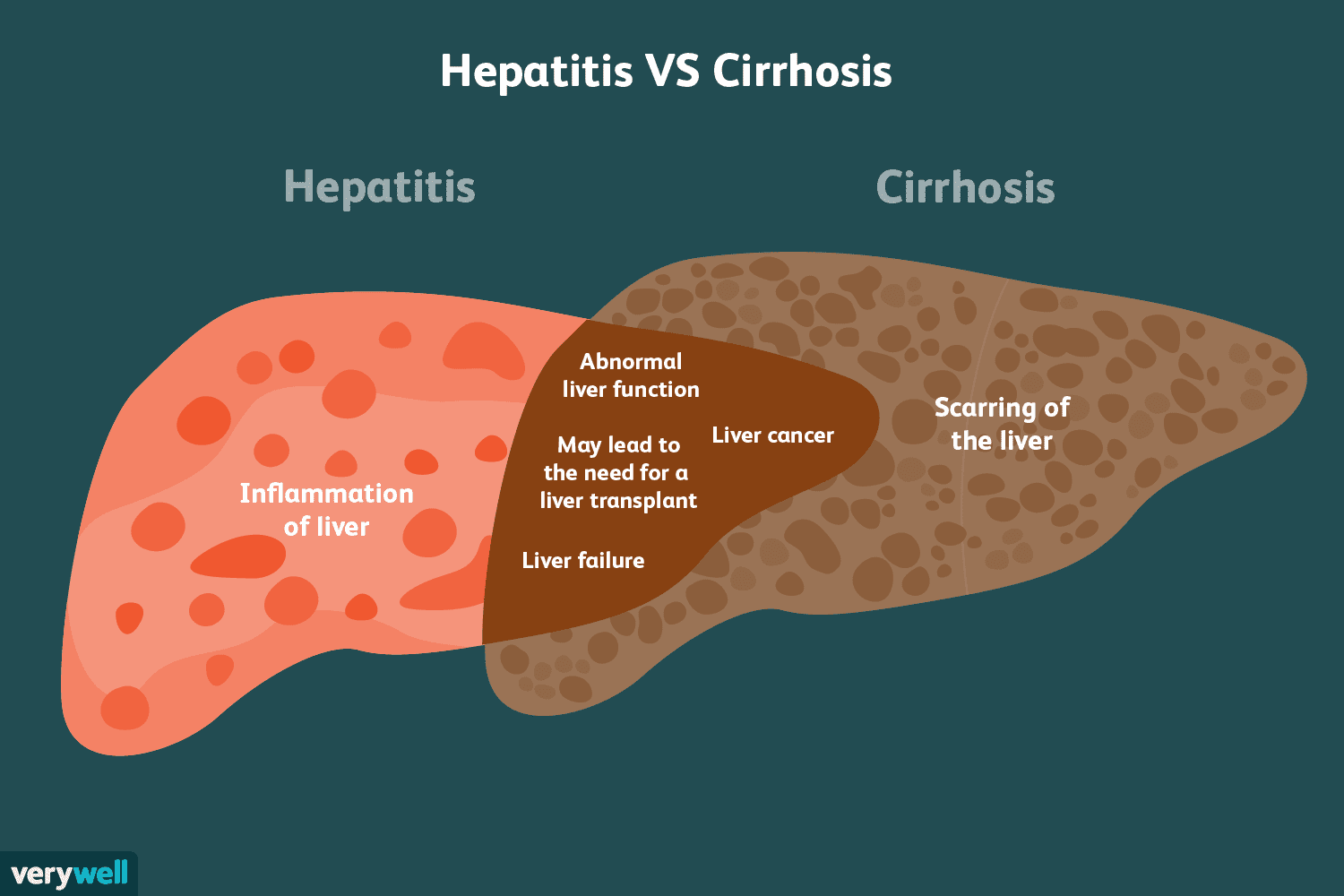
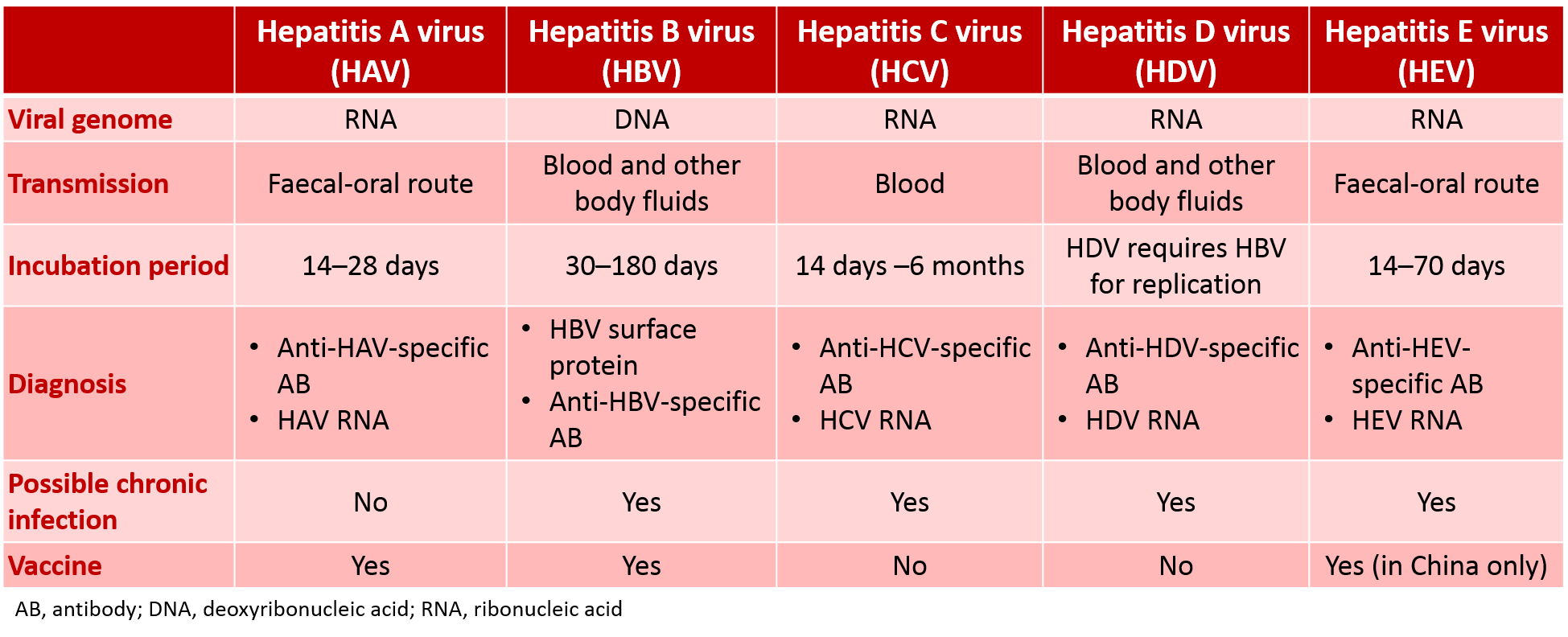
Causes Of Acute Viral Hepatitis
Other viruses can also cause acute viral hepatitis. These viruses include the Epstein-Barr virus , which is the virus that causes infectious mononucleosis Infectious Mononucleosis Epstein-Barr virus causes a number of diseases, including infectious mononucleosis. The virus is spread through kissing. Symptoms vary, but the most common are extreme fatigue, fever, sore throat… read more .
Engaging in certain activities, such as getting a tattoo or body piercing, sharing needles to inject drugs, or having several sex partners, increases the risk of developing hepatitis.
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis C To Others
If you have hepatitis C, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Tell your sex partner you have hepatitis C, and talk with your doctor about safe sex practices. In addition, you can protect others from infection by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care providers that you have hepatitis C. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
What Is The Difference Between Relapse And Nonresponse
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis C is to completely clear the virus. This means that your viral load is zero or so low that the virus cant be detected with standard blood tests.
Without treatment, the hepatitis C virus in liver cells constantly makes copies of itself, and the virus ends up not just in liver cells but also in the bloodstream. Treatment is intended to completely stop reproduction of the virus so that it doesnt continue to enter the bloodstream or cause any more injury to liver cells.
Successful treatment results in a sustained virological response. This means the virus becomes completely undetectable before the treatment is finished, and it remains undetectable for 6 months after treatment is stopped.
