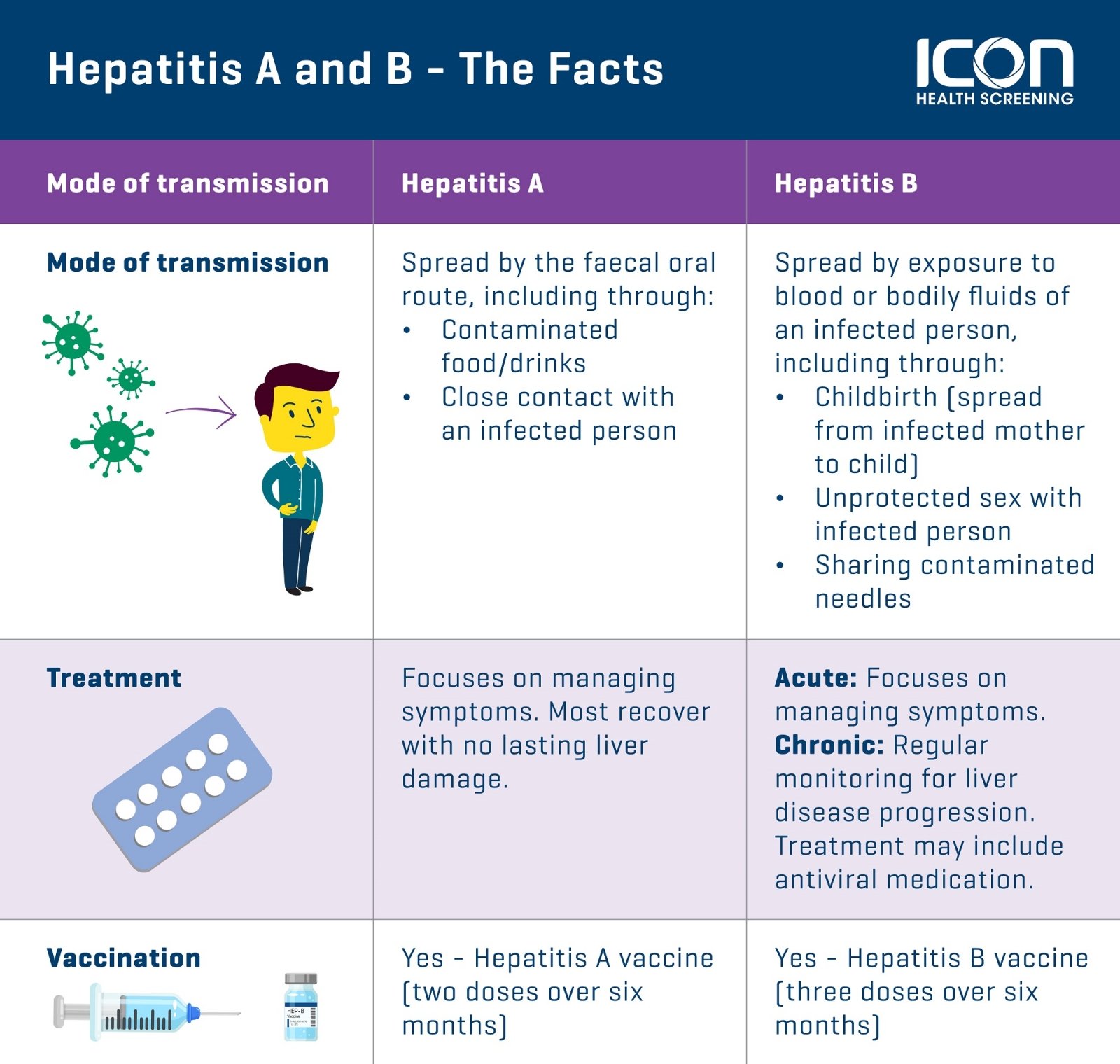
Hepatitis A: What Happens
Hepatitis A is highly contagious and can spread from person to person in many different settings. It typically causes only a mild illness, and many people who are infected may never realize they’re sick at all. The virus almost always goes away on its own and does not cause long-term liver damage.
