Codified Diagnostic Criteria Of The Iaihg
The diagnostic criteria of the IAIHG require the presence of compatible laboratory , serological and histological findings .19 Diseases that can resemble autoimmune hepatitis must also be excluded by appropriate tests, and these include virus-related, drug-induced, alcoholic, hereditary , metabolic , and immune-mediated cholestatic diseases .19 The designation of definite or probable autoimmune hepatitis reflects the level of confidence in the diagnosis based on the compatibility of the clinical features with classical autoimmune hepatitis. Two scoring systems are available for challenging cases.19,20
How To Diagnose Autoimmune Hepatitis
The diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis is pretty complex and requires multiple steps to rule out other reasons for liver damage.
Case History – When a person visits a doctor after noticing the symptoms, the doctor will ask for some information like any medical condition that he or she is already suffering from, stress history, alcohol drinking habit, and its frequency. The doctor would ask the patient to go for a physical examination and complete a blood test and liver biopsy.
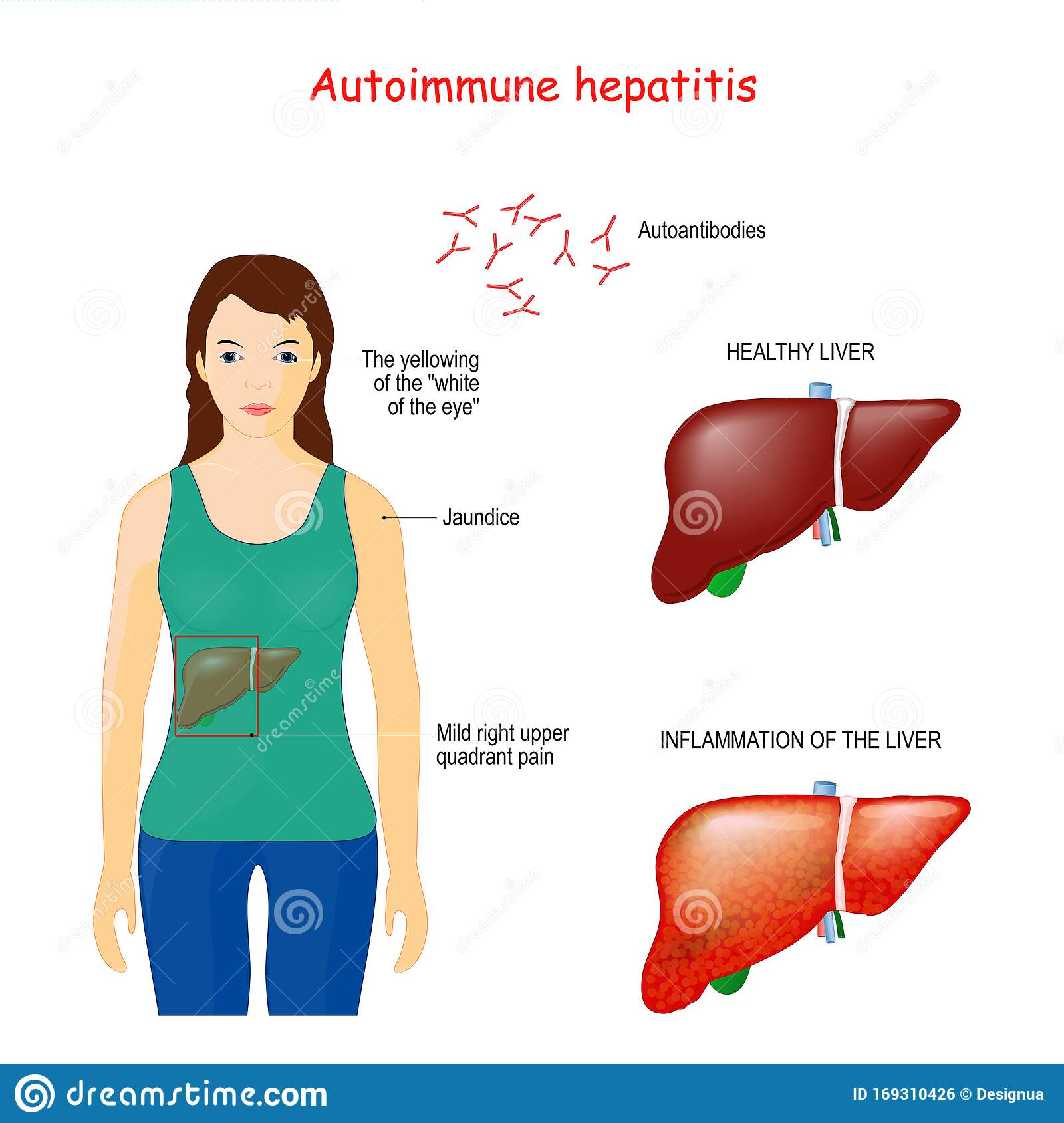
Blood Tests – Blood tests will include liver function tests and antibody tests, among others. This will help in checking the inflammation of the liver. Increased levels of antibodies such as an antinuclear antibody and IgG antibody indicate the cause of damage is an autoimmune disorder. However, it is not indicative of autoimmune hepatitis. Prothrombin time, albumin levels, and bilirubin levels are also checked for the proper functionality of the liver. Other blood tests are also done to rule out any other infections of the liver, like hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, and blood alcohol levels.
