Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as “required” by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
“Routine” vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
- tetanus
History And Physical Exam
To diagnose all forms of hepatitis, your doctor will first take your history to determine any risk factors you may have.
During a physical examination, your doctor may press down gently on your abdomen to see if thereâs pain or tenderness. Your doctor may also check for any swelling of the liver and any yellow discoloration in your eyes or skin.
Different Anemia Types Definitions
Common Anemia definition is a medical condition characterized by a decrease in RBCs, hemoglobin, and hematocrit below the normal range for healthy people of the same age, sex, and race, and under similar environmental conditions.Early Anemia signs include high ferritin level and normal iron level in the blood results as well as general weakness and fatigue.Iron Deficiency Anemia definition is the commonest type of anemia worldwide, its a condition in which human blood lacks adequate healthy red blood cells because of inadequate iron levels to produce the cells hemoglobin.
- Mild iron deficiency is unnoticed in CBC test results, however you may find low iron and normal hemoglobin,
- but moderate iron deficiency anemia shows markedly decreased iron, iron stores , and hemoglobin, however iron deficiency anemia show general weakness and fatigue as well as pallor appearance.
- Medical short form is IDA.
- Best cure for iron deficiency anemia is dietary changes and Iron supplements, severe iron deficiency is curable after blood transfusion to raise hemoglobin levels firstly.
What is sickle cell anemia? define sickle cell anemiaSickle Cell Anemia definition is a severe hereditary anemia that is common between African people, describe a group of inherited abnormal hemoglobin disorders.
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia:
What cure is for sickle cell anemia?
- Transplantation of Blood and Marrow Stem Cell.
Don’t Miss: How Would You Know If You Have Hepatitis
Hepatitis C: How Does It Spread
It spreads through infected blood. In the U.S., sharing needles or other items used to inject drugs is the most common cause of infection. Getting a tattoo or body piercing with an infected needle is another means of exposure. A mother may pass the virus to their child at birth. In rare cases, unprotected sex spreads hepatitis C, but the risk appears small. Having multiple sex partners, HIV, or rough sex seems to raise risk for spreading hepatitis C.
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Also Check: What Does It Mean To Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
Nursing Education To Provide To Patients With Hepatitis
Handwashing
Eat low fat and high carb meals
Personal hygiene products NOT to be shared
Activity conservationpatient needs to REST to help the liver heal
Toxic substances AVOIDEDespecially over-the-counter products that are liver toxic: alcohol, sedative, aspirin, acetaminophen etc.
Individual bathroomsdont share bathroom with family members
Test results:
- Hepatitis A: anti-HAV IgM and anti-HAV IgG
- Hepatitis B: HBsAG and anti-HBV
Interferon and Immune globulin for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B Immune globulin
Small but frequent mealsthis may help with the nausea and patient should NOT cook for others until not infectious.
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
Recommended Reading: How Is Hepatitis C Transferred From Person To Person
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is an inflammation of your liver that’s caused by a virus. There are five types, but the most common ones in the U.S. are hepatitis A, B, and C. All of them affect your liver. Some of the symptoms are similar, but they have different treatments.
Hepatitis A. This type won’t lead to long-term infection and usually doesn’t cause any complications. Your liver heals in about 2 months. You can prevent it with a vaccine.
Hepatitis B. Most people recover from this type in 6 months. Sometimes, though, it causes a long-term infection that could lead to liver damage. Once you’ve got the disease, you can spread the virus even if you don’t feel sick. You won’t catch it if you get a vaccine.
Hepatitis C. Many people with this type don’t have symptoms. About 80% of those with the disease get a long-term infection. It can sometimes lead to cirrhosis, a scarring of the liver. There’s no vaccine to prevent it.
How To Protect Yourself Against Hepatitis A
There is an effective vaccine against hepatitis A that is recommended for all children at age 1. However, most adults probably have not received it because the vaccine wasnt required when they were young. Dr. Fried says you can come in contact with the hepatitis A infection pretty much anywhere, so its a good idea for everyone older than 1 to get the vaccine, whether or not theyve had any known exposure or traveled to regions where hepatitis A is common.
