Hcv Genotypes 4 5 And 6
In the absence of any clinical trial including a sufficient number of patients, the likelihood of an SVR and the optimal treatment schedule remain unknown for the patients infected with HCV genotypes 4, 5 or 6. It is thus recommended to treat them like those infected with HCV genotype 1, i.e. with pegylated IFN alfa at the usual dose, combined with a high dose of ribavirin .1C). In the absence of published data, no stopping rules have been defined and it is recommended to treat these patients for a total of 48 weeks. The virological response must be assessed by means of a sensitive HCV RNA assay at the end of therapy and 24 weeks later 1, 18.
Management Of Antiviral Therapy
The current standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C is the combination of pegylated interferon alfa and ribavirin 18. The efficacy endpoint of hepatitis C treatment is the sustained virological response , defined by the absence of detectable HCV RNA in serum as assessed by an HCV RNA assay with a lower limit of detection of 50 IU/ml or less 24 weeks after the end of treatment 18.
Genomic Organization Of Hcv
The original isolate was a positive-sense RNA virus with approximately 9,400 ribonucleotides, containing a poly tail at the 3 end .1). The sequence contained a 5 untranslated region of 341 bases, a long open reading frame coding for a polyprotein of 3,011 amino acids, and a 3 untranslated region of about 27 bases. This RNA structure is most similar to that of the family Flaviviridae, which encompasses numerous arthropod-borne viruses. Consistent with the known functions of most flavivirus proteins, the three N-terminal HCV proteins are probably structural and the four C-terminal proteins are believed to function in viral replication.
Genomic organization of HCV. First generation, second generation, and third generation refer to serologic assays for detection of HCV antibodies.
The open reading frame length of each genotype is characteristically different. Whereas the open reading frame in type 1 isolates is approximately 9,400 ribonucleotides, that of type 2 isolates is typically 9,099 nucleotides and that of type 3 isolates is typically 9,063 nucleotides . These differences may potentially account for some of the phenotypic differences among genotypes discussed below.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Drinking After Someone
You May Like: How Bad Is Hepatitis C
Zepatiers Mechanism Of Action
Zepatier is a combination of a NS5A replication complex inhibitor elbasvir and a NS3/4A protease inhibitor grazoprevir. Elbasvir prevents replication of viral cells by interacting with the NS5A protein on HCV replicon cells, which are responsible for reducing human interferon antiviral activity.
Grazoprevir stops viral replication by binding to the NS3/4A protease, a serine protease domain that is essential for viral poly-protein maturation and neutralisation of the hosts innate antiviral immunity for HCV.
Pathophysiology And Natural History
There are six known genotypes of HCV. The most common genotypes in the United States, comprising 97% of all U.S. HCV infections, are 1 , 2, and 3.9
The mechanism of hepatocyte damage induced by HCV infection is not completely understood but may involve direct cell injury and a local immune-mediated mechanism that causes a chronic inflammatory state.10,11 Acute HCV infection progresses to chronic disease in 50% to 80% of patients and clears spontaneously in 20% to 50% of patients.10 Of persons with chronic disease, 20% will develop cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease, and/or hepatocellular carcinoma.12
Figure 1 illustrates the natural history of HCV infection.10
Figure 1.
Natural history of hepatitis C virus infection.
Reprinted with permission from Pawlotsky JM. Pathophysiology of hepatitis C virus infection and related liver disease. Trends Microbiol. 2004 12:97.
Figure 1.
Natural history of hepatitis C virus infection.
Reprinted with permission from Pawlotsky JM. Pathophysiology of hepatitis C virus infection and related liver disease. Trends Microbiol. 2004 12:97.
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis
Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 3
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by hepatitis c, a blood-borne virus transmitted through direct contact with infected blood. It causes inflammation of the liver, which leads to diminished liver function or liver failure.
The infection is less likely to exhibit symptoms until the liver gets damaged, which may take several years.
In chronic HCV patients, the infection leads to scarring and poor liver function, leading to complications, including jaundice, fluid accumulation in the abdomen, bleeding and liver cancer.
Genotype 3 is the most treatment-resistant and aggressive hepatitis C that affects 12% of chronic HCV patients in the US.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions estimates, HCV affects 2.7 million Americans and approximately 170 million people worldwide.
Hepatitis C Virus Gt1 And Gt4 Infection
Hepatitis C infection is a liver disease caused by hepatitis C, a blood borne virus. The infection may range from an acute mild illness to a chronic lifelong illness.