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis
Testing is important for anyone with the risk factors we’ve mentioned, particularly injected drug users and people who have had multiple sex partners. Health advocates are also urging people of Asian heritage to get tested. Stanford University’s Asian Liver Center estimates that 1 in 10 Asians living in the U.S. has chronic hepatitis B. Many of them have probably had the virus since birth.
Also, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that health care providers offer a one-time hepatitis C screening for anyone born between 1945 and 1965.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
Symptoms of hepatitis A may include:
- Stomach pain, vomiting, loss of appetite.
- Diarrhea, stools that are light in color .
- Jaundice, which means that skin and eyes are yellow. This happens primarily to older children and adults. Kids younger than 6 years old do not generally have jaundice.
- Urine that is dark yellow in color.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Early Symptoms In Females
Hepatitis B: What Happens
Many adults who get hepatitis B have mild symptoms for a short time and then get better on their own. But some people are not able to clear the virus from the body, which causes a long-term infection. Nearly 90% of infants who get the virus will carry it for life. Over time, hepatitis B can lead to serious problems, such as liver damage, liver failure, and liver cancer.
What To Expect If You Get Cirrhosis
In the early stages of hepatitis C, your liver still has enough cells to do its many jobs. But with time, more cells die, and pressure builds up in the vein leaving the liver.
When that happens, symptoms of cirrhosis like jaundice may show up.
These are some possible complications of cirrhosis:
- Swelling in your legs and abdomen, which can lead to a serious bacterial infection.
- Enlarged blood vessels in your esophagus or stomach, which can burst and cause serious internal bleeding. This requires immediate medical attention.
- Enlarged spleen , which may lead to a low white blood cell or platelet count.
- Gallstones , from bile not flowing freely to and from your gallbladder.
- Greater sensitivity to drugs because your liver canât filter them from your blood.
- Resistance to the hormone insulin , leading to type 2 diabetes.
- Kidney and lung failure.
- Problems fighting infection.
Two other serious complications of cirrhosis are liver cancer and a buildup of toxins in your brain. The latter can interfere with your thinking, and can lead to coma.
