What Are The Symptoms
The period between exposure and onset of symptoms for Hepatitis A virus is generally around 28 days with common symptoms including fever, loss of appetite, nausea and pain in the right upper abdomen, followed within several days by jaundice. This condition results in the yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Symptoms may range from mild to severe, with some individuals displaying none. Children under 6 years of age are often asymptomatic , but they can transmit the infection to others.
The infection can persist for anywhere from 1 to 2 months, and the severity varies from a mild illness to a severely disabling disease lasting several months. Approximately 10%-15% of infected people have prolonged or relapsing symptoms over a 6-to-9-month period. Severe complications, including fulminant Hepatitis and liver failure, are rare but more likely to occur in older adults and people with underlying liver disease.
Where Can I Get Vaccinated
The best place to go for vaccinations is your family medical clinic. They have your medical records and can check to see if youve already had a particular vaccination. Either your doctor or a nurse can give the vaccination.If you dont have a family doctor, you can go to one of the after-hour medical clinics. Ring them first to make sure they can help you with the vaccination you need.You can find a clinic near you on the Healthpoint website. Put in your address and region, and under Select a Service, click on GPs/Accident & Urgent Medical Care.Vaccines on the National Immunisation Schedule are free. Other vaccines are funded only for people at particular risk of disease. You can choose to pay for vaccines that you are not eligible to receive for free.
How Long Are You Protected
Unfortunately, it is still hard to pinpoint the precise duration of the hep A vaccine. On the bright side, children who received a three-dose vaccine and adults who received a two-dose vaccine should be safe for 20 years.
In addition, some studies suggest that the vaccine antibodies may be present for forty or more years. This is particularly true for vaccinated children.
So, it is obvious that the vaccine may last for quite a while. However, you should still get a better understanding of the infection itself and the revaccination requirements.
You May Like: How Much Is A Hepatitis A Shot
I Received My Vaccine Years Ago
If it has been years since you have been vaccinated, you may need or may request a hepatitis B surface antibody titer blood test to confirm that you are still protected. A person is considered protected if they have a positive anti-HBs or HBsAb test result greater than 10 mIU/mL. Sometimes these test results are under 10 and there is concern whether these low levels will still provide protection against hepatitis B. Anti-HBs or HBsAb test results can decrease over time, but an individual can still be protected even if the test results are less than 10 mIU/mL.
If your test results are low, your doctor may recommend a booster shot or a repeat of the series. If you confirm you completed the vaccine series, you can get a booster dose of the vaccine. Your surface antibody level will be tested again 1 or 2 months after the booster. If the blood test result is greater than 10 mIU/mL, then you are protected and will not require an additional booster shot in the future. If a booster shot does not result in a level greater than 10, then complete the remaining two-doses of the vaccine series and recheck the levels again after 1-2 months. Retain a copy of the anti-HBs titer test as proof of protection.
How Long Does Hep B Vaccine Last And Who Should Take It

Hepatitis B vaccine is one of the most common vaccines today. It is used to develop immunity to Hepatitis B, a heavily contagious disease caused by the virus of the same name.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Hepatitis B is in decline in recent years. The figures have dropped from around 200,000 new infections a year in the 1980s to an average of 20,000 in 2016.
Contracting the virus doesnt necessarily put you at risk of a chronic infection. For individuals above the age of five, the chances of that happening are between 5 and 10%. Younger children are at a much higher risk. Under the age of five, the estimation is 25-50%. Infants run a 90% chance of developing a chronic infection if they contract the Hepatitis B virus.
The Hep B vaccine is the most common prevention methods for Hepatitis B, with the first vaccine being approved in the United States in 1981. In 1986, the first recombinant version became available. But how long does Hep B vaccine last? This article will explore the question. The possible side effects, risk factors and risk groups will also be considered.
Also Check: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Will My Immunization Be Recorded
Your immunization records are registered in a computerized network known as the Immunization Records and Yellow Cards. While this one is specific to Ontario, each province has their own.
They can use information obtained in these databases to:
- Maintain immunization data
- Inform you whether or when you or your family members need an immunization
- Track how well vaccinations perform to prevent vaccine-preventable infections
You can also share your immunization history with health care providers for the provision of social health services to aid with assessment and treatment and monitor the spread of infectious illnesses.
Who Is Allowed To Have The Vaccine
The vaccination is routinely available to children as part of the NHS 6-in-1 vaccine schedule from birth at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age.
Although the risk of infection is low in the UK, the virus persists for longer in children than it does adults so to avoid complications such as scarring and even liver cancer theyve given the vaccine.
Other high risk groups of people offered the vaccine include:
close family or sexual partners of someone with hepatitis B male and female sex workers people with any form of chronic liver disease people who inject drugs or have a partner who injects drugs babies born to infected mothers people who change their sexual partners frequently men who have sex with men anyone who receives regular blood transfusions or blood products, and their carers people with chronic kidney disease people who work somewhere that places them at risk of contact with blood or body fluids, such as nurses, prison staff, doctors, dentists and laboratory staff people travelling to high-risk countries prisoners families adopting or fostering children from high-risk countries
Don’t Miss: How Do I Get Hepatitis
What Is In The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Vaccines are given by a course of three injections, usually as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine scheme.
