Hepatitis B Vaccination Booster Dose After 18 Years Maintains Long
Primary vaccination against hepatitis B virus at birth may not provide adequate lifelong antibody levels, but a booster vaccine at age 18 years reinforces antibody levels for at least 4 more years, according to a study published in Infectious Diseases.
Vaccination against HBV is recommended in the first year of life to prevent infection, and studies demonstrate that this provides protection for 90% of the population for 30 years. Data on response to booster doses and long-term protection are lacking therefore, researchers sought to understand the protection duration of the HBV vaccine and the effect of additional doses on the level of protection against infection.
The researchers conducted a retrospective analysis of data from January 2013 to December 2016 of healthcare students in Israel. Participants were aged 19 to 25 years. Immunization history was obtained from medical records, including data for receipt of birth-dose HBV vaccine and booster at age 18 years. This booster is common in Israel, as many teenagers undergo emergency medical technician training that requires HBV vaccination regardless of previous immunization. Baseline antibody titer levels were measured at first clinic visit. A participant was considered protected against HBV if their anti-HBs titer was > 10 MIU/mL any participant with titers below this level received a booster dose of the HBV vaccine.
Reference
Twinrix: The Vaccine For Hepatitis A And B
Both hepatitis A and B are identified by obtaining a blood sample, which you submit to a laboratory test. This test decides whether you have antibodies in the blood unique to those viruses. If the result is positive, you have been subjected to either hepatitis A or B.
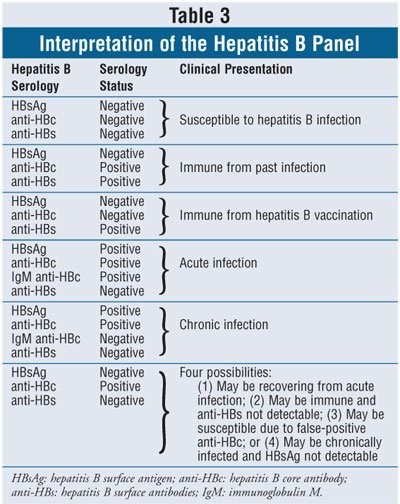
To check whether anyone has hepatitis B, the test will see whether the individual has certain hepatitis B antigen levels.
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Titer Test Quest Diagnostics
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If you’re a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
If you have been vaccinated by your employer’s occupational health service, you can request a blood test to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
Interchangeability Of Hepatitis B Vaccines

The Engerix-B and H-B-Vax II vaccines are manufactured by different processes, and the hepatitis B surface antigen content of an equivalent dose of these vaccines is different. Switching vaccine brands is not recommended.
If the brand of vaccine used for previous doses is not known, use another age-appropriate equivalent dose brand. See:
For example, a study in healthy neonates showed comparable high levels of immunogenicity between 2 different mixed regimens that used 2 monovalent hepatitis B vaccines from different manufacturers.33
You May Like: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Having Sex
Side Effects Of Hepatitis B Vaccines
Immunisations containing components to protect against hepatitis B are effective and safe, although all medication can have unwanted side effects.
Side effects from the vaccine are uncommon and usually mild, but may include:
- Localised pain, redness and swelling at the injection site.
- Low-grade temperature .
- In children being unsettled, irritable, tearful, generally unhappy, drowsy and tired.
- Occasionally, an injection-site lump that may last many weeks, but for which treatment is not needed.
People With Other Medical Conditions
People with chronic liver disease and/or hepatitis C are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine if they are not immune
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for people with chronic liver disease and/or hepatitis C who are seronegative for hepatitis B. This is because they may have an increased risk of hepatitis B and/or severe liver disease after hepatitis B.11
Adult-formulation hepatitis B vaccine should be given in a 3-dose schedule. See Table. Monovalent hepatitis B vaccines for adolescents and adults in Vaccines, dosage and administration.
Levels of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen should be checked after the vaccination course. See Serological testing after hepatitis B vaccination.
The combination hepatitis A-hepatitis B vaccine may be appropriate for people with chronic liver disease and/or hepatitis C if they are not immune to either disease. This is because they have an increased risk of hepatitis B and/or severe liver disease after hepatitis A and B. This is usually given in 3 doses using Twinrix . See Table. Combination hepatitis A-hepatitis B vaccines in Vaccines, dosage and administration.
Low-birthweight and preterm newborns do not respond as well to hepatitis Bcontaining vaccines as full-term infants.12-14
You May Like: Can You Recover From Hepatitis C
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
People At Occupational Risk
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for people who work in any occupation that involves any of:
- direct patient care
- handling human tissue, blood or body fluids
- handling used needles or syringes
These people should also routinely follow standard precautions against exposure to human tissue, blood or body fluids.19
The risk to people in certain occupations differs considerably between settings in different parts of Australia. Workers who have an increased risk of acquiring hepatitis B include:
- healthcare workers
- police, members of the armed forces, emergency services staff and staff of correctional facilities, if they are assigned to duties that may involve exposure to human tissue, blood or body fluids
- funeral workers, embalmers and other workers who have regular contact with human tissue, blood or body fluids, or used needles or syringes
- staff involved in both residential and non-residential care of people with developmental disabilities, because of the high prevalence of markers of past or current infection in people in this setting16-18
- workers who perform skin penetration procedures, such as tattooists and body-piercers
Early childhood educators and carers are normally at minimal risk of hepatitis B transmission. The local public health authority can provide advice about risk if needed.
