Evaluation Of Individuals Suspected Of Having An Hbv Infection
Given the perinatal and childhood vaccination programs already in place in North America, most HBV-infected individuals will likely present with chronic infection. Such individuals are likely to have risk factors that include immigration from high endemicity regions, injection drug use or sexual contact with an infected person 1) . Therefore, the present guideline will provide diagnostic recommendations first for individuals suspected of having chronic HBV infection and, subsequently, for those with acute infection. The diagnosis of HBV infection in any individual has important management implications, including appropriate counselling, monitoring and/or treating and vaccinating family or at-risk contacts.
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Igm Class Antibody To Hav
- If the IgM class antibody to HAV is negative, HAV infection is ruled out in immunocompetent patients .
- If positive, acute HAV infection is likely. As the anti-HAV-IgM may remain detectable for up to two years after infection in a small subset of patients, the history and clinical presentation must be considered in making an accurate diagnosis .
Recommended Reading: Which Is Worse Hepatitis B Or C
Submission And Collection Notes
Freshly drawn whole blood specimens may be stored and/or transported at 2°C to 25°C for up to 24 hours before centrifugation. Following centrifugation, remove serum from cells immediately, and transfer serum into screw-capped cryovial tubes.. Serum specimens may be stored and/or transported at 2°C to 8°C for up to 6 days or at -18°C for up to 12 weeks. If more extended storage of serum specimens is required, it must be frozen at -60°C.
Unspun whole blood must be received at Public Health Ontarios Laboratory within 24 hours of collection before 2:00 p.m. Monday Friday.
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
Also Check: Ok Google What Is Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
There is no specific treatment for acute hepatitis B infections. Symptoms are usually treated with supportive care. This usually involves making sure that you are getting plenty of rest and enough fluids and nutrition by eating and drinking small amounts several times a day.
Chronic forms of hepatitis B may be treated with antiviral medications such as interferon, entecavir, tenofovir, lamivudine, and adefovir. However, some antiviral drugs can have serious side effects and not all people need to be treated. Often, people with chronic hepatitis will be closely monitored to see if they develop cirrhosis or liver cancer. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about your treatment options and the risks and benefits of those currently available.
Interpreting Hcv Rna Test Results
It is essential that the provider understands how to interpret HCV RNA test results, especially during the course of HCV treatment.
| Result of HCV RNA Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A quantified viral load — any exact number | Ongoing HCV infection |
| “Detected” | The HCV RNA is detectable but the number of international units is so low that it cannot be quantified accurately. This indicates extremely low level of virus is present. |
| “< 12 IU/mL” or “< 15 IU/mL” or “< 25 IU/mL” All of these are “less than the LLOQ” | HCV RNA is undetectable. No virus is detected at all in the patient’s serum specimen. |
Recommended Reading: What Is Acute Hepatitis C
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Hep B can be very complex and not every doctor has a good understanding of it. You can check our directoryfor a hep B specialist doctor or use our resources to help you and your doctor through hep B testing.
Your doctor might ask you about your family history of hep B or liver disease, where you were born, and any other possible exposures to hep B such as unprotected sex or injecting drug use.
You can tell your doctor as much or as little as you feel comfortable with. More information can help your doctor make the best decisions for your health, but what you share with them is up to you.
You might be able to access healthcare via your computer or phone.
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients may find it helpful to ask questions about their hepatitis B test results. Questions that may be helpful include:
- What was my test result?
- Do I have an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection?
- Does the test result suggest that I have immunity for hepatitis B?
- Would I benefit from hepatitis B vaccination?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my hepatitis B test results?
You May Like: Hepatitis C Sexually Transmitted Disease
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
How Is It Used
The main uses for hepatitis B virus tests include:
Some of the secondary reasons to perform testing include: to screen for hepatitis B infection in at-risk populations or in blood donors, to determine if someone is a carrier, to detect a resolved infection, and to determine if immunity has developed due to vaccination.