Although there are different types of vaccines, they usually contain one of the proteins from the surface of the hepatitis B virus thats then inserted in to the genetic code into yeast cells which stops the risk of viral DNA getting into the final product.
They also contain small amounts of sodium chloride and aluminium, and can contain yeast and formaldehyde.
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If you’re a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
If you have been vaccinated by your employer’s occupational health service, you can request a blood test to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Treatment In Homeopathy
How Long Does A Hepatitis A Vaccine Last
by Rachel Nall / in Health
Hepatitis A is a highly contagious disease of the liver that can cause severe symptoms, such as fever, nausea, vomiting, stomach or joint pain, tiredness and jaundice. While the disease is rarely fatal, it can cause liver failure, most typically in those ages 50 and older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The disease is transmitted via consuming contaminated foods or drinks, or through some form of close contact with an infected person.
What Is Hepatitis A
In a nutshell, hep A is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus. Since the liver is a major organ, this can be quite serious and some reports suggest that about 42% of the afflicted had to be hospitalized.
Hep A patients often feel very sick. Nevertheless, some people might not exhibit any symptoms at all. But when the symptoms do occur, they appear all of a sudden and include fatigue, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, and fever. Of course, signs of a dysfunctional liver will be on display.
Patients often have dark urine and clay-colored diarrhea. This is usually accompanied by loss of appetite, joint pain, and jaundice. Its worth noting that jaundice does not usually appear in young children .
Hepatitis A infection has quite a long incubation period of about 28 days on average. But, depending on some specific conditions, it may go up to 50 days. In addition, this liver infection is not easy to shake off. The symptoms usually persist for about two months. In 10 to 15% of the cases, the infection may last up to half a year.
This might sound alarming, but you may rest easier to know that hepatitis A is not a chronic condition. In fact, the IG antibodies developed during the infection would prevent it from ever occurring again.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Core Antibody
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
Can You Get A Vaccine To Prevent Hepatitis C
Vaccines are a way to expose your body to a virus before you encounter the live virus naturally. A vaccine contains traces of a dead virus, so your body can form a memory of the virus. Your body then remembers how to attack and destroy the virus if you ever come into contact with it.
There isnt a vaccine for hepatitis C at this time. Hepatitis C has many different subtypes and strains, so creating a vaccine that protects against all the different types is complicated. Vaccines are available for both hepatitis A and B, but one for hepatitis C hasnt been approved.
If you have hepatitis C, your doctor may suggest you get the vaccine for both hepatitis A and B. These two types of viruses cause liver damage, so the added protection is a smart idea.
Read Also: How Does One Contract Hepatitis
Who Should Be Immunised Against Hepatitis A
Travellers to countries outside Western Europe, North America and Australasia should consider being immunised. The highest-risk areas include the Indian subcontinent , Africa, parts of the Far East , South and Central America and the Middle East. Vaccination is generally recommended for anyone over the age of 1 year. Your doctor or practice nurse can advise if you should be immunised against hepatitis A for your travel destination.
You can find out if immunisation against hepatitis A is recommended for any countries you are planning to visit from the NHS website Fitfortravel.
Close contacts of someone with hepatitis A. Occasional outbreaks of hepatitis A occur in the UK within families or in institutions. Close contacts of someone found to have hepatitis A infection may be offered vaccination. This only happens rarely. The most important measure for anybody with hepatitis A is good personal hygiene. In particular, washing hands after going to the toilet or before eating.
People with chronic liver disease. If you have a persistent liver disease it is suggested that you have the hepatitis A vaccine. Hepatitis A infection is not more common in those with chronic liver disease but, if infection does occur, it can cause a more serious illness.
People exposed to hepatitis A at work. For example, laboratory workers who are exposed to hepatitis A during their work and sewage workers are advised to be immunised against hepatitis A.
Can A Person With Hep C Go Away Without Treatment
For these people, hepatitis C will be a short-term acute condition that goes away without treatment. But for most people, acute hepatitis C will likely develop into a chronic condition that does require treatment.
What happens to your liver if you have HEP a?
Unlike other types of viral hepatitis, hepatitis A does not cause long-term liver damage, and it doesnt become chronic. In rare cases, hepatitis A can cause a sudden loss of liver function, especially in older adults or people with chronic liver diseases.
What should you do if you have HEP a?