Youâll need to see your doctor more often to manage these complications. Youâll have tests to see how your body is reacting. Your doctor may try a new combination of medications.
You May Like: Which Hepatitis Is An Std
Can Hepatitis B Positive Become Negative
It can happen, especially in older adults after a long period of inactive hepatitis B infection. About 1 to 3 percent of people with chronic hepatitis B lose HBsAg each year, and about half of all people with chronic infections who live up to age 75 will lose HBsAg, depending on the amount of HBV DNA in their blood.
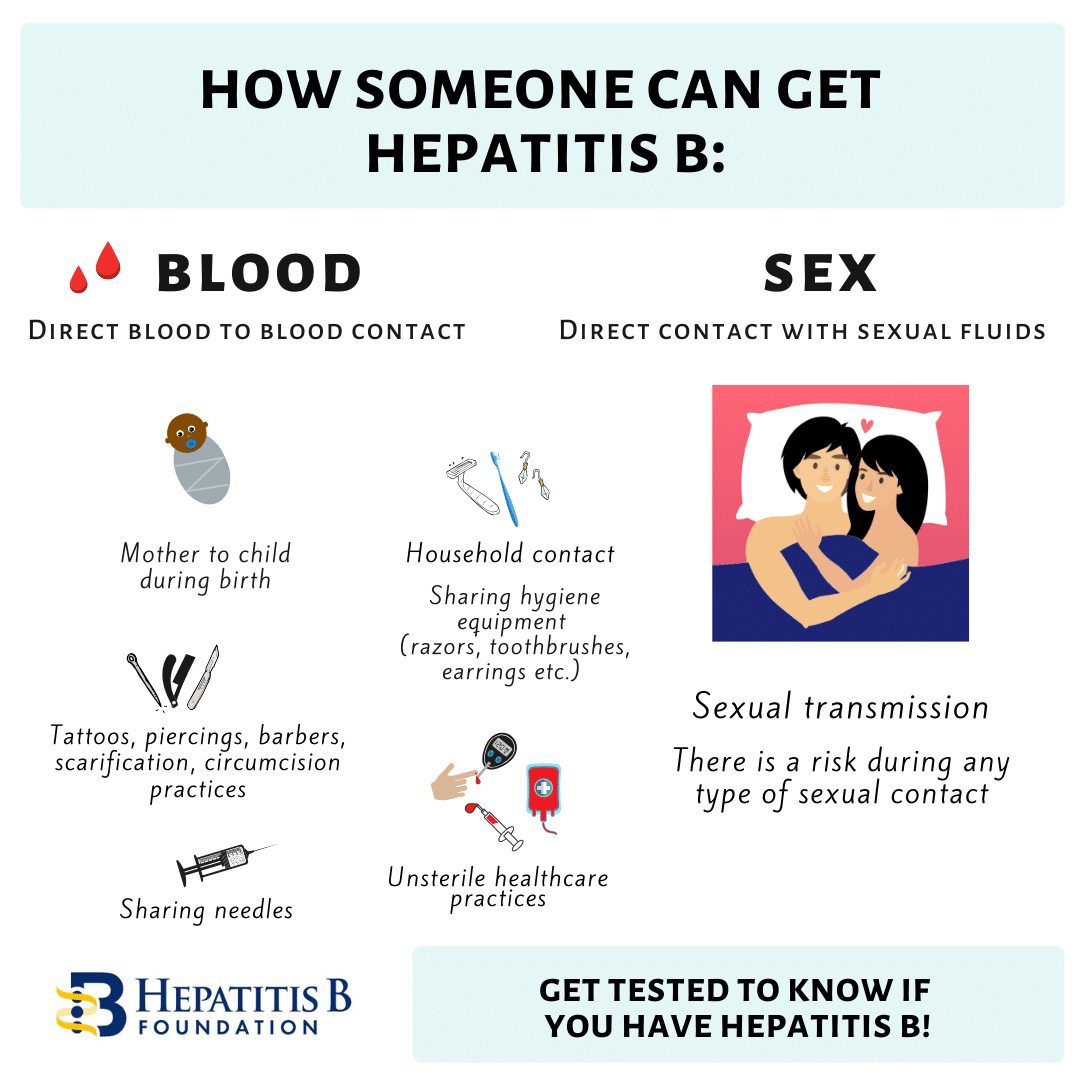
Hepatitis B: How Does It Spread
You can get it through contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person. In the U.S., it’s most often spread through unprotected sex. It’s also possible to get hepatitis B by sharing an infected person’s needles, razors, or toothbrush. And an infected mother can pass the virus to their baby during childbirth. Hepatitis B is not spread by hugging, sharing food, or coughing.
You May Like: Can You Live With Hepatitis C
Do Adults Need Hep A Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends hepatitis A vaccination for all children in the United States when they are one year of age, all children and teens through age 18 who were not pre- viously vaccinated, certain children age 6 through 11 months who are traveling outside the U.S., all adults …
Can I Breastfeed My Baby If I Have Viral Hepatitis
Yes, you can breastfeed your baby if you have viral hepatitis. You cannot pass viral hepatitis through breastmilk.
But, if you have hepatitis C and your nipple or the surrounding skin is cracked or bleeding, stop nursing your baby on that breast until the sores heal. You can pump or hand-express your milk from that breast until it heals. Throw any breastmilk from that breast away, because it might have been contaminated with hepatitis C from the cracked or bleeding skin.
Pumping the breast that is cracked or bleeding will help keep up your milk supply and prevent the breast from getting overly full and painful. You can feed your baby your milk from your healthy breast.24
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Cause Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Hepatitis Cases In Children
The number of cases of hepatitis in children has increased recently. Public health doctors and scientists are looking into what could be causing this.
See a GP if your child has symptoms of hepatitis, including yellowing of the eyes and skin .
Good hygiene, including supervising hand washing in young children, can help to prevent infections that can cause hepatitis.