Generally, one set of tests is used as an initial panel of tests to detect HBV infection or to determine the cause of acute symptoms while another set of tests may be used after a diagnosis is made to monitor possible progression of the disease, to detect chronic infection, and/or to determine carrier status.
The following table summarizes the set of tests typically used for initial testing:
The following table summarizes tests that may be used as follow-up after initial tests detect an HBV infection:
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis Ab And C
Antibody To Hcv Antigens
- If negative, chronic HCV infection is ruled out in immunocompetent individuals. Because the antibody to HCV antigens response in immunocompromised persons can be blunted, a qualitative test for HCV-RNA may be required to rule out occult infection in such individuals. A new HCV core antigen test, which is currently under evaluation, can also be used to confirm active infection . However, the currently available HCV core antigen test is less sensitive, detecting less than 90% to 95% of HCV-RNA-positive specimens . Therefore, the current HCV core antigen should not be used for definitive exclusion of active infection.
- If found to be anti-HCV positive, the patient has been infected with HCV. Because most HCV infections are chronic , the presence of anti-HCV is correlated with active infection however, a qualitative test for HCV-RNA is currently required to confirm active HCV infection .
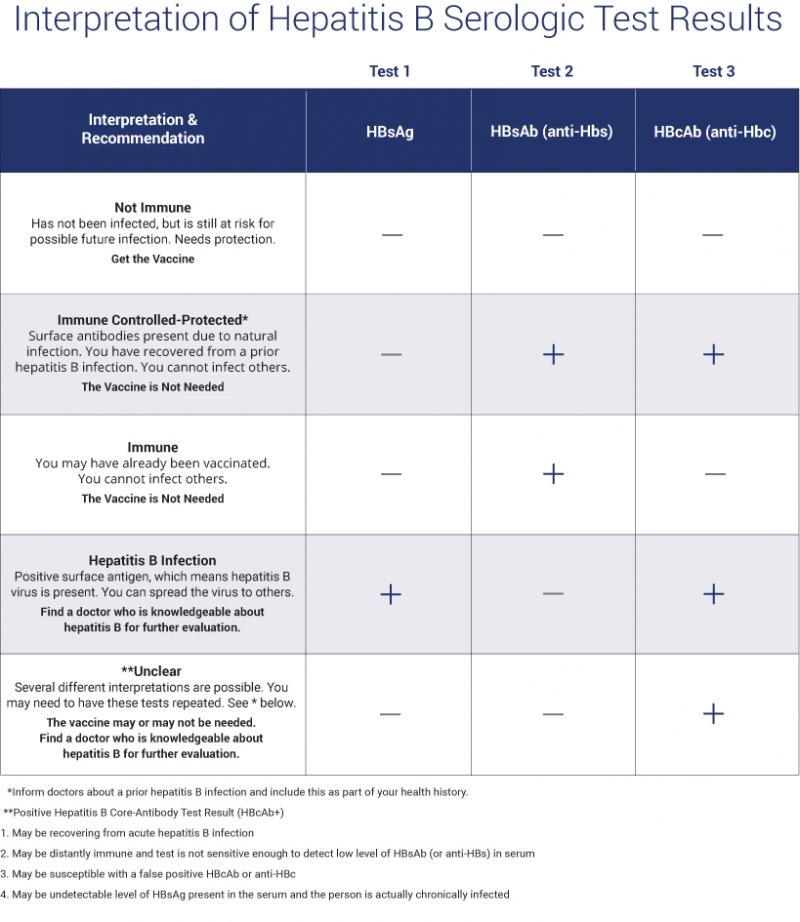
Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel Includes:

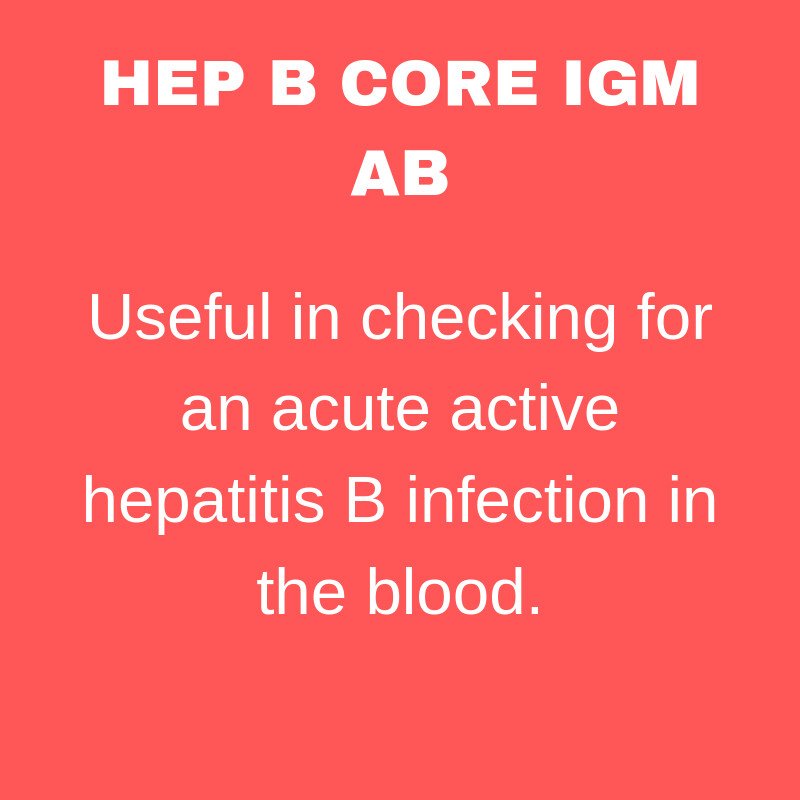
Anti-Hepatitis B Core Antigen is an antibody to the hepatitis B core antigen. The core antigen is found on virus particles but will disappear early in the course of infection. This antibody is produced during and after an acute HBV infection and is normally found in chronic HBV carriers and those who have cleared the virus, and usually persists for life. Anti-HBc testing is either specific for the IgM antibody, anti-HBc, IgM, which will indicate acute infection, or measures total antibody, anti-HBC, which will indicate a past infection, either acute or chronic.
