What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- alcohol
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Lets Not Neglect The Glass
Unfortunately, chemical submission is not something new,
96 cases were confirmed last year alone at the San Carlos Clinical Hospital in Madrid
, although until now the victim ingested liquid ecstasy without being aware of it after his aggressor had poured it into his beverage.
This
modus operandi
continues to this day, so we should not neglect our glass in nightclubs or entertainment venues, and we even have options to turn to, such as the tapas that some places provide to try to put a stop to these crimes.
Conforms to The Trust Project criteria
Know more
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
You May Like: Acute Hepatic Porphyria Treatment Guidelines
Hepatitis Be Antibody Test
This test screens for Hepatitis Be Antibodies. A Be Antibody test is typically used when a person has been diagnosed with Hepatitis B to determine whether or not they have an active infection. Be antibody testing is often done in conjunction with Hepatitis Be Antigen testing. Typically, when the Hepatitis B virus is actively replicating, a person will test positive for Be Antigen and Negative for Be Antibody. During this time, they are more likely to transmit Hepatitis B to others. After being successfully treated, most people will test negative for Be Antigen and positive for Be Antibody. People with a latent Hep B infection are typically recommended to test 1-2 times per year as it is possible for latent Hep B to reactivate periodically.
For additional testing options, please see our Hepatitis Category.
Turnaround for this test is typically 2-6 business days.
Do Hepatitis A Antibodies Disappear
Hepatitis A IgM antibodies can be found as early as 2 weeks after the first infection. They disappear 3 to 12 months after infection. Hepatitis A IgG antibodies appear 8 to 12 weeks after the first infection. They remain in your blood and permanently protect you from hepatitis A.
Can Hepatitis A be cured?
There is currently no cure for hepatitis A, but it normally gets better on its own within a few months. You can usually take care of yourself at home. But its always a good idea to see your GP for a blood test if you think you might have hepatitis A, as more serious conditions can have similar symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis Related To Hiv
What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Being Positive Mean
Q:What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Being Positive Mean?
A:Hepatitis B Core Antibody is one of the blood tests available to diagnose hepatitis B. It is produced by the body in response to a part of the hepatitis B virus.
The meaning of this test often relies on the results of two other tests: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Hepatitis B Surface Antibody .
A positive test has two possible meanings:
- A person is infected with hepatitis B virus, or
- A person was infected in the past but the infection has been cleared.
Keywords: Hepatitis B Core Antibody anti-HBc Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Proportions Of Lf And Aclf In Dep Patients
The median APRI score in the DEP group was 1.66 , which was remarkably higher than that in the HBeAg+/anti-HBe- and HBeAg-/anti-HBe+ groups . The median FIB-4 score in the DEP group was noticeably higher than that in the HBeAg+/anti-HBe- group .
Among cases in the I-AP, the median APRI score in the DEP group was markedly higher than that in the HBeAg+/anti-HBe- and HBeAg-/anti-HBe+ groups . The median FIB-4 score in the DEP group in the I-AP was higher than that in the HBeAg+/anti-HBe- group , while we did not identify a significant difference in FIB-4 score between the DEP and HBeAg-/anti-HBe+ groups.
The proportions of cirrhosis and decompensated cirrhosis in the DEP group were noticeably higher than those in the other two groups . Furthermore, the proportion of ACLF in the DEP group was higher than that in the HBeAg+/anti-HBe- group and HBeAg-/anti-HBe+ group .
In the I-AP, the proportions of cirrhosis , decompensated cirrhosis , and ACLF in the DEP group were greater than those in the HBeAg+/anti-HBe- group , while they were not significantly different between the DEP group and the HBeAg-/anti-HBe+ group .