HCV is a small, enveloped, single-stranded, positive-sense ribonucleic acid virus that occurs in seven major genotypes, which are classified from one to seven. It causes inflammation of the liver and leads to decreased liver function or failure.
The infection is typically asymptomatic until later stages, which takes several years. The chronic viral infection is characterised by cirrhosis, which is associated with complications such as bleeding, jaundice, fluid accumulation in the abdomen, infections or liver cancer.
Approximately three million Americans are estimated to have HCV. Of these, GT1 is most common and GT4 is least common.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Ways Of Transmission
Treatment Of Hcv Genotype 3 Infection In Non
The combination of SOF plus RBV for 24 weeks was the first interferon-free therapy for patients with HCV genotype 3 infection approved by the FDA. International guidelines differ regarding the recommendations for this regimen. EASL guidelines do not recommend this therapeutic regimen for treatment-experienced cirrhotic patients. On the other hand, AASLD recommends SOF plus RBV as an alternative regimen for patients without cirrhosis with previous PegIFN/RBV failure or treatment-naive patients who are IFN-ineligible .
In naive non-cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 3 infection, SOF plus RBV for 12 weeks resulted in an overall SVR of 61-68%. However, extending the treatment to 24 weeks led to an approximate 30% increase in SVR rates, ranging from 90 to 96% .
Two large clinical trials evaluated the efficacy of SOF plus RBV for 12 weeks in naive, non-cirrhotic patients infected with HCV genotype 3. The Fission trial included 145 patients, but only 89 achieved SVR . The Positron trial included 84 naive patients who were interferon-ineligible or intolerant, of which 57 reached SVR . The Boson clinical trial found higher SVR among naive and non-cirrhotic patients treated with SOF plus RBV for 16 weeks. Among 70 patients treated, 58 achieved SVR . Another arm of this study evaluated 72 naive non-cirrhotic patients treated for 24 weeks, with an overall SVR of 90% . SOF plus RBV for 24 weeks was also used in the Valence trial, which included 92 patients and 87 achieved SVR .
Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes
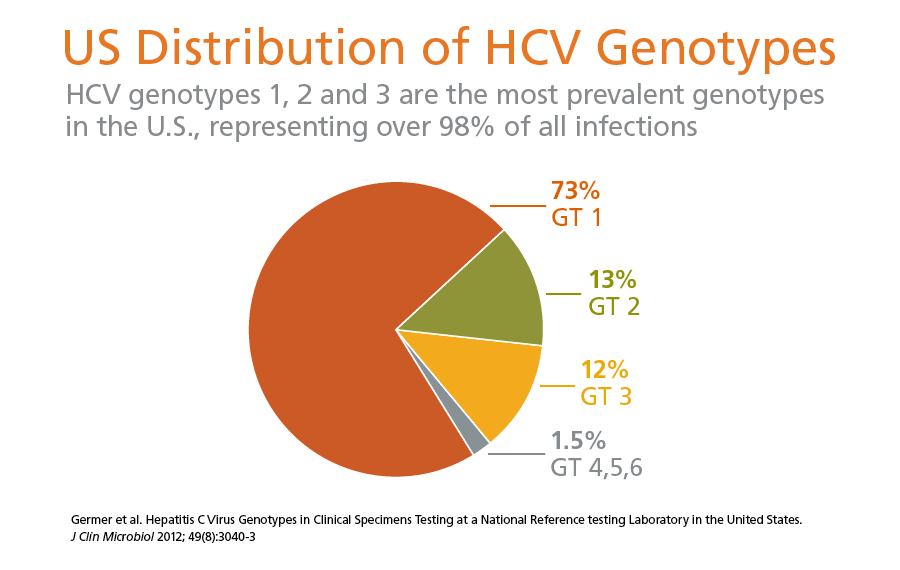
An important variable for all patients with chronic hepatitis C virus is the”genotype” of HCV with which they are infected. This is the strain of the virus towhich they were exposed when they were infected, often many years prior to theirevaluation, and it is determined by a simple blood test. Genotypes of HCV aregenetically distinct groups of the virus that have arisen during its evolution. Approximately 75% of Americans with HCV have genotype 1 of the virus, and 20-25% have genotypes 2 or 3, with small numbers ofpatients infected with genotypes 4, 5, or 6. Most patients with HCVare found to have only one principal genotype, rather than multiple genotypes. Genotype 4 is much more common in Africathan in many other parts of the world, genotype 6 is common in Southeast Asia, andeach area of the world has its own distribution of genotypes.
