How Is Viral Hepatitis Prevented
Prevention of hepatitis involves measures to avoid exposure to the viruses, using immunoglobulin in the event of exposure, and vaccines. Administration of immunoglobulin is called passive protection because antibodies from patients who have had viral hepatitis are given to the patient. Vaccination is called active protection because killed viruses or non-infectious components of viruses are given to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies.
Avoidance of exposure to viruses
Prevention of viral hepatitis, like any other illness, is preferable to reliance upon treatment. Taking precautions to prevent exposure to another individual’s blood , semen , and other bodily secretions and waste will help prevent the spread of all of these viruses.
Use of immunoglobulins
Immune serum globulin is human serum that contains antibodies to hepatitis A. ISG can be administered to prevent infection in individuals who have been exposed to hepatitis A. ISG works immediately upon administration, and the duration of protection is several months. ISG usually is given to travelers to regions of the world where there are high rates of hepatitis A infection and to close or household contacts of patients with hepatitis A infection. ISG is safe with few side effects.
Hepatitis A
Individuals at increased risk of acquiring hepatitis A are:
Some local health authorities or private companies may require hepatitis A vaccination for food handlers.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for:
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B
Blood tests are available to determine if you are or have been infected with hepatitis B. It may take 6 months from the time of infection before a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis B, so follow-up testing may be required. During this 6-month period, until you know whether you are infected or not, take action to prevent potential infection of other people.
There are also tests that can assess liver damage from hepatitis B. The interpretation of these tests can be complicated and specialist advice is needed, so talk to your doctor.
All pregnant women are tested for hepatitis B. If you are found to have chronic hepatitis B, your doctor can help reduce the risk of transferring the infection to your newborn child.
Extrahepatic Manifestations Of Hepatitis B
Extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis B are present in 110% of HBV-infected patients and include serum-sicknesslike syndrome, acute necrotizing vasculitis , membranous glomerulonephritis, and papular acrodermatitis of childhood ., Although the pathogenesis of these disorders is unclear, immune complexmediated injury related to high level of HBV antigenemia is thought to be the cause.
The serum-sicknesslike syndrome occurs in the setting of acute hepatitis B, often preceding the onset of jaundice. The clinical features are fever, skin rash, and polyarteritis. The symptoms often subside shortly after the onset of jaundice, but can persist throughout the duration of acute hepatitis B. The course of this syndrome often parallels the duration and level of HBV viremia: rapid clearance of the virus leads to rapid resolution of the illness. This disorder resembles experimental serum sickness, in which immune complexes activate the complement pathways leading to complement-mediated injury. Patients with this syndrome have low complement levels and high-level circulating immune complexes containing HBV antigens and complement components.
Other immune-mediated hematological disorders, such as essential mixed cryoglobulinemia and aplastic anemia have been described as part of the extrahepatic manifestations of HBV infection, but their association is not as well-defined therefore, they probably should not be considered etiologically linked to HBV.
Read Also: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis C
How Long Do Symptoms Of Hepatitis B Last
Hepatitis B in adults will usually pass within 1 to 3 months. This is known as acute hepatitis B and rarely causes any serious problems.
Occasionally, the infection can last for 6 months or more. This is known as chronic hepatitis B.
Chronic hepatitis B mainly affects babies and young children who get hepatitis B. It’s much less common in people who become infected later in childhood or when they’re an adult.
The symptoms of chronic hepatitis B tend to be quite mild and may come and go. Some people may not have any noticeable symptoms.
But without treatment, people with chronic hepatitis B can develop problems like scarring of the liver .
Page last reviewed: 30 January 2019 Next review due: 30 January 2022
What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis

Patients infected with HBV and HCV can develop chronic hepatitis. Doctors define chronic hepatitis as hepatitis that lasts longer than 6 months. In chronic hepatitis, the viruses live and multiply in the liver for years or decades. For unknown reasons, these patients’ immune systems are unable to eradicate the viruses, and the viruses cause chronic inflammation of the liver. Chronic hepatitis can lead to the development over time of extensive liver scarring , liver failure, and liver cancer. Liver failure from chronic hepatitis C infection is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the U.S. Patients with chronic viral hepatitis can transmit the infection to others with blood or body fluids as well as infrequently by transmission from mother to newborn.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
When To Contact A Doctor
Anyone who suspects that they have come into contact with HBV should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
A doctor can provide postexposure prophylaxis through the vaccines and a drug called hepatitis B immune globulin. PEP can prevent infection and liver damage.
A person should also contact a doctor if they notice any of the symptoms of hepatitis B or if they know they have hepatitis B, and their symptoms worsen.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that impacts the liver.
Can Hepatitis B Be Controlled By Eating Right And Exercising
It is important that people with liver disease follow a healthy, nutritious diet as outlined by Health Canada in Eating Well with Canadas Food Guide.
Alcohol can also damage the liver so it is best that people with hepatitis B do not drink. Following a healthy lifestyle may also prevent fatty liver disease, another liver disease highly prevalent in Canada.
However, hepatitis B cannot be controlled by healthy eating and exercise alone. Hepatitis B can only be controlled by currently available treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor will need to do regular blood tests to know how much of the active virus is in your blood . The viral load test is used to monitor and manage hepatitis B patients. Viral load can tell your doctor if you need treatment for hepatitis B and how well you are responding to treatment.
Also Check: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma Hcc
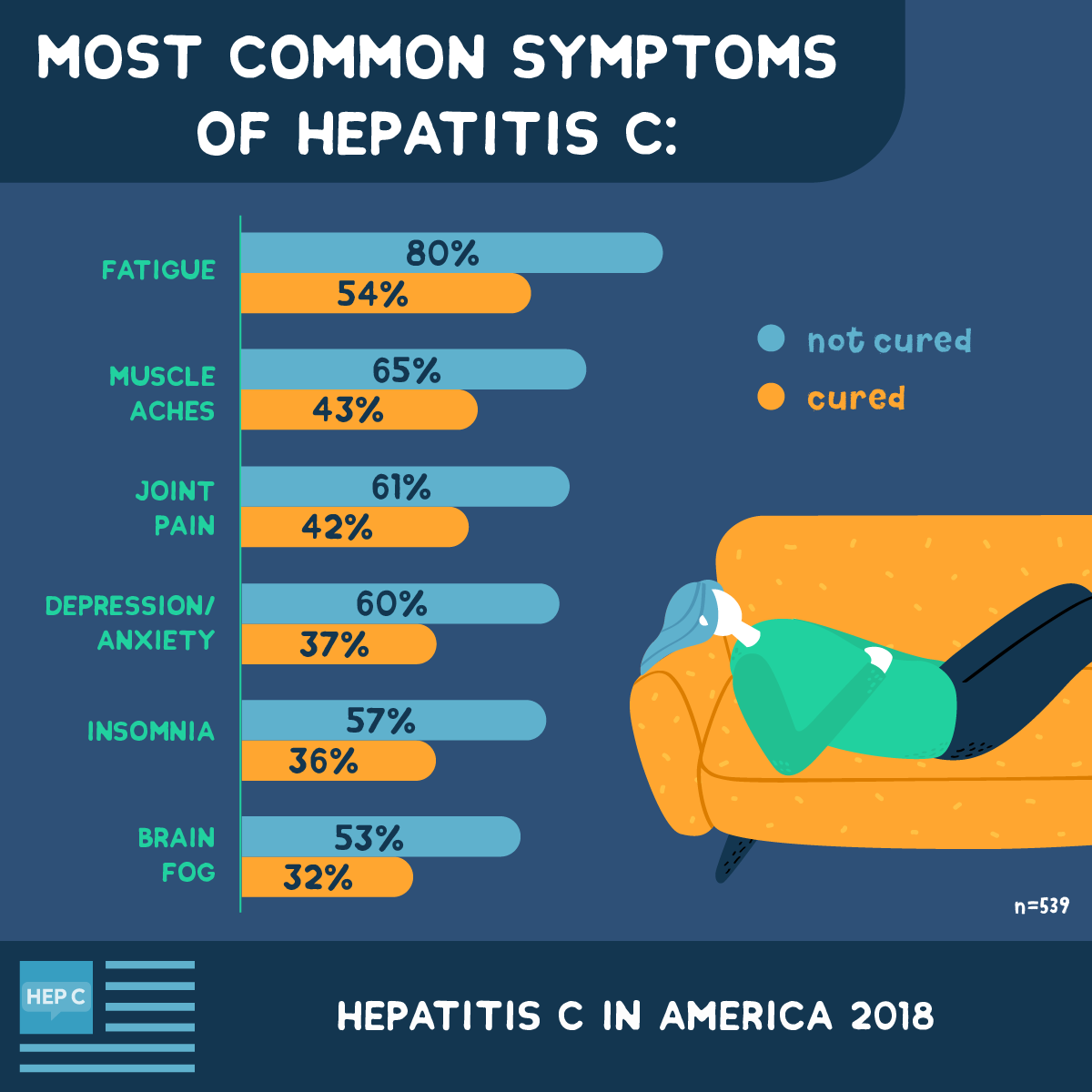
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Symptoms for HCV may not appear for 20 to 30 years, and that is why it is so important to get tested. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control now recommends that all adults 18 years and older are tested at least once for HCV. Some high risk groups may need more frequent testing, and all pregnant women should be tested during every pregnancy.
HCV can actually clear itself from the body in about 15% of people, but most people become infected with the virus chronically.
Early symptoms of acute HCV occur within 1 to 3 months and may last several weeks. These may include:
- yellow-colored skin or eye sclera
- weakness
- nausea and stomach pain
- joint or muscle pain
Chronic, long-term symptoms of HCV can include weight loss, fluid build-up and swelling, poor appetite, fatigue, easy bruising and bleeding, itchy skin, jaundice, dark-colored urine, confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech , and spider-like blood vessels on the skin .
