3/4A protease. Danoprevir and faldaprevir are also second-generation HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitors and used in patients infected HCV genotype-1. In addition to these drugs, there are various other NS3 protease inhibitors like Vaniprevir , Narlaprevir , Asunaprevir , VX 985, and MK-5172 which are used for treatment of HCV infection. There is every possibility that these drugs may be approved for therapeutic use against HCV infection.
Read Also: Where To Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
Factors That Affect Treatment Success
A number of factors can help predict how well hepatitis C treatment is likely to work for you.
Before starting treatment, it is important to have a test to see what genotype of hepatitis C you have. This determines which DAAs will work and predicts treatment response. Some DAAs are pangenotypic or active against all genotypes.
There are at least six major hepatitis C genotypes. Genotype 1 is the most common type in the UK, Europe and the US. It has two subtypes, 1a and 1b. Genotype 1 was hard to treat with interferon-based therapy, but it can be successfully treated with all approved DAAs. However, genotype 1a is harder to treat than 1b.
effectiveness
How well something works . See also efficacy.
Hepatitis C genotype 2 is less common worldwide. It responded best to interferon-based treatment, but is susceptible to fewer DAAs than genotype 1. Genotype 3 is the most common type in the Indian sub-continent and south-east Asia, but it is also found in the UK. Genotype 3 has been the hardest to treat with DAAs, but newer pangenotypic drugs are highly effective against it.
Genotype 4 is the most common type of hepatitis C in the Middle East and North Africa, but it has also been seen in hepatitis C outbreaks in the UK and Europe. Genotype 4 generally responds to the same DAAs as genotype 1. Genotype 5 and 6 are less common and less well studied.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Test For Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Foods To Avoid With Hepatitis C