Also Check: What Is Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Genotype Table: Recommended Treatments For Hepatitis C Genotypes 1 2 3456
| Generic Brand Name | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis c Genotype 1, 4, 5, 6 treatment. It is mainly used to treat Hep C | A combination pill taken once a day. Its usually taken for 12-24 weeks, and sometimes only 8 weeks. | Major side effects are rare. | Natco, Hetero, Mylan, Zydus Cadila, Dr. Reddy | ||
| Hepcinat, Sofovir, Myhep, Sovihep, Resof | 400 mg Sofosbuvir | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 | 1 Sofosbuvir pill and 1 Daclatasvir pill once a day for 12 weeks. Sometimes used with Ribavirin. | Major side effects are rare. | Natco, Hetero, Mylan, Zydus Cadila, Dr. Reddy |
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
Read Also: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Predictors Of Response To Peg
The ability to identify which individuals will respond to HCV treatment remains limited. Pre-treatment predictors of response have became crucial to selecting therapy candidates, and include HCV genotype , ethnicity , low HCV baseline viral load, younger age, histology , metabolic syndrome, and interleukin 28B genotype.
Genetic variants in the region of the IL28B gene were recently shown to have a strong association with the outcome of PEG-IFN and RBV therapy. In the cohort from the Individualized Dosing Efficacy vs Flat Dosing to Assess Optimal Pegylated Interferon Therapy study, carriage of the favourable IL28B genotype was associated with SVR rates of 70%-80% in Caucasian patients treated with 48 wk of PEG-IFN and RBV, compared to 30%-40% in patients carrying one of the unfavourable genotypes. IL28B genotyping was recommended and immediately proved useful for pre-treatment counselling for HCV-1 patients.
Why Do People Have Different Genotypes
A person of any racial or ethnic group can carry any genotype or subtype. However, some may be more prevalent in some racial or ethnic groups than others. In the United States, over 90% of African Americans, compared to 67% of Caucasians, carry genotype 1.
People who travel between regions where different genotypes are more common can be exposed to different HCV genotypes, leading to a mixed infection. HCV is transmitted through contact with blood, such as through contaminated blood products or medical equipment, blood transfusions, kidney dialysis, or the sharing of drug injection equipment, such as syringes, or non-injection equipment, such as pipes, spoons, cotton balls, or straws for snorting drugs.
Don’t Miss: What Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Do
Sofosbuvir Plus Pegylated Interferon/ribavirin
The combination of SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks is the only interferon based therapy recommended by the EASL and AASLD guidelines for the treatment of HCV genotype 3 infection .
In naive non-cirrhotic patients, SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks resulted in an overall SVR of 92-100% . However, efficacy data is scarce: few patients were included in clinical trials and only three studies evaluated the SVR rates in this population. The phase II study included 25 naive non-cirrhotic patients treated with SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks, reaching an overall SVR rate of 92%, but no SVR data according to specific genotype is available 70033-1.). Another phase II study included 17 patients treated with SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for either 12 or 8 weeks and the overall SVR rate was 100% in both arms . The Boson phase III study included 71 naive non-cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 3 infection treated with SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks, achieving an overall SVR rate of 96% .
In non-cirrhotic patients, including naive and with previous failure to PegIFN/RBV, SOF plus PegIFN/RBV for 12 weeks resulted in high SVR rates . It must be noted that non-significant differences in SVR rates were observed among naive and treatment-experienced patients, but these data need to be cautiously analyzed, since only small cohorts were included in the studies.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
What Is The Current Research Into Genotypes And Treatments For Each Type
The most widely used anti-HCV therapy, PEG/ribavirin, doesnt target the virus itself. This treatment regimen primarily affects the persons immune system. Its goal is to rally the immune system to recognize and eliminate cells infected with HCV.
However, variations of HCV in a single person wont necessarily look the same to the immune system. This is one of the reasons that HCV infections persist and become chronic infections.
Even with this genetic diversity, researchers have identified proteins that are required for the reproduction of HCV in the body. These proteins are present in essentially all of the many HCV variants.
The new treatments for HCV target these proteins. That means they target the virus. Direct-acting antiviral therapy uses small molecules designed to specifically inhibit these viral proteins.
Many DAA drugs have been under development during the past decade. Each drug targets one of the handful of essential HCV proteins.
The first two DAA drugs, boceprevir and telaprevir, got approval for use in the United States in 2011. Both target a particular type of HCV enzyme known as protease. These drugs are used in combination with PEG/ribavirin.
