Chronic Phase Of Hepatitis C
When infection with hepatitis C lasts for longer than six months, it is known as chronic hepatitis C infection. The course of the chronic infection varies considerably between people and it is very unpredictable. Of those people who develop chronic infection:
- Some people have mild or no symptoms. However, even if you have no symptoms, you can still pass on HCV to others who may develop problems.
- Some people develop some symptoms due to persistent inflammation of the liver. For example, feeling sick, lack of appetite, intolerance of alcohol, pains over the liver, jaundice and depression. The most common symptoms of chronic hepatitis C are extreme tiredness, poor concentration and memory problems, and muscle and joint aches. There is actually no relationship between the severity of symptoms and the degree of liver damage. This means that some people can have liver inflammation without having any symptoms.
- About one third of people with chronic hepatitis C infection develop cirrhosis over a period of about 20-30 years. Cirrhosis is like a scarring of the liver, which can cause serious problems and liver failure when it is severe. See the separate leaflet called Cirrhosis. Some people with chronic hepatitis C have no symptoms for many years until they develop cirrhosis. Only when the liver starts to fail with cirrhosis do symptoms appear.
- A small number of people who develop cirrhosis go on to develop liver cancer.
How We Care For Hepatitis C
The Center for Childhood Liver Disease at Boston Childrens Hospital is one of the leading centers in the world for the care of children with hepatitis C. The centers director, Maureen Jonas, MD is a national leader in the care, diagnosis and treatment for children with viral hepatitis. Dr. Jonas, along with her team, wrote the clinical guidelines that shape the way pediatric GI specialists and pediatricians around the country treat hepatitis C.
In addition to the standard treatments, our team of certified pediatric hepatologists is also at the forefront of treatment research, treating adolescents with newly approved treatments for adults and conducting clinical trials to help make them available to children as young as 3 years of age.
Parenteral Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis B Hepatitis D And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses are all transmitted by what is known as the parenteral route. Parenteral simply means that these viruses can be introduced by all routes except through the intestinal tract, which leaves the door wide open in terms of possible exposure. Lets look at the possible transmission routes for each of these types of hepatitis virus more closely.
You May Like: The Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
You May Like: How Can You Get Hepatitis B
Treatment And Medication Options For Hepatitis C
The last few years have seen extraordinary advances in the treatment of hepatitis C.
For decades, the standard treatment was a combination antiviral therapy consisting of a pegylated interferon and ribavirin, sometimes called PEG-riba therapy. This involved weekly injections of the pegylated interferons along with twice-daily oral doses of ribavirin. Sometimes interferon was prescribed without ribavirin.
The treatment by interferon lasted six months to a year, and cured only 40 to 50 percent of hepatitis C patients. The painful injections often made patients feel ill with flu-like symptoms.
But now, hepatitis C can be treated with a number of direct-acting antiviral pills that act faster and much more effectively than the older interferon treatment. These combination oral medicines have 90 to 100 percent cure rates, and they work in weeks instead of months. Some of these drugs may be used in combination with ribavirin.
Eating Diet And Nutrition For Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, you should eat a balanced, healthy diet. Obesity can increase the chance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and NAFLD can increase liver damage in people who have hepatitis B. Talk with your doctor about healthy eating and maintaining a healthy weight.
You should also avoid alcohol because it can cause more liver damage.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
What Causes Hepatitis C Infection
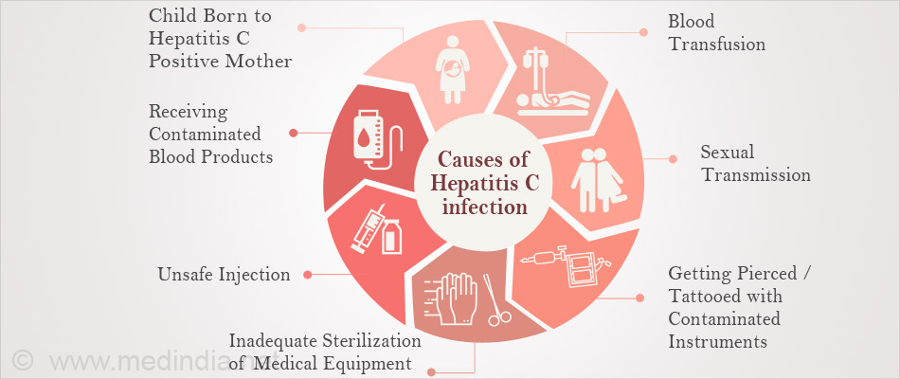
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus. It is spread by contact with an infected person’s blood.
