How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
Your health care provider will ask about your medical history and symptoms. Especially important is your history of Hepatitis B risk factors such as IV drug abuse.Your provider will examine your skin and eyes for signs of Hepatitis B. Your provider will check your abdomen to see if the liver is enlarged or tender.You will have blood tests. If blood tests show that your liver is not working normally, your provider will do tests to see if you are infected with the Hepatitis B virus.
Questions about online blood testing or how to order a lab test?
Other Ways To Get A Hepatitis B Test
People can get a hepatitis B test at a doctors office, community health clinic, or community health department. Doctors may ask about a persons family history of hepatitis B or liver disease and any possible exposures.
According to Planned Parenthood, people should tell a doctor if they want to get a test for hepatitis B or other sexually transmitted infections.
Some frequently asked questions about hepatitis B testing include the following:
Results And Next Steps
The results of a hepatitis B titer panel can help a doctor determine a persons hepatitis B status. The results can be confusing if a person has never been through this type of testing before, but the doctor can explain the findings.
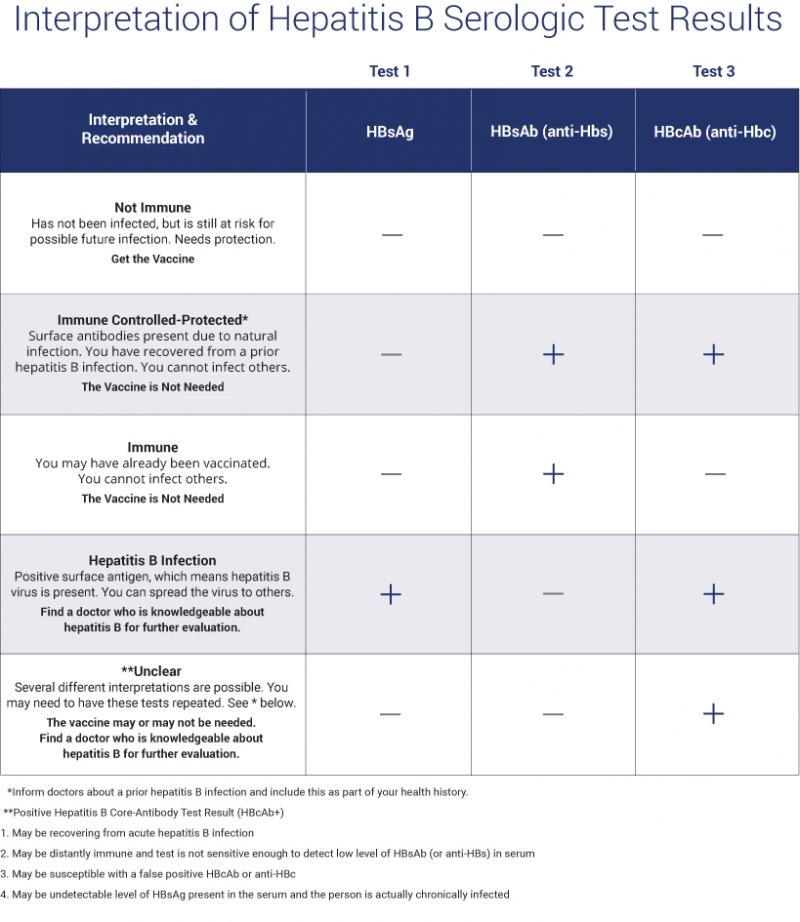
The results for the titer come back as either negative or positive on each subtest of the panel. Positive means that the virus or antibodies showed up on the test, while negative means that they did not.
The following table outlines what positive and negative results mean on different parts of the test and the possible next steps.
The information comes from the Immunization Action Coalition:
| Test |
|---|
Don’t Miss: Will Hepatitis C Go Away
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Preparing Clients For Screening
Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
You May Like: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex
Whats The Hepatitis B Titer Test Used For
A hepatitis B titer test measures antibodies in your blood to see if youre immune either due to vaccination or previous infection.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that targets your liver. It can be transmitted by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person. A person with the virus can also infect their child during birth.
Hepatitis B can develop into a chronic infection. Chronic infection occurs when your body cant fight off the virus within six months. Chronic hepatitis B infections most commonly develop less than six years old, especially in infants.
Hepatitis B titer tests can be used to evaluate:
- whether a high-risk person is immune to hepatitis B
- whether hepatitis B immunoglobulin is needed after a needle prick
- men who have sex with men
- people born in countries with a hepatitis B prevalence greater than 2 percent
- people born in the United States not vaccinated as children and with parents born in regions with more than 8 percent hepatitis B prevalence
You may need your titer test results as proof of hepatitis B immunity in order to get into healthcare programs at many schools for example, the nursing program at Lone Star College. In the United States, employers are not allowed to withdraw a job offer if they learn you have hepatitis B.
Chronic Hbv Carriers At Greatest Risk Of Hepatic Sequelae
Sustained elevations in ALT, although an imperfect marker for hepatic damage, can help identify chronic HBV carriers at greatest risk of sequelae and those most likely to benefit from current treatments . Chronically infected patients with sustained ALT elevations greater than the upper limit of normal may be candidates for treatment and should undergo additional prognostic hepatitis marker testing as outlined below. Chronic carriers whose ALT is within the normal range should be tested for this marker periodically because ALT levels can fluctuate with this illness. Determination of ALT levels and HBV serological and nucleic acid markers, although valuable in following infection, is not adequate to assess the severity of infection and the resulting liver damage. Before appropriate treatment can be initiated, consultation with a specialist and assessment of the disease through histological examination of a liver biopsy is strongly recommended.
Read Also: How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed
When And How To Perform Post
Which test to use: If testing is needed following vaccination, use quantitated HBsAb only
- Post-vaccination testing is needed for certain groups who are at especially high risk for HBV infection
- The purpose of post-vaccination testing is to confirm if patients have achieved adequate immune response as measured by hepatitis B surface antibody
- Perform testing 1-2 months after final dose of the HBV vaccine series
- Persons with HBsAb concentrations of > 10 mIU/ml are considered immune
- Post-vaccination testing is recommended for some patients:
- Infants born to HBsAg+ women
- Infants born to women whose HBSAg status remains unknown
- Health care personnel and public safety workers at risk for blood or body fluid exposure
- Hemodialysis patients
- Other immunocompromised persons such as hematopoietic stem-cell transplant patients or persons receiving chemotherapy
- Sex partners of HBSAg+ persons
Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel
A Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel includes a Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total , Hepatitis B Surface Antigen , Hepatitis B Surface Antibody .
CPT Code: See Individual Tests
Also Known As:
No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results:
2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
CPT Code: See Individual Tests
Also Known As:
No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results:
2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Antibody Titer Test
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
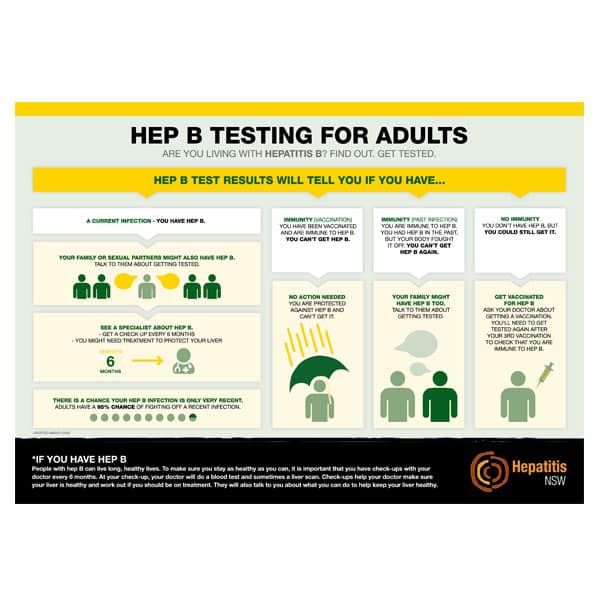
How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Like all STDs, the only way to know for sure if you have hepatitis B is to get tested whether or not you have symptoms.
If youre showing any signs of hepatitis B, you should get tested. Its also a good idea to get a test if you had unprotected sex or shared a needle, razor, or toothbrush with someone who has hepatitis B .
Your nurse or doctor will take a quick blood sample to test you for hepatitis B. It may take up to two months after infection for the test to be accurate but if youre not feeling well, dont wait to see a doctor or nurse.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine 3rd Dose
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people with hepatitis B will be ill for only a few weeks. This is known as an acute infection. For others, the disease progresses to a lifelong illness, known as chronic hepatitis B.
Some people with acute hepatitis B have no symptoms at all or only mild illness. For others, it causes a more severe illness and they’ll need to go to hospital.
Often people are able to clear the virus from their bodies without treatment. This is especially the case if they get the infection as an adult. But in some cases, acute hepatitis B leads to chronic hepatitis B. Over time, chronic hepatitis B can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis and liver cancer.
How Does Hepatitis B Occur
Hepatitis B is caused by the Hepatitis B virus. You get Hepatitis B by direct contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person. For example, you can get it from:
- Having unprotected sex with someone infected with Hepatitis B
- Sharing needles for drug injection with an infected person
- Your mother if she had Hepatitis B at the time she gave birth to you
- Getting a body part pierced or a permanent tattoo with nonsterile equipment.
The disease can be spread by people who do not have any symptoms and may not know they carry the virus. These people are called asymptomatic carriers.
Read Also: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Of The Liver
When Is It Ordered
Hepatitis B tests may be ordered when someone has signs and symptoms associated with acute hepatitis to determine if they are due to infection with HBV. Some of these include:
Hepatitis B tests may be done as follow up when routine tests results such as ALT and/or AST are elevated. Sometimes acute forms of hepatitis may be detected this way since they may cause only mild symptoms that can be confused with the flu. Chronic hepatitis more often has no symptoms and is more commonly detected when routine test results are abnormal.
A test for hepatitis B surface antigen may be used for screening when someone falls into one of the high-risk categories for chronic hepatitis B. Joint guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and American College of Physicians were published in December 2017 and recommend the following groups be tested for HBsAg:
When hepatitis B tests are used to monitor people with chronic hepatitis B infections, they may be performed on a regular basis. Hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen , often along with HBV DNA, are usually measured about every 6 months to a year since, in some people, HBeAg will go away on their own. In those who are being treated for chronic HBV, HBeAg and HBV DNA tests can be used to determine whether the treatment is successful.
Assessment Of Hbv Immune Status
Immunity to HBV is acquired from a resolved infection or from vaccination .2). The HBV vaccine has been shown to induce protective immunity in 90% to 95% of vaccinees. Most vaccinees will have protective levels of anti-HBs for five to 10 years after vaccination, although the exact duration of immunity remains undefined. When anti-HBs levels have waned below the protective threshold of 10 mIU/mL, a booster dose of HBV vaccine has been shown to induce a strong anamnestic immune response in such individuals. It is therefore probable that protection from chronic HBV infection may last for decades and may well be lifelong .
Investigation of hepatitis B virus immunity. Anti-HBc-Total Total antibody to hepatitis B core protein Anti-HBs/HBsAb Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen
The HBV immune status can be determined using the tests outlined below, but testing for vaccine immunity in the general population is not indicated unless the individual is at high risk of infection .3). Nonimmune individuals should be offered HBV vaccination where clinically appropriate.
Recommended Reading: Can Chronic Hepatitis C Be Cured
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Is There Anything Else I Should Know
Even if you don’t have symptoms, an HBV infection can damage your liver and you can spread the infection to others. For this reason, it is important to get tested if you think you have been exposed to HBV.
Blood banks screen all donated blood for the hepatitis B virus , hepatitis B surface antigen , and hepatitis B core antibody . Donors are notified of any confirmed positive reactions. People who receive a notice regarding possible infection with hepatitis B after donating should visit their healthcare provider for further testing. The healthcare practitioner will order additional tests to make a proper diagnosis and determine if treatment is necessary.
If exposed to HBV and you haven’t been vaccinated, an infection can be avoided by getting a shot of hepatitis B immune globulin within 24 hours and typically you will also be given the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine.
A test is available to determine the specific type of hepatitis B virus that is causing a person’s infection. This is called HBV genotyping. However, this testing is currently mainly used in research settings and not for clinical purposes.
Also Check: Causative Agent For Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis B
This can happen when people share needles, syringes, or other drug injection devices or during sexual activity. People can also pass the virus to their baby during childbirth.
Hepatitis B is not curable, but a vaccine can prevent the infection.
There are three types of blood tests for hepatitis B:
Comprehensive Hepatitis B Profile Test
This panel includes 6 tests that can aid in diagnosing infection with Hepatitis B. Hepatitis B is a viral liver infection that is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis. Hep B is spread through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. The most common means of transmission are through sexual contact or sharing needles used for intravenous drug use. Infected mothers can also pass the virus to their infants during childbirth. Hepatitis B infections often show no symptoms but when symptoms do occur they can include abdominal pain, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, joint pain, fatigue, jaundice, and dark-colored urine. Chronic Hep B infections can cause serious health complications like Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer. Vaccination against Hep B is available which can provide immunity to the virus. People who are successfully treated for Hep B typically develop a natural immunity that can protect against future infections.
This panel combines 6 tests that can provide more information when used together than any single test. Used in combination, these tests can help to determine if a person has been exposed to Hep B and whether they have an active infection. These tests can also be useful for determining if a person has immunity to the Hep B Virus. Results for these tests may have more than one interpretation and should be reviewed by a personâs doctor.
This panel includes:
You May Like: How To Catch Hepatitis B And C