A relapse means the viral load drops to an undetectable level before treatment is completed, but becomes detectable again within 6 months after treatment is stopped. Even if the virus returns at a level that is lower than it was before treatment, a relapse is still considered to have occurred. A relapse can be determined if the viral load starts to rise during treatment, or at any time after the virus becomes undetectable.
A nonresponse means the viral load never drops significantly and the virus remains detectable throughout the course of treatment.
Dont Miss: What Does It Mean If You Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Given the exhaustive conditions that can cause acute hepatitis, the management of this clinical condition requires an interprofessional, collaborative team approach that would aid in making a timely diagnosis resulting in appropriate management. Clinical presentation of acute hepatitis in patients can range from being asymptomatic with incidental abnormal liver biochemical test results to being critically ill with signs concerning for acute liver failure. In clinical practice, acute hepatitis is primarily encountered by primary care physicians, emergency medicine physicians, and internists. Depending on the etiology and the severity, other specialists may need to be involved in the care team, including gastroenterologists, hepatologists, pharmacists, nursing staff, toxicologists, infectious disease specialists, transplant surgeons, intensive care teams, or liver transplant centers.In some instances of acute hepatitis caused by drug overdose or drug abuse, the involvement of behavioral health experts and substance abuse professionals is imperative. Clinical pharmacists should thoroughly review the patient’s medication profile and assist with appropriate drug dosing to prevent further insult from hepatotoxicity from drugs and drug-drug interactions.
What Does A Hepatitis Panel Involve
Hepatitis panels are simple blood tests. They do not involve any preparation and have a very low risk of side effects.
To perform the test, a healthcare professional will insert a needle into a vein in the arm. They will collect a small blood sample in a test tube and seal it. The needle may sting a little, but the process takes only a few minutes. A person may feel a small amount of pain or bruising around the vein, but this should subside quickly.
People can also get at-home testing kits for hepatitis. These come with a sterile lancet that a person uses to prick their finger to collect the blood sample.
When using at-home kits, be sure to take safety precautions to prevent others from coming into contact with blood. Even dry blood or tiny amounts of blood can potentially transmit HBV or HCV to others.
Dispose of items that come into contact with blood in a sealed bag and wash the blood from the skin using soap. Completely cover the finger prick wound with a sterile dressing until it heals.
- of the population have hepatitis B and have not had a vaccination
- spent time in a facility that had a hepatitis outbreak, such as a hospital or prison
- received a blood transfusion that did not undergo hepatitis screening
In the United States, screening eliminated HCV from donated blood in 1992. People who received blood transfusions before 1992 should ask their doctor for a hepatitis C test.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know When You Have Hepatitis
How Should I Take Care Of Myself If I Have Hepatitis C
Good health habits are essential for those who have hepatitis C. You should especially avoid alcohol and medicines and drugs that can put stress on the liver. You should eat a healthy diet and start exercising regularly. Your family doctor can help you plan a diet that is healthy and practical.
Talk to your doctor about any medicines that you are taking, including over-the-counter medicine. Many medicines, including acetaminophen , are broken down by the liver. Because of this, they may increase the speed of liver damage. You should also limit alcohol use. It speeds the progression of liver diseases like hepatitis C. An occasional alcoholic drink may be okay, but check with your doctor first.
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But it’s important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Child
But Even If You’ve Been Cured It Can Have Lifelong Health Implications
“Hepatitis C is a lot more than just a liver disease,” Reau says. “It has been associated with many medical conditions, such as an increased risk of developing diabetes, kidney disease and cancer.”
While curing hepatitis C significantly reduces the risk of serious complications, like liver failure, liver cancer and the need for transplantation, it doesn’t completely eliminate the health risks associated with the disease.
“Hep C is linked to scarring of the liver or cirrhosis and the more scar tissue that develops, the greater the likelihood of complications,” Reau says. “If there is a lot of scarring, you will need lifelong monitoring.”
Reau also recommends leading a healthy lifestyle to help prevent re-infection and further liver damage: Limit alcohol consumption, control your weight, avoid high-risk activities and manage diabetes if you have it.