How Does A Liver Biopsy Confirm Autoimmune Hepatitis
Liver biopsy
Tests and procedures used to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis include: Blood tests. Testing a sample of your blood for antibodies can distinguish autoimmune hepatitis from viral hepatitis and other conditions with similar symptoms. Antibody tests also help pinpoint the type of autoimmune hepatitis you have.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
Revised Original Diagnostic Scoring System Of The Iaihg
The revised original scoring system is a comprehensive template that evaluates 13 clinical categories and renders 27 possible grades .19 This comprehensive scoring system was originally developed as a research tool by which to ensure the homogeneity of patient populations in clinical studies.139 It has emerged subsequently as a template by which to ensure the systematic evaluation of patients, and it can serve as a mechanism by which to bolster clinical judgment.21,140 The scoring system can accommodate deficiencies or inconsistencies in the clinical presentation and support the diagnosis in difficult cases by rendering a composite score before and after corticosteroid treatment.
What Are The Treatments Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
The treatment plan usually differs from patient to patient. Every patient reacts differently to the line of treatment. Doctors do not recommend any treatment until there are any visible symptoms. Treatment starts if symptoms can be seen or the blood test reports are bad.
1) Medication –
- In order to subside the inflammation of liver cells, the most common drug used is a corticosteroid named Prednisone. A higher dose of Prednisone is prescribed, and the dosage is lowered along the course of treatment. Another drug called Azathioprine or Purinethol, also a corticosteroid, would be added to the line of treatment after lowering the dose of Prednisone.
- The alternative treatment to Azathioprine is Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus. People may have side effects because they are under steroid medication, such as weak bones, high blood sugar levels, and increased urge to eat, leading to increased weight, eye problems, anxiety, and depression.
- After treatment of about three years, the majority of the patient’s symptoms and blood tests are under the normal range. Few doctors recommend immunosuppressants for life, or else recurrence rates are really high. Few others recommend that patients can stop medication after the symptoms have subsided and blood reports are normal, but the patient has been continuously being observed by their doctor, and their medication would start again once there is a relapse.
Also Check: What Is The Most Common Cause Of Hepatitis
Treatments For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Treatment works best when AIH is diagnosed early. The goal in treating AIH is to slow or stop the bodys immune system from attacking the liver. The medications used are immunosuppressants, such as prednisone and Imuran® . Physicians usually prescribe a high initial dose of prednisone, and then taper it down progressively as symptoms and liver enzymes improve. Most people will need to take medication for the rest of their lives. Since prednisone can cause a wide range of side effects, Imuran® is often used in conjunction to allow for a lower dose of the prednisone.
Some people may go into remission, during which physicians can effectively discontinue treatment others will relapse after stopping treatment, and will then need to restart the medication and continue on long-term maintenance therapy. A few patients may eventually be tapered off the prednisone completely and stay solely on Imuran®. For those who do not respond to, or relapse from, the combination regimen, then stronger immunosuppressive agents such as mycophenolate mofetil, cyclosporine, or tacrolimus may be considered. When medications do not halt the progress of the disease, or complications from cirrhosis have developed, the remaining option is a liver transplant. Fortunately, the success rate of transplantation in people with AIH is excellent.
Can An Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosis Be Something Else
Some symptoms and lab findings found in autoimmune hepatitis are also common in other chronic conditions. Your medical team will work to rule out any other possible causes for your symptoms. Some diseases to rule out include other types of hepatitis, certain viral infections, and other liver conditions such as cirrhosis and fatty liver disease.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted Disease
What Are The Types Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is classified into several types. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common form in North America. Type 1 can occur at any age however, it most often starts in adolescence or young adulthood. About 70 percent of people with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis are female.1
People with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis commonly have other autoimmune disorders, such as
Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis is less common and occurs more often in children than adults.1 People with type 2 can also have any of the above autoimmune disorders.