Hepatitis C: How Does It Spread
It spreads through infected blood. In the U.S., sharing needles or other items used to inject drugs is the most common cause of infection. Getting a tattoo or body piercing with an infected needle is another means of exposure. A mother may pass the virus to their child at birth. In rare cases, unprotected sex spreads hepatitis C, but the risk appears small. Having multiple sex partners, HIV, or rough sex seems to raise risk for spreading hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Rx Vitamins For Pets Hepato Support
Sexual Transmission And Hepatitis A
Transmission of hepatitis A virus can occur from any sexual activity with an infected person and is not limited to fecal-oral contact. People who are sexually active are considered at risk for hepatitis A if they are MSM, live with or are having sex with an infected person, or inject drugs. Vaccination is the most effective means of preventing hepatitis A transmission among people at risk for infection. CDC has published recommendations for prevention of hepatitis A that identify all groups recommended for vaccination, including hepatitis A vaccination for MSM.
What Is The Risk

Because universal vaccination of newborns has been recommended since 1991, rates of Hepatitis B in the United States have been going down. But certain groups are still at higher risk, including:
- Infants born to mothers with hepatitis B
- People born outside the United States, or those who travel to areas like Asia or sub-Saharan Africa, where hepatitis B is more common
- Sexual partners of people with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs and share needles or syringes
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatic Steatosis Mean
Causes Of Noninfectious Hepatitis
Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue and liver failure.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. Itâs three times more common in women than in men.
What Can Happen If Viral Hepatitis Is Not Treated
Most people recover from hepatitis A with no treatment or long-lasting health problems.
Chronic hepatitis B and C can lead to serious health problems, such as:19
- Cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver
People with liver failure may need a liver transplant to survive. In the United States, cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C is currently the most common reason for needing a liver transplant.20 Viral hepatitis is also the most common cause of liver cancer.21
Read Also: Where Can You Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
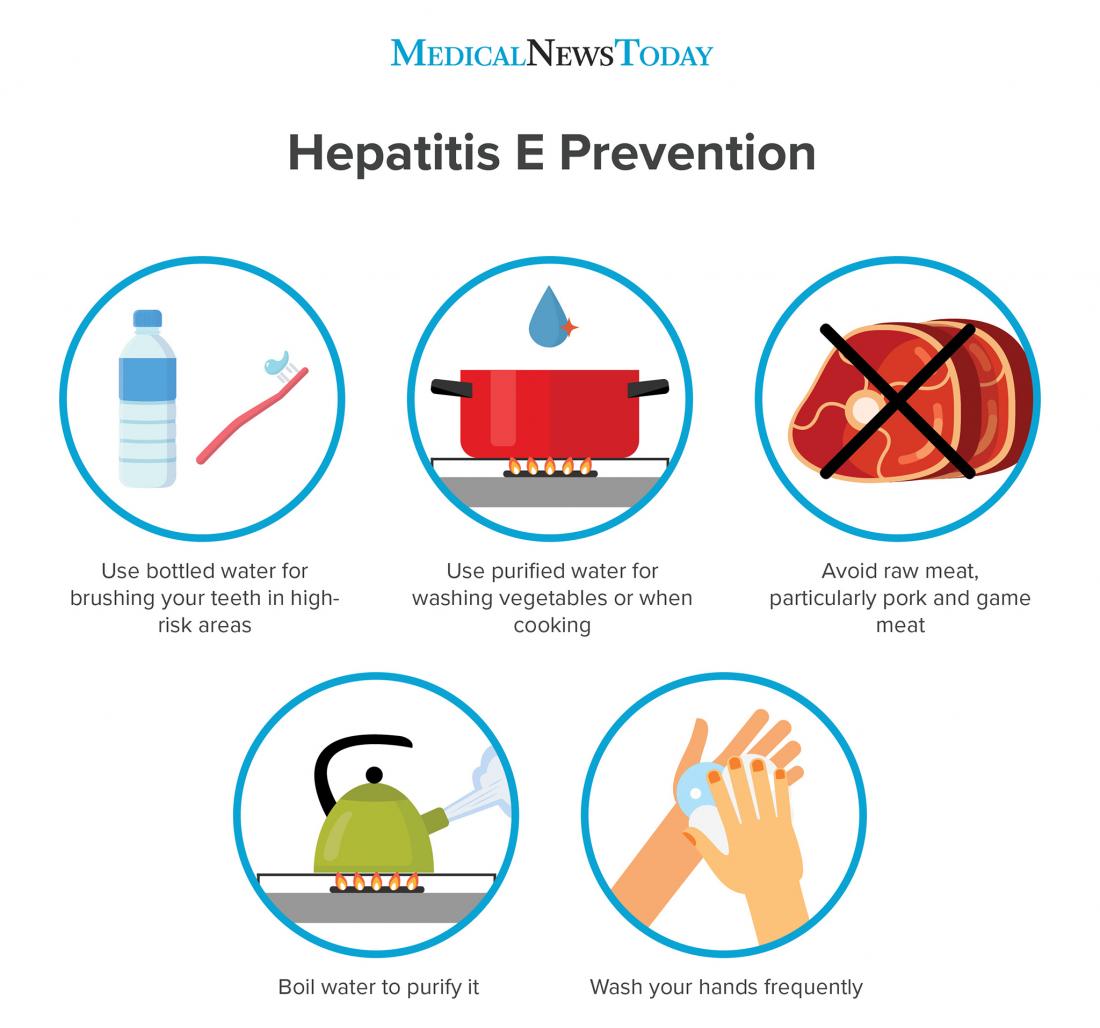
Can Hepatitis A Be Prevented Or Avoided
The best way to protect yourself against hepatitis A is to get the vaccine. The hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all children older than age 1. It begins to protect you only 4 weeks after you are vaccinated. A 6- to 12-month booster is required for long-term protection. Ask your doctor if the vaccination is right for you.