You can get hepatitis C if:
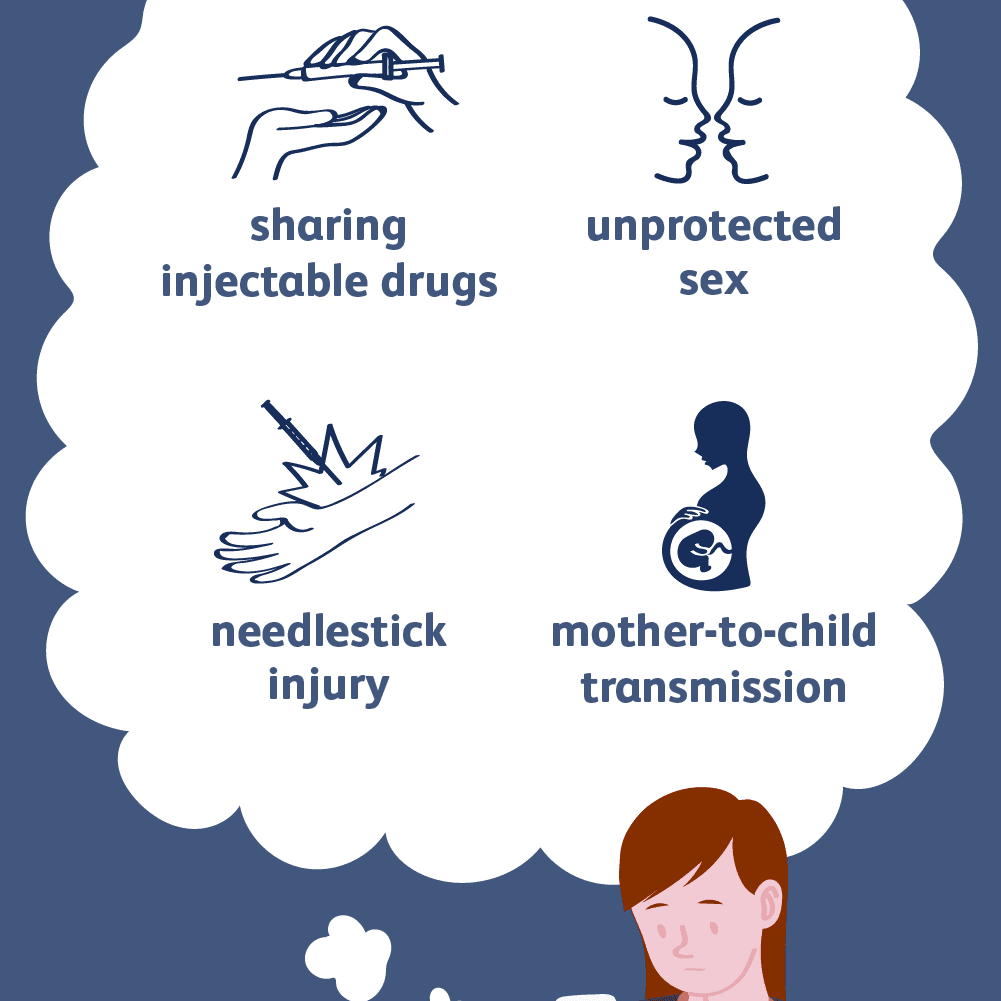
- You share needles and other equipment used to inject illegal drugs. This is the most common way to get hepatitis C in the United States.
- You had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992. As of 1992 in the United States, all donated blood and organs are screened for hepatitis C.
- You get a shot with a needle that has infected blood on it. This happens in some developing countries where they use needles more than once when giving shots.
- You get a tattoo or a piercing with a needle that has infected blood on it. This can happen if equipment isn’t cleaned properly after it is used.
In rare cases, a mother with hepatitis C spreads the virus to her baby at birth, or a health care worker is accidentally exposed to blood that is infected with hepatitis C.
The risk of getting hepatitis C through sexual contact is very small. The risk is higher if you have many sex partners.
If you live with someone who has hepatitis C or you know someone who has hepatitis C, you generally don’t need to worry about getting the disease from that person. You can help protect yourself by not sharing anything that may have blood on it, such as razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers.
You May Like: How Did I Get Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Read Also: How Many Types Of Hepatitis C Are There
What Happens With Hepatitis C
Is hepatitis C a virus? Yes. With acute hepatitis C, the virus is eliminated in 25% of people. The rest of the people become chronically infected and later may develop serious complications such as liver failure and liver cancer. There is treatment, however, for hepatitis C that usually can prevent the complications.
Symptoms Of Your Diagnosis
One of main symptoms of hepatitis C is jaundice, a yellow color to the skin or whites of the eyes. The jaundice is caused by the excess bilirubin in the blood. The excess bilirubin can also lead to other symptoms such as pale or clay-colored stools, dark urine and generalized itching. Flu-like symptoms of fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, and low-grade fever may occur several days before the jaundice appears.
