What Are The Symptoms Of Hbv
Hepatitis B virus can cause an acute illness with symptoms that last several weeks, including yellowing of the skin and eyes , dark urine, extreme fatigue, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. Most of the time HBV infection is ASYMPTOMATIC.
Joint pains, muscle aches, rash, and jaundice may occur in some people. People can take several months to a year to recover from the symptoms. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure.
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
Treatment Of Acute Hepatitis B
-
General measures
Liver transplantation Liver Transplantation Liver transplantation is the surgical removal of a healthy liver or sometimes a part of a liver from a living person and then its transfer into a person whose liver no longer functions. (See… read more is the most effective treatment for fulminant hepatitis B and is the best hope of survival, particularly for adults.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis C
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or “HBsAg”. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or “HBcAg,” which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
How Can I Avoid Getting Hepatitis B

There is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect you from getting hepatitis B. The vaccine is usually given in three doses over a six month period. The vaccine will give you long-lasting protection. A combined vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B is also available.
Other ways to protect yourself or your loved ones include:
- Adopt safe sex practices.
- Avoid sharing personal hygiene items
- If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus , an injection of hepatitis B immune globulin may help protect you.
- If you are pregnant, make sure you are screened for hepatitis B. If the test result shows that you have the virus, make sure your baby receives the free hepatitis B vaccine. If you have hepatitis B, breastfeeding is safe if the baby has received both protective antibody called immune globulin, and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within the first 12 hours of life. Talk to your doctor about having your newborn immunized .
- If you decide to have a tattoo, piercing, manicure or pedicure, ensure that the facility uses single-use needles and inks and/or follows proper sterilization procedures.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Virus Surface Ab
What Are The Complications Of Hepatitis B
The course of hepatitis B infection depends mostly on the age at which a person is infected.
People infected as infants are likely to develop long term infection and can get complications such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer. Infants have a 9 in 10 chance and children have a 3 in 10 chance of developing a chronic, lifelong infection.
People infected as teenagers or adults are likely to become unwell with symptoms , but have a smaller chance of developing a chronic infection. Others develop a silent infection, without any symptoms.
Most people infected as adults clear the virus from the body within 6 months. They develop immunity to future hepatitis B infections and do not develop long-term liver damage.
However, approximately 1 in 20 adults cannot clear the virus and develop chronic hepatitis B. They are at risk of developing complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer in the longer term.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection in the world. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks and injures the liver. Two billion people have been infected and about 300 million people are living with a chronic hepatitis B infection. Each year up to 1 million people die from hepatitis B despite the fact that it is preventable and treatable.
Hepatitis B is transmitted through direct contact with infected blood or certain bodily fluids. The virus is most commonly transmitted from an infected pregnant person to their baby during childbirth, due to the blood exchange that happens between mother and baby. It is also transmitted through unsterile medical or dental equipment, unprotected sex, or unsterile needles, or by sharing personal items such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, body jewelry.
Hepatitis B is a silent epidemic because most people do not have symptoms when they are newly infected or chronically infected. Thus, they can unknowingly spread the virus to others and continue the silent spread of hepatitis B. For people who are chronically infected but dont have any symptoms, their liver is still being silently damaged which can develop into serious liver disease such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine In Newborns
The Link Between Hepatitis B And Liver Cancer
October is Liver Cancer Awareness Month! Despite the aggressive nature of this cancer only one out of every five diagnosed patients survive beyond five years liver cancer receives little attention from those outside of the health field. To help raise awareness and support those who have been affected, we are using our #justBcampaign to share the stories of individuals who have been directly impacted by liver cancer throughout the month of October. The stories are featured throughout the month on the Hepatitis B Foundation, Liver Cancer Connect and Hep B United social media outlets. Check out Alice, Bunmi, Dai, and Kims stories.
What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer occurs when normal liver cells begin to grow uncontrollably and form a mass called a tumor. Cancerous tumors are dangerous because they begin to damage healthy cells that make up the organ and impair the livers functionality. Of the nine different types of liver cancer, Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common and often results from chronic hepatitis B. In the United States, new cases of liver cancer and liver cancer deaths are steadily rising. In fact, a recent study has shown that there has been a 53% increase in liver cancer deaths since 2000.
Hepatitis B and Liver Cancer
Liver Cancer by the Numbers:
Preventing Liver Cancer
When Is That Pain Hep B
When people with chronic hepatitis B experience abdominal pain, we often wonder if its related to our liver and if our hepatitis B is getting worse.
According to experts, hepatitis B rarely causes abdominal pain. Here are some insights to help you understand what might be behind your abdominal pain when you live with chronic hepatitis B.
First, its not called the silent infection for nothing. When first infected, most children and nearly 70 percent of adults never experience any direct symptoms from hepatitis B. When people do have symptoms, such as aches, nausea and fever, they usually last for only a few days. Only a very small percentage have symptoms that persist long-term.
But chronic hepatitis B is different. Most of us have had this infection since childhood and over time it rarely causes us any symptoms. Usually, disease causes pain, it is natures way of telling us that a health problem is getting worse. However, with diseases such as chronic hepatitis B, diabetes or high blood pressure, we often dont feel any symptoms until the disease reaches an advanced state.
This palpable pushing against the membrane is why fatty liver disease, for example, causes abdominal pain, while early-stage hepatitis B does not. The fatty liver is enlarged from the fat thats accumulated and its accompanying inflammation, it has literally outgrown its membrane.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Curable Or Not
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is less easily transmitted than hepatitis A. Transmission commonly occurs when needles are reused without being first sterilizedas when people share needles to inject drugs or when needles are reused to apply tattoos.
Transmission through blood transfusions is possible but is now rare in the United States because blood is screened.