Innate Immunity To Hcv Infection
An acute viral infection triggers the activation of several antiviral effectors in mammalian cells. This innate antiviral response is an early host defense mechanism that occurs prior to adaptive immune responses.41 The recent discovery of pathogen-associated molecular patterns that are recognized by specific toll-like receptors have dramatically advanced our understanding of the innate host response to viral infection.42 For example, HCV RNA contains pathogen-associated molecular pattern motifs43,44 that could bind to toll-like receptor 3 at the cell surface and intracellularly through retinoic acidinducible gene 1 to induce type I interferons in hepatocytes.43,45 Type I interferons regulate the antigen-processing machinery through the induction of immunoproteasome subunits, their incorporation into the proteasome complex, and the generation of an immunoproteasome-dependent CD8 T cell epitope.46 Moreover, type I interferons activate the expression of more than 300 interferon-stimulated genes that also have antiviral functions. The best characterized include the RNA-dependent protein kinase , 25-oligoadenylate synthetase, RNase L, adenosine deaminase , and the Mx protein GTPases.
Read Also: How Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
What Is Known About These Hepatitis Cases In Children So Far
It began in October 2021, when five pediatric cases of severe hepatitis with unknown cause were identified in children at an Alabama hospital, the CDC reports. The children had significant liver illness, including some with liver failure. All tested negative for hepatitis A, B, and C, but positive for adenovirus.
The children, who ranged in age from 1 to 6, were previously healthy and came from different parts of the state with no known contact or common exposures. Furthermore, none of the children in Alabamawhich later grew to nine reported caseshad any signs of COVID-19 infection prior to or during hospitalization.
Since then, more cases of pediatric hepatitis with unknown origin have been reported in other states and around the world. Adenovirus has been detected in some of these patients, but not all. In the cases in the U.S. so far, 50% had adenovirus, the CDC says. Investigators around the world are looking into other possible causes and contributing factors.
For now, the CDC recommends that doctors who treat children with unexplained hepatitis consider testing them for adenovirus.
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis C testing identifies antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, detects viral RNA, and/or determines the strain of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C testing may involve several different tests:
- Hepatitis C antibody test: Antibodies are a part of the bodys response to an infection. Testing for hepatitis C antibodies determines whether or not a patient has been exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in their life. If this test is positive, the next step is to test for hepatitis C RNA which can tell you if you have a current infection.
- Hepatitis C RNA test: RNA is a type of genetic material from the hepatitis C virus that can be detected in the blood. If test results are positive after a hepatitis C antibody test, doctors use a hepatitis C RNA test to look for and/or measure the amount of the virus in the blood. Qualitative HCV RNA tests can detect the presence of HCV RNA, while quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of HCV RNA. Understanding the amount of HCV in the blood helps to monitor response to treatment.
- Genotype test: There are at least six types of hepatitis C, which are also called strains or genotypes. Treatment for hepatitis C depends on the strain, so genotype testing to guide treatment is performed in patients who are diagnosed with an HCV infection.
Read Also: How Us Hepatitis C Transmitted
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can be spread from person to person. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood.
Hepatitis C can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Although no vaccine for hepatitis C is available, you can take steps to protect yourself from hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, talk with your doctor about treatment. Medicines can cure most cases of hepatitis C.
How Can I Make A Difference For People With Hepatitis C
Anyone can help raise awareness about this widespread disease. Citizens can write letters to their state representatives or local newspapers and get involved in volunteer efforts with liver disease or Veteran-affiliated organizations . Speaking at support groups and sharing your experience is also a good way to help others with HCV.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B And How Do You Get It
Also Check: What Is The Schedule For Hepatitis B Vaccine For Adults
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Recommended Testing For Diagnosing Acute Hcv Infection
RECOMMENDED RATING HCV antibody and HCV RNA testing are recommended when acute HCV infection is suspected due to exposure, clinical presentation, or elevated aminotransferase levels . I, C
Recommendations for HCV testing are also found in the Testing and Linkage to Care section.
Diagnosis of acute HCV infection enables estimation of annual incidence rates and transmission patterns, thereby facilitating implementation and assessment of prevention programs. At the individual level, a diagnosis of acute infection expedites linkage to care, counseling regarding high-risk behavior, and timely interventions to reduce virus transmission and liver disease progression . Some persons involved in high-risk behaviors practice serosorting, defined as using HCV antibody serostatus to determine whether to engage in high-risk behaviors with certain individuals . Thus, undiagnosed acutely infected persons may be at greater risk of transmitting HCV to their presumably seronegative contacts than would be expected by chance.
The best laboratory evidence to support a diagnosis of acute HCV infection is a positive HCV RNA test in the setting of a negative HCV antibody test , or a positive HCV antibody test after a prior negative HCV antibody test . There are rare instances in which these approaches may be misleading, such as in immunosuppressed individuals with impaired antibody production .
Discrete Exposure
No Discrete Exposure
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost Walmart
I Have Hepatitis C And Im Thinking About Having Children What Should I Know
Hepatitis C does not prevent a man or woman from having children.
The hepatitis C virus infection does not cause infertility in either sexit does not affect a womans ovarian or uterine function, or a mans sperm production or sperm characteristics.
If you are a woman with hepatitis C, talk to your provider about treatment before pregnancy. Treatment before pregnancy can help reduce the risk of hepatitis C transmission to your baby. If you are already pregnant, treatment will usually take place after pregnancy and you may need to be tested for hepatitis C again prior to starting treatment.
If you are a man with hepatitis C, talk to your provider about being treated prior to conceiving. Although the risk of transmission during sex is low, it is still important to treat hepatitis C for your personal health.
What Is Acute Severe Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Depending on the cause, the disease can be very sudden and progress to liver failure over a few days to weeks . Some types of hepatitis can be treated and most cases recover. Acute severe hepatitis in children is a rare condition in Canada, and in many cases, an underlying or contributing cause is not known.
Recommended Reading: Early Signs Of Hepatitis C And Treatments To Know
When To Seek Medical Advice
See your GP if you persistently have any of the later symptoms listed, or if they keep returning. They may recommend having a blood test that can check for hepatitis C.
Read more about diagnosing hepatitis C
None of these symptoms mean you definitely have hepatitis C, but it’s important to get them checked out.
You should also speak to your GP about getting tested if there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you don’t have any symptoms. This particularly includes people who inject drugs or have done so in the past.
Read about the causes of hepatitis C for more information about who’s at risk of having the infection.
Page last reviewed: 27 October 2021 Next review due: 27 October 2024
Cases Reported In Canada
As of May 20, 2022, there are ten cases of acute severe hepatitis in children in Canada meeting the national case definition. The breakdown by province is as follows:
- Alberta
- Ontario
- Quebec
The children, who are between 1 and 13 years old, became sick between November 3, 2021 and April 23, 2022. All children were hospitalized. Two children have required a liver transplant. No deaths have been reported. Some children may live in one jurisdiction and receive treatment in another jurisdiction. These children are being counted in the province where they live.
It is important to note that the definition being used to include cases in the national investigation is very broad. This means that any children with acute severe hepatitis where a cause is not certain are being included in initial investigations. Some of these children may have a diagnosis for their liver condition, but they are being included to explore possible factors that may have triggered the condition. PHAC is reporting information to the World Health Organization. Additional information for cases is being reviewed, and the investigation into the possible causes is ongoing.
Read Also: What R The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Recommended Regimens For Patients With Acute Hcv Infection
RECOMMENDED RATING Owing to high efficacy and safety, the same regimens that are recommended for chronic HCV infection are recommended for acute infection. IIa, C
A number of studies have evaluated DAA treatment of acute HCV infection. Small single-arm, uncontrolled studies have evaluated 6 or 8 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir. One such study demonstrated 100% SVR with 8 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir among 27 men with acute HCV and HIV-coinfection . Investigators conducting another study evaluated 6 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir in a similar cohort . Among participants with genotype 1 infection, 79% achieved SVR12 71% of those with genotype 4 infection achieved SVR12 with this shortened regimen. Among the 6 individuals whose treatment did not lead to SVR12, there were 3 relapses . Three participants achieved SVR4 but were lost to follow-up . A phase 2 study followed a similar treatment protocol among 20 individuals with genotype 1 HCV monoinfection, all of whom achieved SVR12 .
An open-label, single-arm, multicenter pilot study evaluated the efficacy of 6 weeks of the pangenotypic regimen glecaprevir/pibrentasvir among persons with acute/recent HCV infection . SVR12 was 90% a single virological failure occurred in a man with genotype 1a, HIV coinfection, and a viral load of 7.7 log10 IU/mL. This patient was successfully retreated .
- Related References
- Additional Reading