The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody is the most common test. Its presence will indicate previous exposure to HBV, but the virus is no longer present and the person cannot pass the virus on to others. The antibody will also protect the body from future HBV infection. In addition to exposure to HBV, these antibodies can also be acquired from successful vaccination. This test is performed to determine the need for vaccination , or following the completion of vaccination against the disease, or following an active infection.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen is a protein antigen produced by HBV. This antigen is the earliest indicator of acute hepatitis B and often identifies infected people before symptoms appear. HBsAg will disappear from the blood during the recovery period. In some people , chronic infection with HBV may occur and HBsAg will remain positive.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Virus
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Time For Processing Hcv Ab Test Results
The turnaround time for 3rd-generation EIAs is at least 1 day. Many labs do not perform the tests on site and must send specimens to another lab for processing, which may further increase the turnaround time.
A point-of-care test is also available. The OraQuick® HCV Rapid Antibody Test is an FDA-approved test that can be performed with a fingerstick . It is also a CLIA-waived test and therefore can be used in clinic offices and outreach facilities. Results are reported as reactive or nonreactive within 20 minutes. Just as for the standard HCV Ab test done in the lab, a positive OraQuick® test must be confirmed by an HCV RNA test. The sensitivity and specificity of the test is similar to that of the laboratory-based assays.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost Cvs
Preparing Clients For Screening
Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
Are There Blood Tests For Hepatitis B
Yes. Many chronically infected persons show no outward signs of hepatitis B infection. Therefore, screening for hepatitis B is important and necessary. Ask your doctor for the following blood tests:
HEPATITIS B SURFACE ANTIGEN : Tells if you have chronic hepatitis B. Only the HBsAg blood test can tell if you have chronic hepatitis B.