Read Also: How Did Naomi Judd Get Hepatitis C
Factors Associated With Lf And Aclf
Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 scores was conducted using ULS and MLS analyses. MLS analysis demonstrated that DEP was associated with both APRI > 1.5 = 1.96, 95% CI: 1.273.03) and FIB-4 > 1.45 . Gender, higher HBV DNA level, history of alcohol consumption, history of antiviral treatment and I-AP were independently associated with APRI > 1.5, while age 45 years old, gender, history of alcohol consumption, history of antiviral treatment, and I-AP were independently associated with FIB-4 > 1.45.
|
Table 4 Factors Associated with APRI 1.5 and FIB-4 > 1.45 in C-HBVI Cases |
ACLF was also evaluated by ULS and MLS analyses . ULS analysis indicated that ACLF was associated with DEP, gender , history of alcohol consumption, history of antiviral treatment, I-AP, and a higher HBV DNA level. MLS analysis revealed that DEP , gender , a higher HBV DNA level, history of antiviral treatment , and I-AP were independently associated with ACLF.
|
Table 5 Factors Associated with ACLF in C-HBVI Cases |
Hepatitis Viruses B And C
Seroconversion for virus antibody may take 3 months so antibody tests may give false negative results when a patient presents with acute hepatitis.
Hepatitis B virus testing is for hepatitis B surface antigen and IgM anti-HBc antibody. If HBsAg-positive, proceed to hepatitis B e antigen and antibody testing. About one in five are HBeAg positive and at high risk of infectivity. Those who have HBsAg should later be screened again at 3 months, and again if still positive. Those positive at 9 months are chronic carriers. Assays for anti-HBc and HBsAg in saliva samples have been used for surveillance and research but are not available for diagnostic use.
Hepatitis C virus testing includes second or third generation ELISA for serum anti-HCV or other immunoassays . Tests to confirm a positive result include a recombinant immunoblot assay , using another ELISA, or proceeding directly to an assay for HCV-RNA by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction or another genome amplification assay.
Chloe Lynne Thio, Claudia Hawkins, in, 2015
Recommended Reading: Can A Person With Hepatitis B Get Vaccinated
If In Most Cases No Substance Is Detected In The Victims Body Why Do They Have Symptoms After The Puncture
Our nervous system consists of a sympathetic and a parasympathetic system.
The first of these is the one that
is activated involuntarily in an alert or dangerous situation
, such as when we feel a puncture in a place of leisure.
Our body
immediately releases a good amount of adrenaline
, our pupils dilate to better perceive everything around us, our heart rate increases, our mouth feels dry, our bronchial tubes dilate, our blood pressure rises, our muscles tighten. tense, sweat production increases and our digestive system paralyzes.
It is
a primitive system of reaction to danger
that prepares us for a fight or flight response.
Its activation in the face of the fear produced by having felt
a prick in a nightclub is more than enough for the victim to begin to feel bad
, regardless of whether or not that prick entails the injection of some substance.
Read Also: What Are The Types Of Hepatitis C
What The Qualitative Results Mean
The qualitative results indicate that HCV is present in your blood. The test result will be either detected or undetected.
Detected means that you do have the virus in your blood. Undetected means that you dont have the virus in your blood, or you have a tiny amount that cant be detected by this test.
The qualitative test results may still be positive even if your viral load has decreased drastically due to treatment.
Read Also: Is A Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
Read Also: Why Is My Doctor Testing Me For Hepatitis C
Why Do I Need This Test
You may need this test if your healthcare provider suspects you have a liver infection caused by HBV. You may also need this test if you have symptoms of hepatitis B. Symptoms usually start slowly. Many people have no symptoms or only feel like they have a mild case of the flu. You may not have symptoms until the infection is chronic or severe.
The most common symptom is extreme tiredness. Other symptoms may include:
-
Nausea
-
Belly pain
-
Swelling and confusion. This is in extreme cases.