You should also wash your hands with soap and warm water before and after cooking, after using the bathroom, and after changing diapers.
Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating and avoid raw or undercooked meat and fish.
You are at higher risk for hepatitis A if you:
- Live with or have sex with someone who has hepatitis A
- Travel to countries where hepatitis A is common
- Are a man who has sex with other men
- Use illegal drugs
- Have a clotting-factor disorder
Also Check: Does Hepatitis B Go Away
How Do You Test For Hepatitis
Blood Tests Your doctor draws a small amount of blood from a vein in your arm and sends it to a laboratory for testing. The results of a blood test can confirm the type of viral hepatitis, the severity of the infection, whether an infection is active or dormant, and whether a person is currently contagious.
How Can I Contract Hepatitis A
You can contract the hepatitis A virus by eating food or drinking beverages that have been contaminated by human fecal waste.
Resort activities that may put you at risk for hepatitis A include:
Eating food handled by an infected worker who did not wash his/her hands properly after using the washroom
Eating raw or undercooked seafood and shellfish that lived in sewage-polluted water
Eating salads or produce rinsed in contaminated water
Drinking contaminated water or drinks with contaminated ice
Bathing, showering, or swimming in contaminated water
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine Used For
How Can I Get Free Or Low
The hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are covered under most insurance plans.
- If you have insurance, check with your insurance provider to find out whats included in your plan.
- Medicare Part B covers hepatitis B vaccines for people at risk.
- If you have Medicaid, the benefits covered are different in each state. Check with your state’s program.
Find a clinic near you where you can get vaccines for hepatitis A and B.
Sexual Transmission And Viral Hepatitis
Certain adults who are sexually active should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
CDC and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommend hepatitis B vaccination for
- sexually active people with more than one sex partner during the previous 6 months
- people seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease
- sex partners of people with hepatitis B and
- men who have sex with men .
CDC recommends one-time hepatitis C testing of all adults and regular testing for people with risk factors.
Don’t Miss: What Should I Do If I Have Hepatitis B
Can Hepatitis B And C Be Prevented
Today, all babies get vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus in a series of three shots over a 6-month period. Doctors also recommend “catch-up” vaccination for all kids and teens younger than 19 years old who didn’t get the vaccine as babies or didn’t get all three doses.
Unfortunately, there’s no vaccine for hep C yet.