Transmission may occur between sex partners, both heterosexual and homosexual. Also at increased risk are people living in close quarters because contact with another person’s body fluid is more likely.
Anyone with hepatitis B, even people who do not have symptoms, can transmit the virus.
Whether insect bites can transmit this virus is not clear.
Many cases of hepatitis B have no known source.
Who Is Most At Risk For Chronic Disease
The likelihood that an HBV infection will become chronic depends upon the age at which a person becomes infected, with young children who become infected with HBV being the most likely to develop chronic infections.
About 90% of infants infected during the first year of life develop chronic infections 30% to 50% of children infected between one to four years of age develop chronic infections. About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood die from HBV-related liver cancer or cirrhosis. About 90% of healthy adults who are infected with HBV will recover and be completely rid of the virus within six months.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Considered An Std
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down – if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate – or create – itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called “bile” to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
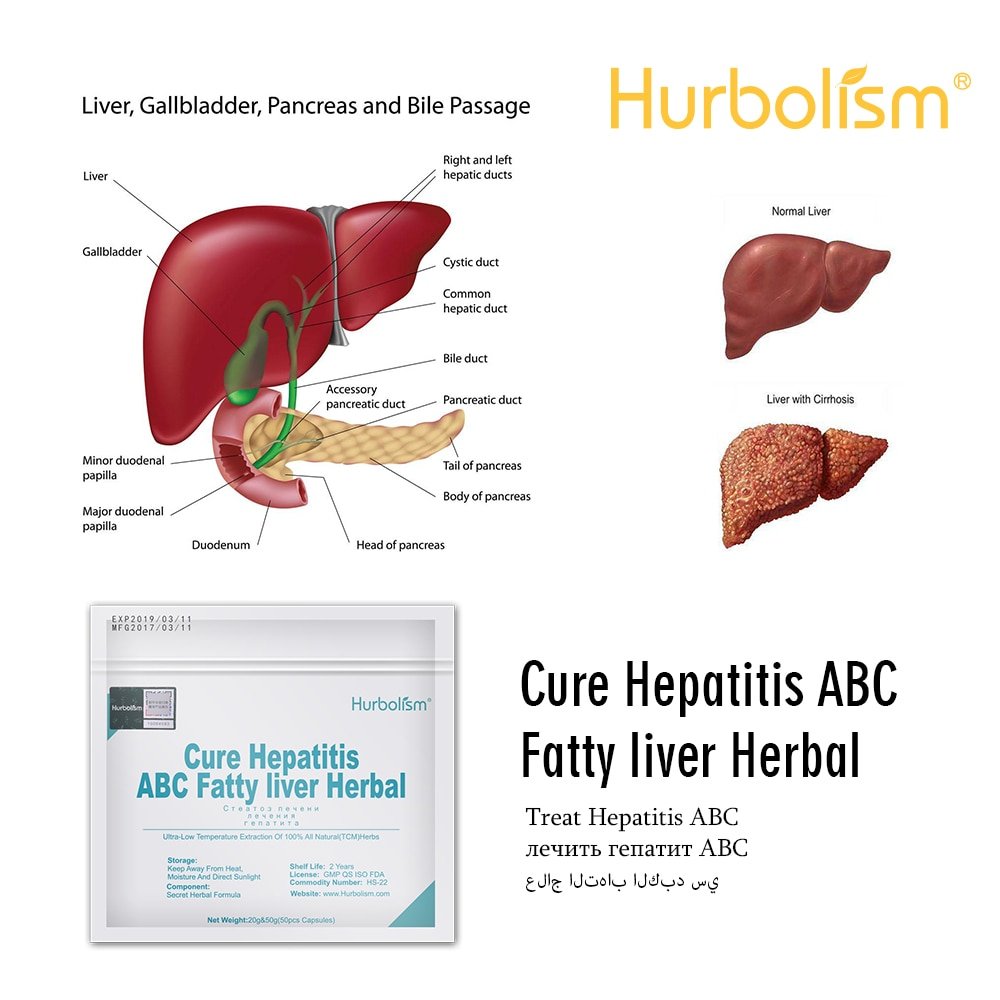
The hepatitis B vaccine is used to prevent hepatitis B. Its usually provided in three doses.
The first dose can be taken on a date you choose. The second dose must be taken 1 month later. The third and final dose must be taken 6 months after the first dose.
Some people may need two or four doses of this vaccine.
There is also a newer hepatitis B vaccine thats offered in two doses.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Genotype 1 Treatment
Role Of Angiogenesis And Hypoxia
In chronically HBV infected hepatocyte, the cirrhotic nodule formation is accompanied by the low level of vasculature in the liver. This occurs in localized regions with the development of a hypoxic environment which in turn can enhance cell migration through the enhanced activity of matrix metalloproteinases. Hypoxia is a major determining factor in cancer development, because it contributes to inflammation, apoptosis and liver regeneration inhibition. The cellular adaptive response to hypoxia triggers the upregulated expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha , which is known to promote angiogenesis by up regulating vascular endothelial growth factor . During HBV infection and protein synthesis, HBx is known to stabilizes HIF1 through direct binding and also stimulates the transcription of HIF1, thus promotes angiogenesis. HBx protein also enhances angiogenesis by activated expression of pro-angiogenic growth factor angiopoietin 2, via the activation of MAPK pathway. In many diseases, the role of angiogenesis has been highlighted by using the kinase inhibitor sorafenib, which specifically target the VEGF receptor . Since both the PI3K-AKT signaling cascade and EGFR are activated by HBx, the pathways of HIF and VEGFR activation emphasize the importance in the pathogenesis of HBV induced HCC.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
You May Like: Can Hiv Lead To Hepatitis
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Hepatitis B Vaccine