Practicing good hygiene, including washing hands frequently, is one of the best ways to protect against hepatitis A. Vaccines are available for people most at risk. Hepatitis A signs and symptoms typically dont appear until youve had the virus for a few weeks. But not everyone with hepatitis A develops them.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis Be Antibody
Check If You Have Hepatitis A
Symptoms of hepatitis A infection include:
- a high temperature
- flu-like symptoms, such as tiredness, headache, and muscle pains
- feeling sick or being sick
- pain in your upper tummy
- diarrhoea or constipation
- pale yellow or pale grey poo
- itchy skin you may also have a raised rash
- yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes
Most children, and some adults, may have mild symptoms or no symptoms.
How You Can Get Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is caused by a virus that spreads in poo.
The infection is more common in parts of Africa, Asia, the Middle East and Central and South America.
You can get hepatitis A from:
- drinking unclean water
- eating food that’s been washed or grown in unclean water
- eating food that’s been handled by an infected person
- close physical contact with an infected person, including having sex and sharing needles to take drugs
Recommended Reading: How To Protect Yourself From Hepatitis C
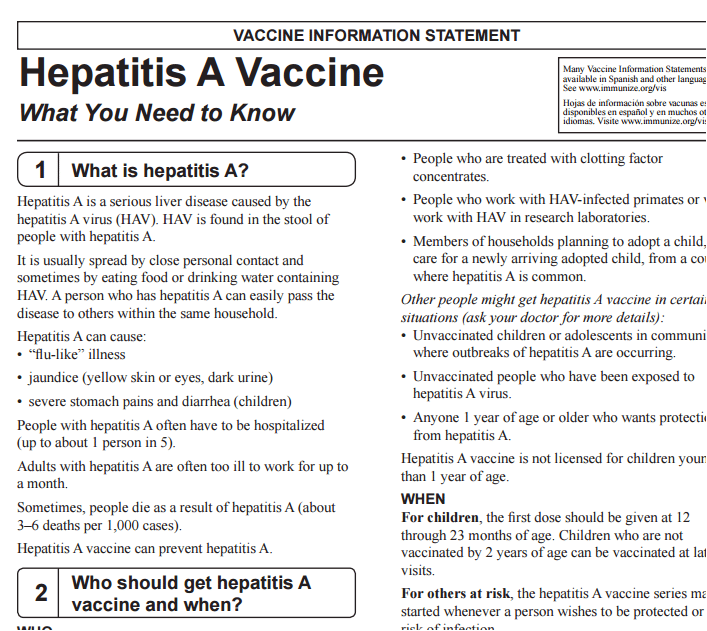
Who Should Get The Hepatitis A Vaccine
The CDC recommends that all children between ages 12 months and 23 months get this vaccine as well as for any infant aged 6 to 11 months who is traveling internationally.
The following people are also at risk for the disease and should be vaccinated:
- Children and teens through age 18 who live in states or communities that have made this vaccination routine because of a high rate of disease
- Men who have sex with men
- Anyone who uses illegal drugs
- People with chronic liver disease
- Anyone treated with blood clotting drugs, such as people with hemophilia
- People who work with HAV-infected primates or in HAV research laboratories.
- Travelers to countries where hepatitis A is common. A good source to check is the CDCâs travelersâ health website, which you can search by the country youâre going to.
- People adopting or close to a child adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common
You should not get the vaccine if you’re allergic to any ingredients in it or if you had a severe allergic reaction to an earlier dose of it. Tell your doctor or pharmacist about any allergies you have.
If you’re pregnant, let your doctor know. The safety of this vaccine for pregnant women is unknown, although the risk is considered to be very low.
How Long Does Hep A Vaccine Last
Thanks to vaccines, many serious infections and diseases that took countless lives are now almost a thing of the past. In fact, hepatitis A incidence rate has dwindled by an amazing 95% since the vaccine was first introduced in the US in 1995.
But in 2016, there has been an increase in hep A cases as a result of food imports. And this makes it all the more important to get a shot of hep A vaccine. But you may still wonder how long does hep A vaccine last?
Don’t Miss: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Another Person
Why Should I Vaccinate My Newborn Child If I Know That I Am Not Infected With Hepatitis B Virus
Before the hepatitis B vaccine, every year in the United States about 18,000 children were infected with hepatitis B virus by the time they were 10 years old. This statistic is especially important because people are much more likely to develop liver cancer or cirrhosis if they are infected early in life, rather than later in life .
About 9,000 of the 18,000 children infected in the first 10 years of life caught the virus from their mother during birth. However, many young children didnt catch the disease from their mother. They caught it from either another family member or someone else who came in contact with the child. Because hepatitis B can be transmitted by relatively casual contact with items contaminated with the blood of an infected person, and because many people who are infected with hepatitis B virus dont know that they have it, it is virtually impossible to be careful enough to avoid this infection.
For these reasons, all young children are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The best time to receive the first dose is right after birth. This will ensure that the child will be protected as early as possible from catching hepatitis B from people who dont know that they are infected with the virus.
Listen to Dr. Offit explain why newborns get the hepatitis B vaccine by watching this short video, part of the series Talking About Vaccines with Dr. Paul Offit.