What Are The Symptoms Of Viral Hepatitis
The symptoms of viral hepatitis are similar for all types of hepatitis.9 They include:
- Low-grade fever
- Jaundice , which is when the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow
People who are newly infected are most likely to have one or more of these symptoms, but some people with viral hepatitis do not have any symptoms. New hepatitis A infections usually cause symptoms, but as many as half the people with new hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections do not have symptoms.
Certain blood tests can show if you have hepatitis, even if you do not have symptoms. People with chronic hepatitis B or C often develop symptoms when their liver becomes damaged.
Also Check: Difference Between Hiv And Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
Chronic hepatitis can quietly attack the liver for years without causing any symptoms. Unless the infection is diagnosed, monitored, and treated, many of these people will eventually have serious liver damage. Fortunately, blood tests can determine whether you have viral hepatitis, and if so, which kind.
How Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis Treated
If you have chronic viral hepatitis, your treatment depends on the type of hepatitis you have:
- Hepatitis B. You will probably meet with your doctor regularly, every six to 12 months, to watch for signs of liver disease and liver cancer. If you plan to become pregnant in the future, talk to your doctor first. You may need antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis B, but many people do not need medicine. The Food and Drug Administration has a list of approved medicines to treat hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, talk with your doctor about whether you need medicine. Recently approved antiviral medicines treat and may cure hepatitis C in adults. The FDA has a list of approved medicines to treat hepatitis C. If you have health insurance, ask about your copay or coinsurance and which medicines are covered under your plan.
Don’t Miss: Pictures Of Hepatitis Skin Rashes
What Is Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to an inflammatory condition of the liver. It is commonly the result of a viral infection, but there are other possible causes of hepatitis.
These include autoimmune hepatitis and hepatitis that occurs as a secondary result of medications, drugs, toxins, and alcohol. Autoimmune hepatitis is a disease that occurs when your body makes antibodies against your liver tissue.
The five main viral classifications of hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. A different virus is responsible for each type of viral hepatitis.
The World Health Organization estimates that people currently live with chronic hepatitis B and C globally.
How Is It Treated
There are no medicines for treating hepatitis A. Ifyou have been exposed to hepatitis A virus, tell yourhealth care provider. They may be able to give you aprotein that fights hepatitis A virus to help keep youfrom getting sick. Most people with hepatitis A recoverwithout treatment in a few months. A few people willneed to be hospitalized for hepatitis A.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Antibody 0.1 Meaning
Does Viral Hepatitis Affect Women Differently Than Men
Yes, certain types of viral hepatitis affect women differently than men.
Hepatitis A affects women and men in similar ways.
Hepatitis B affects women differently than men:
- Birth control. Women with severe liver damage may not be able to use birth control.1 This is because a damaged liver may have problems breaking down estrogen.
- Pregnancy. The risk of passing hepatitis B to your baby during pregnancy is high. Hepatitis B raises your risk for pregnancy complications.2 Talk to your doctor about taking hepatitis B medicine to lower the risk of passing hepatitis B to your baby. Certain hepatitis B medicines are safe to take during pregnancy but are not recommended for everyone. Learn more about hepatitis B during pregnancy.
Hepatitis C affects women differently than men:
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually given in three doses over six months. The vaccine is recommended for:28
- All children at birth
- All children and teens younger than 19 who have not been vaccinated
- Men who have sex with men
- People who live with or have sex with someone who is infected with hepatitis B
- People with more than one sex partner
- People who share equipment to inject drugs
- People with chronic liver or kidney disease
- People with HIV
- People younger than 60 with diabetes
- People whose jobs expose them to human blood or other body fluids
- Residents and staff of facilities for people with developmental disabilities
- People who travel to parts of the world where hepatitis B is common, such as Southeast Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, the Amazon Basin in South America, the Pacific Islands, parts of Eastern Europe, and parts of the Middle East.29 See the CDCs Travelers Health information page.
Read Also: Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus . In the USA, hepatitis A infections have declined by 90% since the hepatitis A vaccine first became available in 1995. Still, there are cases of hepatitis A reported to the San Francisco Department of Public Health every year among San Francisco residents. Hepatitis A is still common in Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and eastern Europe.