Both of these new medications are most effective for HCV genotype 1. Theyre moderately effective for genotype 2, and not effective for genotype 3.
Initially, they were only approved for use in people with genotype 1 HCV in combination with PEG/ribavirin.
You May Like: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Ifn Monotherapy In Acute Hepatitis C
Although the short courses of standard IFN monotherapy introduced in the 1980s by Hoofnagle et al, Davis et al, and Di Bisceglie et al led to sustained improvement in liver disease and loss of virus in less than 10% of patients, these therapies were the first to cure chronic viral hepatitis.
Jaeckel et al reported that treatment with IFN alfa-2b prevented chronic infection in 98% of a group of 44 German patients with acute hepatitis C. In this study, patients received 5 million U/day of IFN alfa-2b subcutaneously for 4 weeks and then three times per week for another 20 weeks the IFN alfa-2b was well tolerated in all patients but one.
Because it has the poorest safety profile of all the HCV antiviral agents, with few exceptions PEG-IFN is no longer recommended in combination regimens. Spontaneous resolution of acute HCV infection may occur in 15% to 50% of patients. Monitoring for spontaneous clearance for a minimum of 6 months before initiating any treatment is therefore recommended.
References
World Health Organization. Hepatitis C: fact sheet. Available at . Updated: October 2017 Accessed: January 23, 2018.
Frank C, Mohamed MK, Strickland GT, et al. The role of parenteral antischistosomal therapy in the spread of hepatitis C virus in Egypt. Lancet. 2000 Mar 11. 355:887-91. .
Kim A. Hepatitis C virus. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Sep 6. 165 :ITC33-ITC48. .
Model Structure And Assumptions
In this study, an established Markov model , developed in Microsoft Excel 2013, was used from Chinese payer perspective to estimate the lifetime outcomes of treating a cohort of HCV genotype 1b treatment-naïve patients with two hypothetical regimens, DCV+ASV and PR . The model runs in annual cycles over a lifetime horizon and an annual discount rate of 5% was applied.
Also Check: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis
How Genotypes Affect Treatment
Medications known as direct acting antivirals, or DAAs, stop the hep C virus from making copies of itself. Some DAAs appear to work well on all hepatitis C genotypes. Others work on only one or some.
Your doctor will probably prescribe some combination of these medications:
- Velpatasvir
Some pills combine two drugs into one pill.
Youll probably take these meds for anywhere from 8 to 12 weeks. But they may not be right for everyone because of things like cost or other illnesses.
Your specific genotype can tell your doctor important things about how to use those medications, what to watch for, and other drugs you might need.
For example, you may have a higher chance for cirrhosis if you have genotype 1.
Genotype 3, the second most common subtype worldwide, may not respond as well to DAAs alone. In addition, this type might suggest that:
- Liver cancer is more likely.
- Insulin resistance might happen. When your body resists or doesnt respond to insulin as well as normal, you have a higher chance of heart disease and diabetes.
- You might need longer, more challenging treatment
Your doctor might adjust or change your DAA treatment if you have:
Show Sources
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: âInitial Treatment of Adults with HCV Infection,â âHCV Guidance: Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C.â
CDC: âHepatitis C Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Infohep.org: âHepatitis C treatment factsheet: Harvoni .â
Genotypes And Hcv Genetic Heterogeneity As Epidemiologic Markers
Because of geographic clustering of distinct HCV genotypes, genotyping may be a useful tool for tracing the source of an HCV outbreak in a given population. Examples include tracing the source of HCV infection in a group of Irish women to contaminated anti-D immunoglobulins . All of these women were infected with HCV genotype 1b, a genotype identical to the isolate obtained from the implicated batch of anti-D immunoglobulin. Hohne et al. used genotyping to trace the sources of outbreaks in Germany . More recently, genotyping and molecular characterization of HCV isolates provided evidence for a patient-to-patient transmission of HCV during colonoscopy . The index case as well as the two other infected patients had HCV genotype 1b. Nucleotide sequencing of the NS3 region showed that the three patients had the same isolate , strongly suggesting a common source of infection.
Although Zein et al. found no association between HCV genotypes and the mode of HCV acquisition in their population, others have provided evidence for such an association . It has been suggested that genotypes 3a and 1a are closely associated with intravenous drug use and that genotype 1b is seen more often in patients who acquired HCV through blood transfusion. This information may be useful in tracing sources of HCV epidemics.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C And Is It Contagious