If chronic hepatitis C develops, the symptoms can vary. Some individuals may remain well. Others will have severe and persistent liver inflammation. This may eventually lead to scarring of the liver, called cirrhosis, and liver failure. The scarring does not allow the liver to do its job of removing toxic substances from the blood.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does Hepatitis C Treatment Cost
Undercooked And Raw Shellfish
Shellfish are animals that filter the water from their surroundings. Because of this, they can become contaminated with hepatitis A virus if they are grown in polluted waters. To be safe, cook shellfish thoroughly before eating it. Undercooked shellfish like oysters, mussels, and clams may harbor and transmit hepatitis A. You may prefer the taste of raw oysters, but cooked shellfish really is safer. Protect your health and skip the raw oyster bar.
Needlestick Injuries In Healthcare Settings
Nurses, physicians, and all healthcare professionals who routinely use needles while providing medical care are at risk for needlestick injuries. In fact, it is estimated that more than 600,000 needlestick injuries happen each year, with nurses being at highest risk. An average of about 2 percent of needlestick injuries where there has been exposure to the virus will result in acute hepatitis C.
Also Check: How Can You Get Hepatitis A
Hepatitis C: How Does It Spread
It spreads through infected blood. In the U.S., sharing needles or other items used to inject drugs is the most common cause of infection. Getting a tattoo or body piercing with an infected needle is another means of exposure. A mother may pass the virus to their child at birth. In rare cases, unprotected sex spreads hepatitis C, but the risk appears small. Having multiple sex partners, HIV, or rough sex seems to raise risk for spreading hepatitis C.
Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated with antiviral medications that aim to clear the virus from your body.
New all-tablet treatments have greatly improved the outcomes for people with hepatitis C. These treatments can cure more than 95% of individuals with chronic hepatitis C. There are several new tablets that are used in combination to treat all hepatitis C strains . They are effective for people with no liver damage and those who have more advanced liver damage or cirrhosis.
These new tablet medications are available and subsidised on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, and can be prescribed by specialists, general practitioners and specialised nurse practitioners.
There are no restrictions on accessing treatment it is available for all adults with a Medicare card. People under 18 are able to access treatment and it is recommended they are referred to a pediatrician experienced in the treatment of hepatitis C.
For more information on the new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C, see our video: Hepatitis C Cure what it means for Victorians.
If your doctor does not know about the new treatments, you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Talk with your doctor about treatment options and the potential for interactions with other medications, herbal preparations and other drugs. If you take prescribed medication this will be managed so you can access treatment.
In general, if you have hepatitis C you will feel better if you:
You May Like: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
How Hcv Is Spread
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through blood to blood contact, meaning that a person can become infected with the virus should the blood of a person who carries the virus be introduced into another persons bloodstream.
Therefore, as with hepatitis B, blood transfusions , tattooing and body piercing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, and intravenous drug use can all lead to possible exposure to the virus. Unlike hepatitis B, however, sexual contact and childbirth have both been shown to be an inefficient route of exposure to HCV.
The hepatitis G virus is thought to be transmitted in a similar way to HCV.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults Missed Dose
Testing Treating And Reducing Risk Of Hepatitis
If you think youre at risk for hepatitis infection, talk to your healthcare provider about getting tested. A blood test is usually done to see if you have been exposed to the virus. Women who are pregnant or trying to become pregnant should get tested for hepatitis.
Get treated for hepatitis infection
There are treatments for hepatitis. Treating long-lasting hepatitis B or C infection can reduce the amount of the virus in a person, which may lower the risk of liver cancer.
What If I Am Pregnant And I Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be passed from a mother to her child during pregnancy and during delivery. Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , approximately 6 of every 100 infants born to HCV-infected mothers become infected with the virus. The risk is 2-3 times greater when the mother has HIV as well.
You and your doctor should discuss and decide if you should receive treatment for hepatitis C during your pregnancy.
Read Also: What Is The New Drug For Hepatitis C
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C

Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
You May Like: Where Can I Get A Hepatitis A Shot
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
There are some very effective options for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. They are listed on the Medicare PBS , which makes them available at a much lower cost.
Newer treatments differ from those available previously:
- they cure more than 95% of people
- their side effects are minimal
- treatments last just 8 to 12 weeks
- they involve just a few pills each day, with no injections required
Curing hepatitis C means clearing the virus from the body. It helps reduce liver inflammation and can also help reverse scarring and cirrhosis. You can be re-treated if your treatment doesnt work the first time.
You should check with your doctor before taking any other medication or supplements, and whether you need vaccinations against hepatitis A and hepatitis B. You should also avoid alcohol if you have hepatitis. If you have liver damage, you may also need to see a liver specialist
For more information on how to get treatment, contact the National Hepatitis Info Line on 1800 437 222.
What Is Hepatitis C Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, and hepatitis C is liver inflammation caused by the hepatitis C virus .
Journal of Clinical MicrobiologyJournal of Infectious Diseases
Though these genotypes appear to affect people similarly, they respond differently to treatments, and it’s possible to be infected with more than one HCV genotype at the same time.
Whatever the genotype, hepatitis C is considered either acute or chronic .
Also Check: How To Catch Hepatitis C