What Are The Side Effects Of Drug Treatment
Common side effects for some treatments for hepatitis C may include the following:
- nausea
- fatigue
- depression
Side effects are usually worst during the first few weeks of treatment. They become less severe over time. If you are having trouble dealing with the side effects of your medicine, talk to your doctor. He or she can suggest ways to relieve some of the side effects. For example, if your medicine makes you feel nauseated, it may help to take it right before you go to sleep.
Dont Miss: Liver Cancer Caused By Hepatitis C
How Long Before I Have Symptoms
Many people have mild symptoms or no symptoms, which is why hepatitis is sometimes called a âsilentâ disease.
Hepatitis A. The symptoms usually show up 2 to 6 weeks after the virus enters your body. They usually last for less than 2 months, though sometimes you can be sick for as long as 6 months.
Some warning signs that you may have hepatitis A are:
Hepatitis B. The symptoms are the same as hepatitis A, and you usually get them 3 months after you’re infected. They could show up, though, anywhere from 6 weeks to 6 months later.
Sometimes the symptoms are mild and last just a few weeks. For some people, the hep B virus stays in the body and leads to long-term liver problems.
Hepatitis C. The early symptoms are the same as hepatitis A and B, and they usually happen 6 to 7 weeks after the virus gets in your body. But you could notice them anywhere from 2 weeks to 6 months later.
For about 25% of people who get hep C, the virus goes away on its own without treatment. In other cases, it sticks around for years. When that happens, your liver might get damaged.
Remember, it’s possible to spread all the types of hepatitis even if you don’t show any signs of being sick.
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Screen For Hepatitis C
Undercooked And Raw Shellfish
Shellfish are animals that filter the water from their surroundings. Because of this, they can become contaminated with hepatitis A virus if they are grown in polluted waters. To be safe, cook shellfish thoroughly before eating it. Undercooked shellfish like oysters, mussels, and clams may harbor and transmit hepatitis A. You may prefer the taste of raw oysters, but cooked shellfish really is safer. Protect your health and skip the raw oyster bar.
Questions For Your Doctor

When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Is It Curable
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
What Drugs Treat And Cure Hepatitis C
The treatment of chronic hepatitis C has gone through several generations of medications. Not long ago, treatment was limited to interferon alpha-2b or pegylated interferon alpha-2b , and ribavirin . Interferon and pegylated interferon need to be injected under the skin , while ribavirin is taken by mouth. This combination therapy is infrequently used today, being recommended for only the least common genotypes of hepatitis C virus .
Since 2010, direct-acting antiviral drugs have been in use. The second generation of antivirals for HCV was the protease inhibitors telaprevir and boceprevir , both taken by mouth. These were used in combination with the earlier drugs to increase effectiveness . These drugs are also no longer in common use, and have been replaced by better options.
As more has been learned about how hepatitis C virus multiplies within the liver cells, new drugs continue to be developed to interfere with this multiplication at different stages. As such, we no longer think in terms of generations of drugs, but rather categories of action. Research and development of these direct-acting antivirals continue, with new agents coming to market every few months. Each category is improved and expanded by the addition of new drugs, which are safer and more effective.
Currently available and commonly used direct-acting antiviral drugs include:
- simeprevir
- Muscle aches
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Cdc Fact Sheet
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Women
Many women dont have symptoms until the disease is in a later stage. Women who have signs of the disease in the earliest stage may brush off symptoms or attribute them to other factors, such as anemia, depression, or menopause.
Early symptoms of hepatitis C in women can include:
- fatigue
- muscle and joint pain
- poor appetite
Some hepatitis C infections are acute and the infection clears or improves on its own without treatment within a few months. Acute infections are more common in women .
Hepatitis C can also be chronic, meaning the infection doesnt clear on its own, but rather progresses and damages the liver. Symptoms of chronic hepatitis and liver damage include:
- bruising or bleeding
- spider veins
- confusion
The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C occur in both men and women, but the disease can progress slower in women. However, some women experience rapid progression of the disease and liver damage after menopause.
Having these symptoms doesnt mean you have hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C spreads from person-to-person through contact with infected blood. If you work in an industry where you might come in contact with blood, theres a slight risk of exposure. This includes personal care such as:
- manicurists
Living With Hepatitis C Infection
Many people are living with hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, there are several important things that you can do to help yourself and others such as:
- Eat a healthy diet and get plenty of rest.
- To avoid further liver damage:
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take medicine that can cause liver damage .
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A & B if you are not already immune.
- Do not to pass the infection to anyone else by taking the following precautions, such as:
- Do not share toothbrushes or razors with others.
- Do not to let anyone else come into contact with your blood, urine or feces.
- Use condoms during sexual activity.
- Limit the number of sex partners you have.
- If you use injection drugs, do not share needles or syringes with anyone else.
- It is best to not get tattoos or body piercings.
Although often uncomfortable, you should notify your partner of your hepatitis C prior to having sex. You also must notify all your health care professionals of your infection, so they can take precautions.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Hepatitis C
What Medications Cure Hepatitis C Infection
Interferons, for example, Roferon-A and Infergen, and pegylated interferons such as Peg-IntronT, Pegasys, were mainstays of treatment for years. Interferons produced sustained viral response of up to 15%. Later, peglatedll forms produced SVR of 50%-80%. These drugs were injected, had many adverse effects, required frequent monitoring, and were often combined with oral ribavirin, which caused anemia. Treatment durations ranged up to 48 weeks.
Direct-acting anti-viral agents are antiviral drugs that act directly on hepatitis C multiplication.
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Find out more on how to prevent hepatitis C.
Also Check: How Do You Get Viral Hepatitis
The Types Of Viral Hepatitis
There are five main types of viral hepatitis known as hepatitis A , hepatitis B , hepatitis C , hepatitis D , and hepatitis E . That said, there have been cases of acute hepatitis that could not be attributed to one of these five types of hepatitis viruses, alcohol, drugs, or autoimmune disease, which lead researchers to try to find another cause.
Though the etiology of these viruses have not yet been fully established, researchers have identified three other types of viral hepatitis , which they have named hepatitis F , hepatitis G , and transfusions transmitted virus . As relatively new diseases and viral discoveries, information about them and how they work is relatively scarce. We do know, however, that cases of TTV have only been associated with hepatitis in people who have had a blood transfusion.
Hepatitis C And Injecting Drugs
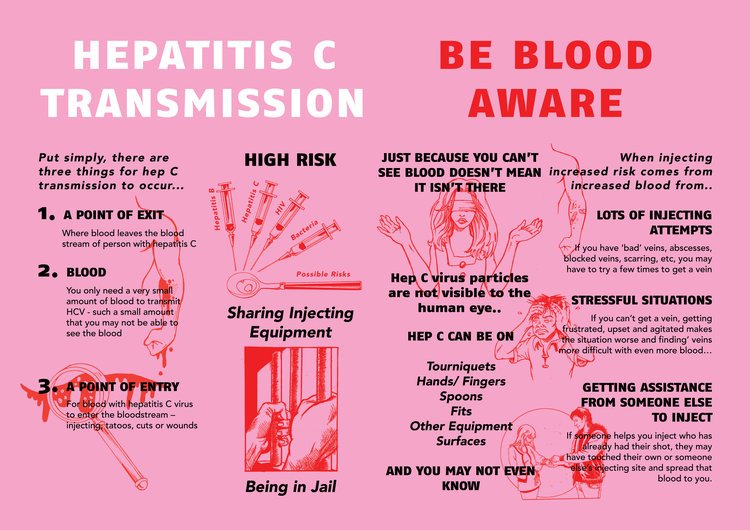
If you inject drugs, avoid sharing needles, syringes or other equipment such as tourniquets, spoons, swabs or water.
Where possible, always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available free of charge from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. To find out where you can obtain free needles, syringes and other injecting equipment, contact DirectLine
Try to wash your hands before and after injecting. If you cant do this, use hand sanitiser or alcohol swabs from a needle and syringe program service.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis B Curable Or Treatable
What Is Hepatitis C Infection How Many People Are Infected
Hepatitis C virus infection is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus . It is difficult for the human immune system to eliminate hepatitis C from the body, and infection with hepatitis C usually becomes chronic. Over decades, chronic infection with hepatitis C damages the liver and can cause liver failure. In the U.S., the CDC has estimated that approximately 41,200 new cases of hepatitis C occurred in 2016. When the virus first enters the body there usually are no symptoms, so this number is an estimate. About 75%-85% of newly infected people become chronically infected. In the U.S., more than 2 million people are estimated to be chronically infected with hepatitis C. Infection is most commonly detected among people who are 40 to 60 years of age, reflecting the high rates of infection in the 1970s and 1980s. There are 8,000 to 10,000 deaths each year in the U.S. related to hepatitis C infection. HCV infection is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the U.S. and is a risk factor for liver cancer. In 2016, 18,153 death certificates listed HCV as a contributing cause of death this is believed to be an underestimate.
Those who have cirrhosis from HCV also have a yearly risk of liver cancer of about 1%-5%.
Keep Personal Items Personal
Any tools or implements that may have a bit of blood on them from infected people are potential sources of hepatitis B or C transmission. Toothbrushes, nail clippers, razors, needles, and washcloths may all contain trace amounts of blood that can transmit infection. Keep personal items such as these to yourself and never use personal items that belong to others.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Virus Symptoms And Treatment
How Do You Get Hiv From Semen Or Vaginal Fluid
Body fluids including semen and vaginal secretions can contain HIV. If a person has HIV and a detectable viral load, HIV can passed on to someone if their semen or vaginal secretions get into the body of a sexual partner during vaginal or anal sex.
If a man has HIV and a detectable viral load, one of his body fluids where the virus is found is his semen.
If he has a detectable viral load and his semen gets into the body of his sexual partner during sex, then HIV can get into the other persons bloodstream.
Pre-cum also contains HIV this is why there is a risk of infection even if a man pulls out of his partner before he ejaculates.
If a woman has HIV and she has a detectable viral load, one of her body fluids where the virus is found is in her vaginal secretions.
If these come into contact with a penis during sex, then HIV could be transmitted. The virus in her secretions can enter through the delicate skin of the penis or foreskin.
Dont Miss: Nba Youngboy Std
Preventive Measures For Hcv Infection
Treatment options for hepatitis C are expensive, noncurative, and out of reach for the majority of people living in less-developed countries. Hence, prevention of infection remains an important public health goal.
HCV has a high mutation rate and multiple genotypes, which have challenged the development of an HCV vaccine. As a result, the primary means of prevention include infection-control practices in health care settings , the screening and testing of blood and organ donors, and viral inactivation in plasma-derived products. The development in the 1990s of highly effective assays to screen for HCV in donor blood greatly reduced the transmission of the virus in health care settings.
Risk-reduction counseling may help prevent the transmission of HCV among individuals who inject drugs.
Don’t Miss: Natural Treatment For Hepatitis C
Conditions By Which Hiv Can Survive
If HIV were to survive outside of the body for more than a few minutes, it could only do so under these specific environmental conditions:
- Colder temperatures: Temperatures below 39 degrees Fahrenheit are considered ideal for HIV to thrive. By contrast, HIV does not do well at room temperature and continues to decline as it reaches and exceeds body temperature .
- Ideal pH: The ideal pH level for HIV is between 7.0 and 8.0, with an optimal pH of 7.1. Anything above or below these levels is considered unsuitable for survival.
- Dried blood: HIV can survive in dried blood at room temperature for up to six days, although the concentrations of virus in dried blood will invariably be low to negligible.
- No UV exposure: HIV survives longer when is not exposed to ultraviolet radiation. UV light quickly degrades viral DNA as well as the lipids that make up the virus shell, rendering it incapable of attaching to and infecting other cells.
Even given these parameters, there has yet to be a documented case of infection by means of a discarded syringe in a public place.
In 2008, the largest retrospective study investigating child needlestick injuries concluded that not one case of HIV occurred following contact with a discarded needle.
Moreover, in 2015, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention could only confirm one infection by means of a needlestick injury since 1999, and that case involved a lab researcher who was working with a live HIV culture.
What If I Am Pregnant And I Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her child during pregnancy and during delivery. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 6 of every 100 infants born to HCV-infected mothers become infected with the virus. The risk is 2-3 times greater when the mother has HIV as well.
You and your doctor should discuss and decide if you should receive treatment for hepatitis C during your pregnancy.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Is More Infectious Than Hiv
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Hepatitis Of The Liver