HEPATITIS B SURFACE ANTIBODY : Tells if you are protected against hepatitis B.
| Test Result |
| Chronic HBV infection |
Don’t Miss: Unspecified Hepatic Cirrhosis Type Hcc
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can contract hepatitis B. However, certain groups are at greater risk. According to the CDC, the following groups are at highest risk for contracting hepatitis B:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- People who inject drugs or share needles
- Sexual partners of people infected with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People living in close proximity to a person with hepatitis B
- Health care workers or others exposed to blood in their work environments
- Hemodialysis patients
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
You May Like: What Type Of Hepatitis Can Be Cured
Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
Doctors must closely monitor pregnant people who have HBV.
There is a risk that the virus can pass from parent to child during delivery without the correct treatment. Therefore, all people should receive hepatitis B testing during pregnancy. A person with chronic hepatitis B should talk with a doctor about the risks and benefits of antiviral treatment while pregnant.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, if someone has HBV, their newborn must immediately receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of birth. The infant should then receive the second and third doses of the vaccine according to the standard childhood immunization schedule.
Pregnant people unsure of their vaccination status can receive the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy and breastfeeding or chestfeeding.
However, there is currently not enough safety information about Heplisav-B and PreHevbrio, so pregnant people
What Is Hepatitis D And How Is It Associated With Hepatitis B
Hepatitis D is another virus that can cause liver infections, but only if hepatitis B is also present. A person may become infected with both viruses at the same time or may first be infected with hepatitis B and then become infected with HDV . In the U.S., the incidence of HDV is low. There is no vaccine for HDV, but since it causes infections only in the presence of HBV, it may be prevented with the HBV vaccine.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C And Is It Curable
Who Should Get Screened For Hepatitis B
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control calls for HBV screening of all foreign-born persons from regions where hepatitis B is common regardless of their vaccination history.
Additionally, all pregnant women should be screened for HBV at an early prenatal visit during each pregnancy, even if they have been previously tested or vaccinated.
Other groups recommended for HBV screening include:
- Anyone seeking protection from the HBV infection
- Healthcare and public safety workers
- Household, sex, or needle-sharing contacts of persons infected with HBV
- Intravenous drug users
Why It Is Done
You may need testing if:
- You have symptoms of hepatitis.
- You may have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus. You are more likely to have been exposed to the virus if you inject drugs, have many sex partners, or are likely to be exposed to body fluids .
- You’ve had other tests that show you have liver problems.
- You are pregnant.
- You or your doctor wants to know if you are protected from getting the disease.
The tests also are done to help your doctor decide about your treatment and see how well it’s working.
Also Check: Hepatitis B And C Coinfection Treatment 2020
Recommended Tests To Investigate Acute Hbv Infection And The Interpretation Of Results
Acute HBV infection generally presents after an incubation period of six weeks to several months with an onset of nonspecific symptoms that may include fever, malaise, anorexia and nausea, followed by the onset of jaundice, dark urine and pale stools. Approximately 25% to 40% of infected adults will be symptomatic, and most will demonstrate elevations in ALT however, infants, toddlers and immunosuppressed individuals may not manifest signs or symptoms of infection. The management of acute infections is largely supportive unless fulminant hepatitis develops, in which case the patient should be referred to a liver specialist. Because the clinical features of acute hepatitis are very similar for HAV, HBV and HCV, testing for all three agents should be performed when working up an acute case. While the sexual transmission of HCV is rare, varying between zero to six cases per 1000 person-years , HAV that is typically spread by the fecal-oral route poses a clear risk to sexual partners. Figure Figure11 and Table Table22 outline the appropriate serological tests to investigate acute hepatitis.