In addition to getting vaccinated, you should wash your hands every time you go to the bathroom and before handling or serving food or drinks. Also be sure to wash and rinse raw produce before eating or serving it. Cooking raw produce further reduces the risk of infection.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contract Hepatitis C
Causes Of Noninfectious Hepatitis
Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue and liver failure.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. Itâs three times more common in women than in men.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Just like hepatitis B, you can get this type by sharing needles or having contact with infected blood. You can also catch it by having sex with somebody who’s infected, but that’s less common.
If you had a blood transfusion before new screening rules were put in place in 1992, you are at risk for hepatitis C. If not, the blood used in transfusions today is safe. It gets checked beforehand to make sure it’s free of the virus that causes hepatitis B and C.
It’s rare, but if you’re pregnant and have the disease, it’s possible to pass it to your newborn.
There are some myths out there about how you get hepatitis C, so let’s set the record straight. It’s not spread by food and water . And you canât spread it by doing any of these things:
- Joint pain
See your doctor as soon as possible if you have any of these symptoms.
Sometimes, people have no symptoms. To be sure you have hepatitis, youâll need to get tested.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Non Reactive Means
The 5 Types Of Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis can be caused by five varieties of the hepatitis virus. According to the international classification, each virus is named after a letter of the alphabet: A, B, C, D, and E.
Below, discover what happens when someone becomes infected with any of these viruses.
1. Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is the mildest of this group of viral infections. Its transmitted through the fecal-oral route. In other words, an infected person expels it through their feces, contaminates food or water that another person eats or drinks, and the virus finds a new host.
Hepatitis A patients suffer from gastroenteritis symptoms with liver involvement. Thus, fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting appear.
As the liver is inflamed, the bile stagnates and doesnt circulate. As a result, the skin turns yellowish . This occurs because bilirubin impregnates the skin and mucous membranes, which is why the whites of the eyes also turn yellow. Excess bilirubin is eliminated through the urine, which also becomes darker.
The usual symptoms last about 15 days. Although the disease can last for a month or more, this isnt common. Patients tend to recover without any major problems and, if there was no dehydration, they wont suffer from any lasting effects.
The most dangerous symptom is fluid loss, especially in young children. Due to how fast it spreads, extreme precautionary measures should be taken when there are outbreaks in closed populations, such as schools.
2. Hepatitis B
3. Hepatitis C
What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
There are five different types of hepatitis, labeled Hep A, B, C, D and E. Each type has slightly different symptoms, and most types can be treated successfully. Hepatitis C, however, can cause lifelong illness and extreme damage to the liver. Teachers and medical workers are at increased risk of contracting most forms of this disease through exposure to blood or bodily fluids in their work settings.
Hepatitis A is usually contracted through sharing food or water with an infected person. It may also be contracted through sexual contact or contact with body fluids, like infected blood or urine. Most people who contract this form completely recover, though the condition can make people very ill. Like all other forms of hepatitis, Hep A causes inflammation of the liver.
The treatment for Hep A is usually rest, and it may take as long as six months to fully recover. Initial symptoms are fever, aches and exhaustion, which can persist for several months. During this time, the person with hepatitis is contagious and can pass the illness to others, through the above listed means of transmission.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex Hcv Rna Quant Rt Pcr
How Is Hepatitis Treated In A Child
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Your childs treatment will depend on whats causing his or her hepatitis. The goal of treatment is to stop damage to your childs liver. Its also to help ease symptoms. Your childs treatment may include:
-
Medicines. These can control itching, treat the virus, or control an autoimmune disease.
-
Supportive care. This includes eating a healthy diet and getting enough rest.
-
Reducing risk. Not using alcohol or illegal drugs.
-
Blood testing. This can tell if the disease is progressing.
-
Hospital stay. This is done in severe cases.
-
Liver transplant. This is done for end-stage liver failure.
-
Helping to prevent the spread of viral hepatitis. Having good personal health habits, such as handwashing.
Killed Or Inactivated Vaccines
One alternative to attenuated vaccines is a killed or inactivated vaccine. Vaccines of this type are created by inactivating a pathogen, typically using heat or chemicals such as formaldehyde or formalin. This destroys the pathogens ability to replicate, but keeps it intact so that the immune system can still recognize it.
Because killed or inactivated pathogens cant replicate at all, they cant revert to a more virulent form capable of causing disease . However, they tend to provide a shorter length of protection than live vaccines, and are more likely to require boosters to create long-term immunity. Killed or inactivated vaccines on the U.S. Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule include the inactivated polio vaccine and the seasonal influenza vaccine .