Mycophenolate Mofetil As Frontline And Salvage Therapy
Mycophenolate mofetil, a next generation purine antagonist, has been used as a frontline and salvage therapy for autoimmune hepatitis.34 As a frontline treatment in 59 patients treated for 3 to 92 months , mycophenolate mofetil in combination with prednisolone normalized serum ALT and -globulin levels in 88%, induced a partial laboratory improvement in 12%, allowed the withdrawal of corticosteroids in 58%, and induced treatment-ending side effects in 3% .47 Therapy with mycophenolate mofetil and prednisolone can be effective and safe in treatment-naïve patients, but comparative clinical trials with standard therapy are necessary to establish its preference.
Mycophenolate mofetil has also been used as a salvage therapy for patients with corticosteroid-refractory liver disease or azathioprine intolerance.34 Composite analysis of the several, small, single center experiences indicates that mycophenolate mofetil can induce improvement of laboratory tests in 45%, facilitate the withdrawal of corticosteroids in 40%, and cause treatment-ending side effects in 15% .34,50 Outcomes can be improved by using the treatment in a selective fashion. Therapy with mycophenolate mofetil has rescued patients who are azathioprine intolerant more commonly than patients who are refractory to conventional corticosteroid treatment ,34,41,45,46,50 whereas children with autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis have not responded.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis Cause Low Platelets
What Is The Prognosis For Patients Who Have Autoimmune Hepatitis
If autoimmune hepatitis is diagnosed early, and treated with the proper medication, the liver may begin to heal and will be able to make healthy cells again to replace the inflamed and scarred cells. The patients symptoms will ease and the liver may begin to work normally.
The patient will need to be monitored and managed for the rest of his or her life, even if he or she is feeling better and liver function has improved. In many cases, the patient will need to be on medication for the rest of his or her life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2018.
References
What Abnormal Results Mean
Blood tests for autoimmune diseases are not wholly accurate. They can have false negative results and false positive results .
A weakly positive or low titer positive test for autoimmune disease is often not due to any disease.
A positive test on the panel may be a sign of autoimmune hepatitis or other autoimmune liver disease.
If the test is positive mostly for anti-mitochondrial antibodies, you are likely to have primary biliary cholangitis. If the immune proteins are high and albumin is low, you may have liver cirrhosis or chronic active hepatitis.
Recommended Reading: A Cure For Hepatitis C
Dos And Donts In Managing Autoimmune Hepatitis:
- DO remember that monitoring of your condition is important. Report any new symptoms to your health care provider promptly.
- DO call your health care provider if you notice skin color changes, side effects from medicines, joint pains, or abdominal swelling.
- DONT ignore drug side effects, such as weight gain, anxiety, confusion, thinning of bones , thinning of the hair and skin, diabetes, high blood pressure, and cataracts.
- DONT use alcohol. It may further damage your liver.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will look at your health history and give you a physical exam.
Some lab blood tests used to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis include:
- Liver function tests. These check for inflammation or damage to your liver.
- Complete blood count or CBC. Looks at the number and types of cells in your blood.
- Coagulation panel. This test looks at how well the clotting proteins are working.
- Electrolyte panel. Checks to see if you have an electrolyte imbalance.
- Autoimmune antibodies. These are used to see if you have autoimmune hepatitis or another liver disease with similar symptoms.
- Other liver tests. These are done to check for other possible types of liver disease.
You may also have imaging tests such as:
Also Check: Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
How Autoimmune Hepatitis Is Diagnosed
Autoimmune hepatitis is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the bodys immune system attacks the liver by mistake. The exact cause is unknown but believed to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
There is no one test to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis. The diagnostic process usually involves a physical exam, detailed history, lab tests, imaging studies, and a liver biopsy.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
Limitations Of The Diagnostic Scoring Systems
The diagnostic scoring systems have been extensively evaluated and refined by retrospective analyses of patients that have been characterized in single medical centers and diagnosed by experts in autoimmune liver disease.20,21,140143 These characterizations have not followed a predefined protocol pooled experiences have been limited and comparative studies between medical centers have not been performed.141 Furthermore, assessments have not always been uniform or complete in each patient.20 Collaborative prospective clinical studies that adhere to a pre-established protocol and that ensure a uniform and complete assessment of each patient are necessary to validate the scoring systems.