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Approaches By Virus Life Cycle Stage
consist of a and sometimes a few stored in a capsule made of , and sometimes covered with a layer . Viruses cannot reproduce on their own and instead propagate by subjugating a host cell to produce copies of themselves, thus producing the next generation.
Researchers working on such “” strategies for developing antivirals have tried to attack viruses at every stage of their life cycles. Some species of mushrooms have been found to contain multiple antiviral chemicals with similar synergistic effects.Compounds isolated from fruiting bodies and filtrates of various mushrooms have broad-spectrum antiviral activities, but successful production and availability of such compounds as frontline antiviral is a long way away. Viral life cycles vary in their precise details depending on the type of virus, but they all share a general pattern:
Before cell entry
This stage of viral replication can be inhibited in two ways:
Uncoating inhibitor
Inhibitors of uncoating have also been investigated.
During Viral Synthesis
Reverse transcription
Transcription
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Test Non Reactive
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
What Can Happen If Chronic Hepatitis B Isnot Treated
Chronic hepatitis B is a serious disease that can resultin long-term health problems. Up to 1 in 4 people withchronic hepatitis B develop serious liver problems.These include:
- Liver damage and scarring
- Liver failure
- Asking sexual partner and people living in close contact with you to be tested and vaccinated.
You May Like: How Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
- Antiviral medications, interferon injections and a liver transplant are options for treatment of ongoing infections. Not everyone will need these treatments.
- Medicines known as direct-acting antiviral agents are now available that can lead to a cure in 8 to 12 weeks in many patients with hepatitis C, but hepatitis B may require long-term treatment.
- There is a vaccine that is used to prevent hepatitis B infection in both adults and newborns, but there is no vaccine yet for hepatitis C.
The newer direct-acting antiviral agents medications to treat HCV include:
How Common Is Hepatitis B
The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
Recommended Reading: Standard Process Canine Hepatic Support
Viral Hepatitis Definition And Overview
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Many illnesses and conditions can cause inflammation of the liver, for example, drugs, alcohol, chemicals, and autoimmune diseases. Many viruses, for example, the virus causing mononucleosis and the cytomegalovirus, can inflame the liver. Most viruses, however, do not attack primarily the liver the liver is just one of several organs that the viruses affect. When most doctors speak of viral hepatitis, they are using the definition that means hepatitis caused by a few specific viruses that primarily attack the liver and are responsible for about half of all human hepatitis. There are several hepatitis viruses they have been named types A, B, C, D, E, F , and G. As our knowledge of hepatitis viruses grows, it is likely that this alphabetical list will become longer. The most common hepatitis viruses are types A, B, and C. Reference to the hepatitis viruses often occurs in an abbreviated form The focus of this article is on these viruses that cause the majority of human viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis viruses replicate primarily in the liver cells. This can cause the liver to be unable to perform its functions. The following is a list of major functions of the liver:
Does Hepatitis A Always Cause Symptoms
There’s a lot of variety in how people feel when they have the disease. It’s possible you might not have any symptoms. But people often feel and look sick. You might even need to go to the hospital.
Symptoms and complications are more common as you get older. Most children under age 6 with hep A don’t have any.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C Through Saliva
If I Have No Symptoms How Would I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
To confirm whether or not you have hepatitis B, you will need blood tests.
If you have at least one risk factor , you should ask your health care provider to be tested for hepatitis B. Also, you should be tested for hepatitis B if:
- you were born in a region where hepatitis B is more common, including Asia, Africa, southern and eastern Europe, the Pacific Islands, the Middle East, and the Arctic
- one or both of your parents immigrated from a region where hepatitis B is more common
- you live or travel to regions where hepatitis B is more common
- you have a family history of liver disease or liver cancer
- you have been in prison
- you are pregnant
- you have ever used injection drugs, even just once
- you have unexplained abnormal liver enzymes or if
- you receive medicines that suppress the immune system.
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Don’t Miss: Sign Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
When To See A Healthcare Provider
If you develop any of the symptoms of chronic hepatitis, liver damage, or liver cancer, see your healthcare provider. It takes only a blood test to detect the presence of a hepatitis virus in your body .
A blood test also can determine which hepatitis virus you’re infected with, which will determine what your treatment should be .
Who Is At Risk Of Hepatitis B

Anyone can get hepatitis B if not vaccinated. However, in the U.S., you may be at a higher risk if you:
- Have sex partners that have hepatitis B
- Have HIV or another STD
- Inject drugs or share needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Are undergoing dialysis
- Have diabetes
- Travel to areas that have moderate to high rates of hepatitis B
- Work in health care or public safety and are exposed to blood or body fluids on the job
- Are an infant born to an infected mother
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Treatment Options For Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B usually doesnt require treatment. Most people will overcome an acute infection on their own. However, rest and hydration will help you recover.
Antiviral medications are used to treat chronic hepatitis B. These help you fight the virus. They may also reduce the risk of future liver complications.
You may need a liver transplant if hepatitis B has severely damaged your liver. A liver transplant means a surgeon will remove your liver and replace it with a donor liver. Most donor livers come from deceased donors.