You may also have this test if you have a history that puts you at risk for being in contact with the virus. Risk factors for hepatitis B infection include:
-
Having sex with someone infected with the virus
-
Living in close contact with someone who has the virus
-
Being a man who has sex with men
-
Being a child born to a mother who has the virus
-
Sharing needles for intravenous drug use
-
Working in a healthcare center where you are exposed to blood
-
Getting a blood transfusion or organ transplant. This is less common with active screening.
Are There Supplements That Are Good For My Liver
If a person eats a balanced diet, they will normally get enough vitamins and minerals. People with liver disease should avoid taking large amounts of supplements or mega-vitamins. This is because the liver has to do extra work to process them. Your provider may put you on a general multivitamin without iron.
Don’t Miss: Different Types Of Hepatitis Chart
Hepatitis B Envelope Antigen And Antibody
- Hepatitis B e Ag and Ab by EIA
- Lab Code
- Hepatitis B Envelope Antigen and Antibody
- Description
-
The Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus e antigen and Hepatitis B virus e antibody in human sera by the FDA approved LIASON® IgG Assay.
The presence of HBeAg in serum is associated with presence of Dane particles and Hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase enzyme. These markers suggest active HBV replication. Hepatitis B Surface antigen positive and HBeAg positive persons are much more likely to transmit infections to others. The development of anti-HBe during acute Hepatitis B infection is a marker of resolution of illness.
- Synonyms
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver that leads to decreased liver function and potential damage to the liver.
Although hepatitis can be caused by heavy alcohol consumption, toxins, certain medical conditions, and some medications, the most common cause of hepatitis is a viral infection due to hepatitis A, B, and C virus.
Two types of hepatitis C include:
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Natural Course Of Disease And Hbeag Seroconversion
Chronic HBV infection is a dynamic state of complex interactions involving the virus, the hepatocyte, and the hosts immune response. The nature of these interrelationships, together with the influence of various external factors, ultimately determines disease severity and progression . Accordingly, the natural course of chronic HBV infection consists of distinct phases: an immune-tolerant phase, an immune clearance phase, and an inactive or residual phase . The patients serologic profile with respect to HBV-DNA, HBsAg, and HBeAg levels changes with transition through the different phases of CHB. Patients in the immune-tolerant phase are usually young, HBeAg seropositive, and have high viral loads , yet normal serum alanine aminotransferase levels and few clinicopathologic changes. Individuals with perinatal acquisition of HBV typically have a prolonged immune-tolerant phase that can last up to three decades. A 5-year follow-up study of individuals who remain in the immune-tolerant phase showed no or minimal disease progression . In natural history studies of Asian HBsAg-positive children, the rate of spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion is low: < 2% per year among children 3 years or younger and 45% per year in older children . Approximately 90% of HBsAg carriers who acquire HBV in early life remain HBeAg positive at age 1520 years, whereas HBeAg positivity decreases with increasing age and is < 10% in patients older than 40 years .
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Cure For Hepatitis A
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system encodes antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Infection
What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Mean
Hepatitis B is an inflammation of the liver caused by a virus. Signs of hepatitis include tiredness or fatigue, fevers, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, itchy skin, muscle soreness , jaundice , dark urine, and light stools.Here are some hepatitis B facts:
1. HBV infections will occur in one out of every 20 people at some time in the United States
2. Your risk of HBV is greater if you have sex with someone who has HBV.
3. Your risk is greater if you have a job that places you in contact with human blood.
4. Your risk is greater if you travel to areas where HBV is common.
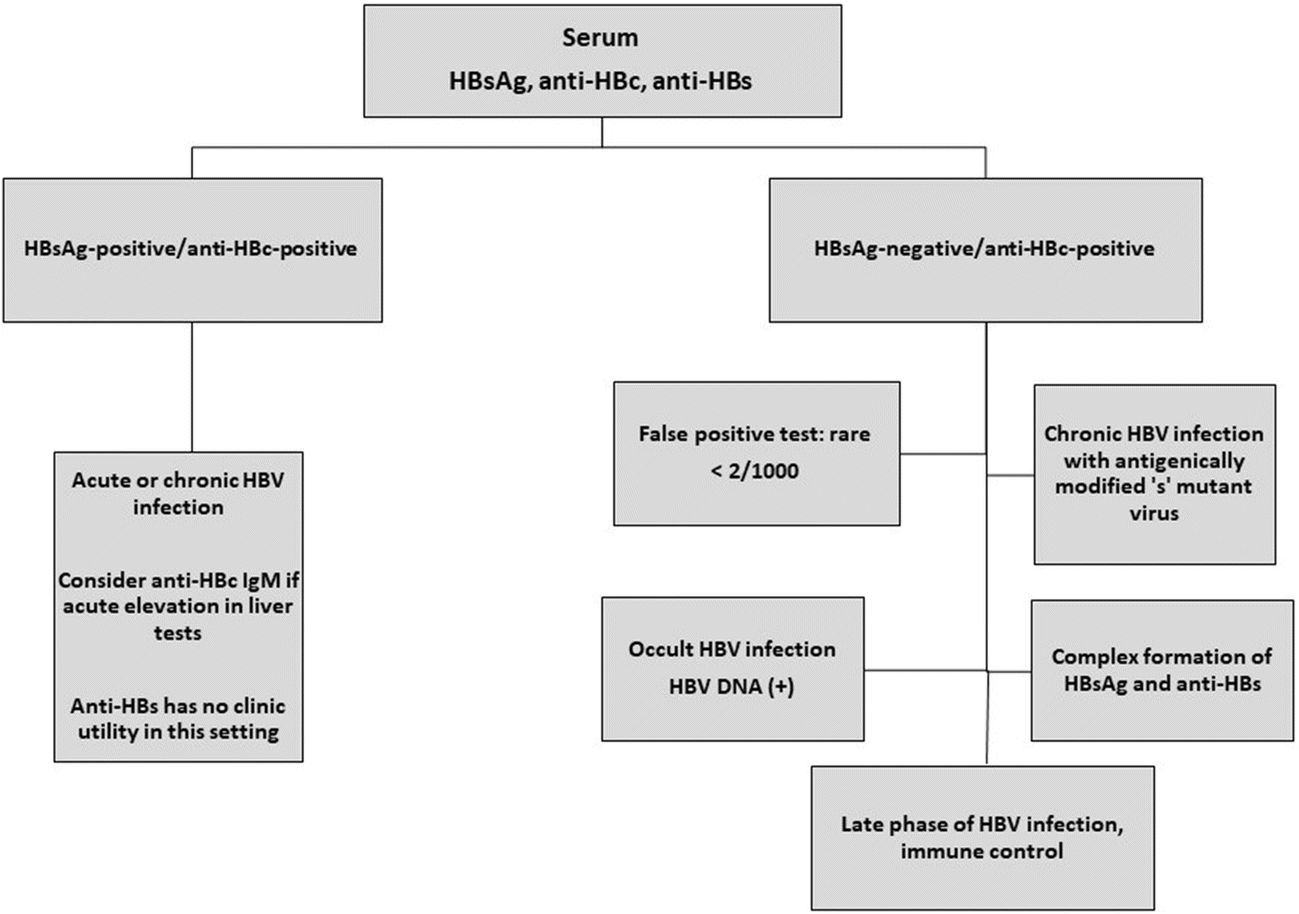
Some people who donate blood get a letter from the blood bank saying that they are hepatitis B core antibody positive. Dont panic. This does not mean that you have hepatitis B, but you should get a more thorough screening. There are three blood tests that are used to diagnose hepatitis B: hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis B surface antibody, and hepatitis B core antibody positive. If your blood tests show that you are hepatitis B core body positive, it means that you either have a present infection or that you were infected in the past. There is a possibility of having a false hepatitis B core antibody positive. Blood banks only screen for hepatitis B core antibody positive and not for surface antigens or antibodies.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva