What Are The Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis In A Child
Autoimmune hepatitis can cause scar tissue to start forming on the damaged liver . This makes it harder for the liver to work properly. Over time, lots of scar tissue can build up in the liver . This can block the blood flowing through the liver and may lead to problems such as bleeding in the esophagus or stomach, or water in the belly . Cirrhosis also can cause the liver to fail signs may be jaundice , bleeding/bruising, or confusion.
What Are Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are disorders in which the body’s immune system attacks the body’s own cells and organs with proteins called autoantibodies this process is called autoimmunity.
Autoimmune Hepatitis is a Chronic Disease of the Liver
The body’s immune system normally makes large numbers of proteins called antibodies to help the body fight off infections. In some cases, however, the body makes autoantibodies. Certain environmental triggers can lead to autoimmunity. Environmental triggers are things originating outside the body, such as bacteria, viruses, toxins, and medications.
Do Medicines Used To Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis Have Side Effects
Medicines for autoimmune hepatitis can cause side effects. Your doctor will monitor any side effects and help you manage them while you take these medicines. Your doctor also may adjust the doses or change the medicines you take. You may need to stop taking corticosteroids or azathioprine if you have severe side effects.
Side effects of corticosteroids may include
- changes in how you look, which may include weight gain, a fuller face, acne, or more facial hair
Corticosteroids and azathioprine suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, which increases your risk for infections. These medicines can also increase your risk of developing cancers, especially skin cancers.
Also Check: What Do You Get Hepatitis C From
Potential Outcomes Of Immunosuppressant Therapy
The goal of treatment is disease remission. In remission, patients experience the improvement of symptoms, the normalization of abnormal liver chemistries and gamma globulin levels, and the reduction or elimination of inflammatory activity on liver biopsy.
Most patients who embark on a course of immunosuppressant therapy respond well initially. More than 90% of adults started on corticosteroid treatment experience improvements in liver chemistries and gamma globulin levels within 2 weeks.
Remission, if it is to be achieved, typically requires 18-24 months of immunosuppressant therapy. Remission can be achieved in about 65% of patients within 18 months and 80% of patients within 3 years. Once a drug-induced remission is achieved, an attempt should be made to withdraw immunosuppression. However, a sustained remission after total drug withdrawal is seen in 13% of patients at 5 years. Patients who relapse need to restart long-term immunosuppressant therapy in an effort to normalize their biochemical abnormalities and to delay the progression of liver disease. Many such patients are maintained on chronic maintenance therapy with azathioprine.
About 13% of patients experience an incomplete response to treatment, without worsening of their condition. Most incomplete responders need long-term immunosuppression in an attempt to stabilize levels of aspartate transaminase and alanine aminotransferase andby extensionprevent disease progression.
References
What Is The Outcome During/after Treatment
In about 7 out of 10 individuals, the disease goes into remission within 3 years of starting treatment. Some people can eventually discontinue treatment although others will see symptoms return. Because autoimmune hepatitis cannot be cured, most people need to continue taking prednisone for years and sometimes for life. Unfortunately, long term use of steroids may cause serious side effects such as diabetes, high blood pressure, glaucoma, weight gain and decreased resistance to infection, therefore, other drugs may be necessary to treat the side effects.
Azathioprine can lower white blood cell counts and sometimes causes nausea and poor appetite. Rare side effects are allergic reaction, liver damage and pancreatitis, which is an inflammation of the pancreas with severe stomach pain.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B And How Do You Get It
Why Choose Upmc For Liver Disease Care
Doctors at the UPMC Center for Liver Diseases treat the full range of liver conditions, no matter the severity of your disease.
Our world renowned hepatologists will work with you to:
- Diagnose your liver disease early.
- Treat your liver disease at any stage, with lifestyle changes, medicine, or surgery.
- Improve your quality of life.
Our doctors work closely with experts at the UPMC Liver Transplant Program, one of the most experienced transplant centers in the country. Together, we care for those with severe liver damage and disease.
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated In A Child
Autoimmune hepatitis is a serious, long-lasting disease. Right now, there is no cure for autoimmune hepatitis. Fortunately, most children with autoimmune hepatitis respond well to treatment.
The goal of autoimmune hepatitis treatment is remission. This means symptoms become less severe and liver damage slows or stops. Some children are able to stop taking medicine after two or three years. These children will still need to be watched for a return of autoimmune hepatitis symptoms and other health issues.
Two main types of medicine are used to help control autoimmune hepatitis in children:
- Corticosteroids . Prednisone helps stop the immune system from attacking the liver. It also reduces liver inflammation. Budesonide is another corticosteroid that is sometimes used it has less side effects, but it is mostly given later on when the disease is under control already.
- Immunosuppressants. Azathioprine or mercaptopurine are often added to the treatment they work together with prednisone to get the immune system under control. There are other medications to suppress the immune system that can be used if the standard treatment is not working well.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Medication For Hepatitis C
What Are The Current Treatment Options
Very mild cases or inactive phases of the disease may not require treatment. However, for more serious cases, treatment to fight acute episodes is important.
For many individuals, lifelong medication use may be required to keep the bodys autoimmune response under control and preserve liver health.
The two main medications used to treat autoimmune hepatitis are:
- prednisone: a corticosteroid
- azathioprine: an immunomodulator or steroid-sparing agent
Other medications may be added in severe cases. If medications are no longer effective and liver failure is likely, a liver transplant may be necessary.
If possible, your treatment should be supervised by a hepatologist, which is a physician who specializes in liver health.
How To Diagnose Autoimmune Hepatitis
The diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis is pretty complex and requires multiple steps to rule out other reasons for liver damage.
Case History – When a person visits a doctor after noticing the symptoms, the doctor will ask for some information like any medical condition that he or she is already suffering from, stress history, alcohol drinking habit, and its frequency. The doctor would ask the patient to go for a physical examination and complete a blood test and liver biopsy.
Blood Tests – Blood tests will include liver function tests and antibody tests, among others. This will help in checking the inflammation of the liver. Increased levels of antibodies such as an antinuclear antibody and IgG antibody indicate the cause of damage is an autoimmune disorder. However, it is not indicative of autoimmune hepatitis. Prothrombin time, albumin levels, and bilirubin levels are also checked for the proper functionality of the liver. Other blood tests are also done to rule out any other infections of the liver, like hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, and blood alcohol levels.
You May Like: What Drug Is Used To Treat Hepatitis B
What Is An Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease causes your immune system to attack healthy cells in your body by mistake. It can affect different parts of your body. There are more than 80 types of autoimmune diseases.
Verywell / Danie Drankwalter
Fortunately, autoimmune hepatitis is treatable with corticosteroids and outcomes are good in patients who seek early treatment.
Overlap And Outlier Syndromes
A sizeable percentage of cases of autoimmune liver disease that generally fit into one diagnostic category will show clinical, serologic, or histologic features more characteristic of another type of autoimmune liver disease. When overlap in all three areas is present, the diagnosis of an overlap syndrome should be considered. However, it should be noted that it is controversial whether these overlap syndromes are distinct entities or variants of the major autoimmune hepatopathies, and standardization of diagnostic criteria and terminology is lacking.
The term overlap syndrome is used primarily to describe variant forms of autoimmune liver disease that present with both cholestatic and hepatitic features that do not fit readily into the usual diagnostic categories,, and which generally have overlapping characteristics of AIH+PBC or AIH+PSC .
Table 6 Variants of autoimmune liver disease
Evidence for a PSC-PBC overlap syndrome is limited and based upon case reports.
Recommended Reading: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
Autoimmune Liver Diseases Occur When The Bodys Immune System Attacks The Liver Causing Inflammation If Left Untreated The Liver Inflammation May Eventually Cause Cirrhosis Of The Liver Which May Lead To Liver Cancer And Liver Failure
Overview and Symptoms
Although a number of autoimmune conditions may involve the liver, the three most common autoimmune liver diseases are autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. These conditions may occur individually or as part of overlap syndromes.
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
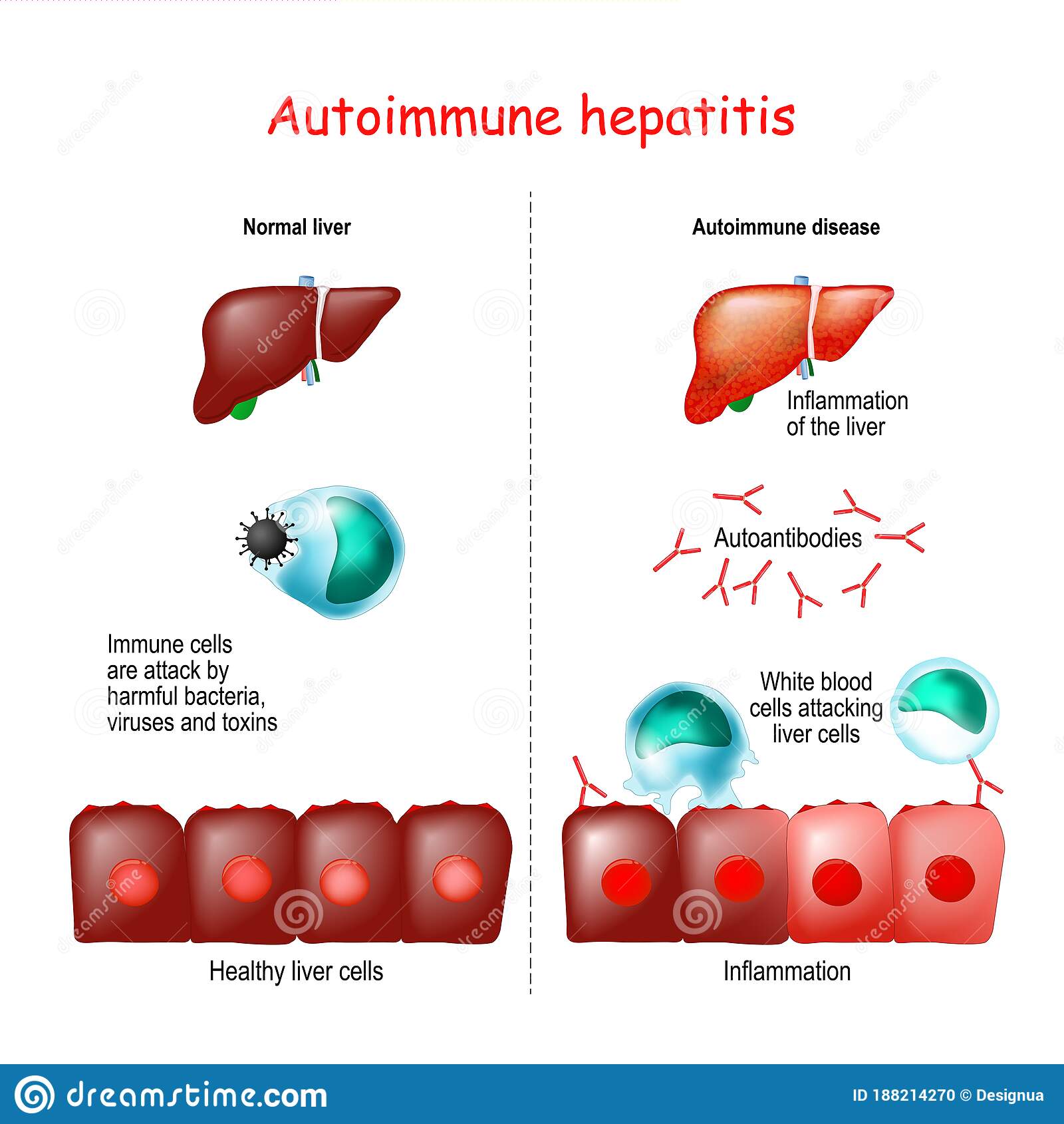
Experts dont know what causes autoimmune hepatitis, but it is more likely to show up in people with other autoimmune conditions, including:
- Fluid buildup in the belly
- Rectal bleeding or vomiting blood
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis may look like other health problems. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Hepatitis C Screening
What Are The Symptoms And Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Often, the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are minor. When symptoms do occur, the most common are fatigue, abdominal discomfort, aching joints, itching, jaundice , enlarged liver, nausea and spider angiomas on the skin. Other symptoms may include dark urine, loss of appetite, pale stools and absence of menstruation. More severe complications can include ascites and mental confusion. In 10%-20% of cases, autoimmune hepatitis may present with symptoms like an acute hepatitis.
When The Liver Is Under Attack
In people with autoimmune hepatitis, immune cells inappropriately mistake the liver’s normal cells as abnormal and attack them. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, scarring , impaired liver function, and even cirrhosis , which can result in liver failure, and death if not treated. Some people may eventually need a liver transplant. The liver disease specialists at NewYork-Presbyterians Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation are experienced in diagnosing and treating autoimmune hepatitis.
You May Like: Hepatitis B And C Vaccine
Treatments For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Treatment works best when AIH is diagnosed early. The goal in treating AIH is to slow or stop the bodys immune system from attacking the liver. The medications used are immunosuppressants, such as prednisone and Imuran® . Physicians usually prescribe a high initial dose of prednisone, and then taper it down progressively as symptoms and liver enzymes improve. Most people will need to take medication for the rest of their lives. Since prednisone can cause a wide range of side effects, Imuran® is often used in conjunction to allow for a lower dose of the prednisone.
Some people may go into remission, during which physicians can effectively discontinue treatment others will relapse after stopping treatment, and will then need to restart the medication and continue on long-term maintenance therapy. A few patients may eventually be tapered off the prednisone completely and stay solely on Imuran®. For those who do not respond to, or relapse from, the combination regimen, then stronger immunosuppressive agents such as mycophenolate mofetil, cyclosporine, or tacrolimus may be considered. When medications do not halt the progress of the disease, or complications from cirrhosis have developed, the remaining option is a liver transplant. Fortunately, the success rate of transplantation in people with AIH is excellent.
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
You May Like: Chronic Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
What Are The Symptoms Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
People with autoimmune hepatitis may have some of the following symptoms
- pain over the liver, in the upper part of the abdomen
- yellowish color of the whites of the eyes and skin, called jaundice
- darkening of the color of urine
- lightening of the color of stools
- skin conditions, such as rash, psoriasis, vitiligo, or acne
When symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are present, they can range from mild to severe.
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have no symptoms. In such cases, doctors may find evidence of liver problems during routine blood tests that leads to a diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. People without symptoms at diagnosis may develop symptoms later.
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis dont have symptoms until they develop complications due to cirrhosis. These symptoms include
- feeling tired or weak
- bloating from a buildup of fluid in the abdomen, called ascites
- swelling of the lower legs, ankles, or feet, called edema
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated
Treatment works best when autoimmune hepatitis is found early. The goal of treatment is to control the disease and to reduce or get rid of any symptoms .
To do this, medicines are used to help slow down or suppress your overactive immune system. They also stop your body from attacking your liver.
Once you have started treatment, it can take 6 months to a few years for the disease to go into remission. Some people can stop taking medicine, but often the disease comes back. You may need treatment now and then for the rest of your life. Some people need to remain on treatment if they have relapsed many times or if their disease is severe.
In some cases autoimmune hepatitis may go away without taking any medicines. But for most people, autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease.
It can lead to scarring of the liver . The liver can become so badly damaged that it no longer works. This is called liver failure.
If you have liver failure, a liver transplant may be needed.
Be sure to ask your healthcare provider about recommended vaccines. These include vaccines for viruses that can cause liver disease.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
What Are The Treatments Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
The treatment plan usually differs from patient to patient. Every patient reacts differently to the line of treatment. Doctors do not recommend any treatment until there are any visible symptoms. Treatment starts if symptoms can be seen or the blood test reports are bad.
1) Medication –
- In order to subside the inflammation of liver cells, the most common drug used is a corticosteroid named Prednisone. A higher dose of Prednisone is prescribed, and the dosage is lowered along the course of treatment. Another drug called Azathioprine or Purinethol, also a corticosteroid, would be added to the line of treatment after lowering the dose of Prednisone.
- The alternative treatment to Azathioprine is Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus. People may have side effects because they are under steroid medication, such as weak bones, high blood sugar levels, and increased urge to eat, leading to increased weight, eye problems, anxiety, and depression.
- After treatment of about three years, the majority of the patient’s symptoms and blood tests are under the normal range. Few doctors recommend immunosuppressants for life, or else recurrence rates are really high. Few others recommend that patients can stop medication after the symptoms have subsided and blood reports are normal, but the patient has been continuously being observed by their doctor, and their medication would start again once there is a relapse.
What Are The Types Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is classified into several types. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common form in North America. Type 1 can occur at any age however, it most often starts in adolescence or young adulthood. About 70 percent of people with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis are female.1
People with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis commonly have other autoimmune disorders, such as
Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis is less common and occurs more often in children than adults.1 People with type 2 can also have any of the above autoimmune disorders.
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis From Sex
Types Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
There are two types of autoimmune hepatitis. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common kind in the United States, while type 2 is more commonly seen in Europe and tends to be a more severe disease. The two forms of autoimmune hepatitis are characterized by the presence of different types of antibodies, proteins released by the immune system to fight bacteria and viruses. They are:
- Type 1 is the most common, accounting for 96% of autoimmune hepatitis cases in North America. It usually affects young women who have other autoimmune conditions, such as type 1 diabetes, thyroiditis, and celiac disease. People with this type of autoimmune hepatitis have antinuclear antibodies and antismooth muscle antibody .
- Type 2 is less common in North America, making up only 4% of all autoimmune hepatitis cases. It typically affects females ages 214. Individuals with this type of autoimmune hepatitis have anti-liver kidney microsomal antibody type 1 and/or anti-liver cytosol type 1 autoantibodies.