Adult-formulation hepatitis B vaccine should be given in a 3-dose schedule. See Table. Monovalent hepatitis B vaccines for adolescents and adults in Vaccines, dosage and administration.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis A B C
Before Taking This Medicine
Havrix vaccine will not protect against infection with hepatitis B, C, and E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It may also not protect against hepatitis A if you are already infected with the virus, even without showing symptoms.
You should not receive Havrix if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis A, or if you are allergic to neomycin.
Before receiving this vaccine, tell your doctor if you have:
-
an allergy to latex rubber or
-
a weak immune system .
You can still receive a vaccine if you have a minor cold. In the case of a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, wait until you get better before receiving Havrix.
Vaccines may be harmful to an unborn baby and generally should not be given to a pregnant woman. However, not vaccinating the mother could be more harmful to the baby if the mother becomes infected with a disease that Havrix could prevent. Your doctor will decide whether you should receive this vaccine, especially if you have a high risk of infection with hepatitis A.
It is not known if hepatitis A vaccine passes into breast milk or if it could harm a nursing baby. Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding a baby.
Havrix is not FDA-approved for use by anyone younger than 12 months old.
People With Chronic Hepatitis B
The vaccine does not affect people with chronic hepatitis B virus infection there are no therapeutic benefits or associated adverse events. The vaccine is also safe in people who are already immune to hepatitis B through past natural infection, but it offers no additional benefit.
Hepatitis B is an infection caused by hepatitis B virus. It affects the liver.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A B C Difference
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
Exactly How Long Does Hep Vaccine Last
Years ago, the standard 3-round Hepatitis B vaccine provided protection for up to seven years. However, todays vaccines provide you with more than 20 years of protection.
This means that booster doses are largely unneeded these days. However, it is recommended for certain groups to take subsequent booster doses. At-risk groups include hemodialysis patients and other individuals with seriously compromised immune systems, such as people infected with HIV, chemotherapy patients, and recipients of hematopoietic stem-cell transplants.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
Us Children And Adult Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm as a three-dose series on a 0, 1, and 6-month schedule. Alternative schedules may be considered, noting that a third dose at 6 months, meeting minimum intervals between doses, is needed for maximum, long-term protection. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection.
There are four, 3-dose vaccine brands approved in the U.S.
- PreHevbrio PreHevbrio is only approved for adults age 18 and over.
2-Dose Vaccine Series
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A Curable Or Not
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B For Children
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis B infection and is recommended for all infants and young children, adolescents and those in high-risk groups. Immunisation can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule.
In Victoria, immunisation against hepatitis B is free for all babies and children including:
- Babies at birth immunisation against hepatitis B alone as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 9 years of age.
Serological Testing After Hepatitis B Vaccination
It is recommended that levels of hepatitis B surface antigen in infants born to mothers with chronic hepatitis B are measured 312 months after they complete the infant vaccine course. Do not test the infant before 9 months of age, to avoid detecting anti-HBs
Post-vaccination serological testing is recommended 48 weeks after completing the vaccine course for:
- people at significant occupational risk, such as healthcare workers whose work involves frequent exposure to human tissue, blood or body fluids
- people at risk of severe or complicated hepatitis B, such as people who are immunocompromised and people with pre-existing liver disease not related to hepatitis B
- people who may respond poorly to hepatitis B vaccination, such as haemodialysis patients and people with bleeding disorders who received the vaccine subcutaneously
- close contacts of people who are infected with hepatitis B virus, including sexual partners, household contacts and household-like contacts22
If serological testing 48 weeks after the vaccine course shows levels of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen of < 10 mIU per mL, check the person for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection by testing for serological markers, including antibodies to anti-HBs and hepatitis B core antigen.
After the booster dose, check for anti-HBs
A non-responder is a person who:
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Hepatitis A
Primary Hepatitis B Vaccinations For Children In The Uk
In the UK, children born after August 2017 are eligible to be given hepatitis B vaccines when they are young.
This consists of three doses of a hepatitis B vaccine. These doses are given at eight, 12 and 16 weeks of age. Babies at high risk of developing the hepatitis B infection from infected mothers are given additional doses of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, four weeks and one year of age.
However, if your child was born before this time, they are likely unvaccinated. If you are unsure which vaccinations your child has received, you should consult your doctor.
Prevalence Of Chronic Hepatitis B
The prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection varies between and within countries:58-61
- < 0.5% among Caucasians in the United States, northern Europe and Australia
- 15% in Mediterranean countries, parts of eastern Europe, Africa, and Central and South America
- > 10% in many sub-Saharan African, East and Southeast Asian, and Pacific island populations
Regions where 2% of the population is positive to hepatitis B surface antigen are considered to have moderate to high prevalence. In these regions, people mainly acquire the infection perinatally or in early childhood.55
Read Also: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic Formula Canned Dog Food
How Is Havrix Given
Havrix is given as an injection into a muscle. You will receive this injection in a doctor’s office or clinic setting.
You will most likely receive 2 separate injections of Havrix at 6 to 12 months apart, depending on your exposure or risk of infection.
To prevent hepatitis A while traveling, you should receive Havrix at least 2 weeks before your trip. Your healthcare provider will determine the best dosing schedule for your situation.
Your doctor may recommend treating fever and pain with an aspirin free pain reliever such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen when the shot is given and for the next 24 hours. Follow the label directions or your doctor’s instructions about how much of this medicine to use.