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C Ab
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
- older adults
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Also Check: Food To Cure Hepatitis B
What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Patients infected with HBV and HCV can develop chronic hepatitis. Doctors define chronic hepatitis as hepatitis that lasts longer than 6 months. In chronic hepatitis, the viruses live and multiply in the liver for years or decades. For unknown reasons, these patients’ immune systems are unable to eradicate the viruses, and the viruses cause chronic inflammation of the liver. Chronic hepatitis can lead to the development over time of extensive liver scarring , liver failure, and liver cancer. Liver failure from chronic hepatitis C infection is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the U.S. Patients with chronic viral hepatitis can transmit the infection to others with blood or body fluids as well as infrequently by transmission from mother to newborn.
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
Read Also: What Is Chronic Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis Contracted
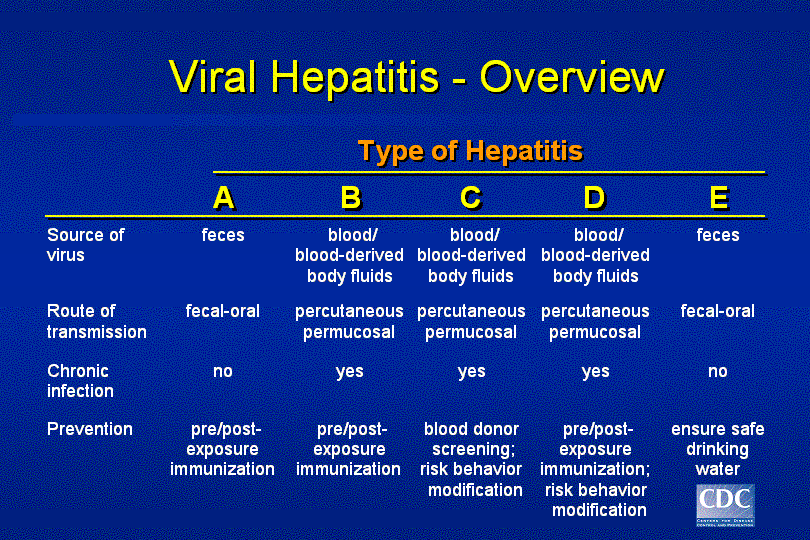
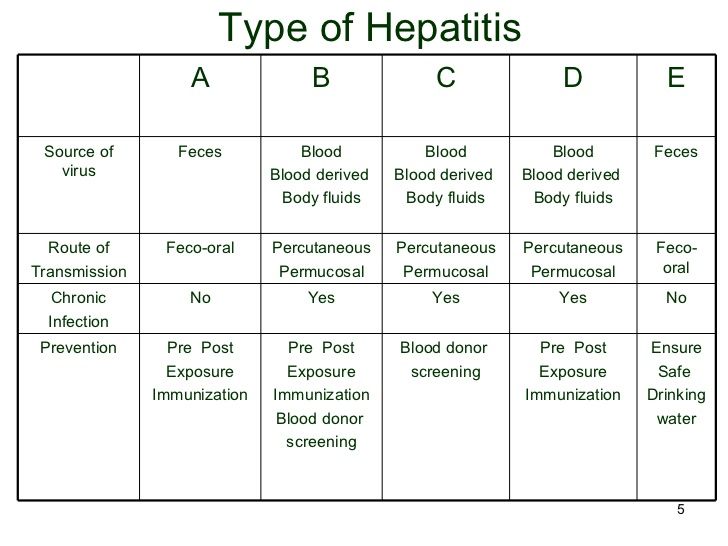
There are various ways of contracting hepatitis, depending on the type. Contracting a viral form of hepatitis depends on the mode of transmission, which the table above shows.
A person may sometimes contract hepatitis nonvirally. In autoimmune hepatitis, the immune system attacks the liver cells. Ingesting substances that contain toxins, such as alcohol, can also induce some types of hepatitis.
A doctor may use a blood test to diagnose viral hepatitis.