The scoring systems have been applied beyond their original design and intention. They have been used inappropriately to determine the presence of autoimmune hepatitis in patients with PBC,144146 and this application has been discouraged.130 The scoring systems have also been used but not validated in patients with acute severe liver failure141,147 and in patients with graft dysfunction after liver transplantation.113
Read Also: How You Get Hepatitis B
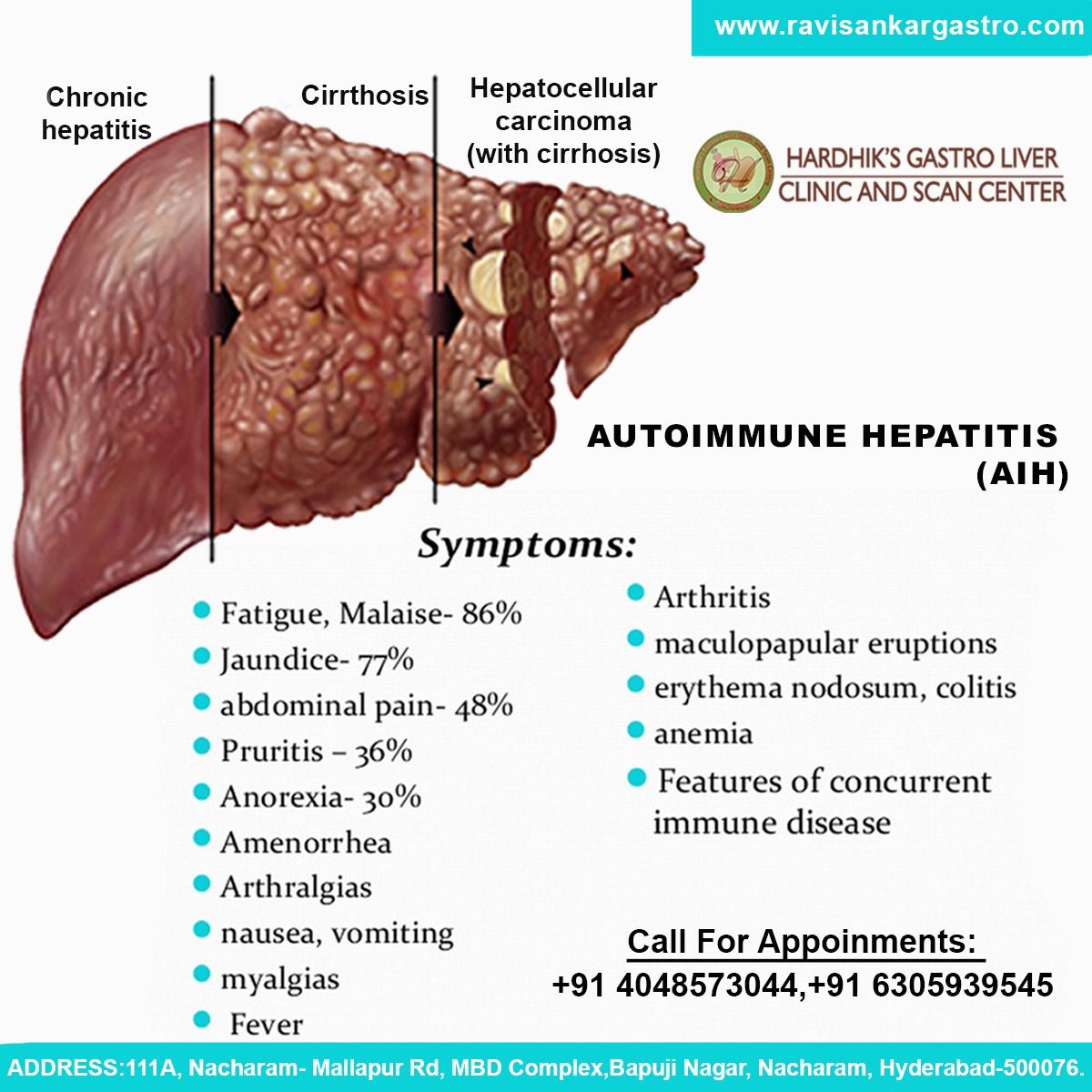
Acute And Acute Severe Hepatitis
An acute presentation occurs in 25% to 75% of patients with autoimmune hepatitis,6165 and an acute severe presentation, characterized by the development of hepatic encephalopathy within 26 weeks of disease discovery, occurs in 3% to 6% of North American and European patients .66,67 Each presentation can suggest an acute viral, toxic, or drug-induced liver injury, and each can delay recognition and proper treatment of autoimmune hepatitis.
Complete Blood Cell Count And Other Blood Studies
Other hematologic abnormalities may include the following:
-
Mild leukopenia
-
Thrombocytopenia
-
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Eosinophilia is uncommon, but counts ranging from 9% to 48% are described. Autoimmune hepatitis has even been described as the sole presenting feature of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome .
Read Also: Causes Of Hepatitis C Transmission
When The Liver Is Under Attack
In people with autoimmune hepatitis, immune cells inappropriately mistake the liver’s normal cells as abnormal and attack them. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, scarring , impaired liver function, and even cirrhosis , which can result in liver failure, and death if not treated. Some people may eventually need a liver transplant. The liver disease specialists at NewYork-Presbyterians Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation are experienced in diagnosing and treating autoimmune hepatitis.
Managing The Suboptimal Response
Liver tests worsen during therapy in 7% of patients,252 and they improve but not to normal levels in 14%.242,253 Treatment-ending side effects associated with corticosteroid therapy occur in 12% to 29%, and they are mainly intolerable cosmetic changes, obesity, emotional instability, and vertebral compression.74,245,254 Treatment ending side effects associated with azathioprine therapy occur in 5% to 10% of patients, and they are mainly nausea, vomiting, rash, cytopenia , pancreatitis, and liver toxicity.223,254,255 Patients with cirrhosis develop corticosteroid-induced side effects more commonly than patients without cirrhosis presumably because of increased systemic levels of unbound prednisolone,48,223 and they develop cytopenia that can suggest azathioprine toxicity more often .239,240
1) Treatment failure
Patients who fail conventional treatment are treated with high doses of the original medication . The dose of prednisone or prednisolone is increased to 30 mg daily and the dose of azathioprine is increased to 150 mg daily.18,34,39,253,256 Patients receiving monotherapy are treated with prednisone or prednisolone, 60 mg daily. Treatment is continued at a fixed dose for one month. Thereafter, the doses of medication are reduced by 10 mg of prednisone or prednisolone and 50 mg of azathioprine after each month of laboratory and clinical improvement until conventional maintenance levels for that particular regimen are reached.
2) Incomplete response
3) Drug-intolerance
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Transferred Sexually
What Is The Cause Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
The accurate cause of this disorder is unrecognized as of now. Since it is an autoimmune disease, somehow, something activates the defense mechanism of the body to think that the liver cells are harmful and attacks them, leading to inflammation of the liver cells and damage to the liver. Medicines like Statins or antibiotics such as Minocycline, stress, and viral infections like hepatitis, herpes, and measles can trigger the immune system. Some believe that it might be caused due to interaction of genes. People with weak immune systems are more vulnerable to the disease.
Is An Aih Diagnosis Fatal
If left untreated, autoimmune hepatitis could be fatal. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to achieving a good prognosis.
For individuals who respond positively to treatment, the 10-year survival rate is about 83.8% to 94%. Without any treatment, 40% to 50% of individuals with severe autoimmune hepatitis will die within six months to five years.
National Organization for Rare Disorders. Autoimmune hepatitis.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B Viral Or Bacterial
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated
Treatment works best when autoimmune hepatitis is found early. The goal of treatment is to control the disease and to reduce or get rid of any symptoms .
To do this, medicines are used to help slow down or suppress your overactive immune system. They also stop your body from attacking your liver.
Once you have started treatment, it can take 6 months to a few years for the disease to go into remission. Some people can stop taking medicine, but often the disease comes back. You may need treatment now and then for the rest of your life. Some people need to remain on treatment if they have relapsed many times or if their disease is severe.
In some cases autoimmune hepatitis may go away without taking any medicines. But for most people, autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease.
It can lead to scarring of the liver . The liver can become so badly damaged that it no longer works. This is called liver failure.
If you have liver failure, a liver transplant may be needed.
Be sure to ask your healthcare provider about recommended vaccines. These include vaccines for viruses that can cause liver disease.
Who Is At Risk For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis affects one in every 100,000 people. The disease is more common in women than in men, and women are typically diagnosed in their 40s or 50s. Girls between two and 14 years old may also get the disease.
Those who may suffer from other autoimmune conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease and celiac disease, are also at risk to develop autoimmune hepatitis .
A person who has a family history of autoimmune hepatitis also has a higher risk of developing the disease.
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Cause Itching
How We Care For Autoimmune Hepatitis
The Center for Childhood Liver Disease at Boston Childrens Hospital specializes in helping infants, children, adolescents, and young adults with a wide variety of liver disorders. Children with liver disease come to us from all over the world because of our extensive experience, dedication, and commitment to finding solutions.
We offer comprehensive care plans focused on your childs long-term health and wellbeing. Our clinical services include invasive and noninvasive testing and follow up based on your childs needs. When autoimmune hepatitis is part of a broader disorder involving multiple autoimmune diseases, we collaborate with experts in the Rheumatology Program and Immunology Program to develop the best possible care plan for the child. These, and the many other resources we offer, make Boston Childrens a unique and powerful force in fighting autoimmune hepatitis.