A healthcare professional will check a persons blood for:
- HAV-specific immunoglobulin G antibodies to diagnose HAV
- the surface antigen HBsAg to diagnose HBV
- anti-HCV antibodies to diagnose HCV
- high immunoglobulin G and anti-HDV immunoglobulin M levels to diagnose HDV
- virusspecific IgM antibodies to identify HEV
To autoimmune hepatitis, a doctor may consider:
- symptoms
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
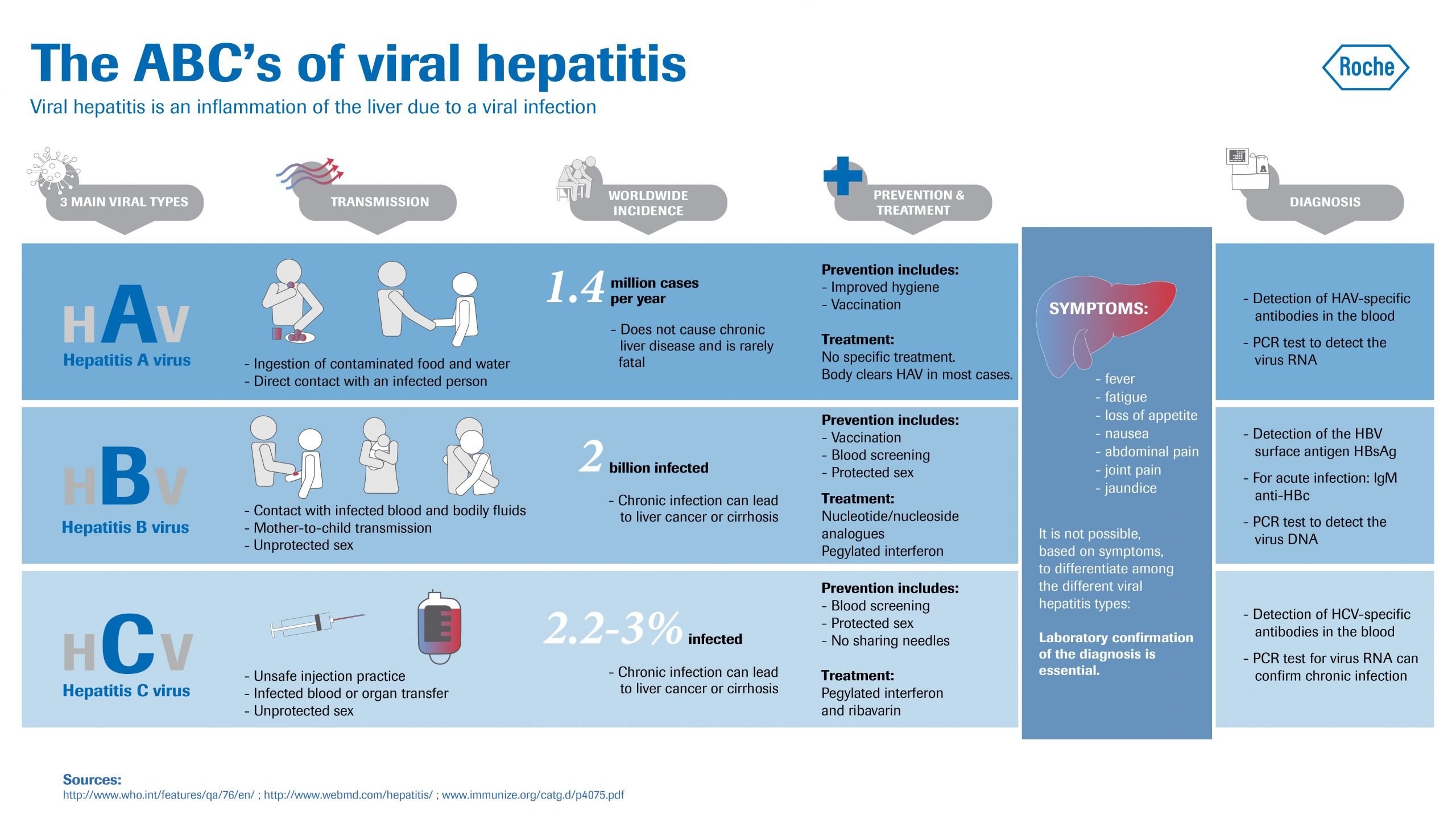
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as “types” of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- HIV patients
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Also Check: How To Get Hepatitis A Virus